Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference between starter and alternator
In the dynamic landscape of automotive components, understanding the difference between a starter and an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers. Sourcing reliable electrical system components, such as starters and alternators, can present challenges, especially when considering the diverse needs of markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Germany and Nigeria. Each region has unique operational environments and regulatory frameworks that influence purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential distinctions between starters and alternators, covering various types, applications, and performance metrics. We will explore how these components work together within a vehicle’s electrical system, the signs of potential failures, and best practices for maintenance. Additionally, the guide offers insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and regional market trends.
By equipping B2B buyers with in-depth knowledge and actionable insights, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Buyers will be better positioned to select the right components that meet their operational needs while ensuring compliance with local regulations. As you navigate the complexities of sourcing starters and alternators, this resource will serve as an invaluable tool in optimizing your procurement strategy and enhancing your supply chain efficiency.
Índice
- Top 1 Difference Between Starter And Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference between starter and alternator
- Understanding difference between starter and alternator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of difference between starter and alternator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference between starter and alternator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference between starter and alternator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference between starter and alternator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference between starter and alternator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference between starter and alternator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference between starter and alternator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference between starter and alternator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference between starter and alternator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference between starter and alternator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference between starter and alternator
- Aviso legal importante y condiciones de uso
Understanding difference between starter and alternator Types and Variations
| Nombre del tipo | Características distintivas clave | Aplicaciones B2B principales | Breves ventajas y desventajas para los compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arrancador convencional | Engages with the engine flywheel using a solenoid. | Talleres de reparación de automóviles, fabricantes de equipos originales (OEM) | Ventajas: Diseño sencillo, rentable. Contras: Vida útil limitada; puede requerir sustituciones frecuentes. |
| Arrancador con reducción de engranajes | Uses gears to increase torque, suitable for larger engines. | Maquinaria pesada, vehículos comerciales | Ventajas: High torque output, reliable for heavy-duty applications. Contras: Más voluminoso, potencialmente más caro. |
| Alternador de imán permanente | Utilizes permanent magnets for power generation. | Vehículos eléctricos, sistemas híbridos | Ventajas: Compact design, efficient energy conversion. Contras: May have lower output compared to traditional alternators. |
| Alternador sin escobillas | Eliminates brushes for longer lifespan and reduced maintenance. | Industrial applications, marine engines | Ventajas: Higher efficiency, lower wear and tear. Contras: Higher initial cost, may require specialized knowledge for repair. |
| Alternador inteligente | Features integrated electronics for better energy management. | Advanced automotive systems, fleet management | Ventajas: Optimizes battery life, enhances vehicle performance. Contras: Complex systems may lead to higher repair costs. |
What are the characteristics of Conventional Starters and their B2B applications?
Conventional starters are the most commonly used type in automotive applications. They operate using a solenoid to engage the starter motor with the engine’s flywheel, providing the necessary torque to crank the engine. They are typically affordable and straightforward to replace, making them suitable for automotive repair shops and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) focusing on cost-effective solutions. However, their lifespan can be limited, leading to potential repeat purchases and maintenance costs.
How do Gear Reduction Starters differ and where are they used?
Gear reduction starters are designed for larger engines and heavy machinery. They utilize a gear system to amplify torque, making them ideal for high-compression engines found in commercial vehicles and industrial equipment. The increased torque output allows these starters to handle more demanding applications. While they are more reliable for heavy-duty operations, their size and cost can be a drawback for some buyers, necessitating careful consideration of application requirements.
What advantages do Permanent Magnet Alternators offer?
Permanent magnet alternators leverage permanent magnets to generate electrical power, resulting in a more compact and lightweight design. This type is particularly advantageous in electric and hybrid vehicles, where space and weight are critical factors. They offer efficient energy conversion but may produce lower output than conventional alternators. B2B buyers should consider the specific energy requirements of their applications when opting for this technology, as it may not suit all vehicle types.
Why are Brushless Alternators becoming popular in industrial applications?
Brushless alternators are gaining traction in industrial settings due to their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements. By eliminating brushes, these alternators minimize wear and tear, leading to higher efficiency and reliability. They are particularly well-suited for marine engines and other industrial applications where consistent performance is crucial. However, their higher initial cost and the need for specialized knowledge for repairs can be barriers for some businesses.
What makes Smart Alternators a valuable investment for advanced automotive systems?
Smart alternators incorporate advanced electronics to optimize energy management, enhancing overall vehicle performance and battery life. They are increasingly used in modern automotive systems and fleet management due to their ability to adapt to varying power demands. While they provide significant benefits, the complexity of smart alternators can lead to higher repair costs and the need for specialized technicians. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages against potential service challenges when considering this technology for their fleets.
Key Industrial Applications of difference between starter and alternator
| Industria/Sector | Specific Application of difference between starter and alternator | Valor/beneficio para la empresa | Consideraciones clave sobre el abastecimiento para esta aplicación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabricación de automóviles | Understanding the distinct roles of starters and alternators in vehicle assembly | Enhances production efficiency and reduces downtime | Quality assurance of components, compatibility with various vehicle types, and supplier reliability |
| Transporte y logística | Maintenance protocols for fleet vehicles focusing on starter and alternator diagnostics | Minimizes vehicle breakdowns and operational costs | Access to comprehensive diagnostic tools, reliable replacement parts, and skilled technicians |
| Sistemas de energía renovable | Integration of starters and alternators in hybrid and electric vehicles | Supports innovation in energy-efficient transportation | Compliance with international standards, sourcing from eco-friendly suppliers, and technology compatibility |
| Maquinaria pesada | Utilization of starters and alternators in construction and agricultural equipment | Improves equipment reliability and reduces repair costs | Evaluation of environmental conditions, durability of components, and after-sales support |
| Marine & Aviation | Application in marine engines and aircraft for reliable starting and power generation | Ensures safety and operational efficiency in critical applications | Adherence to safety regulations, sourcing from certified manufacturers, and availability of specialized parts |
How Does the Difference Between Starter and Alternator Impact Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, a clear understanding of the roles of starters and alternators is essential. Starters are responsible for initiating engine operation, while alternators maintain battery charge during vehicle use. Recognizing these differences allows manufacturers to streamline assembly processes, ensuring that each vehicle is equipped with reliable components. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality starters and alternators that meet specific vehicle requirements is crucial to enhance production efficiency and minimize downtime.
What Are the Benefits of Understanding Starters and Alternators in Transportation & Logistics?
In transportation and logistics, knowledge of starter and alternator functions is vital for fleet maintenance. Regular diagnostics can prevent vehicle breakdowns, ensuring that logistics operations remain uninterrupted. This understanding helps fleet managers implement effective maintenance protocols, ultimately reducing operational costs associated with vehicle repairs. International buyers should prioritize sourcing diagnostic tools and replacement parts that are compatible with a diverse range of vehicle makes and models to optimize their fleets.
Why Is the Difference Between Starter and Alternator Important in Renewable Energy Systems?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly with hybrid and electric vehicles, the roles of starters and alternators are evolving. Starters are used to initiate engine operation, while modern alternators play a critical role in power generation and battery management. Businesses in this industry benefit from understanding these differences as they innovate towards more energy-efficient transportation solutions. International buyers must consider compliance with international standards and the technology compatibility of sourced components to ensure successful integration.
How Does Knowledge of Starters and Alternators Enhance Heavy Machinery Reliability?
Heavy machinery in construction and agriculture relies heavily on the functionality of starters and alternators. Starters ensure that equipment can start efficiently, while alternators keep the electrical systems operational. Understanding these components helps businesses maintain equipment reliability, reducing the frequency of repairs and downtime. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the environmental conditions in which their machinery operates to select durable components that can withstand harsh conditions.
What Role Do Starters and Alternators Play in Marine and Aviation Industries?
In marine and aviation applications, the reliability of starters and alternators is paramount for safety and operational efficiency. Starters are crucial for engine ignition, while alternators provide necessary electrical power during operation. Understanding these components ensures that vessels and aircraft remain operational under critical conditions. Buyers in these industries must source components from certified manufacturers to meet stringent safety regulations and ensure the availability of specialized parts for maintenance and repairs.

Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference between starter and alternator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misdiagnosing Electrical Issues in Fleet Vehicles
El problema: Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing fleets in regions with fluctuating climates such as Africa and Europe, encounter frequent vehicle breakdowns. A common pain point arises when drivers report starting issues that can be attributed to either the starter or the alternator. Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary repairs, resulting in increased downtime and repair costs, as well as potential disruptions in service delivery.
La solución: To effectively differentiate between starter and alternator issues, implement a systematic troubleshooting protocol. Begin with a thorough visual inspection of all electrical connections, looking for corrosion or loose cables that can affect performance. Utilize diagnostic tools to check the battery voltage and alternator output, ensuring that the alternator is supplying adequate power while the vehicle is running.
Educate your maintenance team on recognizing specific symptoms: a clicking noise or dashboard lights illuminating without starting typically indicates a starter issue, while dimming headlights or electrical components failing suggest alternator failure. By training staff to accurately diagnose the problem, you can reduce misdiagnosis rates, streamline repairs, and maintain fleet efficiency.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Parts for International Markets
El problema: Buyers in regions like South America and the Middle East often face challenges in sourcing quality starter and alternator parts. The market may be flooded with counterfeit or substandard components, which can lead to premature failures and increased maintenance costs. Additionally, differences in automotive specifications between regions can complicate sourcing efforts, making it difficult to find the right fit for specific vehicles.
La solución: Establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record of providing OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or high-quality aftermarket parts. Conduct thorough research on suppliers, focusing on reviews, certifications, and their adherence to international standards. Engage in direct communication to clarify specifications and ensure compatibility with your fleet’s vehicle models.
Consider leveraging technology by utilizing platforms that facilitate international procurement, allowing you to compare options and prices from various suppliers. Regularly assess the performance of sourced components, and maintain an inventory of frequently used parts to minimize downtime due to sourcing delays. By prioritizing quality and reliable sourcing strategies, you can enhance the longevity of your fleet’s starters and alternators, ultimately reducing operational costs.
Scenario 3: Unclear Maintenance Protocols for Electrical Systems
El problema: B2B buyers managing vehicle maintenance often struggle with unclear protocols regarding the care of starters and alternators. Without a standardized maintenance plan, vehicles may suffer from neglect, leading to unexpected failures and costly repairs. This is particularly prevalent in businesses operating in regions with extreme weather conditions that accelerate wear and tear.
La solución: Develop a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of starters and alternators, focusing on critical components such as battery health and electrical connections. Implement a routine check-up protocol that aligns with vehicle usage patterns and environmental conditions. For instance, vehicles operating in hotter climates may require more frequent checks on battery fluid levels and alternator performance.
Provide training sessions for maintenance staff to ensure they understand how to assess the condition of electrical systems effectively. Utilize diagnostic tools to regularly test battery charge levels and alternator output, and keep detailed records of maintenance activities. By establishing clear guidelines and proactive maintenance practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unexpected failures, ensuring your vehicles remain operational and efficient.

Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference between starter and alternator
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starters and Alternators?
In the manufacturing of starters and alternators, the choice of materials is crucial for ensuring product performance, reliability, and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Cobre
Propiedades clave: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for electrical connections in starters and alternators.
Ventajas y desventajas: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of electrical systems. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, and its weight can be a drawback in applications where weight reduction is critical. Additionally, copper can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impacto en la aplicación: Copper is ideal for components that require reliable electrical connections, such as wiring and terminals in starters and alternators. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice.
Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
Consideraciones para compradores internacionales: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability and cost fluctuations of copper. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM can also impact procurement strategies.
2. Aluminio
Propiedades clave: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and offers decent electrical conductivity, albeit lower than copper. It can operate effectively at moderate temperatures.
Ventajas y desventajas: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it an attractive option for automotive applications, helping to improve fuel efficiency. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper can lead to inefficiencies in electrical systems. Additionally, aluminum can be more susceptible to mechanical wear.
Impacto en la aplicación: Aluminum is often used in the casing and structural components of alternators, where weight savings are essential. Its corrosion resistance is beneficial in harsh environments.
Consideraciones para compradores internacionales: In Europe and the Middle East, aluminum is widely used, and compliance with DIN standards is crucial. Buyers should also assess the local supply chain for aluminum components.
3. Acero
Propiedades clave: Steel is known for its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to deformation. It can withstand high pressure and temperature, making it suitable for mechanical components.
Ventajas y desventajas: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and durability, which makes it ideal for structural components in starters and alternators. However, steel is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to rust if not properly coated. The manufacturing complexity can also increase costs.
Impacto en la aplicación: Steel is commonly used in the frames and gears of starters, where strength is critical. Its robustness ensures longevity, especially in demanding environments.
Consideraciones para compradores internacionales: Buyers in regions like Germany should ensure compliance with JIS and DIN standards for steel components. The local availability of high-quality steel can also affect procurement decisions.
4. Compuestos plásticos
Propiedades clave: Plastic composites are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into complex shapes. They can withstand moderate temperatures but may not handle extreme conditions as well as metals.
Ventajas y desventajas: The main advantage of plastic composites is their versatility and lightweight nature, which can contribute to overall vehicle efficiency. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals and can be affected by UV exposure over time.
Impacto en la aplicación: Plastic composites are often used for insulative components and housings in starters and alternators. Their resistance to corrosion makes them suitable for various environmental conditions.
Consideraciones para compradores internacionales: Buyers in the Middle East should consider the UV resistance of plastic composites due to the region’s climate. Compliance with local standards and regulations regarding plastic materials is also important.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starters and Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for difference between starter and alternator | Ventaja clave | Desventaja/limitación clave | Coste relativo (bajo/medio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobre | Cableado y conexiones eléctricas | Conductividad eléctrica superior | High cost, prone to corrosion | Alto |
| Aluminio | Casing and structural components | Ligero, buena resistencia a la corrosión | Conductividad inferior a la del cobre. | Medio |
| Acero | Frames and gears | Alta resistencia y durabilidad | Más pesado, propenso a oxidarse | Medio |
| Compuestos plásticos | Insulative components and housings | Ligero, resistente a la corrosión | Menos duraderos que los metales | Bajo |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in starters and alternators, highlighting the considerations that international B2B buyers should keep in mind when selecting components for their automotive applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference between starter and alternator
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Starters and Alternators?
The manufacturing of starters and alternators involves several key stages that ensure the final products meet the necessary performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source reliable components for their operations.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Starters and Alternators?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation. For starters, common materials include high-grade steel for the housing and copper for the windings. Alternators also use similar materials, with the addition of aluminum for the casing and components like the rotor and stator, which are critical for electrical efficiency. Suppliers often source materials that comply with international standards to ensure durability and performance.
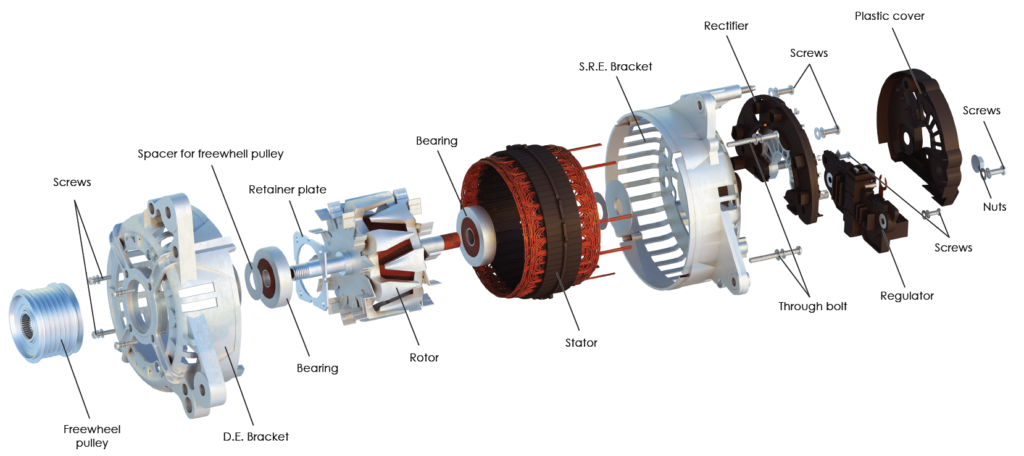
How Are Starters and Alternators Formed?
The next stage is forming, where raw materials are shaped into specific components. Techniques such as stamping, machining, and forging are used. For starters, the gear and motor housing are typically stamped from metal sheets, while alternators undergo processes like die-casting for the rotor and stator. Precision during this stage is critical; any defects can lead to significant performance issues later.
What Is Involved in the Assembly of Starters and Alternators?
Once components are formed, the assembly phase begins. This process involves fitting together various parts, including the motor, solenoid, and electrical connections for starters, and the rotor, stator, and rectifier for alternators. Automated assembly lines are common, but manual assembly may be employed for complex components. Quality checks are integrated at this stage to identify any assembly errors early.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted for Quality Assurance?
The final stage is finishing, which includes painting, coating, and final testing. Starters and alternators often receive protective coatings to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. This step is vital, especially for buyers in regions with harsh environmental conditions. Final testing involves checking electrical performance and ensuring that all components function correctly under load conditions.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For in Starters and Alternators?
Quality assurance is an essential aspect of the manufacturing process for starters and alternators. B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international standards that govern product quality.

Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
What Are the Key International Standards for Manufacturing Quality?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management standard that many manufacturers adhere to. It ensures that companies have a systematic approach to managing their processes and delivering high-quality products. Additionally, CE marking may be required for products sold in Europe, indicating compliance with safety and environmental standards.
How Do Industry-Specific Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
In specific industries, such as automotive or aerospace, additional standards like API (American Petroleum Institute) or IATF 16949 (automotive quality management) may apply. These standards emphasize continuous improvement and defect prevention, crucial for components that must operate reliably under varying conditions.
¿Cuáles son los principales puntos de control de calidad en el proceso de fabricación?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Understanding these checkpoints is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they receive high-quality products.
What Are the Different Types of QC Checkpoints?
-
Control de calidad de entrada (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Materials are tested for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
-
Control de calidad durante el proceso (IPQC): During manufacturing, inspections are conducted at various stages to ensure that components are being produced according to quality standards. This could involve measuring dimensions, testing electrical properties, or assessing the integrity of welds.
-
Control de calidad final (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing. This includes performance testing under load and visual inspections for any defects. Only products that pass this stage are approved for shipping.
¿Cómo pueden los compradores B2B verificar los procesos de control de calidad de los proveedores?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable insights on how to accomplish this:
Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
What Methods Can Buyers Use to Assess Supplier Quality?
-
Auditorías de proveedores: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This includes reviewing their adherence to ISO 9001 or other relevant standards.
-
Informes de calidad: Request detailed quality reports from suppliers, which should include data from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checkpoints. This documentation can help buyers understand the consistency of product quality.
-
Inspecciones por terceros: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. This is particularly beneficial for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary.
¿Qué matices del control de calidad deben tener en cuenta los compradores internacionales?
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that can affect sourcing decisions.
How Do Regional Standards Influence Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that affect the quality of products. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East might look for compliance with local safety standards. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for ensuring compliance and product acceptance.
What Are the Challenges in Ensuring Quality Across Borders?
Logistical challenges can impact the quality of starters and alternators, especially when components are sourced from multiple countries. Variations in manufacturing practices, material quality, and environmental conditions can lead to inconsistencies. Establishing strong communication channels with suppliers and implementing stringent quality checks can mitigate these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starters and alternators, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference between starter and alternator’
Introducción
Understanding the difference between a starter and an alternator is essential for B2B buyers in the automotive parts sector. This guide will help you navigate the sourcing process by outlining key steps to ensure you procure the right components for your needs. With an emphasis on performance, compatibility, and supplier reliability, following this checklist will facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Paso 1: Defina sus especificaciones técnicas
Before starting your search, clarify the specific requirements for starters and alternators. This includes understanding the vehicle types they will be used for, such as passenger cars, trucks, or heavy machinery. Ensure you gather details on voltage, amperage, and compatibility with existing systems to avoid mismatches that could lead to performance issues.
Paso 2: Identificar proveedores reputados
Research and compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in automotive electrical components. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and positive reviews from other businesses in your industry. Networking within automotive forums or industry associations can also lead you to reliable sources.

Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
Paso 3: Evaluar las certificaciones de los proveedores
Before making a commitment, verify that your chosen suppliers meet industry standards and certifications. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with regional automotive regulations, which can indicate quality assurance in manufacturing processes. This step ensures that the products you purchase are reliable and meet safety standards.
Paso 4: Solicitar muestras de productos
Ask suppliers for samples of their starters and alternators to assess quality and compatibility with your requirements. Testing samples helps you evaluate the build quality and performance under real-world conditions. Look for signs of durability and efficiency, which can prevent costly returns or replacements later.
Paso 5: Infórmese sobre la garantía y la asistencia
Understand the warranty policies offered by your suppliers for both starters and alternators. A strong warranty not only reflects the supplier’s confidence in their products but also provides peace of mind regarding potential defects. Additionally, inquire about customer support services and their responsiveness to any issues that may arise post-purchase.

Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
Paso 6: Analizar precios y condiciones de pago
Compare pricing across different suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling. Evaluate payment terms and conditions to ensure they align with your cash flow and budgeting strategies. Some suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, which could be beneficial for larger orders.
Paso 7: Finalize Logistics and Delivery Schedule
Once you have chosen your supplier, confirm the logistics of your order, including delivery timelines and shipping methods. Ensure the supplier can meet your deadlines, especially if you are working on a project with tight timelines. Clear communication regarding delivery expectations can prevent delays and help maintain your production schedules.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively differentiate between starters and alternators, ensuring they make well-informed purchasing decisions that support their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference between starter and alternator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starters and Alternators?
When sourcing starters and alternators for automotive applications, several key cost components contribute to the overall price. Understanding these components can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
-
Materiales: The primary materials used in starters and alternators include copper, aluminum, and various metals for housing and internal components. The cost of these raw materials fluctuates based on market demand and supply chain conditions. In regions like Africa and South America, where material sourcing can be more challenging, prices may be higher.
-
Trabajo: Labor costs vary significantly across different regions. In Europe, for example, labor costs are typically higher than in countries like Nigeria or Brazil. Additionally, skilled labor is required for the assembly and testing of these components, impacting overall pricing.
-
Gastos generales de fabricación: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, making it essential for suppliers to optimize their operations to remain competitive.
-
Herramientas: Specialized tooling is often required for the production of starters and alternators. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, and this cost is usually amortized over the production run. Custom tooling for specific designs can significantly increase costs, so understanding the tooling requirements upfront is crucial.
-
Control de calidad (QC): Ensuring that starters and alternators meet industry standards requires rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with testing and quality assurance are critical to maintaining product reliability, which can affect the price.
-
Logística: Shipping and handling costs are vital, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, transportation modes, and customs duties can impact overall logistics costs. For buyers in regions like the Middle East, understanding local import regulations is essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margen: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing structure. This margin can vary depending on market competition, demand, and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences Prices for Starters and Alternators?
Several factors influence the pricing of starters and alternators, especially for international B2B buyers:
Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
-
Volumen/MOQ (cantidad mínima de pedido): Larger orders often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing.
-
Especificaciones y personalización: Customized products can increase costs. Buyers should clarify their specifications upfront to receive accurate quotes.
-
Calidad de los materiales y certificaciones: Higher-quality materials and compliance with international certifications (like ISO or TS16949) can lead to higher prices but also improve reliability and longevity.
-
Factores relacionados con los proveedores: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to their proven track record and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact total costs.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negociar condiciones: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules with suppliers to achieve better deals. Leveraging long-term relationships can also yield discounts.
-
Tenga en cuenta el coste total de propiedad (TCO).: Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also long-term costs such as maintenance, warranty, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality components may reduce TCO.
-
Manténgase informado sobre las tendencias del mercado: Keep abreast of market conditions affecting material costs and labor, especially in the regions where you operate. This knowledge can aid in timing purchases to maximize cost savings.
-
Build Supplier Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to preferential pricing, better service, and priority during shortages.
-
Evaluate Local Suppliers: In some cases, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, enhancing overall efficiency.
Descargo de responsabilidad sobre precios indicativos
The prices for starters and alternators can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. Buyers are encouraged to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure they are making cost-effective purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference between starter and alternator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the Difference Between Starter and Alternator
When evaluating the differences between starters and alternators, it’s essential to consider alternative solutions that could fulfill similar functions in automotive or industrial applications. While starters and alternators are integral components of conventional internal combustion engines, technological advancements have introduced alternative methods for vehicle operation and energy generation. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application.
Tabla comparativa
| Aspecto comparativo | Difference Between Starter and Alternator | Electric Vehicle (EV) Systems | Hybrid Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rendimiento | Essential for engine ignition and battery charging | Instant torque, no idling, regenerative braking | Combines combustion engine with electric power for efficiency |
| Coste | Moderate initial cost, with variable replacement costs | Higher upfront costs, but lower operating costs | Moderate initial investment, good fuel efficiency |
| Facilidad de implementación | Standard installation in ICE vehicles | Requires infrastructure for charging | More complex integration of systems |
| Mantenimiento | Regular checks needed; typically long-lasting | Minimal maintenance; software updates required | Regular maintenance for both systems |
| Mejor caso de uso | Conventional vehicles needing reliable starting and charging | Urban environments with charging stations | Mixed-use scenarios for efficiency in fuel consumption |
Desglose detallado de las alternativas
Electric Vehicle (EV) Systems
Electric vehicles represent a significant shift in automotive technology, relying on electric motors powered by batteries rather than traditional starters and alternators. The primary advantage of EV systems is their efficiency and reduced emissions, making them ideal for urban environments where air quality is a concern. However, the initial investment is often higher due to the cost of batteries and charging infrastructure. Maintenance is typically lower than that of internal combustion engines, but it may require periodic software updates and battery management.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems combine the strengths of internal combustion engines with electric propulsion, utilizing both a starter and alternator alongside an electric motor and battery. This dual approach allows for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, making hybrids a versatile choice for various driving conditions. The complexity of integrating two systems can increase initial costs and maintenance requirements, but the overall operational efficiency can lead to long-term savings. They are particularly effective in mixed-use scenarios, offering flexibility for both short commutes and longer trips.
Conclusión: elegir la solución adecuada para sus necesidades
When considering the differences between starters and alternators versus alternative technologies like electric and hybrid systems, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Each solution has its pros and cons, with electric and hybrid systems offering innovative ways to enhance efficiency and sustainability. By aligning the choice of technology with the specific needs of the application—whether it’s conventional vehicles, urban transport, or mixed-use environments—buyers can make decisions that not only meet their immediate needs but also contribute to long-term operational success.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference between starter and alternator
Understanding the differences between a starter and an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in automotive parts procurement. Both components play vital roles in a vehicle’s electrical system, and knowing their specifications and related terminology can help buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Starters and Alternators?
-
Composición del material
– Definición: Starters are typically made from high-strength steel and aluminum, while alternators often utilize copper windings for electrical conductivity.
– Importancia del B2B: The choice of materials affects durability, efficiency, and cost. Understanding these properties helps buyers evaluate the longevity and performance of the components. -
Power Rating (Voltage and Amperage)
– Definición: Starters usually operate at a voltage of 12V with a peak amperage ranging from 100 to 200 amps, while alternators generate between 13.5V to 14.5V and can output anywhere from 30 to 200 amps.
– Importancia del B2B: Power ratings determine the capability of each component to perform under load. Buyers must match these ratings to the vehicle’s requirements to ensure proper functionality. -
Especificaciones de par
– Definición: The starter motor must produce a specific torque (often between 100 to 300 Nm) to effectively crank the engine, whereas alternators have torque specifications for their pulleys to ensure efficient belt engagement.
– Importancia del B2B: Adequate torque is essential for reliable performance. Buyers should consider torque ratings to avoid premature wear and operational failures. -
Tolerances and Clearances
– Definición: These refer to the allowable variations in dimensions for assembly. Starters and alternators have specific tolerances that must be maintained to ensure proper fit and operation.
– Importancia del B2B: Understanding tolerances helps in avoiding compatibility issues during installation. Buyers need to ensure that components meet the specifications for their specific vehicle models. -
Esperanza de vida útil
– Definición: Starters generally have a lifespan of 50,000 to 100,000 starts, while alternators can last between 100,000 to 150,000 miles, depending on usage and environmental factors.
– Importancia del B2B: Knowing the service life helps businesses anticipate replacement cycles and manage inventory effectively.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starters and Alternators?
-
OEM (fabricante de equipos originales)
– Definición: Refers to components produced by the original vehicle manufacturer.
– Importancia: OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality. Buyers should consider OEM options for reliable performance. -
MOQ (cantidad mínima de pedido)
– Definición: Cantidad mínima de un producto que un proveedor está dispuesto a vender.
– Importancia: Understanding MOQ helps businesses manage cash flow and inventory. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who need to balance order sizes with shipping costs. -
RFQ (Solicitud de presupuesto)
– Definición: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products.
– Importancia: RFQs are essential for obtaining competitive pricing and ensuring that all potential suppliers meet the required specifications. -
Incoterms (Términos comerciales internacionales)
– Definición: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importancia: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation. -
Piezas de recambio
– Definición: Components manufactured by companies other than the OEM that are designed to replace original parts.
– Importancia: Aftermarket parts can provide cost-effective alternatives but may vary in quality. Buyers must assess the reliability of these options before purchasing.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure the right components for their automotive needs while navigating the complexities of global supply chains.

Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference between starter and alternator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Starter and Alternator Sector?
The global automotive industry is undergoing significant transformations, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the market dynamics surrounding starters and alternators is crucial. One key driver is the increasing adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, which often utilize advanced alternator technologies to improve efficiency. This shift necessitates sourcing components that can meet the demands of these new systems, such as lightweight materials and higher efficiency ratings.
Emerging trends in sourcing highlight the importance of digital platforms and e-commerce solutions, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products. For instance, platforms that offer real-time inventory tracking and supplier verification can enhance procurement processes, allowing buyers to make informed decisions. Furthermore, as electric vehicles gain traction, suppliers are focusing on innovative technologies such as smart alternators that can optimize battery management systems, thereby influencing buyer preferences.
Geopolitical factors also play a role in market dynamics. The ongoing trade tensions and regulatory changes can affect the availability and pricing of components, making it essential for buyers to establish diverse supplier networks. Companies that can adapt quickly to these changes, whether through local sourcing or strategic partnerships, will gain a competitive edge in the market.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Starter and Alternator Market?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the starter and alternator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of automotive components is under increasing scrutiny. Ethical sourcing practices are becoming essential, as buyers seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and contribute to reducing carbon footprints.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is gaining traction. Suppliers that offer components made from recycled materials or those that utilize energy-efficient manufacturing processes are becoming more attractive to B2B buyers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability, providing buyers with confidence in their sourcing decisions.
Moreover, there is a growing expectation for transparency within supply chains. Buyers increasingly demand detailed information about the sourcing of materials, labor practices, and the environmental impact of their suppliers. This shift not only reflects consumer demand for ethical products but also aligns with regulatory pressures in various regions, particularly in Europe. Buyers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing will not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the global effort to combat climate change.
What Is the Evolution of Starters and Alternators in the Automotive Industry?
The evolution of starters and alternators has been marked by significant technological advancements that have transformed their functionality and efficiency. Initially, starters were simple DC motors that relied heavily on mechanical components. Over time, advancements in materials and electronic controls have led to the development of high-performance starters that are lighter, more reliable, and capable of handling the demands of modern engines.
Similarly, alternators have evolved from basic designs to sophisticated systems that incorporate features like smart voltage regulation and integrated battery management capabilities. This evolution has been driven by the need for greater efficiency and reliability in an increasingly electrified automotive landscape. The shift towards hybrid and electric vehicles has further accelerated this trend, prompting manufacturers to innovate continually.
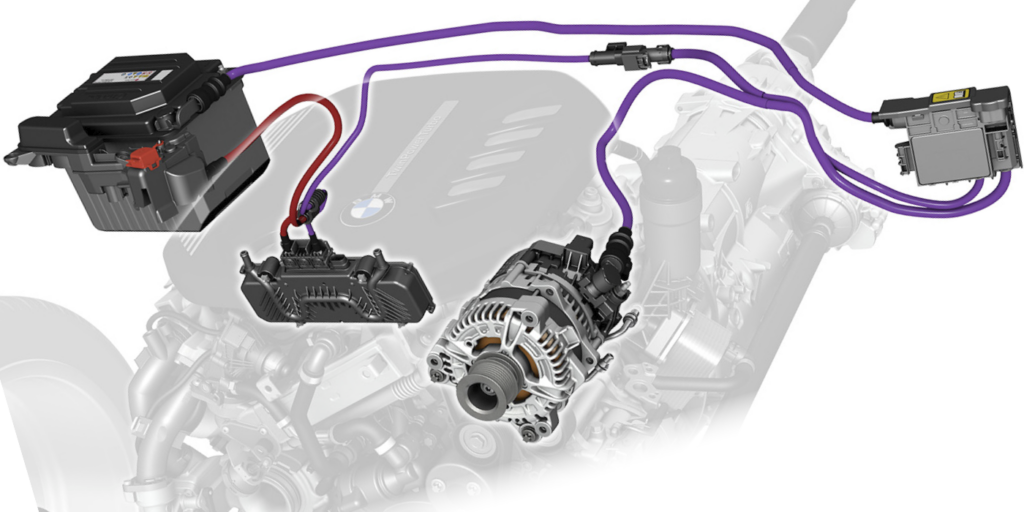
Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
These advancements are crucial for B2B buyers, as they must stay abreast of the latest technologies and trends to ensure they source components that meet the evolving demands of their customers. Understanding the historical context and technological progression of starters and alternators will empower buyers to make informed decisions and capitalize on new opportunities in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference between starter and alternator
-
How do I differentiate between a starter and an alternator in a vehicle?
To differentiate between a starter and an alternator, it’s essential to understand their functions. The starter is an electric motor that initiates engine operation by converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy. In contrast, the alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and supply energy to the vehicle’s electrical systems while the engine runs. Visually, the starter is usually mounted near the engine’s flywheel, while the alternator is typically found at the front of the engine, connected to the drive belt. -
What are the common signs of a failing starter or alternator?
Common symptoms of a failing starter include a clicking noise when turning the key, dashboard lights illuminating without the engine starting, or grinding sounds. For alternators, signs of failure can include dimming headlights, a warning light on the dashboard, or strange noises such as grinding or squealing. Regular maintenance checks can help identify these issues early, ensuring timely replacements and avoiding costly repairs. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing starters and alternators internationally?
When sourcing starters and alternators internationally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, compliance with international standards, and warranty offerings. Evaluate the supplier’s experience in the automotive sector and their ability to provide timely delivery. Additionally, ensure that the products are compatible with the specific vehicle models in your market. Conducting a thorough background check and requesting samples can also aid in making an informed decision. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starters and alternators in B2B transactions?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starters and alternators can vary significantly between suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the component. It is advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your inventory requirements and financial capabilities, ensuring a beneficial partnership. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing starters and alternators?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing starters and alternators, look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certification. Request detailed specifications and quality control processes they implement during manufacturing. Conducting third-party inspections and audits prior to shipment can further help in verifying product quality. Additionally, asking for product samples before committing to larger orders can provide insight into the quality of the components. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers for starters and alternators?
When negotiating payment terms with suppliers for starters and alternators, consider terms that provide a balance of security and flexibility. Common options include 30% upfront payment with the balance due upon delivery, or letter of credit arrangements for larger orders. It’s crucial to ensure that payment terms align with your cash flow and inventory management strategies while also offering protection against potential supplier defaults. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the procurement of starters and alternators?
Logistics and shipping are critical factors in the procurement process for starters and alternators. Consider the shipping methods, lead times, and costs associated with international transportation. Understanding customs regulations in your country and the supplier’s country can also prevent delays and additional fees. Partnering with reliable logistics providers can streamline the shipping process and ensure timely delivery, which is essential for maintaining inventory levels. -
Can I customize starters and alternators for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for starters and alternators to meet specific application requirements. Customization can include modifications in voltage, size, or design features to suit particular vehicle models or operating conditions. When discussing customization with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and ensure that they have the capacity and expertise to meet your needs. Additionally, inquire about lead times and any potential impact on pricing.
Top 1 Difference Between Starter And Alternator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Honda – Starter Issue
Dominio: mecánica.stackexchange.com
Registrado: 2009 (16 años)
Introducción: 2006 Honda Civic EX 1.8L 4 Cylinder; symptoms include weak cranking, failure to start, single click sound when attempting to start; issues identified: potential bad starter or alternator; previous battery replaced; updates indicate starter was the problem.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference between starter and alternator
In summary, understanding the critical differences between starters and alternators is vital for international B2B buyers involved in automotive parts sourcing. Starters are responsible for converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to initiate engine operation, while alternators generate electrical power to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems during operation. Recognizing the signs of potential failure in these components—such as unusual noises, dim lights, or starting issues—can help businesses make informed decisions regarding maintenance and replacement.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality starters and alternators not only enhances vehicle reliability but also supports operational efficiency and reduces downtime. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who offer durable products and robust warranties, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where environmental factors can accelerate wear and tear.
Looking ahead, businesses that invest in understanding these components will be better positioned to optimize their supply chains and ensure customer satisfaction. We encourage you to explore partnerships with trusted suppliers to secure the best solutions for your automotive needs and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Aviso legal importante y condiciones de uso
⚠️ Aviso legal importante
La información proporcionada en esta guía, incluido el contenido relativo a los fabricantes, las especificaciones técnicas y el análisis de mercado, tiene fines meramente informativos y educativos. No constituye asesoramiento profesional en materia de adquisiciones, asesoramiento financiero ni asesoramiento jurídico.
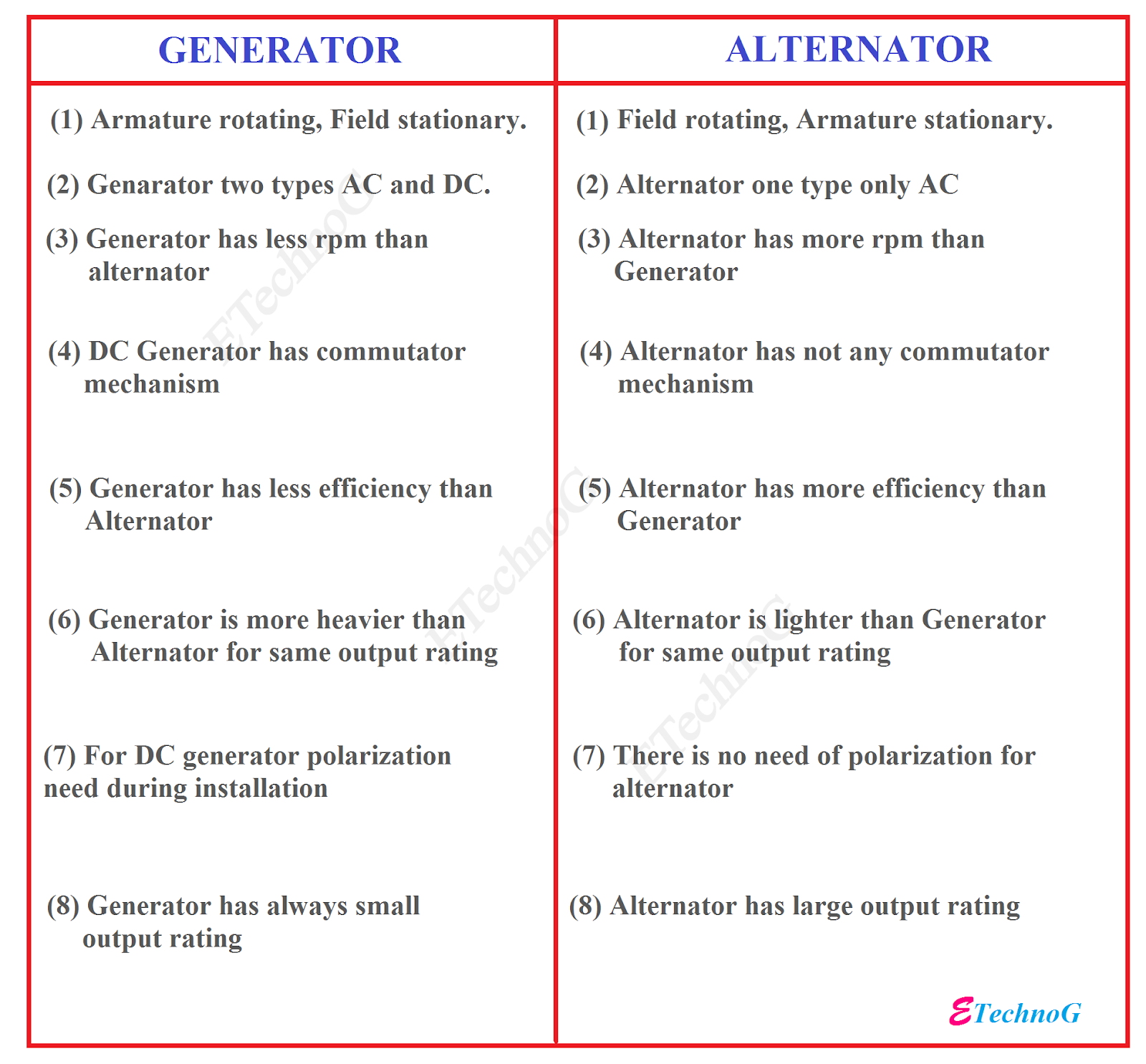
Illustrative image related to difference between starter and alternator
Aunque hemos hecho todo lo posible por garantizar la exactitud y actualidad de la información, no nos hacemos responsables de los errores, omisiones o información desactualizada. Las condiciones del mercado, los datos de las empresas y las normas técnicas están sujetos a cambios.
Los compradores B2B deben llevar a cabo su propia diligencia debida de forma independiente y exhaustiva. antes de tomar cualquier decisión de compra. Esto incluye ponerse en contacto directamente con los proveedores, verificar las certificaciones, solicitar muestras y buscar asesoramiento profesional. El riesgo de confiar en cualquier información contenida en esta guía recae exclusivamente en el lector.