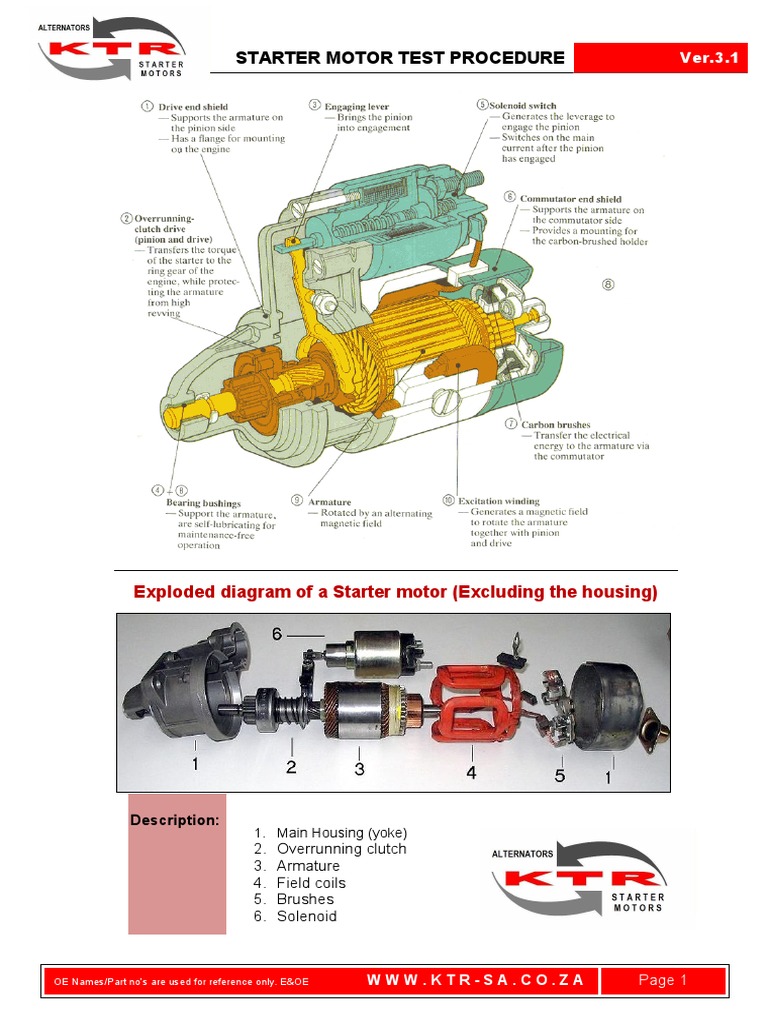
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for test a starter motor
Navigating the complexities of sourcing reliable solutions to test a starter motor can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. The automotive sector is evolving rapidly, and understanding the nuances of starter motor testing is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and reducing downtime. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of testing methods available, their specific applications across different vehicle models, and the importance of selecting the right tools and equipment. Additionally, we will explore critical aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements in testing starter motors.
For businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, making informed purchasing decisions is paramount. This guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights into the testing process, highlighting key factors to consider when evaluating suppliers, and outlining best practices for maintenance and troubleshooting. Whether you are a fleet manager, automotive technician, or procurement officer, this resource will equip you with the knowledge needed to enhance your operations, ultimately leading to more reliable vehicle performance and customer satisfaction. By the end of this guide, you will have a clearer understanding of how to navigate the global market for testing starter motors effectively.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Test A Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for test a starter motor
- Understanding test a starter motor Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of test a starter motor
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘test a starter motor’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for test a starter motor
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for test a starter motor
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘test a starter motor’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for test a starter motor Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing test a starter motor With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for test a starter motor
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the test a starter motor Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of test a starter motor
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for test a starter motor
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding test a starter motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bench Testing | Involves connecting the starter to a battery to check functionality. | Automotive repair shops, heavy machinery maintenance. | Pros: Quick diagnosis; Cons: Requires additional equipment. |
| Resistance Testing | Measures the resistance of the armature and insulation to identify issues. | Electrical equipment manufacturers, automotive parts suppliers. | Pros: Detailed insights into electrical health; Cons: Requires precise tools. |
| Load Testing | Simulates operational conditions to assess performance under load. | Fleet management, industrial equipment maintenance. | Pros: Realistic performance evaluation; Cons: Time-consuming and complex setup. |
| Visual Inspection | Physical examination for mechanical damages or signs of wear. | Automotive service centers, machinery inspections. | Pros: No equipment needed; Cons: May overlook internal issues. |
| Thermal Imaging | Uses infrared technology to detect hotspots indicating electrical faults. | Electrical contractors, predictive maintenance services. | Pros: Non-invasive and highly accurate; Cons: High initial investment for equipment. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Bench Testing for Starter Motors?
Bench testing is a practical method for assessing a starter motor’s functionality by directly connecting it to a power source, typically a battery. This approach enables technicians to observe the starter’s operational performance, ensuring it engages and disengages properly. Bench testing is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and heavy machinery maintenance facilities, where quick and effective diagnostics are essential. Buyers should consider the availability of a suitable power source and proper safety measures, as the process can involve high torque and potential equipment damage.
How Does Resistance Testing Help in Diagnosing Starter Motors?
Resistance testing involves measuring the electrical resistance of the starter motor’s armature and insulation. This method is crucial for identifying faults such as short circuits or insulation breakdowns. It is widely used by electrical equipment manufacturers and automotive parts suppliers, as it provides detailed insights into the motor’s electrical health. Buyers should invest in high-quality digital multimeters capable of measuring low resistance levels accurately, as precision is critical for reliable diagnostics.
What Are the Benefits of Load Testing for Starter Motors?
Load testing simulates operational conditions to evaluate a starter motor’s performance under realistic loads. This testing is vital for fleet management and industrial equipment maintenance, where reliability is paramount. By observing how the starter performs when subjected to actual working conditions, technicians can identify potential failures before they occur. Buyers should be prepared for a more complex and time-consuming setup, as load testing requires additional equipment and careful monitoring.
Why Is Visual Inspection an Important Step in Starter Motor Testing?
Visual inspection is a straightforward and cost-effective method for assessing starter motors. Technicians look for mechanical damages, such as missing bolts or signs of wear and tear. This method is commonly used in automotive service centers and during machinery inspections. While it requires no specialized equipment, buyers should be aware that visual inspections may miss internal electrical faults, making it essential to combine this method with more advanced testing techniques for comprehensive diagnostics.
How Does Thermal Imaging Enhance Starter Motor Testing?
Thermal imaging employs infrared technology to detect hotspots that may indicate electrical faults within the starter motor. This non-invasive technique is increasingly utilized by electrical contractors and predictive maintenance services to identify issues before they lead to failures. The accuracy of thermal imaging can significantly enhance maintenance strategies, although buyers should consider the high initial investment required for the necessary equipment. This method is particularly beneficial for organizations focused on proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Key Industrial Applications of test a starter motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of test a starter motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Testing starter motors for vehicle diagnostics | Reduces downtime by quickly identifying faulty components | Availability of testing equipment and trained personnel |
| Heavy Machinery | Ensuring reliability in construction equipment | Enhances operational efficiency and safety | Compatibility with various machinery types and power sources |
| Transportation & Logistics | Maintenance of fleet vehicles | Minimizes breakdowns, ensuring timely deliveries | Bulk sourcing of parts and equipment for cost efficiency |
| Agriculture | Testing starter motors in agricultural machinery | Increases productivity by reducing machinery failure | Access to specialized testing tools and parts for diverse equipment |
| Renewable Energy | Evaluating starter motors in wind turbines | Optimizes energy production and equipment longevity | Understanding of specific motor requirements and environmental conditions |
How is ‘Testing a Starter Motor’ Used in Automotive Repair Shops?
In automotive repair shops, testing starter motors is crucial for diagnosing vehicle issues. A faulty starter can lead to vehicle breakdowns, resulting in costly repairs and extended downtimes. By utilizing specialized testing equipment, mechanics can quickly identify whether the starter motor is operational or requires replacement. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Nigeria or Brazil, sourcing reliable testing tools and ensuring staff training are essential for maintaining service quality.
What Role Does Testing Starter Motors Play in Heavy Machinery?
Heavy machinery relies heavily on functional starter motors for effective operation. In the construction sector, testing these components ensures that equipment such as excavators and bulldozers starts reliably, minimizing project delays. Buyers in regions with challenging climates, like the Middle East, should consider the durability and compatibility of testing equipment with various machinery types to ensure longevity and reliability.
Why is Testing Starter Motors Important for Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics industry, maintaining a fleet of vehicles is paramount for timely deliveries. Regular testing of starter motors helps prevent unexpected breakdowns that can disrupt supply chains. Businesses should focus on sourcing bulk parts and testing equipment to lower costs and ensure consistent quality across their fleet. Buyers in South America may also prioritize vendors with robust support and service options to minimize operational disruptions.
How Does Testing Impact Agricultural Machinery?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, depends on efficient starter motors for optimal performance. Regular testing helps identify issues before they escalate, ensuring that farmers can operate their equipment without interruptions. For buyers in Africa, understanding the specific requirements of different agricultural machines is critical, as is having access to specialized testing tools that can withstand the rigors of field conditions.
What is the Importance of Testing Starter Motors in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind energy, testing starter motors in turbines is vital for ensuring operational efficiency. A malfunctioning starter can lead to significant energy production losses. Buyers should seek vendors who understand the unique requirements of renewable energy applications, including the environmental conditions that may affect starter motor performance. Proper sourcing of testing equipment can lead to enhanced equipment longevity and improved energy output.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘test a starter motor’ & Their Solutions
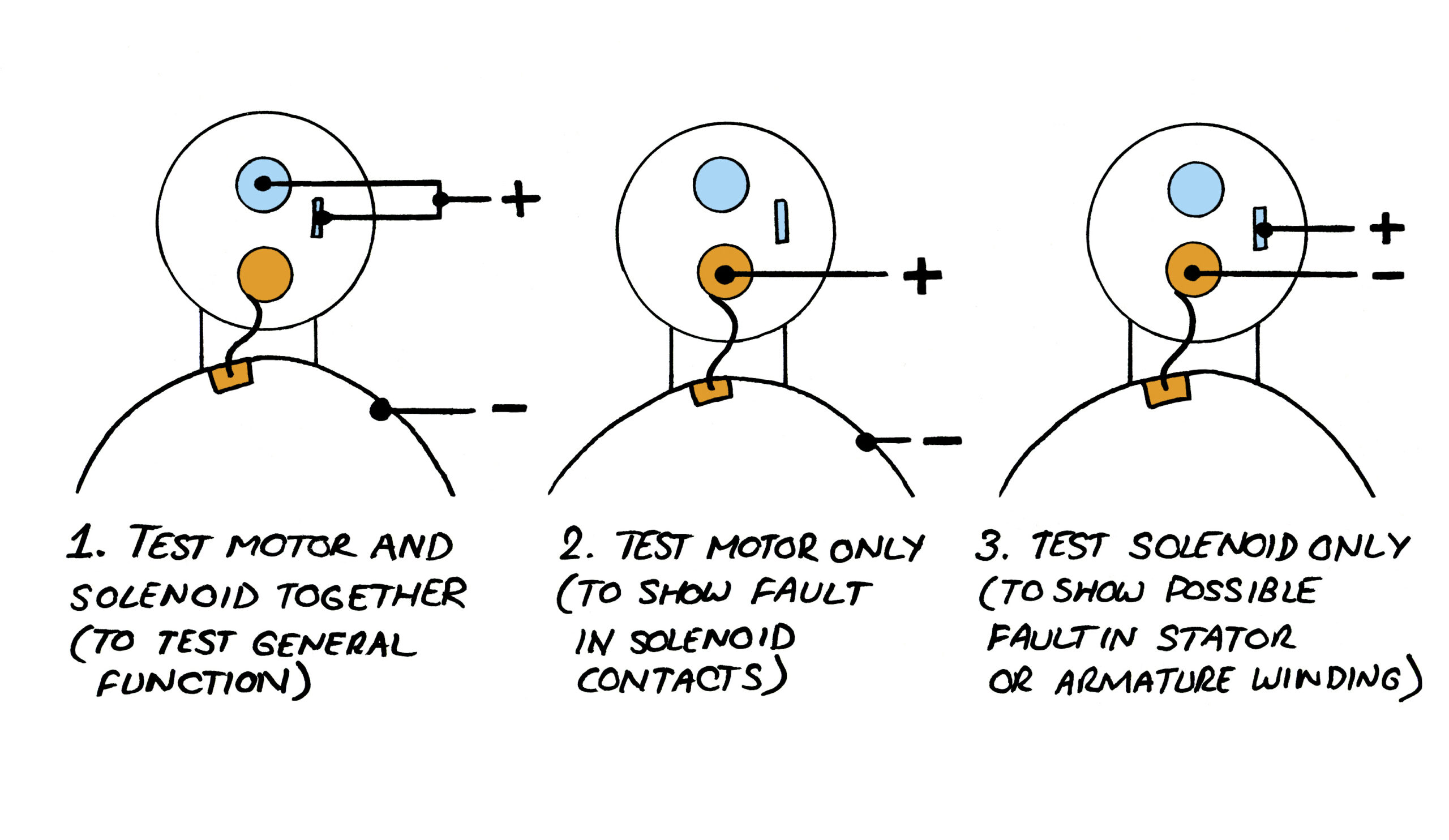
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Testing Results Leading to Misdiagnosis
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of inconsistent testing results when evaluating starter motors. This inconsistency can arise from using incorrect testing procedures or inadequate equipment. For instance, a buyer may perform resistance tests on the armature assembly using a multimeter but receive fluctuating readings, leading to confusion about the motor’s functionality. Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary replacements or repairs, resulting in increased operational costs and lost revenue.

Illustrative image related to test a starter motor
The Solution:
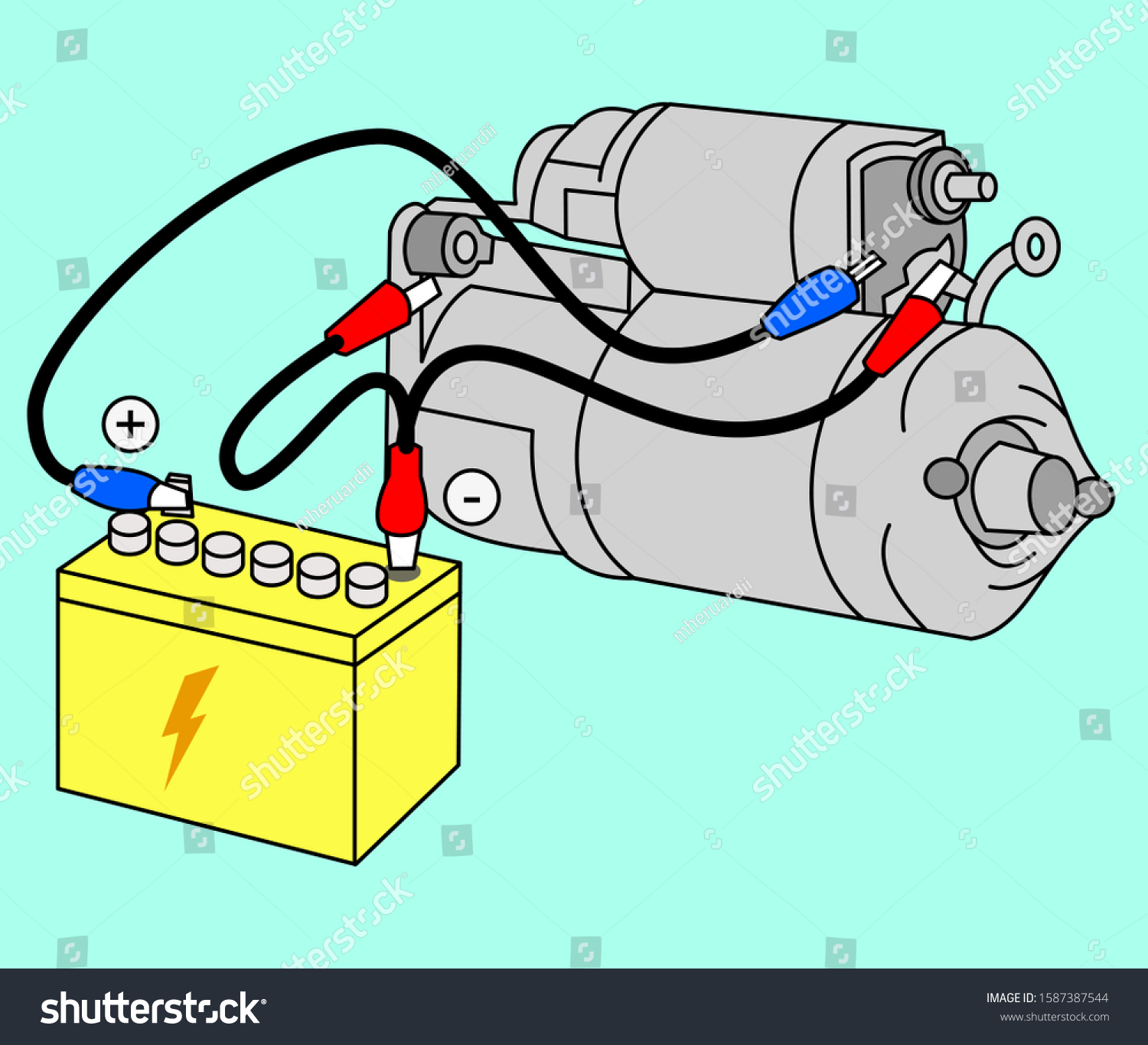
To mitigate this issue, it is crucial to establish a standardized testing protocol. Buyers should invest in high-quality digital multimeters with appropriate ranges for testing resistance, particularly those capable of measuring low resistance accurately. When testing the armature assembly, ensure the multimeter is set to a range that allows for precise readings (ideally below 1 ohm). Additionally, refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for resistance values to guide the testing process. It’s also advisable to perform a bench test by connecting the starter motor to a fully charged 12-volt battery. This test can help confirm the motor’s operational status and provide a more reliable assessment than resistance readings alone. By implementing these practices, B2B buyers can achieve consistent results and make informed decisions regarding starter motor repairs or replacements.
Scenario 2: Lack of Knowledge About Bench Testing Methods
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers may not be familiar with the importance of bench testing starter motors, leading to missed opportunities for accurate diagnostics. Without this knowledge, buyers might rely solely on visual inspections and basic electrical tests, which can overlook critical issues. For example, a starter motor that appears visually intact may still fail to function correctly under load, resulting in unexpected downtime for equipment or vehicles.
The Solution:
To enhance diagnostic accuracy, B2B buyers should prioritize education on proper bench testing techniques. A comprehensive guide on performing bench tests should include step-by-step instructions on connecting the starter motor to a battery and observing its operation. This test should be conducted in a safe environment, preferably with the motor secured in a vice to prevent movement. If the motor fails to turn or exhibits erratic behavior, it may indicate underlying issues such as faulty windings or worn carbon brushes. Providing training sessions or workshops on testing methods can empower technicians and staff, leading to more reliable diagnostics and reduced downtime. Additionally, maintaining a record of test results can help identify patterns over time, enabling proactive maintenance strategies.
Scenario 3: Difficulty Sourcing Quality Replacement Parts
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter challenges when sourcing quality replacement parts for starter motors. This issue can stem from a lack of reliable suppliers or the overwhelming number of options available in the market. In regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains can be less stable, finding authentic parts that meet OEM specifications becomes critical. Substandard replacements can lead to further mechanical failures and increased repair costs.
The Solution:
To address sourcing difficulties, buyers should build relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in automotive components, particularly those with a focus on starter motors. Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that have a proven track record of providing high-quality parts. Utilizing platforms that offer verified ratings and reviews can help streamline this process. Additionally, establishing a direct line of communication with manufacturers can facilitate bulk ordering and ensure access to the latest products. Buyers should also consider implementing a vendor management system that tracks supplier performance, ensuring that only reliable vendors are used for critical components. By prioritizing quality over cost in sourcing, B2B buyers can enhance the longevity and reliability of their starter motors, ultimately reducing operational disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for test a starter motor
What Are the Key Materials Used in Testing a Starter Motor?
When testing a starter motor, the selection of materials plays a critical role in ensuring performance, reliability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the components and tools for testing starter motors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Copper Benefit Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for wiring and connectors in starter motors. It has a high melting point (around 1,984°F or 1,085°C) and good corrosion resistance, especially when coated.
Illustrative image related to test a starter motor
Pros & Cons: The durability of copper is high, but it can be prone to oxidation if not properly coated, which may affect conductivity over time. While copper is relatively inexpensive compared to other conductive materials, its cost can increase significantly if high-purity grades are required. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as copper is easy to shape and solder.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with electrical systems is paramount, ensuring minimal resistance and efficient power transfer. However, in humid or corrosive environments, additional protective measures may be necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local electrical standards and potential variations in copper quality. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 (for copper wire) is essential for ensuring product safety and performance.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has good thermal conductivity. Its melting point is lower than copper’s, at about 1,221°F (660.3°C).
Pros & Cons: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical. However, it has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which may lead to higher resistance in electrical applications. The cost of aluminum is generally lower than that of copper, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in starter motor casings and some connectors, where weight savings are crucial. However, its lower conductivity means it may not be the best choice for high-current applications without careful design considerations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, especially when sourcing from different regions. Understanding local market preferences for aluminum grades can also influence purchasing decisions.
Why Is Steel Important for Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high strength and durability, with a melting point around 2,500°F (1,370°C). It is also resistant to wear and can be treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of steel is its strength, making it suitable for structural components of starter motors. However, steel can be heavier than alternatives like aluminum, which may not be ideal for all applications. The cost of steel is typically moderate, but additional treatments for corrosion resistance can increase overall costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in the housing and mounting components of starter motors, where strength and durability are critical. However, its weight may affect the overall performance of lighter vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding local regulations regarding steel quality and treatment processes is crucial, especially in regions with varying environmental conditions like the Middle East. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is necessary for ensuring product integrity.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into complex shapes. Their thermal stability varies depending on the type of plastic used.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of plastics makes them ideal for non-structural components, reducing overall weight. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress as well as metals. Plastics can be relatively inexpensive, but their manufacturing complexity can vary widely.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used in insulation and protective housings for electrical components in starter motors. However, their limitations in high-temperature environments must be considered.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the specific type of plastic being used and its compliance with international standards such as ISO 1043 for plastic materials. Understanding regional preferences for materials can also influence sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Testing Starter Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for test a starter motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Wiring and connectors | Excellent electrical conductivity | Prone to oxidation | Medium |
| Aluminum | Casings and connectors | Lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Low |
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier than alternatives | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and protective housings | Corrosion-resistant and lightweight | Limited high-temperature tolerance | Low |
This guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to select the appropriate materials for testing starter motors, ensuring compliance and performance across various regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for test a starter motor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Motors?
The manufacturing of starter motors involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Motor Production?
Material preparation is the first stage in manufacturing starter motors. It typically involves sourcing high-grade materials such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and various alloys for internal components. Quality control begins at this stage, with suppliers required to provide certification of material properties to ensure compliance with international standards. The materials are then cut and shaped according to specific design requirements, ensuring that they meet precise specifications necessary for optimal performance.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Forming techniques in starter motor manufacturing primarily involve processes such as stamping, forging, and machining. Stamping is used for creating complex shapes from sheet metal, while forging is often employed for components requiring higher strength. Machining processes, including turning and milling, are utilized to achieve tight tolerances on critical components like the armature and commutator. Each technique is selected based on the component’s design and functional requirements, ensuring the durability and efficiency of the final product.
How Are Starter Motors Assembled?
Assembly is a crucial phase where all prepared components come together. This process typically follows a systematic approach to ensure that each part is correctly installed. Automated assembly lines are increasingly used, allowing for consistent quality and efficiency. Key components such as the armature, brushes, and housing are assembled with precision, often using fixtures that help maintain alignment during the process. Manual inspections during assembly are common to catch any defects early, reducing the likelihood of issues in the final product.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Starter Motors?
The finishing stage includes surface treatment and testing to ensure longevity and performance. Common finishing processes include painting, plating, and heat treatment. These treatments protect against corrosion and enhance the mechanical properties of the motor. Additionally, final assembly includes electrical testing to ensure the starter motor meets all specifications before it is packaged for shipment.

Illustrative image related to test a starter motor
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each starter motor functions reliably and meets international standards. Key practices include adherence to international standards like ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for quality management systems.
How Do International Standards Impact Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications like CE and API play a significant role in quality control. These standards provide frameworks for consistent manufacturing practices, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and of high quality. Compliance with these standards is often a prerequisite for doing business in many markets, especially in regions like Europe and North America.
What Are the Main Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Motor Production?
Quality control checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps identify defects early, allowing for timely corrective actions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product before shipment, ensuring that each starter motor meets performance specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Validate Starter Motors?
Testing methods are crucial for assessing the performance and durability of starter motors. Common tests include:
- Electrical Resistance Testing: Measures the resistance of the armature windings to ensure they are within specified limits.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Assesses the insulation quality to prevent electrical failures.
- Bench Testing: Involves connecting the starter motor to a power source to verify its operational performance.
These tests are often documented in detailed reports that buyers can review to ensure compliance with their requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Buyers should consider the following approaches:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insight into the supplier’s processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports, including results from various tests and inspections, can help assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices and product reliability.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control, particularly regarding compliance with local regulations and standards. For instance, products exported to the European market must meet CE marking requirements, while those sold in the U.S. may need to adhere to different safety standards. Understanding these nuances is crucial for avoiding costly compliance issues and ensuring that products are market-ready.
Illustrative image related to test a starter motor
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with starter motors is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages in production and robust quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘test a starter motor’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to test a starter motor effectively. Whether you are sourcing testing equipment or seeking to evaluate the performance of starter motors, following these steps will ensure that you make informed decisions, reduce risks, and enhance operational efficiency.
1. Identify Your Testing Requirements
Understanding your specific testing needs is the foundation of your procurement process. Determine the types of starter motors you will be testing and the parameters that need to be evaluated, such as resistance levels, insulation quality, and mechanical integrity. This will guide you in selecting the right tools and suppliers.
2. Define Your Technical Specifications
Crafting clear technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance. Include details such as voltage ratings, resistance measurement ranges, and additional features needed in testing equipment. This will help suppliers provide you with accurate solutions that meet your operational demands.
3. Research and Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure they have a solid reputation in the industry. Look for:
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant industry certifications that demonstrate their compliance with international standards.
– Customer Reviews: Seek feedback from other businesses, particularly those in similar markets, to gauge reliability and service quality.
4. Request and Compare Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations. Compare these not only based on price but also on the quality of equipment offered, warranty terms, and after-sales support. A comprehensive comparison will help you find the best value without compromising on quality.
5. Check for Technical Support and Training
Ensure that your chosen supplier provides adequate technical support and training for using the testing equipment. This is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring that your team can perform tests accurately. Ask about:
– User Manuals: Availability of comprehensive manuals and troubleshooting guides.
– Training Sessions: Options for in-person or virtual training sessions for your staff.
6. Verify Warranty and Return Policies
Understanding warranty and return policies is essential to mitigate risks associated with faulty equipment. Check:
– Warranty Duration: Ensure that the warranty covers a reasonable period and includes parts and labor.
– Return Process: Familiarize yourself with the return policy in case the equipment does not meet your expectations or fails to perform as promised.
7. Plan for Long-Term Support and Maintenance
Testing equipment requires ongoing maintenance to ensure accurate results. Establish a relationship with your supplier that includes regular check-ups, servicing, and potential upgrades. This proactive approach will enhance the longevity of your testing equipment and ensure consistent performance.
Following this checklist will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing equipment and services for testing starter motors, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for test a starter motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Testing a Starter Motor?
When sourcing testing services for starter motors, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and supplier negotiations. The primary cost components typically include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials used in testing equipment can significantly influence costs. Components like digital multimeters, insulation testers, and other diagnostic tools may vary widely in price based on brand and specifications.
-
Labor: Skilled technicians are required to perform accurate tests on starter motors. Labor costs will depend on the local wage standards, the complexity of the testing process, and the expertise level of the personnel involved.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and administrative expenses necessary for the operation of the testing facility. Understanding these costs can help buyers gauge the pricing structure of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: Special tools and fixtures used for testing starter motors can incur additional costs. These investments ensure precision and reliability in testing, impacting overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is essential to ensure that the testing results are reliable. The costs associated with QC measures can vary based on the certifications and standards the testing facility adheres to.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs for transporting motors to and from testing facilities can add to the overall expenses. This is particularly relevant for international buyers, as customs duties and tariffs may also apply.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Testing a Starter Motor?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of starter motor testing services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders can lead to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help negotiate better pricing with suppliers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom testing requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly outline specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials for testing tools can affect pricing. Higher-quality equipment may come at a premium, but it can yield more accurate results.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with recognized certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may charge higher prices due to their commitment to quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Suppliers in regions with higher operational costs may charge more.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential as they dictate responsibilities for shipping and logistics, affecting overall pricing.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers Sourcing Starter Motor Testing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Gather data on market prices for testing services to understand fair pricing. Benchmarking against competitors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial costs but also the long-term expenses associated with poor quality or unreliable testing. Emphasizing TCO can persuade suppliers to offer better pricing or terms.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If planning to order in bulk, communicate this to suppliers upfront. Volume commitments can be a powerful negotiation tool.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Providing clear and detailed specifications can prevent misunderstandings and additional costs later in the process.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and facilitate easier communication.
Conclusion
While sourcing testing services for starter motors, it is essential to consider all cost components and price influencers. By employing effective negotiation strategies and focusing on the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to better pricing and overall value. Always remember to consult with multiple suppliers to gather a range of quotes and insights before finalizing your sourcing strategy.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing test a starter motor With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Testing a Starter Motor
In the realm of automotive maintenance and repair, testing a starter motor is critical for ensuring optimal vehicle performance. However, there are various methods and technologies available for diagnosing starter motor issues. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs, budget, and technical capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Test A Starter Motor | Bench Testing | Digital Oscilloscope |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for basic checks | High accuracy for diagnosis | Exceptional signal analysis |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate | High |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, requires basic tools | Requires more setup and expertise | Requires specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Moderate | High |
| Best Use Case | Quick diagnostic checks | Detailed fault isolation | Advanced electrical diagnostics |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Bench Testing
Bench testing involves removing the starter motor and connecting it directly to a power source to observe its operation. This method allows for a thorough assessment of the starter’s functionality without the interference of other vehicle components. The primary advantage of bench testing is its ability to provide precise insights into the starter’s performance, revealing issues like mechanical binding or electrical faults. However, it requires more setup time and expertise compared to simply testing a starter motor in situ, making it less accessible for less experienced technicians. Additionally, while costs remain relatively low, the need for additional equipment can add to the overall investment.
Digital Oscilloscope
A digital oscilloscope offers an advanced method for diagnosing starter motor issues by analyzing the electrical signals produced during operation. This tool provides high-resolution data that can pinpoint specific faults in the starter’s winding or brushes, making it invaluable for in-depth diagnostics. The primary benefit is its ability to deliver detailed insights that can enhance repair accuracy. However, the cost of a digital oscilloscope is significantly higher than both testing a starter motor and bench testing, which may not be feasible for all businesses. Moreover, using this technology requires specialized training and expertise, making it less practical for smaller operations without dedicated technicians.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Testing Solution
When selecting the appropriate method for testing a starter motor, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including budget constraints, the complexity of the diagnosis needed, and the skill level of their technicians. For quick diagnostics, testing a starter motor is a straightforward and cost-effective solution. If more detailed analysis is necessary, bench testing provides a balance between accuracy and accessibility. However, for businesses that require the highest level of diagnostic capability and have the resources to invest in advanced tools, a digital oscilloscope may be the ideal choice. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational needs and strategic goals of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for test a starter motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties When Testing a Starter Motor?
Understanding the technical properties of starter motors is crucial for B2B buyers involved in automotive parts procurement or maintenance. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Resistance Values
The resistance of the armature winding is critical, typically measured in ohms. For instance, a common standard indicates that the commutator should have a resistance between 0.009 and 0.011 ohms. This specification is vital because deviations can indicate winding failures or short circuits, leading to starter malfunction. Ensuring compliance with resistance standards can help prevent costly repairs and enhance vehicle reliability. -
Insulation Resistance
Insulation resistance must typically exceed 1 megaohm (MΩ). This measurement assesses the integrity of the insulation around the windings. Low insulation resistance can lead to electrical leaks, which may result in starter motor failure. For B2B buyers, maintaining proper insulation is essential for ensuring longevity and performance, particularly in harsh operating environments common in regions like Africa and South America. -
Material Composition
The materials used in starter motors, such as copper for windings and high-grade steel for the housing, significantly impact performance. Material quality affects both durability and efficiency. Buyers must consider the grade of materials to ensure they are procuring products that can withstand the demands of their specific applications, particularly in challenging climates. -
Torque Ratings
Torque is a measure of rotational force that the starter motor can generate. This specification is vital for determining whether the starter can effectively engage the engine, particularly in larger vehicles or those with higher compression ratios. Understanding torque ratings helps buyers select appropriate starter motors that meet the power requirements of various vehicle models. -
Operating Voltage
Most automotive starter motors operate at 12 volts, but understanding the specific voltage requirements for different applications is crucial. Variations in voltage can lead to inadequate performance or damage to the starter. B2B buyers should ensure compatibility with the electrical systems of the vehicles they service or sell.
Which Trade Terms Are Essential in the Starter Motor Industry?
Navigating the trade terminology is equally important for effective communication and procurement in the starter motor market. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. When sourcing starter motors, OEM parts are often preferred due to their guaranteed compatibility and quality. Understanding OEM specifications helps buyers ensure that they are procuring parts that meet the manufacturer’s standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to optimize inventory levels and manage cash flow effectively. In regions with fluctuating demand, understanding MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit pricing and terms from suppliers. This process is essential for comparing different suppliers and ensuring competitive pricing. B2B buyers should understand how to draft effective RFQs to receive the best offers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding these terms is crucial for international transactions, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and import duties. This knowledge helps prevent misunderstandings and potential disputes in cross-border trade. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the time frame during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their product. For starter motors, a longer warranty often indicates confidence in product quality. Buyers should always inquire about warranty terms to mitigate risks associated with defective parts.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality starter motors that meet their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the test a starter motor Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Test a Starter Motor Sector?
The test a starter motor sector is experiencing significant changes driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and the increasing complexity of automotive systems. Global drivers such as the rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and stringent emissions regulations are reshaping the market landscape. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (e.g., Brazil and Nigeria) are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality components that ensure reliability and efficiency, especially as the automotive sector transitions to more sustainable practices.
Emerging technologies in the sector include the adoption of advanced diagnostic tools and automated testing equipment, which streamline the testing process and enhance accuracy. Digital solutions, such as IoT-enabled devices, allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and repair costs. B2B buyers should also consider suppliers that leverage data analytics to improve product performance and customer service.
Illustrative image related to test a starter motor
Market dynamics are characterized by a growing emphasis on local sourcing and supply chain resilience, particularly in the wake of global disruptions. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers with robust logistics capabilities and flexible manufacturing processes to mitigate risks associated with international shipping. This trend underscores the importance of establishing long-term relationships with trustworthy suppliers who can adapt to changing market conditions and provide consistent quality.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Test a Starter Motor Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the test a starter motor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of automotive components are under increasing scrutiny. Buyers are urged to seek out suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing waste, conserving energy, and employing sustainable materials in their production processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, as consumers and regulatory bodies alike demand transparency and accountability from manufacturers. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide certifications indicating adherence to environmental standards, such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. Additionally, sourcing components made from recycled materials or those certified as environmentally friendly can significantly enhance a company’s sustainability profile.
As the automotive industry pivots towards electrification, the sourcing of materials for electric starter motors—such as lithium for batteries—will also require ethical considerations. Ensuring that materials are obtained through responsible mining practices is essential for maintaining a positive brand image and meeting regulatory requirements.
What Is the Historical Context of the Test a Starter Motor Sector?
The test a starter motor sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, starter motors were simple mechanical devices with limited testing requirements. As automotive technology advanced, so did the complexity of starter motors, necessitating more sophisticated testing methods to ensure their reliability and performance.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the introduction of electronic components revolutionized the sector, leading to the development of more efficient starter motors. This evolution prompted the need for advanced diagnostic tools capable of assessing both mechanical and electrical functionalities. Today, with the rise of electric vehicles and smart automotive systems, the market is poised for further transformation, emphasizing the need for continual innovation in testing methods and sourcing strategies.
This historical context highlights the importance of staying informed about technological advancements and market trends, enabling B2B buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with industry evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of test a starter motor
-
How do I solve issues with a starter motor that won’t turn?
To troubleshoot a non-responsive starter motor, first check the battery connections and ensure they are clean and secure. Next, use a multimeter to test the battery voltage; it should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged. If the battery is good, perform a bench test on the starter motor by connecting it to a 12-volt battery to see if it spins. If it doesn’t turn, the issue may lie in the armature, brushes, or internal wiring, necessitating further inspection or replacement. -
What is the best method to test a starter motor?
The most effective way to test a starter motor is through a combination of electrical and mechanical assessments. Start with a multimeter to check the resistance of the windings, ensuring they fall within the manufacturer’s specifications. Follow this with an insulation resistance test, ideally using a specialized insulation tester. Finally, perform a bench test by connecting the starter to a charged battery. If the starter engages and spins freely, it is functioning correctly; otherwise, further investigation is required. -
What are the common signs that a starter motor needs to be replaced?
Common indicators of a failing starter motor include unusual noises (clicking or grinding), intermittent starting issues, or a complete failure to start the engine. Additionally, if the starter motor runs but the engine does not crank, it may indicate a mechanical failure within the starter. Visual inspections for burnt or damaged components can also provide insight into its condition. -
How can I vet suppliers for starter motors internationally?
When vetting suppliers for starter motors, prioritize those with a proven track record in your region. Request references and case studies from previous clients, and check their certifications for quality standards such as ISO. Additionally, consider conducting a factory visit or utilizing third-party inspection services to evaluate their production capabilities and adherence to quality assurance practices. Online reviews and industry forums can also provide valuable insights into supplier reliability. -
What are typical payment terms for purchasing starter motors in bulk?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on supplier policies and the nature of the transaction. Common options include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance payable upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established relationships. It is advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow while ensuring the supplier is comfortable with the arrangement. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starter motors?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter motors can differ based on the supplier, the type of motor, and your specific requirements. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to 500 units for standard models, while customized or specialized motors may have higher MOQs. Always clarify these details with the supplier before finalizing any agreements to ensure that your purchasing needs align with their production capabilities. -
How does logistics affect the sourcing of starter motors internationally?
Logistics plays a crucial role in international sourcing, influencing cost, delivery times, and the overall supply chain efficiency. Factors such as shipping routes, customs regulations, and local transportation can impact lead times and product availability. It is essential to work with suppliers who have reliable logistics partners and to consider incoterms that clearly define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid unexpected costs. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect when sourcing starter motors?
When sourcing starter motors, expect suppliers to implement stringent quality assurance measures. This should include regular inspections throughout the production process, compliance with international quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001), and the provision of test reports for each batch. Some suppliers may also offer warranties or guarantees, ensuring that defective products are replaced or repaired. Always request details on their QA processes to ensure alignment with your quality expectations.
Top 3 Test A Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Starter Motor Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Starter motor, direct drive, gear reduction starters, cold weather performance (-25*C and below), pinion gear engagement issues, bench testing methods (jumper cables, screwdriver, vise), electrical connections (positive and ground to a battery).
2. Starter Testing – Essential Guide
Domain: forums.sohc4.net
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Bench testing a starter involves using a loaded battery, connecting the negative lead to the starter body, and the positive lead to the starter terminal. The starter should spin if it is functioning properly. It’s important to check for loose or corroded battery connections, as these can cause power issues. The starter motor circuit is not fused, but the solenoid control circuit is. Common issues …
3. Motoelectrical – Starter Motor Testing Guide
Domain: motoelectrical.co.uk
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Testing a starter motor on a motorcycle, ATV, or UTV involves checking its electrical and mechanical components to ensure it is functioning properly. Tools needed include a digital multimeter and a fully charged battery. The process includes safety precautions, visual inspection of the starter motor, checking battery voltage, performing a voltage drop test, checking solenoid operation, testing for…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for test a starter motor
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for testing starter motors is critical for international B2B buyers seeking reliability and performance in their automotive applications. Key takeaways include the importance of using accurate testing methods, such as digital multimeters and bench tests, to assess the condition of starter motors thoroughly. This not only ensures the quality of components but also mitigates potential mechanical failures that could disrupt operations.
Investing in quality testing equipment and understanding the technical specifications—like resistance measurements and insulation integrity—can significantly enhance procurement decisions. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for reliable automotive parts will only increase.
Looking forward, international buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who offer comprehensive testing solutions and support. By doing so, you can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and drive business growth. Embrace strategic sourcing today to secure a competitive edge in the automotive industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.