Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
In the dynamic landscape of automotive maintenance, one of the most pressing challenges faced by businesses is understanding how to start a vehicle with a bad starter. This common issue can lead to downtime and financial loss, particularly for logistics and transportation companies operating across diverse terrains in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Saudi Arabia. This comprehensive guide offers a deep dive into the various methods available for addressing starter-related problems, catering to the needs of international B2B buyers who require reliable solutions.
Within this guide, readers will explore a range of practical strategies, from identifying the symptoms of a failing starter to employing temporary fixes that can get vehicles running again. We will also cover essential tools and safety measures, as well as the importance of proper supplier vetting when sourcing automotive components. Understanding the cost implications and the potential for long-term savings through effective maintenance practices is crucial for informed purchasing decisions.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and a thorough understanding of the market, this guide empowers companies to navigate the complexities of automotive repairs efficiently. Whether you are managing a fleet of delivery trucks or servicing vehicles in remote areas, the knowledge contained herein will help mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 How To Start A Vehicle With A Bad Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- Understanding how to start a vehicle with a bad starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to start a vehicle with a bad starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to start a vehicle with a bad starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to start a vehicle with a bad starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to start a vehicle with a bad starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to start a vehicle with a bad starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Connection Cleaning | Involves cleaning battery terminals and connections. | Automotive repair shops, fleet services | Pros: Simple fix; low-cost; quick. Cons: Only effective if corrosion is the issue. |
| Tapping the Starter | Utilizing a tool to gently tap the starter to free stuck components. | Small garages, roadside assistance | Pros: Quick temporary solution; requires minimal tools. Cons: Risk of damaging the starter if done improperly. |
| Solenoid Inspection and Repair | Checking and repairing the solenoid connections for functionality. | Automotive parts suppliers, workshops | Pros: Addresses a common issue; can prevent future starter problems. Cons: May require specific knowledge or tools. |
| Push Start (Manual Transmission) | Using physical force to start the vehicle by pushing it. | Auto repair training programs, workshops | Pros: No tools required; effective for manual vehicles. Cons: Not suitable for automatics; requires physical effort. |
| Jump Starting | Using another vehicle to provide power to the starter. | Automotive service providers, fleet management | Pros: Quick and often effective; widely understood. Cons: Only works if the battery is the issue; temporary fix. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Battery Connection Cleaning?
Battery connection cleaning is a straightforward method that focuses on ensuring that the electrical connections between the battery and starter are free of corrosion. This technique is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in automotive repair sectors, as it requires minimal tools and can be executed quickly, making it an ideal first step in diagnostics. Regular maintenance of these connections can enhance vehicle reliability, making it a cost-effective solution for fleet services.
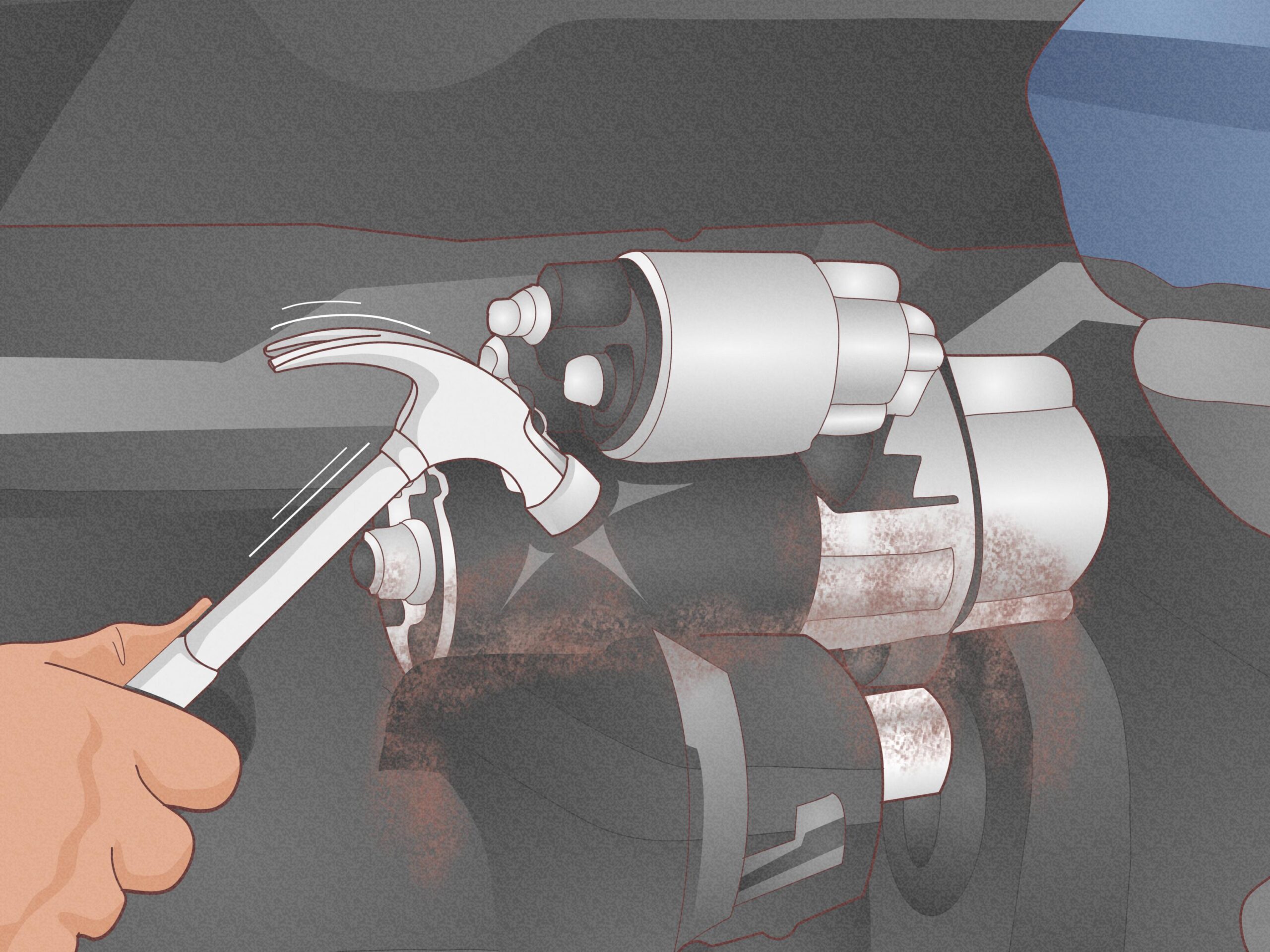
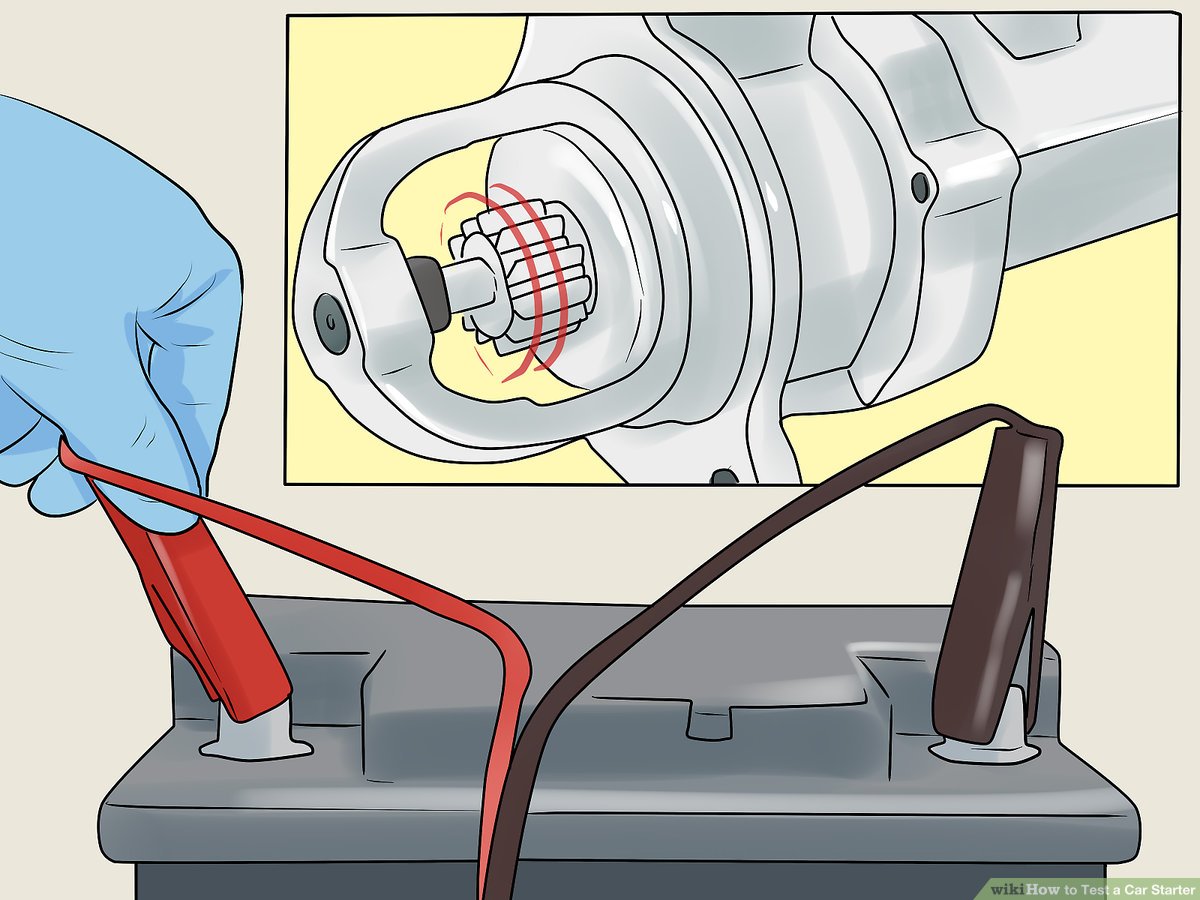
How Does Tapping the Starter Work as a Temporary Solution?
Tapping the starter involves gently striking it with a mallet or hammer to dislodge any stuck components. This method is useful for automotive shops that need to provide quick fixes to customers without extensive repairs. However, it requires a careful approach to avoid causing further damage. This technique is beneficial for small garages that may not have access to replacement parts immediately.
Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Why Is Solenoid Inspection and Repair Important?
Inspecting and repairing the solenoid can be crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of the starter system. This method is particularly applicable in B2B contexts where businesses may deal with a variety of vehicle models. Understanding solenoid issues can lead to more efficient repairs and reduce downtime for clients. Suppliers of automotive parts should emphasize the importance of this inspection in their offerings.
What Are the Benefits of Push Starting a Manual Transmission Vehicle?
Push starting is a technique suitable for manual transmission vehicles where the vehicle is rolled to gain momentum before engaging the ignition. This method is often taught in automotive training programs, providing a hands-on approach to understanding vehicle mechanics. It is an effective solution for workshops that cater to manual vehicles, though it requires physical effort and is not applicable for automatic transmissions.
When Should Jump Starting Be Considered?
Jump starting a vehicle is a common practice that involves connecting the battery of a functioning vehicle to the one with a suspected bad starter. This method is widely understood and can be a quick fix for automotive service providers. However, it is essential to recognize that this solution is only temporary and primarily effective if the battery is the root cause. B2B buyers should consider this method as part of a broader toolkit for addressing starting issues in vehicles.
Key Industrial Applications of how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to start a vehicle with a bad starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Utilizing temporary fixes to diagnose starter issues in customer vehicles | Reduces downtime and enhances customer satisfaction | Reliable tools and diagnostic equipment for effective repairs |
| Transportation & Logistics | Implementing quick-start techniques for delivery vehicles with starter problems | Minimizes delays in transport and maintains service efficiency | Access to durable starter repair tools and training resources |
| Fleet Management | Training staff on troubleshooting starter issues to keep fleet vehicles operational | Increases fleet uptime and reduces maintenance costs | Comprehensive training programs and access to parts suppliers |
| Construction & Heavy Equipment | Employing methods to start construction vehicles with faulty starters | Ensures continuous operation on job sites, preventing project delays | Quality starter repair tools and knowledge of heavy equipment systems |
| Agriculture | Applying starter troubleshooting techniques on agricultural machinery | Facilitates timely harvesting and minimizes equipment downtime | Availability of specialized tools for agricultural machinery |
How Can Automotive Repair Shops Benefit from Understanding How to Start a Vehicle with a Bad Starter?
Automotive repair shops frequently encounter vehicles that refuse to start due to faulty starters. By implementing temporary fixes such as battery terminal cleaning or using a hammer to tap the starter, mechanics can diagnose and address issues promptly. This not only reduces vehicle downtime but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring quick resolutions. For international buyers, sourcing reliable diagnostic tools and repair equipment is crucial to maintain high service standards.
What Advantages Do Transportation & Logistics Companies Gain from Starter Troubleshooting Techniques?
For transportation and logistics companies, the ability to quickly start delivery vehicles with bad starters is vital. Techniques such as jump-starting or utilizing a mallet can minimize delays and ensure that goods are delivered on time. This operational efficiency is essential in maintaining client relationships and service reliability. Companies should prioritize sourcing durable starter repair tools and invest in employee training to maximize these benefits.
How Can Fleet Management Improve Efficiency with Starter Issue Training?
Fleet management operations can significantly enhance vehicle uptime by training staff on how to troubleshoot starter problems. Techniques like checking solenoid connections or conducting push starts can keep vehicles operational and reduce maintenance costs. By investing in comprehensive training programs and ensuring access to quality parts suppliers, fleet managers can optimize their operations and extend the lifespan of their vehicles.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Why Is It Important for Construction & Heavy Equipment Industries to Address Starter Problems?
In the construction and heavy equipment sector, faulty starters can halt operations and lead to costly project delays. Employing methods to address starter issues quickly ensures that machinery remains functional and projects stay on schedule. Businesses in this sector should focus on sourcing quality starter repair tools and gaining knowledge of heavy machinery systems to effectively tackle these challenges.
What Role Does Starter Troubleshooting Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, the ability to start machinery with bad starters is crucial for timely harvesting and overall productivity. Techniques such as cleaning battery connections or using temporary fixes can prevent equipment downtime during critical periods. Agricultural businesses should ensure they have access to specialized tools designed for their machinery, as well as training resources, to handle starter issues effectively and maintain operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to start a vehicle with a bad starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Frustration of Unresponsive Vehicles in Remote Areas
The Problem: For fleet managers operating in remote regions, the inability to start a vehicle due to a bad starter can lead to significant operational downtime. This scenario is particularly pressing in areas where access to professional automotive services is limited. Fleet vehicles are essential for logistics, and a single vehicle failure can disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and hinder service delivery. The frustration is compounded when drivers are not equipped with the necessary skills or tools to diagnose and temporarily remedy the issue themselves.
The Solution: To address this challenge, fleet managers should implement a comprehensive training program for drivers that includes diagnostic skills for common vehicle issues, such as a bad starter. Training should focus on recognizing symptoms—like clicking noises or complete silence upon ignition—and performing basic troubleshooting steps, such as checking battery connections for corrosion. Providing drivers with essential tools, like jumper cables, a mallet for tapping the starter, and a voltmeter, can empower them to attempt quick fixes on-site. Additionally, establishing a clear communication channel with local automotive service providers can ensure that if repairs are needed, they can be executed swiftly, minimizing downtime.
Scenario 2: The Cost Implications of Ignoring Starter Issues
The Problem: Businesses often overlook the signs of a bad starter, leading to more severe vehicle malfunctions and costly repairs. For B2B buyers managing a fleet, the cumulative cost of emergency repairs and vehicle replacements can erode profit margins. Ignoring a faulty starter not only risks the immediate operational capabilities but also can have long-term impacts on the overall reliability of the fleet, which can be detrimental to business reputation and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate these costs, businesses should adopt a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of vehicle starters and batteries. Implementing a checklist that highlights common symptoms of a bad starter—such as unusual sounds during ignition attempts—can aid in early detection. Additionally, creating a partnership with automotive service specialists for routine check-ups can ensure that any issues are addressed before they escalate. Investing in quality starter components and ensuring the use of proper tools during maintenance can lead to longer-lasting solutions and reduced operational disruptions.
Scenario 3: The Challenge of Manual Transmission Vehicles
The Problem: In regions where manual transmission vehicles are still prevalent, the challenge of starting a vehicle with a bad starter is heightened. This issue is especially relevant for businesses in sectors like agriculture or construction, where manual vehicles are common. The inability to start these vehicles not only results in lost productivity but also poses safety risks if the vehicle is stranded in an unsafe location or during adverse weather conditions.
The Solution: Educating drivers on alternative methods to start manual transmission vehicles can provide a temporary solution while awaiting repairs. Techniques such as push-starting can be effective, but they require a team effort and should be conducted in safe environments. Businesses should conduct training sessions that demonstrate this technique, ensuring that all drivers understand the safety protocols involved. Additionally, maintaining a stock of necessary equipment, such as a portable jump starter or a reliable set of tools, can facilitate quicker responses to starter issues. Establishing a network of local mechanics who can provide quick assistance in case of persistent starter failures can also help in managing these scenarios effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
What Materials Are Essential for Starting a Vehicle with a Bad Starter?
When dealing with a vehicle that has a bad starter, selecting the right materials for temporary fixes and tools is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials used in this context, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Copper for Jumper Cables
Key Properties: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, which is essential for jump-starting a vehicle. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and good corrosion resistance when properly coated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, ensuring efficient power transfer. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to aluminum and can corrode if not properly maintained, especially in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Copper jumper cables are highly effective for transferring power from one battery to another, making them ideal for jump-starting vehicles with a bad starter.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B187 is essential. Buyers in regions with high humidity, like parts of South America and Africa, should consider coated copper options to prevent corrosion.
2. Steel for Wrenches and Tools
Key Properties: Steel offers high tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for hand tools. It can withstand significant pressure and has a melting point of around 2,500°F (1,370°C).
Pros & Cons: Steel tools are robust and can handle heavy use, making them suitable for automotive repairs. However, they can be prone to rust if not properly treated, which may affect their longevity.
Impact on Application: Steel wrenches and sockets are essential for safely disconnecting battery terminals and other components when diagnosing starter issues.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for tools that meet standards like ISO 9001 for quality assurance. In regions with high moisture, such as the Middle East, stainless steel options may be preferred to mitigate rust issues.
3. Plastic for Protective Gear
Key Properties: Plastic is lightweight, non-conductive, and resistant to many chemicals, making it suitable for protective gear. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) without deforming.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness. However, it may not provide the same level of protection as more robust materials like rubber or metal in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Plastic is commonly used in gloves and goggles to protect users during repairs, especially when working with electrical components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards such as ANSI Z87.1 is crucial for protective gear. Buyers should also consider the local availability of specific types of plastic, as some regions may have restrictions on certain materials.
4. Rubber for Insulation and Seals
Key Properties: Rubber is highly flexible and provides excellent insulation properties, withstanding temperatures ranging from -40°F (-40°C) to 212°F (100°C). It is also resistant to moisture and various chemicals.
Pros & Cons: Rubber’s flexibility and insulation capabilities make it ideal for electrical applications. However, it can degrade over time when exposed to UV light and extreme temperatures, leading to cracks and loss of effectiveness.
Impact on Application: Rubber is often used in battery terminal covers and seals to prevent corrosion and ensure secure connections, which is vital for starting a vehicle with a bad starter.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that rubber products meet relevant standards like ASTM D2000 for rubber materials. In regions with high UV exposure, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, UV-resistant rubber options may be necessary.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Jumper cables for jump-starting | Excellent electrical conductivity | Expensive and prone to corrosion | High |
| Steel | Wrenches and tools for battery disconnection | High durability and strength | Can rust if untreated | Medium |
| Plastic | Protective gear (gloves, goggles) | Lightweight and cost-effective | May not provide maximum protection | Low |
| Rubber | Insulation and seals for battery connections | Flexible and moisture-resistant | Degrades under UV light | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for starting a vehicle with a bad starter, ensuring informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Components for Starting a Vehicle with a Bad Starter?
The manufacturing process for automotive components related to starting systems involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the reliability and functionality of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality of the components they are sourcing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first stage involves selecting and preparing materials that meet stringent automotive industry standards. Common materials include high-strength steel for the starter housing, copper for electrical connections, and various plastics for insulative components.
During material preparation, suppliers must conduct rigorous testing to ensure that materials can withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and other operational stresses. This can include tensile strength tests, corrosion resistance evaluations, and thermal stability assessments.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped?
Forming processes encompass techniques such as stamping, machining, and molding. For instance, the starter housing may be stamped from a metal sheet, while internal components like gears and brushes could be machined to precise specifications.
Advanced forming techniques, including CNC machining, are often employed to achieve high tolerances and intricate designs. This precision is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together seamlessly and function reliably, minimizing the risk of failure when in use.
Assembly: What Are the Key Considerations?
The assembly stage involves integrating all components—housing, motor, solenoid, and wiring—into a functional starter unit. This process often utilizes automated machinery to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Quality assurance checks are integrated into the assembly line to ensure that each component meets predefined specifications. These checks can include visual inspections, torque testing, and electrical continuity tests to confirm that the starter can withstand operational demands.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared?
Finishing processes involve applying protective coatings, such as paint or galvanization, to prevent corrosion and enhance the aesthetic appeal of the starter. This step is crucial for components expected to operate in harsh environments, especially in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Final inspections are conducted to ensure the integrity of the finish and to verify that all components are securely attached. This attention to detail is vital for maintaining the product’s longevity and performance.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Automotive Components?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the automotive manufacturing process, ensuring that components perform reliably and safely. B2B buyers should be aware of several international and industry-specific standards that govern quality practices.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. It outlines a framework for consistent quality in manufacturing processes, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO 9001, automotive suppliers may also adhere to IATF 16949, which incorporates the requirements of ISO 9001 but is specifically tailored for the automotive sector. Compliance with these standards provides assurance to buyers that the manufacturer has a robust quality management system in place.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
Other certifications that may be relevant include CE marking for products sold in Europe, which indicates compliance with safety and environmental requirements. For suppliers in the oil and gas sector, API certifications may be pertinent, ensuring that components meet specific performance standards.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is embedded at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, enabling early detection of issues and minimizing defects.
What Are the Common QC Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first checkpoint where raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival. Suppliers should verify that materials meet specified standards before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted. These may include measuring dimensional accuracy, electrical testing, and functional evaluations to catch defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a thorough final inspection is performed to ensure that each starter meets quality standards and functions as intended. This may involve performance testing under simulated operational conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. This can involve several strategies:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control systems. Buyers should request documentation demonstrating compliance with relevant standards, including quality manuals, process flow diagrams, and inspection reports.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing and QC processes. These agencies can perform independent audits, ensuring that the supplier adheres to international standards and best practices.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate additional complexities when sourcing automotive components.
How Can Buyers Ensure Compliance with Regional Regulations?
Understanding and complying with local regulations is crucial. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific automotive standards and regulations applicable in their region, as these can vary significantly.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
What Are the Challenges in Verifying Supplier Credentials?
Buyers may face challenges in verifying the credentials of suppliers in less regulated markets. Establishing relationships with trusted local partners can help mitigate risks and ensure that quality standards are maintained.
By focusing on the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices outlined above, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing components for starting systems, ensuring reliability and performance in their automotive applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to start a vehicle with a bad starter’
Introduction
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to address the challenge of starting a vehicle with a bad starter. Understanding the steps involved in diagnosing and temporarily fixing starter issues can save your business time and money while ensuring the reliability of your fleet. This checklist will guide you through essential actions to take when confronted with a faulty starter, helping you to make informed procurement decisions regarding tools and services.
Step 1: Assess the Symptoms of a Bad Starter
Begin by accurately diagnosing the problem with the vehicle. Common symptoms include a clicking noise when turning the key or the engine failing to turn over. This step is crucial to ensure you do not waste resources on unnecessary repairs or replacements.
- Look for signs such as a single click, no sound at all, or rapid clicking, which can indicate different issues, including battery problems or ignition faults.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Tools
Compile the essential tools required for temporary fixes. This includes jumper cables, a wrench for battery connections, a mallet for tapping the starter, and a voltmeter to check battery voltage.
- Ensure you have protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, to maintain safety while performing any checks or repairs.
Step 3: Verify Battery Condition
Before concluding that the starter is at fault, check the battery’s condition. A weak battery can mimic symptoms of a bad starter. Use a voltmeter to measure the voltage.
- A healthy battery should read at least 12.5 volts. If it falls below this threshold, consider jump-starting the vehicle and re-evaluating the starter afterward.
Step 4: Inspect and Clean Connections
Examine the battery terminals and starter connections for corrosion or loose wires. Poor connections can hinder the starter’s operation and are often an easily fixable issue.
- Use a wire brush to clean any corrosion found on the terminals, and ensure all connections are tight before attempting to start the vehicle again.
Step 5: Test the Starter with a Tap
If the starter is suspected to be faulty, gently tap it with a mallet or hammer. This can sometimes free stuck components within the starter motor.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
- Be cautious to avoid damaging the starter; a light tap is often enough to re-establish contact within the motor.
Step 6: Check the Solenoid Connections
For vehicles equipped with an external solenoid, inspect the wiring and connections. A loose or dirty connection can prevent the starter from receiving the necessary current to operate.
- Look for cracked or frayed wires, and ensure all connections are secure and clean to maximize the chances of starting the vehicle.
Step 7: Consider Push-Starting for Manual Vehicles
As a last resort for manual transmission vehicles, push-starting can bypass the starter issue temporarily. This method involves rolling the vehicle and engaging the clutch to start the engine.
- Ensure safety measures are in place, such as having sufficient manpower to push the vehicle and performing this maneuver in a safe location away from traffic.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively diagnose and address starter issues, ensuring operational efficiency and reducing downtime in their vehicle fleets.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Solutions for Starting a Vehicle with a Bad Starter?
When sourcing solutions for starting a vehicle with a bad starter, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The costs associated with sourcing quality tools and components, such as jumper cables, hammers, and voltmeters, can vary significantly based on quality and specifications. High-quality materials tend to be more durable, impacting the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled technicians who diagnose and perform repairs. These costs can differ depending on the region, labor market, and the complexity of the tasks involved.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools for diagnosing and repairing starter issues can be a significant upfront cost. However, these tools are essential for efficient service delivery and can lead to long-term savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the tools and components meet safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Investing in stringent QC measures can prevent costly returns and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Incoterms and shipping methods chosen will directly impact these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s operational efficiency.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Sourcing Solutions?
Several factors influence the pricing of tools and services related to starting a vehicle with a bad starter. Understanding these influencers can aid buyers in making informed decisions.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often provide discounts for bulk purchases. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing based on their anticipated needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions may incur higher costs due to additional design and production processes. Buyers should assess whether standard solutions meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. High-quality materials often come with certifications that ensure safety and reliability, which can justify a higher cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and the quality assurance they provide.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms and responsibilities can affect total landed costs. Different Incoterms can lead to variations in shipping costs and risk management.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices and Ensure Cost-Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance negotiation outcomes and promote cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate with Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers allows buyers to compare prices and leverage competitive offers to negotiate better terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with the tools and solutions rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime.
-
Research Market Trends: Understanding current market conditions can provide insights into pricing trends, allowing buyers to time their purchases more strategically.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Developing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to exclusive offers or products.
-
Be Aware of Regional Differences: Pricing nuances can vary by region due to factors like tariffs, shipping costs, and local market conditions. Buyers should account for these differences when sourcing internationally.
Conclusion
Sourcing solutions for starting a vehicle with a bad starter involves a complex interplay of costs and pricing factors. By understanding these elements, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and optimize their total cost of ownership, ensuring that they receive the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to start a vehicle with a bad starter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions for Starting a Vehicle with a Bad Starter
When dealing with a vehicle that won’t start due to a malfunctioning starter, it is crucial to evaluate various alternatives. Each method has its unique advantages and disadvantages, which can influence the decision-making process for B2B buyers, especially in regions where vehicle reliability is paramount. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses optimize their operations and reduce downtime.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Start A Vehicle With A Bad Starter | Jump Starting | Push Starting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate; works temporarily | High; effective for low battery issues | High; effective for manual vehicles |
| Cost | Low; requires basic tools | Low; minimal equipment needed | Low; no special tools required |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires some mechanical knowledge | Easy; quick process | Moderate; requires help |
| Maintenance | None; temporary fix | None; relies on battery condition | None; relies on vehicle condition |
| Best Use Case | Short-term solution for starter issues | Quick fix for weak batteries | Manual transmission vehicles only |
What are the Pros and Cons of Jump Starting as an Alternative?
Jump starting a vehicle is one of the most common methods used to bypass starter issues, particularly if the underlying problem is a weak battery. The process involves using jumper cables to connect the battery of a functioning vehicle to the battery of the non-starting vehicle.
Pros:
– Quick and effective if the battery is the issue.
– Requires minimal equipment, making it accessible in most situations.
Cons:
– Not effective if the starter is the primary issue.
– Requires another vehicle, which may not always be available.
– Risks potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system if done incorrectly.
How Does Push Starting Work, and What Are Its Benefits?
Push starting is another alternative but is limited to vehicles with manual transmissions. This method uses the vehicle’s momentum to start the engine, bypassing the starter motor.
Pros:
– Highly effective for manual cars when the starter fails.
– No additional equipment or vehicles are needed, making it a practical solution in many situations.
Cons:
– Cannot be used with automatic transmissions.
– Requires the assistance of others, which may not always be feasible.
– Risks stalling if not executed correctly.
Conclusion: Which Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose for Their Needs?
For B2B buyers, the choice between starting a vehicle with a bad starter and exploring alternatives hinges on several factors, including vehicle type, operational context, and urgency of the situation. If immediate action is necessary and the vehicle has a manual transmission, push starting may be the best option. Conversely, if the issue is suspected to be battery-related, jump starting is a quick and effective solution. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs and constraints of your operations will guide you toward the most appropriate method, ensuring minimal disruption and maintaining productivity.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology related to starting a vehicle with a bad starter is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in the automotive sector. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also enhances communication with suppliers and partners.
What Are the Essential Technical Properties to Consider for Vehicle Starters?
-
Material Grade
The material grade of starter components, such as the housing and internal parts, is vital for durability and performance. High-grade materials like aluminum or reinforced plastics can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion, ensuring longevity. For B2B buyers, selecting components made from superior materials can reduce replacement frequency and maintenance costs. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension of starter components. Precise tolerances are crucial for the proper fit and function of the starter motor and its parts. In a B2B context, understanding these specifications helps buyers avoid compatibility issues and ensures optimal performance in various vehicle models. -
Voltage Rating
Starters typically operate at a standard voltage (usually 12V or 24V for larger vehicles). Understanding the voltage rating is essential for ensuring compatibility with vehicle electrical systems. B2B buyers must consider this when sourcing starters to avoid electrical failures that could lead to operational downtime. -
Current Draw
The amount of current a starter draws during operation can impact the battery and overall electrical system of the vehicle. Lower current draw can be advantageous, particularly for vehicles with limited battery capacity. B2B buyers should analyze current draw specifications to select starters that optimize energy efficiency. -
Start Torque
Start torque is the initial rotational force required to start the engine. It is a critical specification that varies by vehicle type and engine size. B2B buyers need to ensure that the starter selected provides adequate torque for the specific vehicles in their fleet, thereby preventing starting issues.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Vehicle Starters?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts that are made by the same manufacturer that produced the original components for the vehicle. In the B2B market, sourcing OEM starters ensures compatibility and quality, which can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce warranty claims. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and reduced excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, effectively utilizing RFQs can lead to competitive pricing and better supplier relationships, ensuring they receive the best deals on starters and related components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standard trade terms used in international contracts to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B transactions involving vehicle starters, understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage logistics and cost expectations effectively. -
Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to parts and accessories that are not sourced from the OEM but are compatible with the vehicle. B2B buyers often consider aftermarket options for cost-effectiveness and availability. However, they must evaluate the quality and compatibility of aftermarket starters to avoid potential issues.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, improve supplier negotiations, and ultimately ensure the reliability of their vehicle fleets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to start a vehicle with a bad starter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Vehicle Starting Sector?
The global automotive sector is undergoing significant transformations, particularly in the realm of vehicle maintenance solutions such as starting a vehicle with a bad starter. Key drivers in this market include the increasing prevalence of older vehicles on the road, particularly in emerging markets across Africa and South America, where budget constraints often lead to extended vehicle lifespans. This trend creates a robust demand for affordable, DIY solutions that allow users to troubleshoot and temporarily fix starting issues without incurring high repair costs.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as mobile applications that guide users through diagnostic processes, are gaining traction. These apps often leverage augmented reality to help users identify starter-related issues visually. Moreover, e-commerce platforms are increasingly becoming vital for sourcing tools and parts, enabling businesses to reach a broader audience while catering to diverse regional needs. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, the focus is shifting towards integrated solutions that not only address immediate starting issues but also provide comprehensive diagnostics and predictive maintenance features.
The rise of digital marketplaces allows for better price comparisons and product sourcing, which is crucial for international buyers. Furthermore, as logistics and supply chain efficiency improve, businesses can expect quicker access to necessary parts, reducing downtime for customers. Understanding these dynamics is essential for B2B buyers seeking to navigate the complexities of the vehicle maintenance market effectively.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in Vehicle Maintenance Solutions?
Sustainability has become a focal point in the sourcing of automotive repair solutions, including those related to starting vehicles with a faulty starter. The environmental impact of automotive waste, particularly concerning batteries and electronic components, is prompting manufacturers to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. B2B buyers must consider suppliers who adhere to sustainable manufacturing processes, ensuring that products are made from recyclable materials and that waste is minimized throughout the supply chain.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are increasingly relevant for businesses looking to partner with responsible suppliers. Buyers should also inquire about the use of ‘green’ materials in the products they source, such as eco-friendly lubricants for starter components or biodegradable cleaning agents for maintenance tasks.
Moreover, as consumer awareness around environmental issues grows, businesses that emphasize sustainability in their offerings can enhance their market appeal, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations like Europe. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, B2B buyers not only contribute to environmental preservation but also position themselves favorably in a competitive marketplace that increasingly values ethical practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Vehicle Starting Solutions and Their Evolution?
The evolution of vehicle starting solutions can be traced back to the introduction of the electric starter motor in the early 20th century, which revolutionized how vehicles were ignited compared to manual cranking. Over the decades, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated starter systems, including solenoid-operated starters that enhance reliability and efficiency.
In recent years, as vehicles have become more complex with the integration of electronics, the methods for diagnosing and addressing starter issues have also evolved. The rise of digital diagnostics tools and mobile applications now allows users to engage in self-service repairs, significantly altering the landscape for both consumers and B2B buyers. This shift not only reflects advancements in technology but also a growing preference for cost-effective and user-friendly solutions in vehicle maintenance, emphasizing the importance of adaptability in sourcing strategies for international buyers.
Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the ongoing trends towards innovation and consumer empowerment in the vehicle maintenance sector, ultimately shaping their purchasing decisions and business strategies.

Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
-
How do I diagnose a bad starter in a vehicle?
Diagnosing a bad starter begins with observing the vehicle’s behavior when you turn the ignition key. If you hear rapid clicking noises, the battery is likely the issue. A single click or no sound at all suggests a potential starter problem. Check the battery terminals for corrosion and ensure they are tightly connected. Using a voltmeter, confirm the battery voltage is at least 12.5 volts. If the battery is fine, but the vehicle still doesn’t start, the starter may need further inspection or replacement. -
What temporary solutions can I use to start a car with a bad starter?
Several temporary solutions can help start a vehicle with a bad starter. Cleaning the battery terminals and ensuring solid connections can sometimes resolve the issue. Tapping the starter gently with a hammer or mallet may free stuck components. If the vehicle has a manual transmission, you can attempt a push start. These methods are not permanent fixes but can provide a quick solution until professional repairs are made. -
What tools do I need to troubleshoot a bad starter?
Essential tools for troubleshooting a bad starter include jumper cables, a wrench or socket set for disconnecting battery terminals, and a voltmeter to check battery voltage. A mallet or hammer can be useful for tapping the starter. It’s also beneficial to have a flashlight for visibility, especially in dimly lit areas. Optional tools like a starter relay tester can help identify electrical issues that may not be immediately visible. -
How do I evaluate suppliers for starter repair parts?
When evaluating suppliers for starter repair parts, consider their reputation, reliability, and the quality of their products. Look for suppliers with positive customer reviews and a history of timely delivery. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Request samples or product specifications to assess quality before making bulk purchases. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can also provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter parts can vary significantly between suppliers. Typically, MOQs are influenced by the type of part, material availability, and the supplier’s production capacity. Some suppliers may allow lower MOQs for first-time buyers or trial orders, while others may require larger quantities to optimize pricing. Always clarify MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs and ensure your purchasing needs align with the supplier’s requirements. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing starter parts internationally?
When sourcing starter parts internationally, consider flexible payment terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, or payment upon delivery. Be aware of the implications of currency exchange rates and transaction fees. Utilizing secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services can also provide added protection against potential fraud or disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for starter parts?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) for starter parts, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier. Request documentation for quality control processes, including testing results and certifications. Implement a system for inspecting received parts for defects or inconsistencies before use. Regular communication with your supplier regarding quality feedback can help improve processes and maintain high standards over time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter parts?
When importing starter parts, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Evaluate the reliability of shipping carriers and ensure they are familiar with handling automotive parts. Understand the customs duties and taxes applicable to your imports to budget accordingly. Effective inventory management is crucial to prevent stockouts, so align your logistics strategy with your demand forecast to ensure timely delivery and availability.
Top 3 How To Start A Vehicle With A Bad Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Honda – 2003 Accord Starter Issue
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 2003 Honda Accord, bad starter, battery full, headlights bright, clicking noise from starter, automatic transmission.
2. WikiHow – Starting a Car with a Bad Starter
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This article provides solutions for starting a car with a bad starter, including tapping the starter with a hammer, push-starting a manual transmission vehicle, and jumping the battery. It emphasizes checking the battery first, as many issues mistaken for starter problems are actually battery-related. The article also advises consulting a mechanic for permanent repairs or replacements of the start…
3. Facebook – Car Starter Solutions
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Car Starter Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
In summary, understanding how to start a vehicle with a bad starter is essential for international B2B buyers in automotive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The insights provided highlight the importance of diagnosing the issue accurately, addressing common problems such as battery connections and solenoid functionality, and employing temporary fixes like jump-starting or push-starting vehicles.
Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in ensuring that businesses have access to reliable parts and tools, enhancing their operational efficiency. By establishing strong relationships with suppliers, companies can secure high-quality components that mitigate the risks associated with vehicle downtime.
As markets evolve, staying ahead of technological advancements in automotive repairs will be paramount. We encourage B2B buyers to explore partnerships with innovative suppliers and invest in training for their teams to adapt to changing automotive technologies. By doing so, businesses can not only improve their service offerings but also enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Embrace these strategies to drive growth and remain competitive in the global automotive industry.
Illustrative image related to how to start a vehicle with a bad starter
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.