Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to change a starter
In today’s fast-paced global market, sourcing reliable information on how to change a starter can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. The starter motor plays a critical role in vehicle functionality, and ensuring its timely replacement is essential for operational efficiency. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the entire process, from understanding various starter types and their applications to supplier vetting and cost considerations.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia—face unique challenges. These include fluctuating supply chains, varying market standards, and differing regional regulations that can complicate purchasing decisions. This guide empowers these buyers by offering in-depth insights into best practices for sourcing, installation procedures, and maintenance tips.
By equipping B2B buyers with essential knowledge about starter motors, this resource not only streamlines the decision-making process but also fosters greater confidence in vendor relationships. With a focus on actionable strategies, buyers can make informed choices that enhance their operational capabilities and minimize downtime, ensuring that they remain competitive in their respective markets.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How To Change A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to change a starter
- Understanding how to change a starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to change a starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to change a starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to change a starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to change a starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to change a starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to change a starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to change a starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to change a starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to change a starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to change a starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to change a starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to change a starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Starter Replacement | Direct replacement of the existing starter motor with a new one. | Automotive repair shops, fleet maintenance. | Pros: Simple process, widely applicable. Cons: May require additional parts if other components are damaged. |
| High-Performance Starter Installation | Upgrading to a high-torque starter for enhanced performance. | Racing teams, performance vehicle shops. | Pros: Improves engine cranking speed, suitable for high-performance applications. Cons: Higher cost, may require modifications. |
| Remanufactured Starter Installation | Utilizing refurbished starters to save costs. | Budget-conscious repair shops, fleet operators. | Pros: Cost-effective, environmentally friendly. Cons: Potentially shorter lifespan than new starters. |
| DIY Starter Replacement | Vehicle owners replace starters themselves, often guided by manuals. | Individual vehicle owners, hobbyists. | Pros: Saves labor costs, promotes hands-on learning. Cons: Requires tools and mechanical knowledge, risk of improper installation. |
| Starter Repair | Repairing the existing starter instead of replacing it. | Small repair shops, mobile mechanics. | Pros: Lower cost, can extend starter lifespan. Cons: May not be reliable long-term, requires skilled technicians. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Starter Replacement?
Standard starter replacement involves removing the faulty starter and installing a new one. This process is straightforward, making it a common choice for automotive repair shops and fleet maintenance services. When considering this option, B2B buyers should evaluate the availability of compatible starter motors and the skill level of their technicians, as this method requires a basic understanding of automotive systems. While it is generally cost-effective, buyers should be mindful of potential additional costs if other components are found to be damaged during the replacement.
How Does High-Performance Starter Installation Differ?
High-performance starter installation focuses on upgrading to a starter that delivers greater torque, suitable for high-performance vehicles or racing applications. This option is particularly beneficial for racing teams or specialty shops that require enhanced engine cranking speed. B2B buyers must consider the specific needs of their vehicles, the potential for modifications, and the increased costs associated with high-performance parts. While this option can significantly improve performance, it may not be necessary for standard vehicles.
What Are the Advantages of Remanufactured Starters?
Using remanufactured starters provides a cost-effective solution for buyers, especially those in budget-sensitive markets like fleet operators or smaller repair shops. These refurbished units can be a more sustainable choice, reducing waste. However, B2B buyers should weigh the potential trade-offs, including shorter lifespans compared to new starters. It is crucial to source remanufactured parts from reputable suppliers to ensure quality and reliability.
Why Consider DIY Starter Replacement?
DIY starter replacement appeals to individual vehicle owners and hobbyists who prefer to handle repairs themselves. This approach can significantly reduce labor costs and foster a deeper understanding of vehicle maintenance. However, it requires the right tools and mechanical knowledge, posing risks if not executed correctly. B2B buyers in this category should consider training resources or manuals to support their technicians and ensure successful installations.
When Is Starter Repair a Viable Option?
Starter repair can be a practical solution for small repair shops or mobile mechanics looking to offer cost-effective services. By repairing rather than replacing starters, businesses can provide customers with a lower-cost alternative while extending the lifespan of the existing component. However, this option may not always be reliable long-term, and it necessitates skilled technicians who can accurately diagnose and fix issues. B2B buyers should assess their team’s capabilities and the demand for such services in their market.
Key Industrial Applications of how to change a starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to change a starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Routine maintenance in workshops for vehicle servicing | Reduces downtime, enhances customer satisfaction, and increases service offerings. | Quality of starter parts, availability of skilled technicians, and compliance with local regulations. |
| Transportation and Logistics | Fleet management for commercial vehicles | Ensures operational efficiency, reduces vehicle breakdowns, and prolongs fleet lifespan. | Cost-effective sourcing, reliable supply chain, and compatibility with diverse vehicle models. |
| Mining and Construction | Maintenance of heavy machinery and equipment | Minimizes equipment failure, enhances productivity, and lowers repair costs. | Durability of parts, availability of technical support, and regional service capabilities. |
| Agriculture | Maintenance of agricultural machinery | Ensures timely operations, increases yield, and reduces unexpected downtimes. | Compatibility with various machinery types, sourcing of OEM parts, and local availability of repair services. |
| Oil and Gas | Maintenance of drilling and extraction equipment | Reduces operational risks, maintains safety standards, and enhances equipment reliability. | Sourcing from reputable suppliers, adherence to safety regulations, and availability of specialized parts. |
How is ‘how to change a starter’ applied in the automotive repair industry?
In the automotive repair sector, changing a starter is a routine maintenance task that is crucial for ensuring vehicles operate efficiently. Workshops can significantly reduce vehicle downtime by providing quick and effective starter replacements, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction. International buyers should consider sourcing high-quality starter parts that comply with local regulations, ensuring they have access to skilled technicians who can perform the replacements efficiently.
What role does changing a starter play in transportation and logistics?
In the transportation and logistics industry, maintaining commercial vehicle fleets is essential for operational efficiency. Regularly changing starters helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, thereby prolonging the lifespan of the vehicles and minimizing service interruptions. Buyers in this sector should focus on cost-effective sourcing options and ensuring that replacement starters are compatible with a wide range of vehicle models to streamline their fleet maintenance processes.
How does changing a starter benefit mining and construction operations?
For mining and construction businesses, maintaining heavy machinery is critical to prevent costly equipment failures. The ability to quickly change starters on machinery ensures that operations remain productive and that repair costs are kept to a minimum. Buyers in these industries should prioritize sourcing durable starter components and seek suppliers that offer technical support and regional service capabilities to address any issues that arise.
What significance does changing a starter hold in agriculture?
In agriculture, the timely operation of machinery is vital for maximizing yields. Changing starters on agricultural equipment ensures that operations run smoothly and reduces the risk of unexpected downtimes during critical planting and harvesting periods. Buyers should consider the compatibility of starter parts with various machinery types and the local availability of repair services to ensure that their equipment remains in peak condition throughout the farming season.

Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
How is changing a starter crucial for the oil and gas industry?
In the oil and gas sector, the maintenance of drilling and extraction equipment is paramount for operational safety and reliability. Regularly changing starters helps mitigate operational risks and ensures that equipment functions as intended. Buyers should source starter parts from reputable suppliers who adhere to safety regulations and offer specialized components tailored to the unique demands of the industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to change a starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Diagnosing Starter Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers managing fleets or automotive services often face challenges in accurately diagnosing starter problems. Symptoms like slow cranking or intermittent clicking can be misleading, making it difficult to ascertain whether the issue lies with the starter motor, the battery, or other components. This uncertainty can lead to unnecessary replacements, increasing operational costs and downtime for vehicles that are crucial for business operations.
The Solution: To streamline the diagnosis process, invest in diagnostic tools that can test both the starter motor and battery efficiently. A digital multimeter can help check the battery voltage and load, while a starter tester can assess the starter’s performance under load. Incorporate a systematic approach to troubleshooting by following a clear checklist: start with the battery connections, check for corrosion, and then test the starter motor. Providing your team with training sessions on these diagnostic tools can further enhance their ability to quickly identify issues, reducing misdiagnosis and unnecessary replacements.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Starter Parts
The Problem: Sourcing reliable starter parts can be a daunting task, especially for B2B buyers operating in regions with less access to quality automotive suppliers. Compromised parts can lead to frequent failures and increased maintenance costs, which is detrimental to business operations. This situation is exacerbated by counterfeit products that may look legitimate but fail to meet performance standards.
The Solution: Establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record for quality. Utilize industry platforms and networks to gather feedback and reviews about potential suppliers. When sourcing starter parts, prioritize OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) components to ensure compatibility and reliability. Implementing a thorough vetting process that includes checking certifications, warranty offers, and customer testimonials can significantly mitigate the risk of acquiring subpar products. Additionally, consider bulk purchasing agreements for better pricing and consistent supply, which can enhance your operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
Scenario 3: Lack of Skilled Labor for Installation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter the challenge of having insufficient skilled labor to carry out starter replacements efficiently. The complexity of modern vehicles often requires specialized knowledge and experience. This lack of skilled technicians can lead to prolonged downtime, increased labor costs, and potential damage to vehicles if installations are not performed correctly.
The Solution: To address this issue, consider investing in training programs for your current staff to enhance their automotive skills, specifically in starter replacement procedures. Collaborate with local vocational schools or training centers to provide apprenticeships that can help cultivate a pipeline of skilled technicians. Additionally, you may want to explore partnerships with professional automotive service providers who can offer their expertise on a contract basis for more complex installations. This hybrid approach not only ensures that you have access to skilled labor when needed but also promotes knowledge transfer within your organization, ultimately reducing dependency on external resources.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to change a starter
What Are the Key Materials Used in Starter Replacement?
When changing a starter, selecting the right materials is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The materials used in starter motors and associated components must withstand various mechanical and thermal stresses while also being resistant to corrosion. Here, we analyze four common materials used in starter components: steel, aluminum, copper, and plastic.
How Does Steel Perform in Starter Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in starter construction, particularly for the housing and mounting brackets. Its key properties include high tensile strength and durability, enabling it to withstand the mechanical stresses during engine cranking. Steel also has good resistance to deformation under load, which is essential for maintaining alignment in starter systems.
Pros: Steel’s durability and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for many manufacturers. It is also readily available and can be easily machined, which simplifies manufacturing processes.
Cons: However, steel is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments. This can lead to premature failure if not properly treated or coated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media is generally good, but it may require protective coatings in corrosive environments, particularly in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure that the steel used complies with local standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications, to guarantee quality and performance.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starter Systems?
Aluminum is often used in starter components due to its lightweight properties and good corrosion resistance. It is commonly found in the casing and some internal components, which helps reduce the overall weight of the starter.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can improve vehicle efficiency. Additionally, aluminum has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat generated during operation.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum is generally less strong than steel, making it more susceptible to deformation under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for applications in coastal areas or regions with high humidity. However, it may not be suitable for high-torque applications without reinforcement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should look for aluminum components that meet EU and GCC standards for automotive parts to ensure compliance and reliability.
Why Is Copper Important in Starter Electrical Systems?
Copper is primarily used in electrical connections and windings within the starter motor due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Its key properties include high thermal and electrical conductivity, which are essential for efficient energy transfer.
Pros: Copper’s conductivity ensures that the starter receives the necessary power quickly, enhancing performance. It also has good resistance to corrosion when properly coated.
Cons: However, copper is more expensive than other materials and can be prone to oxidation if not adequately protected.
Impact on Application: Copper is highly compatible with electrical systems, but its cost can be a limiting factor for budget-conscious buyers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper components comply with international electrical standards, such as IEC or UL, especially in regions like Brazil where specific regulations may apply.

Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
How Does Plastic Contribute to Starter Durability?
Plastic materials are often used for insulation and housing components in starters, particularly in the solenoid and connector areas. Their key properties include lightweight, good electrical insulation, and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: The use of plastic helps reduce weight and provides excellent electrical insulation, which is crucial for safety and performance.
Cons: However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may degrade over time, especially under high-temperature conditions.
Impact on Application: Plastics are generally suitable for non-structural components but should be carefully selected to ensure they can withstand the operational environment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that plastic components meet relevant standards for thermal and electrical performance, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Replacement
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to change a starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Housing and mounting brackets | High durability and strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Casing and internal components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less strength than steel | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical connections and windings | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and oxidation risk | High |
| Plastic | Insulation and non-structural components | Lightweight and good insulation | Less durable under high temperatures | Low |
This material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in starter replacement, enabling informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific operational environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to change a starter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Motors?
The manufacturing process of starter motors involves several critical stages that ensure high-quality products are delivered to the market.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing high-grade materials such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and various alloys for components requiring high strength and durability. Suppliers must provide materials that meet international standards, ensuring consistency and reliability. This step often includes the verification of material certifications to confirm compliance with specifications.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, the forming process begins. This includes machining the metal components to precise specifications, often using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines to ensure accuracy. The forming stage can also involve stamping and forging to create specific shapes required for the motor’s assembly. For B2B buyers, understanding the forming techniques used by suppliers can provide insights into the potential longevity and performance of the starter motors.
Assembly
The assembly stage is where the individual components come together. Skilled technicians or automated systems assemble the starter motor, ensuring that each part fits perfectly. This stage typically includes the installation of the armature, field coils, and the pinion gear. Attention to detail in assembly is critical, as any misalignment can lead to performance issues or early failure. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques used and the qualifications of the personnel involved.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which may involve surface treatments to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. This includes applying protective coatings or paints, as well as conducting final inspections. Finishing techniques can vary significantly among manufacturers, affecting the product’s lifespan and performance. Buyers should assess the finishing processes to ensure they align with their quality expectations.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that starter motors meet specific performance and safety standards.
What International Standards Apply to Starter Motors?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for manufacturers, as they provide a framework for consistent quality management systems. Compliance with these standards can help buyers gauge a supplier’s commitment to quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets and API for automotive parts can further assure buyers of product quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
The quality control process typically involves several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint examines the raw materials and components upon arrival. The focus is on verifying that the materials meet specified standards and are free from defects.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC monitors production to ensure adherence to specifications. This includes regular inspections and testing at various stages, allowing for immediate corrections if issues arise.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the facility, FQC ensures that each starter motor meets all performance and safety criteria. This stage often includes functional testing, where motors are subjected to real-world conditions to assess reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods in quality assurance are critical to validating the performance of starter motors. Common methods include:
-
Electrical Testing: This checks the motor’s electrical characteristics, ensuring that it operates within specified voltage and current ranges.
-
Mechanical Testing: Assessment of the physical components, including torque and alignment checks, to ensure proper function during operation.
-
Durability Testing: Simulating prolonged use to identify potential failure points or weaknesses in the design or materials.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control processes:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide firsthand insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. This may include reviewing their compliance with international standards and internal quality protocols.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed quality reports, including data on testing methods and results, which can help buyers assess product reliability.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and the quality of the final products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances must be considered:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements, which can affect product specifications and quality standards. Buyers should be familiar with local regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Understanding cultural differences can help buyers communicate their quality expectations more effectively. What is considered acceptable in one region may not be viewed the same way in another.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The supply chain’s complexity may impact the quality of products received. Buyers should assess the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, to identify potential quality risks.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter motors, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to change a starter’
In the automotive industry, ensuring your vehicle’s starter is functioning properly is essential for operational efficiency. This guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for sourcing the necessary components and expertise to change a starter effectively. By following these steps, you can streamline your procurement process, ensuring you receive quality products and services.
Step 1: Identify Your Vehicle’s Starter Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your vehicle’s starter is crucial. Different vehicles require starters with varying torque ratings, dimensions, and electrical configurations. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or consult with a knowledgeable technician to determine the exact specifications needed.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Begin by compiling a list of suppliers who specialize in automotive components, particularly starters. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation in the market, and consider their geographical location, especially if you are sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. This can affect shipping times and costs.
- Tip: Utilize online directories and industry forums to find potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Quality Standards
Before committing to a supplier, verify their certifications and adherence to industry standards. Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance measures that indicate a commitment to product quality. This step minimizes the risk of receiving subpar components that could lead to further mechanical issues.
Step 4: Request Samples and Product Specifications
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the starters along with detailed product specifications. This allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the products with your vehicles. Ensure that the materials used meet durability requirements, especially in challenging environments.
- Tip: Check for warranty information and return policies, as these can provide insight into the supplier’s confidence in their products.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. While cost is important, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to greater reliability and lower long-term expenses.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Customer Support and After-Sales Service
Strong customer support is vital for any B2B relationship. Inquire about the supplier’s after-sales service and support availability. Ensure they provide assistance with installation queries, troubleshooting, and warranty claims, which can save time and resources in the future.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Delivery Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate contract terms that include delivery timelines, payment schedules, and any service level agreements. Clarity in these terms helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures timely delivery of the starters, critical for maintaining vehicle uptime.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the process of sourcing starters, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and vehicle reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to change a starter Sourcing
Understanding the costs associated with changing a starter is essential for international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis breaks down the cost components, pricing influencers, and offers practical tips for buyers to optimize their purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
What Are the Key Cost Components for Changing a Starter?
The total cost of changing a starter can be broken down into several components:
-
Materials: The starter motor itself typically ranges from $100 to $400, depending on the vehicle make and model. Additional materials may include wiring harnesses, bolts, and, if necessary, any corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and complexity of the installation. On average, labor can range from $100 to $300 for a professional installation, while DIY efforts can save these costs but may require considerable time and expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with the production of the starter, such as factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and labor involved in manufacturing. These costs are generally factored into the price of the starter.
-
Tooling: If the installation requires specialized tools, this can add to the overall cost. This is particularly relevant for businesses without existing automotive service capabilities.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the starter meets certain quality standards can increase costs. High-quality starters may go through rigorous testing, impacting the final price.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the origin of the parts, the distance to the buyer, and the chosen Incoterms. International shipments may incur additional tariffs or taxes.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically mark up prices to cover their costs and desired profit margins. This can vary widely based on market demand, competition, and supplier reputation.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect the Cost of Starters?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starter motors:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing, which can significantly reduce the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate to find optimal order sizes that balance inventory needs and cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom starters for specific applications or performance enhancements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether customization is necessary for their operations.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or OEM) can increase costs but may also enhance durability and performance. International buyers should evaluate the long-term value of quality versus upfront costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but this can be justified by fewer defects and better customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements and can significantly impact total costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Starter Purchases?
-
Negotiate Pricing: Leverage your purchasing power, especially if you are buying in bulk. Don’t hesitate to negotiate for better pricing or terms, particularly with local suppliers.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also long-term expenses related to maintenance, replacement frequency, and potential downtimes. High-quality starters may have a higher initial cost but could save money over time through enhanced reliability.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import regulations that can affect pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers can provide insights and competitive pricing.
-
Research Supplier Credentials: Ensure that suppliers have a reputation for quality and reliability. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure you receive the best products for your investment.
-
Plan for Logistics Costs: Factor in shipping and handling costs when calculating the total expense of the starter. Choosing suppliers closer to your operations can reduce these costs significantly.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis for changing a starter can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, optimize their budgets, and enhance operational efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to change a starter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Changing a Starter
In the automotive industry, vehicle maintenance and repair often require critical decisions regarding the best methods for resolving issues. When it comes to a failing starter, many vehicle owners and fleet managers face the choice of either changing the starter or considering alternative solutions. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that optimize their operations and minimize downtime.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Change A Starter | Alternative 1: Starter Repair | Alternative 2: Jump Start |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores full function of the starter motor. | Can restore functionality temporarily but may not last. | Provides immediate power to start the engine. |
| Cost | Parts: $100 – $400; Labor: $100 – $300. | Typically lower cost; $50 – $150 depending on extent of repair. | Minimal cost; usually free if using another vehicle. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical skills and tools; installation can take 1-4 hours. | Can be simpler if only minor repairs are needed; often takes less than an hour. | Very easy; requires no special skills or tools. |
| Maintenance | New starter requires standard maintenance; regular checks recommended. | Repairs may need frequent monitoring; potential for future failures. | No maintenance; temporary solution until the starter is replaced. |
| Best Use Case | Best for long-term reliability and when the starter is beyond repair. | Suitable for minor issues and cost-sensitive situations. | Ideal for emergencies or temporary fixes. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Starter Repair?
Starter repair is a viable alternative for businesses looking to save costs on immediate starter replacement. This method involves diagnosing the issue and fixing specific components, such as the solenoid or wiring connections. The primary advantage is the cost-effectiveness, as repairs typically range from $50 to $150. However, the downside is that repairs may only offer a temporary solution, and there is a risk of recurring issues. For businesses managing fleets, frequent repairs can lead to unexpected downtime, making it crucial to assess the longevity of the fix.
How Does Jump Starting Compare as an Immediate Solution?
Jump starting is an alternative that can be employed in emergencies when a vehicle fails to start. This method involves using another vehicle’s battery to provide the necessary power to kickstart the engine. The major benefit is its immediacy and simplicity, as it requires no tools and can be done in minutes. However, jump starting does not address underlying issues with the starter and is not a long-term solution. It is best suited for scenarios where the vehicle can be repaired later or if the issue is suspected to be temporary, such as a weak battery.
Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
Making an Informed Choice for Your Needs
When deciding between changing a starter and exploring alternative solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific circumstances, including budget constraints, the urgency of repairs, and the long-term reliability of their vehicles. While changing a starter ensures full functionality and reliability, alternatives like starter repair and jump starting can offer short-term fixes that may be suitable in specific situations. Ultimately, the choice should align with the operational needs of the business and the condition of the vehicle, ensuring minimal disruption and maximum efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to change a starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Starter Motor?
When considering the replacement of a starter motor, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring the right selection and longevity of the part. Here are several critical specifications to keep in mind:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a starter motor typically includes components made from high-strength steel or aluminum. These materials provide the necessary durability and resistance to thermal expansion, which is vital given the high temperatures generated during engine start-up. For B2B buyers, choosing starters made with high-grade materials ensures reliability and minimizes the risk of premature failure, which can lead to costly downtime. -
Torque Rating
Torque rating is a measure of the rotational force the starter can exert to turn the engine over. Most automotive starters have a torque range from 2 to 10 horsepower. Understanding torque specifications is essential when matching a starter to a vehicle’s engine size and type, as insufficient torque can lead to starting issues. B2B buyers must consider this rating to ensure they are sourcing starters that will effectively meet the demands of their specific applications. -
Voltage Rating
Most automotive starters operate on a 12-volt system. It’s critical to ensure that the starter’s voltage rating matches the vehicle’s electrical system to prevent damage to the starter or the vehicle’s wiring. For international buyers, especially in regions with varying electrical standards, confirming voltage compatibility is crucial to avoid operational issues. -
Temperature Range
The operating temperature range of a starter motor indicates the environmental conditions it can withstand. Starters should function effectively in both extreme cold and heat, which is particularly relevant for buyers in diverse climates. Selecting starters with a suitable temperature range helps ensure consistent performance and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements. -
Durability Rating
This rating often reflects the expected lifespan of the starter under normal operating conditions, typically measured in cycles. A higher durability rating indicates a longer-lasting product, which can enhance the overall value for businesses aiming to minimize maintenance costs. B2B buyers should prioritize products with proven durability, especially in high-demand environments.
What Are Common Terms in the Starter Motor Trade?
Navigating the starter motor market requires familiarity with specific industry terminology. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. These parts are typically of higher quality and fit, as they meet the specifications set forth by the vehicle manufacturer. For B2B buyers, sourcing OEM parts can ensure compatibility and reliability, which is critical for maintaining vehicle performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is essential for businesses to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing needs and operational capacity to optimize their supply chain. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This is a critical step in procurement that allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate favorable terms. For B2B buyers, crafting a clear and detailed RFQ can facilitate better supplier responses and improve purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps businesses clarify shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations. For B2B buyers, familiarity with Incoterms can lead to more effective negotiations and reduced shipping disputes. -
Aftermarket Parts
These are replacement parts made by manufacturers other than the original vehicle manufacturer. While often less expensive than OEM parts, aftermarket parts can vary significantly in quality. B2B buyers should assess the reliability and compatibility of aftermarket starters to ensure they meet their operational needs.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting starter motors, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing long-term costs.
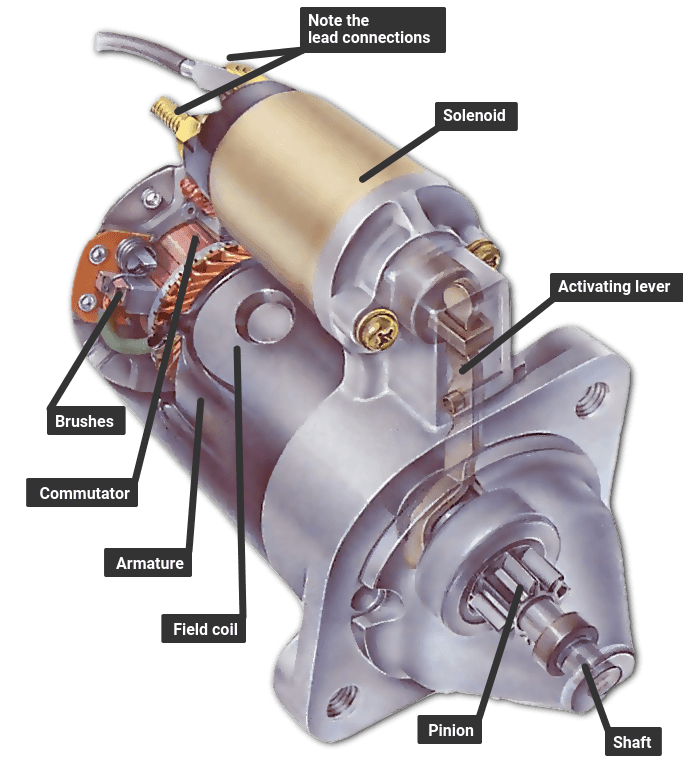
Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to change a starter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Starter Replacement Sector?
The market for starter replacement is influenced by several global drivers, particularly the growing automotive industry in emerging markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. The increasing vehicle ownership rates in these regions are propelling demand for starter motors and related services. Additionally, the rise in e-commerce platforms has transformed the sourcing landscape, allowing international B2B buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products with ease.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced automotive diagnostic tools and IoT integration, are also reshaping how businesses approach starter replacement. These technologies enable mechanics and service centers to quickly identify starter issues and recommend precise solutions, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Furthermore, the trend towards electric vehicles (EVs) is gradually changing the starter market dynamics, pushing suppliers to innovate and adapt their offerings to include compatible starter solutions for hybrid and electric models.
Regional trends indicate a strong preference for cost-effective and reliable components, which has led to a surge in demand for quality aftermarket products. As buyers from regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia seek to optimize their vehicle maintenance budgets, they are increasingly looking for durable yet affordable starter solutions that can withstand diverse operating conditions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Starter Replacement Industry?
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration in the automotive aftermarket, including the starter replacement sector. The environmental impact of traditional starter manufacturing processes, which often involve harmful chemicals and non-recyclable materials, is prompting B2B buyers to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses aim to build trust with their customers and demonstrate corporate responsibility. This has led to a demand for ‘green’ certifications and materials that ensure products are manufactured with minimal environmental harm. Buyers are increasingly seeking out suppliers who use recyclable materials in their starter products and employ eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Moreover, as global regulations regarding emissions and waste management become stricter, businesses that adopt sustainable practices not only comply with legal requirements but also gain a competitive edge. By sourcing starters from manufacturers who are committed to sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
How Has the Starter Replacement Industry Evolved Over Time?
The starter replacement industry has undergone significant changes over the decades, driven by advancements in automotive technology and changing consumer expectations. Initially, starters were simple mechanical devices; however, as vehicles evolved to become more complex, so did the starter systems. The introduction of high-torque starters and improvements in materials and design have led to increased reliability and efficiency.
In recent years, the rise of electric vehicles has further transformed the sector, necessitating new starter designs that cater specifically to the unique requirements of hybrid and fully electric models. Additionally, the shift towards more digital and automated diagnostic tools has improved the accuracy of starter assessments, allowing for more efficient replacement processes. As a result, B2B buyers are now presented with a wider array of options, from traditional starters to advanced solutions tailored for modern vehicles.
In summary, understanding the current market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and acknowledging the industry’s evolution are critical for international B2B buyers seeking to navigate the starter replacement sector effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to change a starter
-
How do I solve common starter problems?
To address common starter issues like slow cranking or unusual noises, first, ensure the battery is fully charged and connections are clean. If the problem persists, inspect the starter for signs of wear, such as corrosion or loose wiring. Testing the starter with a multimeter can identify electrical issues. If replacement is necessary, source high-quality starters from reputable suppliers to avoid future failures. Always consult your vehicle’s service manual for specific troubleshooting steps tailored to your make and model. -
What is the best starter for heavy-duty vehicles?
The best starter for heavy-duty vehicles typically features a high-torque design to handle increased load and frequent use. Look for starters from recognized brands that specialize in heavy machinery or commercial vehicles. Consider factors like the starter’s voltage, durability, and compatibility with your vehicle’s specifications. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers that offer customization options can ensure the starter meets the unique demands of your operational environment. -
How can I vet suppliers for starter motors?
When vetting suppliers for starter motors, prioritize those with a proven track record in the automotive industry. Check for certifications, customer reviews, and case studies that demonstrate reliability and quality. Request samples or prototypes to assess product quality firsthand. Establish clear communication channels to discuss your needs and ensure the supplier can meet your specifications, lead times, and quality assurance standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter motors?
Minimum order quantities for starter motors can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of starter. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units for bulk orders. Discuss your projected demand with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for new partnerships, especially if you commit to future orders, which can help manage inventory costs effectively. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of starter motors?
Payment terms for starter motors can include options like net 30, net 60, or cash in advance, depending on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation skills. Some suppliers might offer discounts for early payments or bulk orders. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing any agreement to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods that protect both parties, especially for international transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for starter motors?
To ensure quality assurance for starter motors, establish a clear quality control process with your suppliers. This can include requesting certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, consider conducting regular audits of the supplier’s facilities and processes. Implementing a testing protocol for each batch received can also help identify defects before they affect your operations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing starters internationally?
When sourcing starters internationally, consider shipping costs, import duties, and local regulations that may impact delivery times. Establish a reliable logistics partner familiar with customs processes to facilitate smooth shipments. Ensure that the supplier can provide accurate documentation to avoid delays. Additionally, plan for potential supply chain disruptions by maintaining open communication with your supplier about inventory levels and lead times. -
How can I customize starter motors for specific applications?
Customizing starter motors involves collaborating closely with your supplier to discuss your specific requirements. This may include adjusting torque specifications, modifying electrical connections, or incorporating unique housing designs. Ensure that the supplier has the capacity to handle custom orders and can provide prototypes for testing before full-scale production. Establish a timeline for development and testing to align with your operational needs.
Top 4 How To Change A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Car Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Replacing a starter is relatively simple, depending on the car model. It typically involves two bolts and a connector or wire and ground lug. The job can take about 30 minutes if the starter is easily accessible. If the starter is located in a difficult spot, the complexity increases. It’s advised to diagnose the issue before replacing parts to avoid unnecessary expenses.
2. Chevrolet – 2019 Colorado Starter Motor
Domain: 2carpros.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 2019 Chevrolet Colorado 3.6L V6 2WD Automatic, 85,000 miles; Starter motor is a high torque motor that utilizes a small pinion gear to contact the flywheel and a starter solenoid to initiate the electrical connection.
3. Electric Starter – Intermediate Installation Guide
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Project Duration: 1 to 2 hours; Skill Level: Intermediate; Starter Type: Electric Starter (Starter Motor); Common Weight: 20 pounds or more; Special Requirements: Correct starter bolts (not regular grade 8 bolts); Tools Needed: Floor jack, jack stands, ramps or wheel cribs, wrenches, sockets, ratchet, extensions; Key Connections: Battery’s positive terminal, trigger wire; Inspection Points: Batter…
4. WikiHow – How to Install a Car Starter
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to install a car starter, including the following key details: 1. Disconnect the battery before starting the installation. 2. Locate the starter, which resembles a large cylinder with a smaller cylinder (the solenoid) attached. 3. Disconnect the wiring from the starter’s solenoid. 4. Remove the retaining bolts that hold the starter in place. 5. Comp…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to change a starter
In conclusion, effectively changing a starter is not just a matter of technical skill; it’s a strategic decision that can have significant implications for operational efficiency and cost management. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of starter replacement can lead to better sourcing decisions. Prioritizing quality parts and reliable suppliers can minimize downtime and enhance vehicle performance, ultimately leading to improved productivity.
Moreover, engaging in strategic sourcing practices allows businesses to forge long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers, ensuring consistent access to high-quality components at competitive prices. This not only safeguards against unexpected failures but also empowers businesses to maintain their fleets effectively.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, remember to evaluate suppliers based on quality, reliability, and support. Investing in a robust supply chain can facilitate smoother operations and better service delivery. Embrace the future of maintenance and repair—prioritize sourcing that aligns with your operational goals and enhances your competitive edge. Now is the time to take action and strengthen your procurement strategies to ensure your business remains resilient and efficient in an ever-evolving market.

Illustrative image related to how to change a starter
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to how to change a starter