Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much to replace starter
Navigating the complexities of how much to replace a starter can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the costs associated with starter replacement is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. This comprehensive guide delves into the various factors influencing starter replacement costs, including the type of starter required, labor expenses, and vehicle make and model.
Moreover, we explore the nuances of sourcing high-quality parts from reliable suppliers, ensuring that your procurement decisions align with both budgetary constraints and performance standards. By outlining essential considerations such as supplier vetting processes and cost breakdowns, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you are a fleet manager seeking to optimize vehicle maintenance or a parts distributor aiming to enhance your product offerings, this resource equips you with the insights needed to navigate the global market effectively. With actionable strategies and expert recommendations, you can streamline your operations and ensure your fleet remains reliable and cost-efficient.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 How Much To Replace Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much to replace starter
- Understanding how much to replace starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much to replace starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much to replace starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much to replace starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much to replace starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much to replace starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much to replace starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much to replace starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much to replace starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much to replace starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much to replace starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much to replace starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how much to replace starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Reduction Starters | More efficient, draws less battery power, higher cost | High-performance vehicles, luxury cars | Pros: Better efficiency, longer battery life. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Direct Drive Starters | Larger, low-speed motor, less efficient, lower cost | Standard vehicles, older models | Pros: Lower cost, easier to replace. Cons: Less efficient, may drain battery faster. |
| Remanufactured Starters | Rebuilt from used parts, often tested for quality | Cost-sensitive businesses, fleet vehicles | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable if sourced well. Cons: Limited warranty, potential quality variability. |
| OEM Starters | Original equipment manufacturer parts, guaranteed fit | Premium vehicles, warranty compliance | Pros: Perfect fit, reliability. Cons: Higher cost, limited availability in some markets. |
| Aftermarket Starters | Non-OEM parts, varied quality and pricing | Budget-conscious buyers, diverse applications | Pros: Wide range of options, competitive pricing. Cons: Quality inconsistency, potential compatibility issues. |
What Are Gear Reduction Starters and Their Benefits for B2B Buyers?
Gear reduction starters are designed to be highly efficient, utilizing a gear mechanism that reduces the amount of power drawn from the battery during startup. This type of starter is ideal for high-performance vehicles and luxury cars where efficiency is paramount. For B2B buyers, especially those in automotive sales or fleet management, investing in gear reduction starters can lead to lower operational costs over time due to reduced battery drain and enhanced overall vehicle performance. However, the higher initial cost may require justification through long-term savings.
How Do Direct Drive Starters Compare in Terms of Cost and Performance?
Direct drive starters feature a larger motor that operates at low speeds, making them less efficient than gear reduction models. They are commonly found in standard vehicles and older models, appealing to businesses that prioritize budget over performance. B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions will find direct drive starters advantageous due to their lower purchase price and ease of replacement. However, the potential for increased battery drain may lead to higher maintenance costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Remanufactured Starters?
Remanufactured starters are rebuilt from used parts, thoroughly tested to ensure functionality. This option is particularly attractive to cost-sensitive businesses, such as those managing fleet vehicles, as it provides a reliable solution at a fraction of the cost of new parts. Buyers should consider the reputation of the supplier and warranty terms, as quality can vary significantly. While remanufactured starters can offer substantial savings, the risk of inconsistent quality should be carefully managed to avoid future operational disruptions.
Why Choose OEM Starters for Your Business Fleet?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) starters are designed to match the specifications of the vehicle they are replacing, ensuring a perfect fit and reliable performance. For businesses operating premium vehicles or those needing to comply with warranty requirements, OEM starters are often the best choice. While they come at a higher price point, their reliability and guaranteed compatibility can lead to lower long-term costs associated with repairs and replacements. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of reliability against the budget constraints of their operations.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Aftermarket Starters?
Aftermarket starters provide a diverse range of options at competitive prices, making them appealing for budget-conscious buyers. They can be suitable for a variety of applications, from everyday vehicles to specialized machinery. However, the quality of aftermarket parts can be inconsistent, leading to potential compatibility issues and varying performance levels. B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on suppliers and consider the long-term implications of their choices, balancing cost savings with the need for reliability and performance.
Key Industrial Applications of how much to replace starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much to replace starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Estimating costs for starter replacement in workshops | Accurate budgeting and customer satisfaction | Access to reliable suppliers, warranty options, and parts availability |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet management for commercial vehicles needing starter replacement | Reduced downtime and operational efficiency | Bulk purchasing agreements, service contracts, and local regulations |
| Construction Equipment | Maintenance of heavy machinery starters | Ensured operational readiness and safety | Compatibility with various machinery models and technical support |
| Agriculture | Replacement of starters in agricultural vehicles | Improved productivity and reduced repair costs | Understanding of seasonal demands and reliable supply chains |
| Mining | Starter replacements for mining equipment | Minimized equipment failure and operational delays | Specialized parts sourcing and adherence to safety regulations |
How Is ‘How Much to Replace Starter’ Relevant in Automotive Repair?
In the automotive repair industry, understanding the cost of starter replacement is crucial for workshops. Accurate estimates help mechanics provide clear quotes to customers, fostering trust and satisfaction. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, must consider local labor rates and parts availability, which can vary significantly. Additionally, knowing the typical costs associated with different car makes and models ensures that repair shops can effectively manage their budgets and maintain profitability.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
Why Is Starter Replacement Important for Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, fleet management hinges on the reliability of vehicles. Frequent starter replacements can lead to reduced downtime, enhancing operational efficiency. Companies must evaluate the cost-effectiveness of bulk purchasing starter parts and consider service contracts with suppliers to ensure timely replacements. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should also be aware of regional differences in labor costs and part specifications to optimize their maintenance budgets effectively.
How Do Construction Equipment Companies Benefit from Starter Knowledge?
For construction companies, maintaining heavy machinery is vital for project timelines. Understanding how much to replace starters allows for proactive maintenance, ensuring machinery is operational when needed. Buyers must source starters compatible with various equipment models and consider the availability of technical support for installation. In regions like Africa, where equipment may be subjected to harsh conditions, selecting durable and reliable starter parts can significantly impact productivity and safety.
What Role Does Starter Replacement Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, the performance of vehicles and machinery is directly linked to productivity. Knowing the costs associated with starter replacements helps farmers plan their maintenance budgets effectively. International buyers should consider seasonal demand fluctuations and the availability of parts to minimize downtime during critical farming periods. Reliable suppliers that can provide timely replacements and support can make a significant difference in maintaining operational efficiency.
How Is Starter Replacement Managed in the Mining Sector?
In mining, the reliability of equipment is paramount, and starter failures can lead to costly operational delays. Companies must understand the costs associated with starter replacements to budget accurately and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Sourcing specialized parts that meet safety regulations is essential, particularly in regions with stringent compliance requirements. Buyers should also assess the availability of local suppliers who can provide timely support to minimize equipment downtime.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much to replace starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Unexpected High Costs After Starter Failure
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those managing fleets or automotive services, often encounter unexpected financial strain when a starter fails. When a vehicle suddenly becomes inoperable, the costs can escalate quickly, especially if the buyer is unaware of the specific starter replacement costs for different vehicle models. This lack of knowledge can lead to rushed decisions, resulting in overpaying for parts and labor without understanding the market rates or the importance of sourcing quality components.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on starter replacement costs specific to their vehicle models. Creating a database of the common starter types used across their fleet can help in budgeting and planning for potential replacements. Additionally, engaging with multiple suppliers for quotes and leveraging bulk purchasing agreements can lead to significant savings. Buyers should also stay updated on average labor costs in their region, as these can vary widely, impacting the total replacement cost. Establishing relationships with trusted local mechanics can provide peace of mind and ensure quality work at competitive prices.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Assessing Starter Condition
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges in accurately diagnosing starter issues, which can lead to premature replacements or missed opportunities for repair. Symptoms like clicking sounds or intermittent starting problems can be misattributed to other components, causing unnecessary expenses. This confusion often stems from a lack of clear communication between vehicle operators and mechanics regarding the symptoms and possible underlying issues.
The Solution: Implementing a standardized diagnostic checklist for vehicle operators can streamline the communication process. This checklist should include specific symptoms, operational context, and any previous starter issues. By documenting these details, buyers can provide mechanics with precise information, enabling more accurate diagnostics. Additionally, investing in training for staff on basic automotive troubleshooting can empower them to identify starter-related issues early. This proactive approach not only saves costs associated with misdiagnosis but also extends the life of the starter by addressing issues before they escalate.
Scenario 3: Uncertainty About DIY vs. Professional Replacement
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the decision of whether to handle starter replacements in-house or outsource to professionals. The allure of saving costs through DIY can be tempting, especially for businesses with skilled technicians. However, the potential for errors, lack of warranty on parts, and time constraints can make this decision complex and fraught with risk.
The Solution: Buyers should assess their capabilities and weigh the pros and cons of each option. For businesses with skilled technicians, investing in proper tools and training can make DIY replacements feasible and cost-effective. However, it is crucial to consider the long-term implications of warranties on parts. If choosing to go the DIY route, buyers should ensure they have access to reliable service manuals and instructional resources specific to the vehicle models in their fleet. On the other hand, for businesses that opt for professional services, establishing a partnership with a reputable mechanic or auto repair facility can yield benefits such as discounted rates and guaranteed workmanship. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and potential downtime, can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much to replace starter
What Are the Key Materials for Starter Replacement?
When considering starter replacement, the choice of materials is crucial for ensuring performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in starter motors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Properties of Copper in Starter Motors?
Copper is frequently used in starter motors for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can handle high temperatures and has a good resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for automotive applications where heat generation is common.
Pros: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of the starter motor. Additionally, copper components tend to have a long lifespan due to their resistance to corrosion and wear.
Cons: However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials like aluminum. Its weight can also be a disadvantage in applications where reducing weight is a priority. Moreover, manufacturing processes involving copper can be complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Copper’s excellent conductivity makes it ideal for high-performance starter motors, particularly in vehicles that require quick starts under various conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of the fluctuating copper prices and the potential for supply chain disruptions. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM for electrical components is also essential.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Starters?
Aluminum is often chosen for its lightweight and cost-effective nature. It has decent electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper, and offers good resistance to corrosion.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
Pros: The lightweight property of aluminum is beneficial for improving fuel efficiency in vehicles. Additionally, it is less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers.
Cons: The downside is that aluminum’s conductivity is lower, which may affect the performance of the starter motor in high-demand situations. It may also require additional treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for standard vehicles where weight reduction is a priority, but it may not perform as well in high-performance applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the manufacturing standards for aluminum components, such as DIN and JIS, to ensure quality and compliance.
What Role Does Steel Play in Starter Manufacturing?
Steel is commonly used in the structural components of starter motors due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high pressures and mechanical stress, making it ideal for components that require robustness.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
Pros: The primary advantage of steel is its strength, which contributes to the overall durability of the starter motor. It is also relatively inexpensive and widely available.
Cons: However, steel is heavier than both copper and aluminum, which can be a drawback in applications where weight is a concern. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is best suited for heavy-duty applications where strength and durability are paramount, such as in commercial vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, like parts of Africa and South America, should ensure that the steel components are properly coated or treated to prevent rust.
Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
Why is Plastic Used in Certain Starter Components?
Plastic is often used for insulation and housing components in starter motors due to its lightweight and insulating properties. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is resistant to many chemicals.
Pros: The main advantage of plastic is its low weight and cost, making it an economical choice for non-structural components. It also provides excellent electrical insulation.
Cons: However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, which can lead to degradation over time. Its mechanical strength is also lower compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for components that do not experience high mechanical stress or extreme temperatures, such as covers and casings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with relevant standards for automotive applications, as different regions may have varying regulations regarding material safety and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Replacement
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much to replace starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections in starter motors | Superior conductivity | High cost | High |
| Aluminum | Structural components in standard vehicles | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications in commercial vehicles | Strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Insulation and housing components | Low weight and cost | Less heat resistance | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for starter replacements, enabling informed purchasing decisions that align with performance needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much to replace starter
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Starters?
The manufacturing process for automotive starters involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets rigorous performance and reliability standards. Below are the main stages of manufacturing, along with key techniques used at each stage.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Starter Manufacturing?
The first step in starter production is material preparation, where raw materials are sourced and processed. Common materials include high-grade steel for the housing, copper for the windings, and various plastics for insulation. These materials are selected based on their electrical and mechanical properties, ensuring durability and efficiency.
Advanced techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining are employed to create precise components from these raw materials. The aim is to minimize waste and ensure that each part can withstand the stresses of operation.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
Forming: How Are Starter Components Shaped?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins, where individual components are shaped. This typically involves processes such as stamping, forging, and die-casting. For instance, the outer casing of the starter may be stamped from sheet metal, while the armature is usually forged or cast to achieve the necessary strength.
Precision is key during this phase, as any deviation can affect the starter’s performance. Manufacturers often use computer-aided design (CAD) software to simulate the forming process and identify potential issues before production begins.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
After forming, the components proceed to the assembly stage. This is where various parts, such as the solenoid, armature, and casing, are brought together. Automated assembly lines are commonly used to enhance efficiency, with robots performing tasks like fastening and wiring.
Quality control is integrated into the assembly process through the use of standardized operating procedures (SOPs) to ensure consistency. Workers are trained to recognize defects and report any irregularities immediately.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
Finishing: How Is the Starter Prepared for Distribution?
The finishing stage involves several processes to prepare the starter for shipment. This may include surface treatments, such as coating or painting, to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Additionally, electrical testing is performed to confirm that each starter meets operational specifications.
Final inspections are critical at this stage. Each unit is checked for functionality and compliance with international standards, ensuring that only products meeting quality benchmarks reach the market.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Starter Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that starters are reliable and safe for use in vehicles. Various international and industry-specific standards govern QC practices in starter production.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most widely recognized international quality management standards. Compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that a manufacturer has established a robust quality management system (QMS) that emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, automotive parts often require compliance with specific regulations like the European Union’s CE marking or API certifications in the oil and gas sector. These certifications indicate that the products meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are critical to ensuring that each starter meets the necessary specifications throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps identify defects early, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Each starter undergoes a final inspection and testing phase to confirm it meets performance and safety standards before being packaged for shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Starter Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the quality and performance of starters. These include:

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
- Electrical Testing: This ensures that the starter operates correctly under various conditions. Tests may include checking for short circuits, open circuits, and proper voltage output.
- Mechanical Testing: Components are subjected to stress tests to evaluate their durability and resistance to wear.
- Thermal Testing: This assesses how well the starter performs under extreme temperature conditions, which is crucial for reliability in varying climates.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are some actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. B2B buyers should request access to audit reports to assess compliance.
- Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality assurance processes, including certifications and testing results. This transparency is vital for building trust.
- Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services: Independent inspection agencies can evaluate the quality of products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance for buyers, especially when sourcing from overseas.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification can be crucial. Different regions may have varying regulations regarding automotive parts, which can affect compliance and certification processes.
- Regional Standards: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and regulations, such as the automotive quality standards in the European Union (IATF 16949) or safety regulations in the Middle East.
- Language Barriers: Documentation may be in different languages, necessitating the need for translation services to ensure understanding of quality processes.
- Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers in different regions may require an understanding of cultural norms and business practices, which can influence communication and negotiations.
By grasping the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place for starter replacement, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing products. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also enhances the overall quality of the automotive components they procure.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much to replace starter’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in understanding the costs associated with replacing a vehicle’s starter. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints, ultimately optimizing your procurement process.
Step 1: Assess Your Vehicle Fleet Needs
Understanding the specific requirements of your vehicle fleet is crucial. Identify the types and models of vehicles you operate, as starter costs can vary significantly based on these factors. This assessment will help you establish a baseline for expected expenses and guide your procurement strategy.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
- Considerations:
- Are your vehicles primarily passenger cars, trucks, or specialized equipment?
- What is the average age and mileage of your fleet, and how might this influence starter longevity?
Step 2: Research Replacement Part Costs
Gather information on the market price range for starters specific to your vehicle types. Prices can vary widely based on make, model, and starter type (gear reduction vs. direct drive).
- Action Items:
- Consult multiple suppliers to compare prices.
- Use online automotive parts marketplaces for transparent pricing.
Step 3: Evaluate Labor Costs for Installation
Labor costs can significantly impact the total expense of replacing a starter. Understanding the average labor rates in your region will help you budget more accurately.
- Key Points:
- Research local labor rates, which typically range from $100 to $250 per hour.
- Consider the complexity of the installation, as some vehicles may require more labor-intensive procedures.
Step 4: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding trustworthy suppliers is essential for maintaining quality and reliability. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation in the automotive parts industry, especially those familiar with your specific vehicle needs.
- Checklist:
- Verify supplier certifications and industry affiliations.
- Request references and case studies from similar businesses to gauge supplier reliability.
Step 5: Consider Warranty and Support Options
Evaluate the warranty and support services offered by potential suppliers. A robust warranty can mitigate risks associated with defective parts and installation issues.
- Focus Areas:
- What is the length and coverage of the warranty?
- Does the supplier offer technical support or installation services, and what are their terms?
Step 6: Review Repair vs. Replacement Options
Before finalizing your decision, analyze whether repairing existing starters might be more cost-effective than outright replacement. This can depend on the age and condition of the starters in your fleet.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
- Important Factors:
- Assess the average lifespan of your starters and the frequency of repairs.
- Consult with mechanics to get insights into potential repair costs versus replacement.
Step 7: Plan for Future Maintenance
Integrate starter replacement into your broader vehicle maintenance plan. Predictive maintenance can help you budget for future replacements and avoid unexpected costs.
- Action Steps:
- Schedule regular inspections of your starters as part of your vehicle maintenance routine.
- Keep records of starter performance and replacement history to inform future procurement decisions.
By adhering to this checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of starter replacement costs, ensuring that your procurement decisions are both strategic and financially sound.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much to replace starter Sourcing
The cost structure for replacing a vehicle starter involves multiple components, each contributing to the overall pricing. Understanding these elements is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source starters, especially when considering factors like labor, materials, and logistics.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Starter Replacement?
-
Materials: The starter itself can range from $100 to over $400, depending on the vehicle’s make and model. High-performance or specialized starters, such as gear reduction types, tend to be more expensive. Additionally, components like solenoids, brushes, and field coils also add to the material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are often the largest single expense in starter replacement, typically ranging from $100 to $250 per hour. The complexity of accessing the starter can significantly affect the time required, which varies based on the vehicle’s design. For instance, replacing a starter in a Toyota may require less time compared to a Mercedes-Benz, which could necessitate the removal of additional components.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with producing starters, such as factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and employee wages. High-quality manufacturers may incorporate advanced technologies and processes, which can elevate costs but also ensure better reliability and longevity.
-
Tooling and Quality Control: Investment in specialized tooling for starter production and rigorous quality control processes can increase initial costs but ultimately lead to higher quality products. Buyers should consider suppliers that prioritize quality assurance to minimize future replacement needs.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting starters from manufacturers to distributors or directly to buyers is another factor. International shipping, customs duties, and handling fees can add significantly to the total cost, especially for buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up prices to cover their operational costs and profit margin. This can vary based on market demand, competition, and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Starter Replacement Costs?
Several factors can influence the price of starters:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized starters designed for specific applications may incur additional costs. However, they can improve performance and longevity, offering better total cost of ownership.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can increase upfront costs but may lead to lower failure rates and maintenance costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: Reliability, reputation, and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Local suppliers may offer quicker turnaround times, while international suppliers might provide cost benefits but involve longer lead times.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (like FOB, CIF) is crucial for calculating total costs. Different terms can affect who bears the shipping risk and responsibility, influencing overall expenses.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Sourcing Starters?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially when ordering large quantities. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Always evaluate the total cost of ownership, not just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, warranty, and expected lifespan when making purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of import tariffs, local taxes, and the impact of currency fluctuations on pricing. Building relationships with local distributors may help mitigate some of these costs.
-
Quality Assurance: Seek suppliers who provide warranties and guarantees on their products. This can reduce long-term costs associated with replacements and repairs.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on specific vehicle models, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always consult with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate and tailored pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much to replace starter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Starter Replacement
When faced with starter issues, B2B buyers must evaluate their options carefully. While replacing a starter is a common solution, alternatives exist that may provide cost-effective or operationally advantageous choices. This analysis will compare the traditional approach of replacing a starter with two viable alternatives: starter repairs and upgrading to a more advanced starting system.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How Much To Replace Starter | Starter Repairs | Upgrading to Advanced Starting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores full functionality | May provide temporary fix | Enhanced reliability and efficiency |
| Cost | $700 – $1,200 | $100 – $400 | $1,200 – $2,500 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional help | Can be DIY or professional | Requires professional installation |
| Maintenance | Low post-replacement upkeep | Potential recurring issues | Higher reliability with minimal upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Older vehicles, preventive maintenance | Newer vehicles or minor issues | Fleets needing efficiency and reliability |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Starter Repairs?
Starter repairs can be an appealing alternative for businesses looking to save costs. This approach typically involves fixing specific components of the starter, such as the solenoid or brushes, which can range from $100 to $400 depending on the issue. The main advantage is the lower upfront cost compared to a full replacement. However, repairs may only offer a temporary solution, especially if the starter is nearing the end of its lifespan. There’s also the risk of recurring issues, which could lead to further downtime and additional repair costs. Thus, while repairs may seem attractive, they may not provide the long-term reliability that many businesses require.
How Does Upgrading to an Advanced Starting System Compare?
Upgrading to a more advanced starting system represents a significant investment, typically costing between $1,200 and $2,500. However, the benefits often outweigh the initial expense, particularly for businesses operating fleets or vehicles that require high reliability. These systems can include features like gear reduction starters, which offer better efficiency and less battery drain. The installation process is usually more complex, necessitating professional assistance, but they often lead to reduced maintenance needs in the long run. This option is ideal for organizations that prioritize operational efficiency and reliability, making it a compelling alternative for those looking to enhance their vehicle performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the best solution for starter issues involves assessing specific operational needs and budget constraints. For businesses with older vehicles or those operating on tight budgets, opting for a starter replacement or repairs may be more feasible. Conversely, companies that rely on their vehicles for extensive operations may find that investing in an advanced starting system pays off through enhanced reliability and efficiency. Ultimately, understanding the long-term implications and the operational context is crucial in making a well-informed decision that aligns with business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much to replace starter
What Are the Critical Technical Properties to Consider When Replacing a Starter?
When evaluating the cost of replacing a starter, several technical properties play a crucial role in determining the overall quality and performance of the replacement part. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a starter motor significantly influences its durability and performance. High-quality starters are typically made from robust materials like stainless steel or high-grade aluminum, which resist corrosion and wear. For B2B buyers, selecting parts made from superior materials can lead to longer lifespans and reduced maintenance costs, ultimately enhancing the value proposition of their investment.
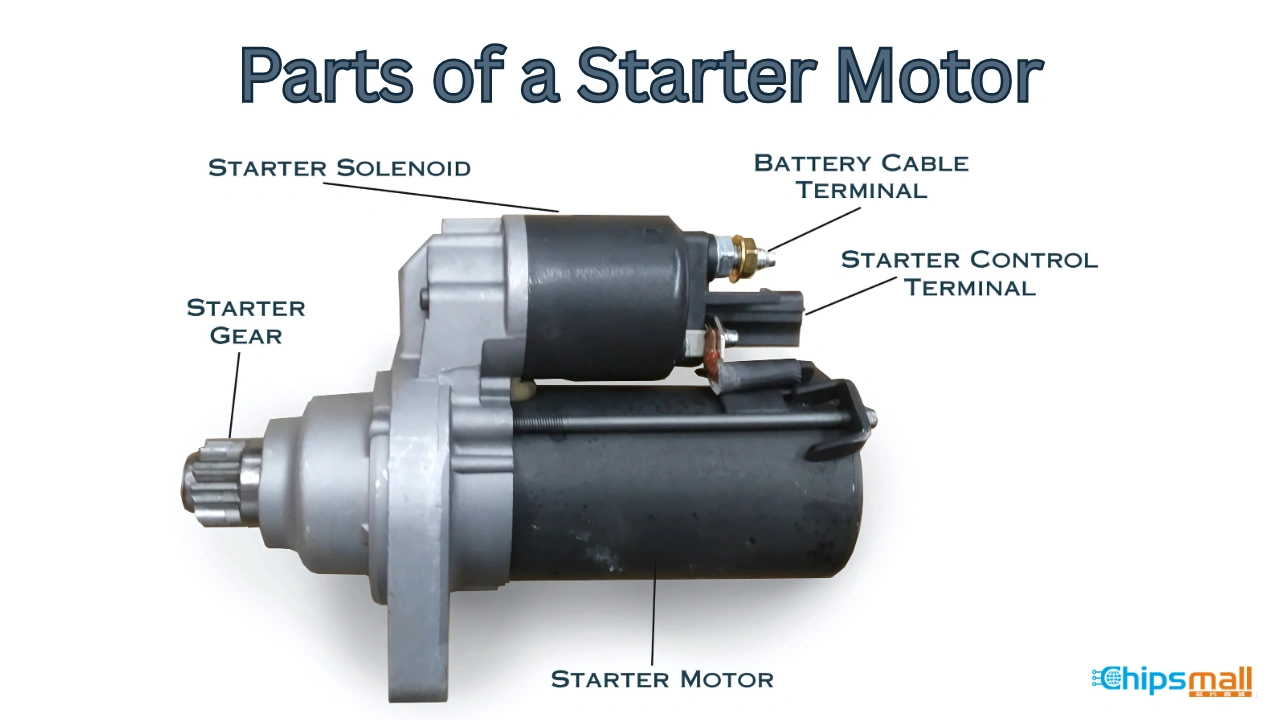
Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
2. Voltage Rating
Most automotive starters operate on a 12-volt system, but variations exist. Understanding the voltage rating is crucial for ensuring compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. A mismatch can lead to inadequate performance or complete failure. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing starters with the correct voltage specifications to avoid operational disruptions.
3. Torque Output
Torque output measures the rotational force a starter can produce to crank the engine. Different vehicles require different torque levels, with larger engines needing starters that provide higher torque. When sourcing starters, B2B buyers should evaluate the torque ratings to ensure they meet the demands of the specific applications for which they are purchasing.
4. Weight
The weight of a starter motor can affect its performance and installation. Heavier starters may require more robust mounting systems and can influence the vehicle’s overall weight and fuel efficiency. B2B buyers should consider the weight specifications to ensure they are selecting products that align with their performance and efficiency objectives.
5. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the acceptable limits of variation in dimensions and performance characteristics of the starter components. High precision in manufacturing ensures that parts fit correctly and function efficiently. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can help in assessing quality and reliability, reducing the risk of premature failures.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Replacement Costs?
Navigating the landscape of starter replacement involves familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the vehicle’s original manufacturer, ensuring compatibility and quality. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts due to their reliability and warranty coverage. Understanding the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory management. It can also influence supplier selection, particularly for companies looking to maintain cost-effective stock levels.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. It’s a vital tool in the procurement process, allowing B2B buyers to compare prices, terms, and conditions from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal for starter replacements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liabilities during transportation. B2B buyers need to understand Incoterms to negotiate favorable shipping terms and ensure compliance with international trade regulations.
5. Warranty Terms
Warranty terms specify the conditions under which a product is guaranteed against defects. For starters, these terms can vary significantly between manufacturers. B2B buyers should carefully review warranty provisions to ensure they are protected against potential failures, which can impact overall operational costs.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions about starter replacements, ensuring they select the right products that meet their operational needs while optimizing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much to replace starter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Starter Replacement Costs?
The global automotive market is witnessing significant transformations that impact the costs associated with starter replacements. Key drivers include advancements in technology, increasing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles, and evolving consumer preferences toward more sustainable options. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping the starter motor sector, as traditional starters are being replaced by more sophisticated systems. This shift necessitates that B2B buyers stay informed about the technical specifications and costs associated with these new technologies.
Emerging sourcing trends in the industry reveal a growing inclination towards online platforms and digital marketplaces. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are leveraging these platforms to access a broader range of suppliers and competitive pricing. Enhanced supply chain transparency and logistics optimization are becoming crucial as companies seek to mitigate risks associated with sourcing from different geographical regions. Understanding local market dynamics, including labor costs and regional pricing variations, is essential for B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
Furthermore, the complexity of vehicles today means that labor costs constitute a significant portion of the total replacement expense. The need for skilled technicians to handle intricate installations and repairs is driving the demand for training and certification programs, which in turn affects labor availability and pricing. Buyers must consider these factors when evaluating potential suppliers and repair services.

Illustrative image related to how much to replace starter
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Starter Replacement Decisions?
Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern in the automotive industry, influencing how B2B buyers approach sourcing starter replacements. The environmental impact of automotive components, including starter motors, cannot be understated. The extraction and processing of raw materials contribute significantly to carbon emissions, and the industry is increasingly held accountable for its ecological footprint.
As a response, many suppliers are adopting ethical sourcing practices and pursuing certifications that demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that utilize ‘green’ materials and processes, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly manufacturing techniques. Certifications like ISO 14001 or the Global Automotive Sustainability Principles can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to minimizing environmental impact.
Incorporating sustainable practices into sourcing decisions not only enhances corporate responsibility but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. For instance, using remanufactured starters can significantly reduce waste and energy consumption compared to new parts. Buyers who prioritize sustainability may find themselves better positioned in a market that increasingly values eco-conscious practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Replacement Costs?
The evolution of starter motors dates back to the early 20th century when electric starters replaced hand-cranked engines, revolutionizing vehicle operation. Initially, starter motors were relatively simple and inexpensive. However, as automotive technology advanced, the complexity of starter systems increased, leading to higher replacement costs.
In recent decades, the introduction of more advanced starter technologies, such as gear reduction starters, has further escalated costs. These systems offer improved efficiency but come at a premium price. The historical context of starter motors illustrates how technological advancements continually reshape the market, influencing sourcing decisions for B2B buyers. Understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed purchasing choices in today’s dynamic automotive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much to replace starter
-
How do I determine the cost of replacing a starter for my vehicle?
To accurately determine the cost of replacing a starter, consider several factors: the make and model of the vehicle, the type of starter required, and the labor costs associated with installation. Generally, part prices range from $100 to $400, while labor can vary significantly based on location and the complexity of the job, typically totaling between $700 and $1,200. Engaging with local mechanics or suppliers can provide specific quotes tailored to your vehicle’s requirements. -
What factors influence the price of a starter replacement?
The price of a starter replacement is influenced by the vehicle’s make and model, the starter type (gear reduction vs. direct drive), and the complexity of access to the starter under the hood. Labor costs can vary widely, with rates ranging from $100 to $250 per hour. Additionally, geographical location and the availability of parts can further affect overall pricing, so it is advisable to research local suppliers and mechanics for accurate estimates. -
What are the common signs that indicate a starter needs replacement?
Common signs of a failing starter include slow engine cranking, clicking sounds when turning the key, and the starter running continuously after the engine starts. If the dashboard warning lights illuminate without the engine cranking, this may also indicate a starter issue. Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent more extensive damage and facilitate timely replacement, ensuring operational efficiency for your fleet. -
How can I source quality starters for my fleet?
To source quality starters, it’s essential to vet suppliers based on their reputation, product offerings, and customer reviews. Look for manufacturers that provide warranties and have a track record of quality assurance. Engaging in trade shows and industry-specific expos can help you meet potential suppliers face-to-face, allowing you to assess product quality firsthand. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer customization options to better fit your fleet’s unique specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starters from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of starter and the supplier’s production capabilities. Typically, MOQs can range from a single unit for smaller suppliers to hundreds for larger manufacturers. When negotiating, inquire about flexibility in MOQs to accommodate your specific needs, especially if you are sourcing for a diverse fleet. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering starters internationally?
Payment terms for international orders can vary, but common practices include upfront payments, partial payments before shipment, or net payment terms after delivery. It is crucial to discuss payment methods that suit both parties, such as letters of credit or escrow services, which can provide security. Ensure to clarify any potential taxes, tariffs, or additional fees that may apply to your shipment, as these can affect your overall cost. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for starters sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced starters, establish clear quality standards and specifications with your supplier upfront. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate their performance before committing to a larger order. Additionally, consider incorporating third-party inspection services to conduct quality checks before shipment. Establishing a strong line of communication with your supplier can also help address any quality concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing starters?
When sourcing starters internationally, logistics considerations are critical. Evaluate shipping options, including air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost efficiency. Ensure you understand the import regulations of your destination country, including customs duties and taxes. Additionally, plan for lead times, including production and shipping durations, to maintain your fleet’s operational readiness. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in automotive parts can streamline this process.
Top 5 How Much To Replace Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Starter Replacement – Cost Breakdown
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement, labor charges, part price, diagnostics fee, OEM starter pricing, labor hours, markup on parts.
2. AAA – Car Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: The average cost to replace a car starter ranges from $700 to $1,200, depending on the make and model of the vehicle and labor hours required. The replacement part itself costs between $100 and $400. Labor rates within the AAA Approved Auto Repair network range from $100 to $250 per hour. Factors influencing cost include car make and model, type of starter (gear reduction or direct drive), and whe…
3. Facebook – Starter Replacement
4. CarTalk – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cost to replace a starter: $600 to $900 for common vehicles; $900 to $1,400 for luxury models. Symptoms of a bad starter include clicking sounds, screeching, and intermittent functionality. Starters can be new, remanufactured, or repaired, with remanufactured starters being common. Modern vehicles with stop-start systems have starters designed to last longer, reducing concerns about premature fail…
5. Tundras – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: tundras.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement for a 2007 Toyota Tundra CrewMax; quoted cost: $1500 (labor: $900, part: $650); part number: Denso 428000-4640; vehicle mileage: 174k; mechanic shop: Brakes Plus; discussion on DIY challenges and potential battery issues.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much to replace starter
In navigating the complexities of starter replacement costs, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize their procurement processes. Understanding the full scope of replacement expenses—ranging from $700 to $1,200—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational budgets. Key factors influencing costs include labor rates, the specific make and model of vehicles, and the type of starter required. For businesses with fleets or a significant investment in automotive assets, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to better pricing agreements with suppliers and mechanics, ultimately reducing total cost of ownership.
Furthermore, proactive maintenance and timely diagnostics can prevent costly future repairs, underscoring the value of establishing reliable relationships with qualified service providers. As markets evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of supply chain trends and service capabilities will be crucial.
Investing in strategic sourcing not only streamlines operations but also fosters resilience against fluctuating costs. Engage with trusted suppliers and automotive experts to ensure your fleet remains efficient and cost-effective. The future of your automotive operations hinges on these decisions—act now to secure the best outcomes for your business.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.