Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for battery vs alternator problems
In the global automotive market, effectively addressing battery vs alternator problems is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. B2B buyers often face the challenge of accurately diagnosing these issues to avoid costly repairs and disruptions in their fleet management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of battery and alternator failures, providing insights into their distinct roles within a vehicle’s electrical system, common symptoms, and best practices for maintenance.
By exploring various types of batteries and alternators, their applications in different vehicle models, and criteria for vetting suppliers, this resource equips international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Vietnam—with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, it addresses cost considerations, helping businesses to budget effectively for both preventative measures and emergency repairs.
Understanding the nuances of these components not only enhances vehicle performance but also empowers organizations to implement strategic maintenance schedules. This guide ultimately serves as a vital tool for businesses looking to optimize their automotive operations while mitigating risks associated with battery and alternator failures.
Table Of Contents
- Top 1 Battery Vs Alternator Problems Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for battery vs alternator problems
- Understanding battery vs alternator problems Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of battery vs alternator problems
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘battery vs alternator problems’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for battery vs alternator problems
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for battery vs alternator problems
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘battery vs alternator problems’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for battery vs alternator problems Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing battery vs alternator problems With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for battery vs alternator problems
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the battery vs alternator problems Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of battery vs alternator problems
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for battery vs alternator problems
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding battery vs alternator problems Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Failure | Slow cranking, frequent jump-starts, corrosion | Automotive repair shops, fleet management | Pros: Easy to diagnose; Cons: Short lifespan (3-5 years). |
| Alternator Malfunction | Flickering lights, electrical accessory issues, stalling | Commercial vehicle maintenance, logistics | Pros: Can be repaired; Cons: Costly if ignored. |
| Corrosion Issues | Visible corrosion on terminals, poor electrical flow | Battery suppliers, automotive parts retailers | Pros: Preventable with maintenance; Cons: Can lead to total failure. |
| Overloading Electrical System | Dimming lights, malfunctioning accessories | Fleet operations, automotive service centers | Pros: Identifies need for upgrades; Cons: Strain on older vehicles. |
| Temperature-Related Problems | Battery drain in extreme conditions | Automotive parts distributors, repair shops | Pros: Seasonal awareness can prevent issues; Cons: Requires regular checks. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Battery Failure?
Battery failure is often characterized by symptoms such as slow engine cranking, frequent jump-starts, and visible corrosion around terminals. This type of failure is prevalent in automotive repair shops and fleet management businesses, where reliable vehicle performance is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the battery’s lifespan, typically ranging from 3 to 5 years, and the ease of diagnosis. While battery issues are straightforward to address, their relatively short life can lead to unexpected costs if not monitored regularly.
How to Identify Alternator Malfunction?
Alternator malfunctions present distinct signs, including flickering lights, issues with electrical accessories, and engine stalling. This type of problem is particularly relevant for commercial vehicle maintenance and logistics companies, where operational efficiency is vital. Buyers should weigh the benefits of repair versus replacement, as ignoring alternator issues can lead to costly breakdowns. While repairs can be effective, the potential for failure increases with age and wear, making regular inspections essential.
What Are the Implications of Corrosion Issues?
Corrosion issues can significantly impact the electrical flow in a vehicle, leading to poor performance and starting difficulties. This problem is relevant for battery suppliers and automotive parts retailers, who can offer preventative maintenance solutions. Buyers should prioritize routine checks to minimize corrosion-related failures, as these issues are often preventable. While addressing corrosion can extend the life of both the battery and alternator, neglecting it can result in total system failure, causing additional expenses.
How Does Overloading the Electrical System Affect Performance?
Overloading the electrical system can lead to symptoms such as dimming lights and malfunctioning accessories, which are critical concerns for fleet operations and automotive service centers. Understanding the strain placed on older vehicles is essential for B2B buyers looking to maintain operational efficiency. While identifying overloading issues can prompt necessary upgrades, it may also indicate the need for a thorough assessment of the vehicle’s electrical system. Buyers should consider the implications of overloading, as it can lead to premature wear on both batteries and alternators.
Why Are Temperature-Related Problems Significant?
Temperature-related problems can cause battery drain, particularly in extreme weather conditions. This issue is pertinent for automotive parts distributors and repair shops that service vehicles in varying climates. B2B buyers must recognize the importance of seasonal awareness and regular checks to prevent battery failures linked to temperature fluctuations. While proactive measures can mitigate these risks, buyers should also prepare for potential replacements, as extreme temperatures can accelerate wear and reduce battery lifespan.
Key Industrial Applications of battery vs alternator problems
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of battery vs alternator problems | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in battery and alternator production | Ensures reliability and safety of vehicles | Supplier certifications, quality standards, testing capabilities |
| Renewable Energy | Integration of battery storage systems | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces downtime | Compatibility with existing systems, scalability, durability |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet maintenance and management | Minimizes operational disruptions and costs | Comprehensive service contracts, rapid response times, parts availability |
| Agriculture | Powering machinery and equipment | Increases productivity and reduces downtime | Local support services, battery longevity, and warranty options |
| Mining | Reliability of heavy machinery | Ensures continuous operation in demanding environments | Heavy-duty specifications, environmental resistance, service support |
How Do Automotive Manufacturers Benefit from Understanding Battery and Alternator Issues?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, understanding battery and alternator problems is crucial for quality control. Manufacturers must ensure that their vehicles can reliably start and operate under various conditions. This involves rigorous testing of batteries and alternators to meet safety and performance standards. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers with proven quality certifications and robust testing capabilities to mitigate risks associated with vehicle failures.
Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Why Is Battery Storage Important in Renewable Energy Applications?
In renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, battery storage systems are essential for managing energy supply. Problems with batteries or alternators can lead to inefficiencies and system downtimes, affecting energy distribution. Buyers in this sector should look for components that offer compatibility with existing systems, scalability for future expansion, and robust durability to withstand environmental conditions. This ensures that energy storage solutions remain effective and reliable.
How Do Transportation and Logistics Companies Manage Fleet Reliability?
Transportation and logistics companies rely heavily on the performance of their fleet’s electrical systems. Regular maintenance of batteries and alternators helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, which can disrupt operations and increase costs. For B2B buyers in this industry, sourcing comprehensive service contracts and ensuring rapid response times for maintenance are key considerations. Additionally, ensuring the availability of replacement parts can minimize downtime and maintain operational efficiency.
What Role Do Batteries Play in Agricultural Machinery?
In agriculture, machinery often relies on batteries for power, especially in remote areas. Any failure in the battery or alternator can lead to significant productivity losses. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing batteries that offer longevity and robust performance under varying environmental conditions. Local support services are also critical to ensure timely repairs and replacements, keeping agricultural operations running smoothly.
How Is Reliability Critical in Mining Operations?
Mining operations depend on heavy machinery that requires reliable power sources. Problems with batteries or alternators can lead to costly delays and safety hazards. Buyers in the mining sector should prioritize sourcing heavy-duty batteries and alternators that meet stringent environmental resistance criteria. Furthermore, having reliable service support is essential to address any issues quickly, ensuring continuous operation in challenging environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘battery vs alternator problems’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Frequent Downtime Due to Electrical Failures
The Problem: Many businesses relying on fleets or heavy machinery face significant downtime when vehicles fail to start or when electrical systems malfunction. For instance, a logistics company might find its delivery trucks incapacitated due to either a failing battery or alternator, leading to missed deadlines and dissatisfied customers. This not only impacts operational efficiency but also increases repair costs and damages the company’s reputation in the market.
The Solution: To mitigate such disruptions, businesses should implement a proactive maintenance schedule focused on the electrical systems of their vehicles. Regular inspections of both batteries and alternators can identify early signs of wear, such as corrosion or reduced voltage output. Collaborating with reliable automotive service providers to conduct comprehensive diagnostics can help pinpoint issues before they escalate. Furthermore, investing in high-quality, durable batteries and alternators tailored to the specific needs of the vehicle can enhance reliability and performance, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Scenario 2: Inaccurate Diagnostics Leading to Unnecessary Repairs
The Problem: B2B buyers, especially those in automotive maintenance and repair services, often face challenges in accurately diagnosing whether a vehicle’s issue stems from a bad battery or a faulty alternator. Misdiagnosing the problem can lead to unnecessary repairs, wasted resources, and increased frustration for both the service provider and the end customer. For example, a repair shop might replace a battery when the real culprit is a malfunctioning alternator, resulting in lost revenue and customer trust.
The Solution: To address this pain point, businesses should invest in advanced diagnostic tools that can effectively differentiate between battery and alternator issues. Training staff on the signs and symptoms associated with each component is crucial; for example, teaching them to recognize that flickering lights often indicate alternator problems, while slow engine cranking usually points to battery issues. Additionally, establishing a protocol for systematic testing—such as checking the battery voltage and alternator output—before making any repairs will ensure accurate diagnostics and enhance customer satisfaction.
Scenario 3: High Replacement Costs Due to Poor Component Selection
The Problem: Another pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of selecting the right batteries and alternators for their specific applications. Companies may inadvertently purchase low-quality components that fail prematurely, leading to higher replacement costs and increased vehicle downtime. For instance, a construction company may opt for cheaper batteries to save on initial costs, only to find that they have to replace them frequently, negating any savings.
The Solution: To avoid costly mistakes, businesses should focus on sourcing components from reputable suppliers who provide warranties and detailed specifications. Conducting thorough research into the compatibility and performance ratings of batteries and alternators for specific vehicle models is essential. Establishing long-term partnerships with trusted manufacturers can also yield benefits such as bulk pricing and insights into the latest technology improvements. Additionally, utilizing fleet management software to track performance and maintenance history can help identify trends that guide future purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to better investments and reduced operational costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for battery vs alternator problems
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Battery and Alternator Applications?
When addressing battery and alternator problems, the selection of materials is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing and maintenance of batteries and alternators, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Lead-Acid for Batteries: What Are Its Key Properties?
Lead-acid batteries are the most prevalent type used in automotive applications. They typically feature a temperature rating of -20°C to 50°C and offer good corrosion resistance when properly maintained.
Pros: Lead-acid batteries are relatively inexpensive and straightforward to manufacture. They provide high surge currents, making them excellent for starting engines.
Cons: However, they have a shorter lifespan (3-5 years) compared to other battery types and can suffer from sulfation if not regularly charged. Additionally, they are heavy, which can affect vehicle weight and efficiency.
Impact on Application: Lead-acid batteries are suitable for applications requiring high power output for short durations, such as engine starting.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ISO 9001 is essential for quality assurance. In regions like Africa and South America, where battery recycling practices may vary, buyers should ensure suppliers adhere to environmental regulations.
Lithium-Ion for Advanced Battery Solutions: What Are Its Benefits?
Lithium-ion batteries are gaining traction in the automotive sector due to their high energy density and lightweight properties. They can operate effectively in a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C.
Pros: These batteries have a longer lifespan (up to 10 years), faster charging capabilities, and are significantly lighter than lead-acid batteries, improving vehicle efficiency.
Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Cons: The manufacturing process is more complex and costly. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries require sophisticated management systems to prevent overheating and ensure safety.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are ideal for electric vehicles and hybrid systems where weight and efficiency are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, should be aware of the EU Battery Directive, which mandates recycling and sustainability measures. Compliance with standards such as IEC 62133 is also crucial.
Copper for Conductors: Why Is It Widely Used?
Copper is a common material for electrical conductors in both batteries and alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity, rated at 59.6 x 10^6 S/m.
Pros: It offers low resistance, ensuring efficient power transfer. Copper is also durable and resistant to corrosion when coated.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, as copper prices can fluctuate significantly. Additionally, copper wiring can be heavy, contributing to overall vehicle weight.
Impact on Application: Copper is essential for wiring and connections in both batteries and alternators, directly impacting performance and reliability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of copper in their regions and any import tariffs that may affect cost. Compliance with international standards like ASTM B3 is also important.
Aluminum for Lightweight Applications: What Are Its Advantages?
Aluminum is increasingly used in alternator housings and components due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It typically has a temperature rating of -40°C to 120°C.
Pros: Aluminum reduces overall vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency. It is also resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Cons: While aluminum is cheaper than copper, it has lower electrical conductivity, which can affect performance in high-load applications. Additionally, it may require protective coatings for enhanced durability.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority, such as in electric vehicles and hybrid systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy grades that meet their application requirements and ensure compliance with standards like DIN 1725 for aluminum materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for battery vs alternator problems | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Automotive batteries for starting engines | High surge current, low cost | Short lifespan, heavy | Low |
| Lithium-Ion | Electric and hybrid vehicle batteries | Long lifespan, lightweight | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | Electrical conductors in batteries and alternators | Excellent conductivity | High cost, heavy | Med |
| Aluminum | Housings and components in alternators | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity, may need coatings | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in battery and alternator applications, enabling informed decision-making for optimal performance and compliance in various international markets.
Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for battery vs alternator problems
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Batteries and Alternators?
The manufacturing process for batteries and alternators involves several critical stages that ensure product reliability and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers more effectively.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. For batteries, this includes lead, sulfuric acid, and polypropylene, while alternators require copper, aluminum, and various plastics. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet international standards and are suitable for the intended application. This stage often involves rigorous testing to confirm material properties, such as conductivity and corrosion resistance, which are crucial for performance.
Forming
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into functional components. For batteries, this includes casting lead plates and assembling them into cells. Advanced techniques like die-casting or injection molding are often used to ensure precision in alternator component manufacturing. For instance, alternator stators and rotors are formed using computer numerical control (CNC) machines, enhancing accuracy and reducing waste.
Assembly
The assembly process is where the various components come together to create the final product. Battery cells are assembled into battery packs, ensuring proper alignment and connection. In alternators, components like the rotor, stator, and rectifier are assembled with strict adherence to specifications. Automation plays a significant role in this stage, improving efficiency and reducing human error.

Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Finishing
The final stage involves applying protective coatings, labeling, and packaging. For batteries, this may include adding a durable outer shell to prevent leaks and corrosion. Alternators may receive surface treatments to enhance durability. Quality checks are essential during this phase to ensure that the products meet both aesthetic and functional standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Crucial for Battery and Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specific standards and are reliable for end-users. International buyers must be familiar with relevant QA practices to make informed decisions.
Relevant International Standards
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which specifies requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard assures buyers that the manufacturer is committed to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) for specific applications are vital indicators of product quality.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that any defects are identified and addressed early. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they are used in production. Buyers should ensure that suppliers perform rigorous testing at this stage.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help catch defects early. This may include checking dimensions, weights, and electrical properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage involves comprehensive testing of the finished product, including performance tests and safety checks, before products are shipped.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Battery and Alternator Quality Control?
Testing methods are essential to ensure that batteries and alternators function correctly and meet performance standards. Buyers should be aware of the various testing methodologies used in the industry.
Common Testing Methods
-
Electrical Testing: This includes measuring voltage, current, and resistance to ensure that the battery or alternator operates within specified limits. Load testing is also performed to simulate real-world conditions.
-
Performance Testing: Batteries may undergo cycle testing to assess their longevity, while alternators are often tested for output under varying load conditions.
-
Environmental Testing: Given the impact of temperature and humidity on performance, manufacturers may conduct tests to simulate extreme conditions. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions with harsh climates.
-
Mechanical Testing: This involves stress tests to evaluate the physical durability of components, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of daily use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure product reliability. Here are several actionable strategies:
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess compliance with international standards and internal QA processes. These audits may involve reviewing documentation, observing manufacturing practices, and testing samples.

Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports from suppliers that outline testing methods, results, and corrective actions taken for any identified issues. This transparency fosters trust and ensures accountability.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. These services can conduct random inspections and testing, ensuring adherence to quality standards.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate specific nuances in quality control to ensure they receive high-quality products.
Regional Certifications
Understanding the certification requirements of the target market is vital. For instance, batteries sold in the European market must comply with CE certification, while those in North America may require UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification.
Language and Communication Barriers
Effective communication is critical in the QA process. Buyers should ensure that all documentation is available in a language they understand, and that they can communicate effectively with suppliers regarding quality expectations.
Cultural Differences
Cultural differences can impact quality expectations and practices. Buyers should consider engaging local experts to help navigate these complexities and foster better relationships with suppliers.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for batteries and alternators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain’s reliability and performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘battery vs alternator problems’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring components related to battery and alternator issues. Understanding the differences between these two critical vehicle components can enhance your purchasing decisions, ensuring that you choose the right products for your needs and ultimately improve operational efficiency.
Step 1: Identify Your Technical Requirements
Understanding the technical specifications of the batteries and alternators you need is essential. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, amp-hour capacity, and compatibility with vehicle models. This step ensures that you procure components that fit seamlessly into your existing systems and meet performance expectations.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Before proceeding with any procurement, it’s vital to verify the credentials of potential suppliers. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or other industry-specific quality standards. This verification not only enhances trust but also assures you that the supplier adheres to high-quality manufacturing processes.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Quality and Reliability
Assess the quality and reliability of the products offered by suppliers. Request samples or product specifications and check for any warranties or guarantees. High-quality batteries and alternators can lead to lower failure rates, reducing maintenance costs and downtime in the long run.
Step 4: Compare Pricing Structures
Conduct a thorough analysis of pricing structures among various suppliers. While the lowest price may be tempting, consider the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance. Look for suppliers that offer transparent pricing and value-added services, as these can significantly impact your overall expenditure.
Step 5: Understand After-Sales Support
Investigate the after-sales support provided by potential suppliers. Effective support can include installation assistance, troubleshooting, and ongoing maintenance services. Reliable after-sales service can save you time and costs associated with operational disruptions due to faulty components.
Step 6: Gather Feedback from Existing Clients
Seek testimonials and reviews from other businesses that have previously worked with the suppliers you are considering. This firsthand feedback can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, product performance, and customer service. Engaging with other clients can help you avoid potential pitfalls and make more informed decisions.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, it’s time to negotiate terms and conditions. Discuss aspects like payment terms, delivery timelines, and any penalties for non-compliance. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process, fostering long-term relationships with your suppliers.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing components related to battery and alternator issues, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for battery vs alternator problems Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Batteries and Alternators?
When sourcing batteries and alternators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.

Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Materials represent a significant portion of the total cost, as both batteries and alternators require specific raw materials like lead, lithium, copper, and steel. The fluctuations in global commodity prices can directly affect sourcing costs.
Labor costs vary significantly depending on the region, with countries in Africa, South America, and parts of Europe often experiencing different wage structures.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs, which can influence overall pricing.
Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Tooling costs are associated with the machinery and equipment used in production, which can be substantial for custom or high-specification products.
Quality control ensures that the final products meet the required standards and certifications, an essential factor for components that are critical to vehicle performance.
Finally, logistics costs include transportation, warehousing, and import/export duties, which can vary based on the Incoterms agreed upon in the transaction.
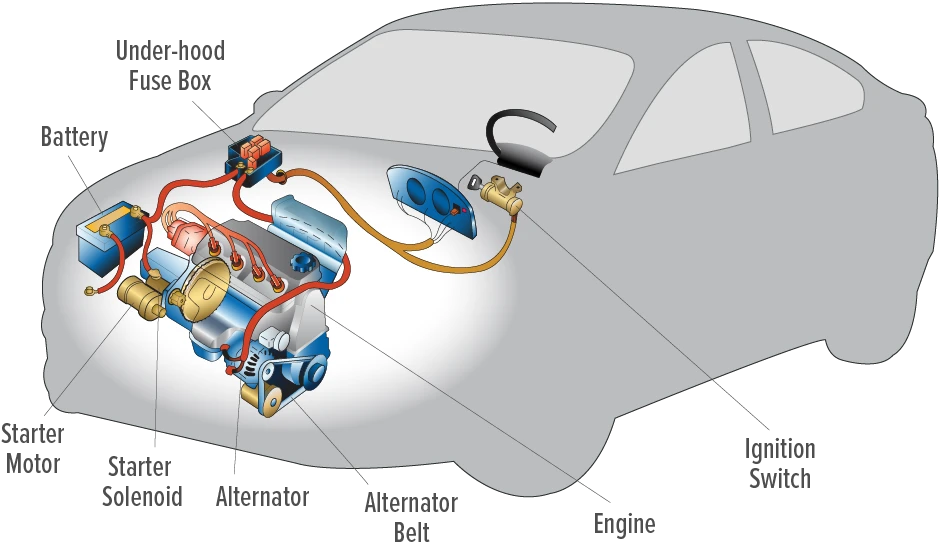
Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
How Do Price Influencers Impact Battery and Alternator Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of batteries and alternators. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) play a significant role; larger orders often lead to discounted pricing due to economies of scale.
Specifications and customization can also impact pricing. Custom designs or specific performance standards may require additional materials or specialized labor, increasing costs.
The quality and certifications of the products are vital, especially in regions with stringent automotive regulations. Higher-quality components with recognized certifications typically command higher prices but can lead to long-term cost savings through improved reliability and performance.
Supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better service and support.

Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are strategic approaches to enhance cost-efficiency.
Negotiation is essential. Buyers should engage in discussions to secure better terms, especially for large orders or long-term partnerships.
Considering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is crucial. While initial purchase prices are important, buyers should also evaluate the potential long-term savings from improved performance, durability, and reduced maintenance costs.
Understanding the pricing nuances for international buyers is also critical. Factors such as currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local taxes can significantly impact overall costs.

Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Furthermore, buyers should be aware of Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Choosing favorable terms can lead to cost savings.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Costs and Pricing Structures Matters
Navigating the complexities of sourcing batteries and alternators requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and pricing influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics, focusing on total cost considerations, and being aware of international pricing nuances, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and profitability. Keep in mind that prices can vary widely based on market conditions and supplier relationships, so always seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing battery vs alternator problems With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Battery and Alternator Problems
In the automotive industry, addressing battery and alternator issues is crucial for maintaining vehicle reliability. However, businesses seeking solutions may also consider alternative technologies or methods that provide similar outcomes. This section explores how traditional battery and alternator problems compare with alternative solutions, such as hybrid systems and solar power technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Battery Vs Alternator Problems | Hybrid Energy Systems | Solar Power Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for starting engines; limited lifespan (3-10 years) | Enhanced efficiency; combines internal combustion with electric power | Sustainable energy; limited by sunlight availability |
| Cost | Moderate upfront costs; replacement costs can be high | Higher initial investment; potential long-term savings on fuel | High initial installation costs; long-term savings on energy |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard in most vehicles; requires basic maintenance | Requires specific vehicle modifications; more complex | Installation requires space and proper setup; may need regulatory approvals |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed; battery replacement required every few years | Maintenance of both electric and combustion components; more complex | Minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning and checks |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for conventional vehicles; short trips and everyday use | Best for urban settings with stop-and-go traffic; eco-conscious consumers | Suitable for off-grid locations or eco-friendly initiatives; less dependence on fossil fuels |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hybrid Energy Systems
Hybrid systems combine traditional internal combustion engines with electric power sources. This technology enhances vehicle efficiency and reduces fuel consumption, making it an attractive alternative for businesses focused on sustainability. The performance of hybrid systems often exceeds that of standard batteries and alternators, especially in urban settings where frequent stopping and starting occur. However, the initial investment is higher, and the complexity of maintenance can pose challenges for fleet managers.
Solar Power Solutions
Solar power systems harness energy from the sun to charge batteries, providing a renewable energy source for vehicles. This technology is particularly appealing for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint. While solar power can significantly lower energy costs in the long run, the initial setup can be expensive and requires adequate space for installation. Additionally, solar solutions may not be viable in regions with limited sunlight, making them less reliable compared to traditional battery and alternator setups.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between battery and alternator problems or exploring alternative solutions, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and environmental goals. For businesses relying on traditional vehicles for short trips, standard battery and alternator setups may suffice. However, for those interested in reducing fuel costs and environmental impact, hybrid systems or solar power technologies present viable alternatives. Ultimately, the right choice hinges on balancing performance, cost, and maintenance considerations to align with organizational objectives.

Illustrative image related to battery vs alternator problems
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for battery vs alternator problems
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Batteries and Alternators?
Understanding the technical properties of batteries and alternators is crucial for B2B buyers involved in automotive maintenance and repair. Here are some essential specifications that should be considered:
-
Voltage Rating
– Definition: This indicates the electrical potential difference that the battery or alternator can provide. Most automotive batteries have a standard voltage rating of 12 volts, while alternators typically generate between 13.5 to 14.5 volts.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the correct voltage rating ensures compatibility with vehicle systems. Mismatched voltage can lead to inefficient performance or damage to electrical components. -
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
– Definition: CCA measures a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, specifically the number of amps it can deliver at 0°F for 30 seconds while maintaining at least 7.2 volts.
– B2B Importance: For buyers in colder regions, selecting batteries with higher CCA ratings is critical. This ensures reliable starts and minimizes warranty claims due to battery failures in extreme conditions. -
Reserve Capacity (RC)
– Definition: This spec indicates how long a battery can sustain a load in the event of an alternator failure, measured in minutes.
– B2B Importance: A higher reserve capacity means that vehicles can still function temporarily during alternator malfunctions, providing essential power for safety systems and reducing potential downtime. -
Efficiency Rating
– Definition: This refers to the percentage of energy that a battery or alternator converts from input to usable output. High-efficiency components waste less energy, resulting in better performance.
– B2B Importance: Efficient systems lead to reduced operational costs and lower emissions. Buyers should prioritize high-efficiency products to align with sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. -
Temperature Tolerance
– Definition: This property describes the operating temperature range for batteries and alternators. Most automotive batteries function well between -40°F to 140°F, while alternators can typically handle a slightly wider range.
– B2B Importance: Understanding temperature tolerance helps in selecting the right components for specific climates, which is especially relevant for buyers in diverse geographical regions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Battery and Alternator Issues?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive sector. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: Refers to products made by the manufacturer of the original parts used in vehicles.
– Importance: OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality, making them a reliable choice for B2B buyers looking to maintain high standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is crucial for inventory management and cost control. Buyers must ensure they can meet these requirements without overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs streamline the purchasing process, enabling buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping goods.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities, which are critical for international transactions. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The duration during which a product is guaranteed to be free from defects and functional as promised by the manufacturer.
– Importance: A comprehensive warranty can significantly influence purchasing decisions, offering peace of mind and potential cost savings in the event of product failure.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when dealing with battery and alternator issues, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the battery vs alternator problems Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting Battery and Alternator Issues?
The global automotive industry is undergoing significant transformations, influenced by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. One of the most pressing trends is the increasing reliance on electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models. As these vehicles become more prevalent, the demand for high-quality batteries is surging. This shift necessitates a deeper understanding of battery technology, performance metrics, and sourcing strategies.
Moreover, the rise of smart technology in vehicles is changing how alternators and batteries interact. Advanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance tools are being integrated into automotive systems, allowing for early detection of issues related to battery and alternator performance. This trend emphasizes the importance of sourcing high-tech components that can seamlessly integrate with these smart systems.
Supply chain dynamics are also evolving. B2B buyers must navigate a landscape characterized by fluctuating raw material prices, especially for lithium and cobalt, essential for battery production. Strategic partnerships with suppliers who can provide transparency regarding sourcing practices and materials will be vital for maintaining competitive advantage.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Battery and Alternator Markets?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B procurement strategies, particularly in the automotive sector. The environmental impact of battery production and disposal has come under scrutiny, leading to increased demand for sustainable practices. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate responsible sourcing of materials and adherence to ethical production standards. This shift not only mitigates environmental risks but also enhances brand reputation.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to international labor laws and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other “green” certifications can help buyers identify suppliers committed to sustainability.
Furthermore, the integration of recycled materials in battery production is gaining traction. Companies that leverage recycled components can reduce their carbon footprint and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers. As a result, sourcing strategies are increasingly focusing on suppliers who incorporate sustainable practices in their operations.
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Battery and Alternator Sector?
The evolution of the battery and alternator sector has been marked by significant technological advancements. Initially, lead-acid batteries dominated the market, primarily due to their affordability and availability. However, the limitations of lead-acid batteries in terms of lifespan and performance led to the rise of lithium-ion technology, especially with the advent of electric vehicles.
Over the years, alternators have also evolved from simple mechanical devices to sophisticated systems capable of managing complex electrical loads in modern vehicles. The introduction of smart alternators, which can adjust output based on real-time demands, has further enhanced vehicle performance and reliability.
These historical developments have laid the groundwork for today’s market dynamics, influencing everything from sourcing strategies to product development. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic procurement decisions that align with both current market demands and future innovations.
By comprehensively understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical developments, international B2B buyers can position themselves effectively in the evolving landscape of battery and alternator solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of battery vs alternator problems
-
How do I solve battery or alternator problems in my vehicle fleet?
To address battery or alternator issues, first, conduct a thorough inspection of each vehicle’s electrical system. Look for signs of wear, such as slow engine cranking, dim lights, or corrosion on terminals. Regular maintenance schedules should include testing the battery’s charge and the alternator’s output. If problems persist, consider sourcing high-quality replacement parts from reputable suppliers to ensure reliability and longevity. Establishing a preventive maintenance program will also help minimize downtime and avoid unexpected failures. -
What is the best battery type for heavy-duty vehicles?
For heavy-duty vehicles, AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries are often the best choice. They provide superior performance, especially in extreme conditions, and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. AGM batteries are also more resistant to vibrations, making them ideal for rugged environments. When sourcing batteries, ensure your supplier can provide the necessary specifications and certifications to meet international quality standards. -
How can I identify a reliable supplier for batteries and alternators?
When vetting suppliers, consider their track record in the industry, customer reviews, and certifications. Request samples to assess product quality and ensure they meet your specifications. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers who understand your market’s unique challenges, especially in regions like Africa or South America, can lead to better service and support. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for batteries and alternators?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, for batteries and alternators, MOQs can range from 50 to 500 units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your inventory and financial strategies. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time orders or trial runs, which can be beneficial for testing product performance in your market. -
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing batteries and alternators internationally?
When negotiating payment terms, consider options such as letters of credit, net 30/60/90 days, or upfront deposits. These terms should reflect the trust level between you and the supplier. Ensure that the terms align with your cash flow requirements and the supplier’s policies. Be aware of currency fluctuations and consider using stable currencies for transactions to mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for imported batteries and alternators?
Implement a robust QA process that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing. Collaborate with suppliers to establish quality benchmarks that align with your standards. Consider third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipment. Additionally, maintain clear communication with suppliers about your quality expectations to ensure compliance throughout the manufacturing process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing batteries and alternators?
When importing, consider the shipping method, delivery timelines, and customs regulations. Batteries, especially lithium-ion types, may have specific shipping restrictions due to safety regulations. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling such products to ensure compliance and minimize delays. Additionally, factor in warehousing solutions in your target market to streamline distribution and manage inventory effectively. -
How do extreme temperatures affect battery and alternator performance?
Extreme temperatures can significantly impact battery and alternator performance. Cold weather can reduce battery capacity and make it harder for engines to start, while heat can accelerate battery degradation and affect alternator efficiency. When sourcing products for regions with extreme climates, choose batteries and alternators designed to withstand such conditions. Discuss these specifications with suppliers to ensure you select the right components for your operational needs.
Top 1 Battery Vs Alternator Problems Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AAA – Battery vs. Alternator Guide
Domain: aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: 1. Bad Alternator vs. Bad Battery: A Quick Guide 2. Battery provides energy to crank the engine and start the vehicle. 3. Starting a car requires 400-2,000 amps depending on engine size. 4. Battery powers electrical systems when the engine is off. 5. Alternator recharges the battery and powers electrical systems when the engine is running. 6. Signs of a bad battery: a. Car struggles to start consi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for battery vs alternator problems
How Can Strategic Sourcing Mitigate Battery and Alternator Issues in Your Fleet?
In conclusion, understanding the distinct roles and common issues associated with batteries and alternators is essential for optimizing vehicle performance and minimizing downtime. Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in ensuring that international B2B buyers secure high-quality components that can withstand the unique challenges posed by varying climates and driving conditions across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By investing in reliable suppliers and maintaining a proactive maintenance schedule, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of unexpected vehicle failures.
Key takeaways for B2B buyers include the importance of regularly assessing the age and performance of both batteries and alternators, as well as being vigilant for early warning signs of failure. Establishing partnerships with trusted suppliers who offer quality products and timely service can enhance operational efficiency and reduce long-term costs.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, staying ahead of potential issues will empower businesses to maintain a competitive edge. Engage with suppliers who understand your market’s unique demands and invest in solutions that promise reliability and performance. The future of your fleet’s efficiency starts with informed sourcing decisions today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.