Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for average cost to replace starter
In an increasingly competitive global market, understanding the average cost to replace a starter can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re managing a fleet of vehicles or sourcing parts for automotive repair shops, the financial implications of starter replacements can impact your bottom line. This guide offers a comprehensive analysis of costs associated with starter replacements, covering a range of factors including vehicle type, labor considerations, and geographical variations.
Buyers will find insights into the nuances of sourcing starter parts, from standard models for popular sedans to specialized units for luxury vehicles, as well as the implications of local labor costs in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Germany and Brazil. Additionally, this guide provides essential tips on vetting suppliers, ensuring product quality, and understanding warranty options to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical strategies, this resource empowers you to navigate the complexities of the starter replacement market effectively. Whether you’re looking to minimize costs or enhance the efficiency of your operations, understanding these key aspects will enable you to make well-informed choices that align with your business objectives.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Average Cost To Replace Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for average cost to replace starter
- Understanding average cost to replace starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of average cost to replace starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘average cost to replace starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for average cost to replace starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for average cost to replace starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘average cost to replace starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for average cost to replace starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing average cost to replace starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for average cost to replace starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the average cost to replace starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of average cost to replace starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for average cost to replace starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding average cost to replace starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Replacement Starter | Basic model, often OEM parts, straightforward installation | General automotive repair shops | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited warranty, may have lower durability. |
| Rebuilt Starter | Remanufactured parts with a mix of new and used components | Fleet maintenance, budget-conscious repair shops | Pros: Lower cost than new, environmentally friendly. Cons: Potentially shorter lifespan, variable quality. |
| High-Performance Starter | Enhanced components for quicker engine turnover | Performance automotive shops, racing teams | Pros: Improved reliability, faster starts. Cons: Higher initial investment, may require specific vehicle compatibility. |
| Integrated Starter/Alternator | Combines starter and alternator functions | Electric vehicle manufacturers, hybrid vehicles | Pros: Space-saving design, improved efficiency. Cons: Higher complexity, often more expensive to replace. |
| Luxury Vehicle Starter | Specialized components for high-end vehicles | Luxury automotive service centers | Pros: Tailored for performance, often includes advanced technology. Cons: High cost, limited availability of parts. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Replacement Starters?
Standard replacement starters are typically original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts designed for straightforward installation. They are the most common type found in automotive repair shops and are suitable for a wide range of vehicles. B2B buyers often choose these starters for their cost-effectiveness and ease of sourcing. However, they may come with limited warranties and could be less durable than other types, making them a good option for routine repairs rather than high-performance applications.
How Do Rebuilt Starters Benefit B2B Buyers?
Rebuilt starters are remanufactured components that combine new and refurbished parts. They offer a more budget-friendly option for businesses managing fleet vehicles or operating in cost-sensitive markets. While they are environmentally friendly and generally less expensive than new starters, B2B buyers should be cautious about the variability in quality and potential shorter lifespans compared to brand-new units. It’s essential to source rebuilt starters from reputable suppliers to mitigate these risks.
What Makes High-Performance Starters Ideal for Specific Applications?
High-performance starters are designed to provide faster engine turnover and improved reliability, making them popular among performance automotive shops and racing teams. These starters often include enhanced components that enable quicker starts, which can be crucial in competitive environments. While they provide significant advantages in performance, B2B buyers need to consider the higher initial investment and ensure compatibility with specific vehicle models, which may limit their applicability.
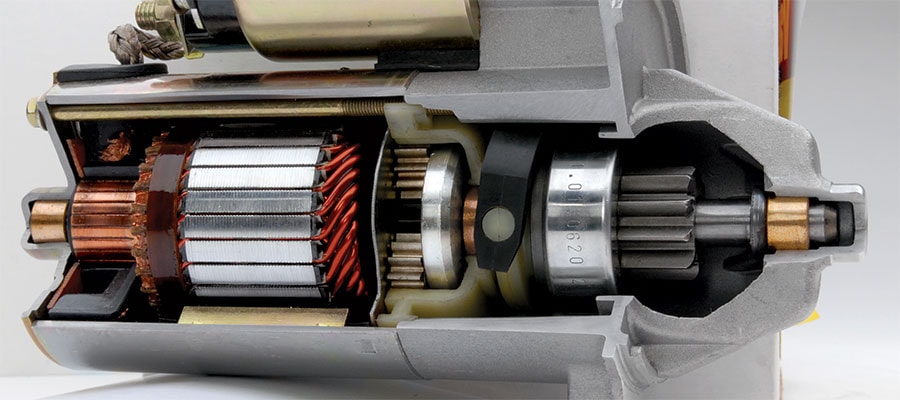
Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
Why Choose Integrated Starter/Alternators for Electric Vehicles?
Integrated starter/alternators combine the functions of both components into a single unit, optimizing space and enhancing efficiency. This type is increasingly utilized in electric and hybrid vehicles, making it a vital option for manufacturers and service centers specializing in these technologies. Although they offer advanced functionality, the complexity of these systems can lead to higher replacement costs and specialized repair needs, which B2B buyers should factor into their purchasing decisions.
What Are the Unique Considerations for Luxury Vehicle Starters?
Luxury vehicle starters are crafted with specialized components tailored for high-end automobiles, often incorporating advanced technology for better performance. They are primarily used by luxury automotive service centers that cater to premium brands. While these starters provide exceptional performance and reliability, they come with a high price tag and may have limited availability of parts. Buyers in this segment must be prepared for the associated costs and ensure they have access to the necessary components for maintenance and repair.
Key Industrial Applications of average cost to replace starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of average cost to replace starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Fleet maintenance for commercial vehicles | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Quality of parts, availability of skilled labor |
| Construction | Heavy machinery starter replacement | Ensures operational efficiency and safety | Compatibility with machinery models, sourcing speed |
| Transportation & Logistics | Truck and trailer starter servicing | Minimizes disruptions in logistics operations | Cost-effectiveness, reliability of parts, warranty |
| Agriculture | Agricultural equipment starter repairs | Enhances productivity and reduces harvest delays | Supplier reputation, part durability, local support |
| Mining | Starter replacement for mining equipment | Maintains continuous operation and reduces costs | Compliance with industry standards, part availability |
How is the Average Cost to Replace Starters Applied in the Automotive Repair Industry?
In the automotive repair industry, understanding the average cost to replace starters is critical for fleet maintenance. Companies managing commercial vehicle fleets need to minimize downtime, as each hour a vehicle is off the road can lead to significant financial losses. By sourcing reliable starters at competitive prices, businesses can ensure that their vehicles remain operational, thus enhancing overall productivity. Additionally, the availability of skilled mechanics who can perform these replacements efficiently is crucial, particularly in regions where labor shortages may impact service delivery.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
What Role Does Starter Replacement Play in the Construction Sector?
In the construction sector, heavy machinery is essential for project completion. The average cost to replace starters in this context is vital for ensuring that equipment operates smoothly. Delays caused by faulty starters can lead to project overruns and increased labor costs. Therefore, businesses must consider the compatibility of replacement parts with various machinery models. Quick sourcing and availability of high-quality starters can significantly enhance operational efficiency and safety on construction sites, thereby preventing costly interruptions.
How Does Starter Replacement Impact the Transportation and Logistics Industry?
In transportation and logistics, the reliability of trucks and trailers is paramount. The average cost to replace starters can directly affect logistics operations by minimizing disruptions caused by vehicle breakdowns. Companies often seek cost-effective solutions that do not compromise quality, as unreliable starters can lead to delays in deliveries and increased operational costs. When sourcing replacements, businesses should prioritize suppliers that offer reliable parts with robust warranties to ensure long-term performance.
Why is Starter Repair Important for Agricultural Operations?
Agricultural operations rely heavily on various equipment, including tractors and harvesters, which require functional starters to operate efficiently. The average cost to replace starters in this sector can significantly impact productivity during critical harvest periods. Delays due to starter issues can lead to lost revenue and wasted resources. Buyers in agriculture should consider the durability of parts and the reputation of suppliers, ensuring that they receive support during peak seasons when equipment performance is crucial.
How Does the Mining Industry Benefit from Understanding Starter Replacement Costs?
In the mining industry, equipment uptime is essential for profitability. The average cost to replace starters for mining equipment is a crucial factor in maintaining continuous operations. Companies must ensure compliance with industry standards while sourcing parts, as failures can lead to costly safety incidents and operational halts. Understanding the cost implications allows mining businesses to budget effectively and choose suppliers that can provide timely support, ensuring that their operations remain efficient and profitable.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘average cost to replace starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Replacement Costs for Diverse Vehicle Models
The Problem: B2B buyers managing fleets often face significant financial strain when it comes to the cost of replacing starters. The variability in replacement costs across different vehicle makes and models can lead to unexpected budget overruns. For example, replacing a starter in a luxury vehicle like an Audi can cost significantly more than in a standard sedan. This unpredictability can complicate financial planning, especially for businesses operating on tight margins or those looking to optimize operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate these costs, B2B buyers should establish a comprehensive understanding of their vehicle fleet’s specifications. Creating a detailed database that includes each vehicle’s make, model, year, and historical replacement costs can facilitate more accurate budgeting. Additionally, consider forming partnerships with reliable parts suppliers who offer competitive pricing and volume discounts. Regularly review and update the database with current market prices and trends to ensure you’re making informed decisions. Utilizing tools that allow for bulk purchasing or long-term contracts can further reduce costs and streamline the replacement process, ensuring your fleet remains operational without excessive financial strain.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Identifying Starter Issues
The Problem: Another common challenge for B2B buyers is accurately diagnosing starter-related issues. Many symptoms, such as erratic cranking or unusual noises, can be attributed to multiple components in the starting system, including the battery or ignition system. This ambiguity can lead to unnecessary replacements and increased costs if the problem is misdiagnosed. Moreover, without proper knowledge, buyers may rush into replacing starters that might not need to be replaced, further escalating expenses.
Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
The Solution: To address this challenge, investing in diagnostic tools and training for maintenance staff is crucial. Implementing a systematic troubleshooting guide can help technicians accurately pinpoint starter issues without prematurely replacing parts. Additionally, fostering relationships with experienced mechanics or automotive consultants can provide valuable insights into common symptoms and their corresponding solutions. Regular training sessions on the latest diagnostic techniques can empower your team to make informed decisions, ultimately reducing misdiagnosis and unnecessary replacement costs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Starters
The Problem: Sourcing quality replacement starters at a reasonable price can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. The market is flooded with options, ranging from low-cost aftermarket parts to OEM components, leading to confusion about which products offer the best value. Poor-quality starters can lead to frequent failures, increasing maintenance costs and downtime for vehicles, which can have a cascading negative impact on overall business operations.
The Solution: To streamline sourcing, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on reputable suppliers that specialize in automotive parts. Establish criteria for assessing suppliers, such as their industry reputation, customer reviews, and warranty policies. Creating a preferred vendor list can simplify the purchasing process and ensure that only high-quality starters are procured. Moreover, consider engaging in direct negotiations with suppliers for better pricing, especially for bulk orders. Implementing a quality assurance process that includes performance testing for new starters before installation can help ensure reliability and reduce the likelihood of premature failures, ultimately enhancing fleet performance and reducing long-term costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for average cost to replace starter
When selecting materials for automotive starters, particularly in the context of replacement costs, several factors come into play. The choice of materials not only influences the performance and durability of the starter but also affects the overall cost and complexity of manufacturing. Below is an analysis of common materials used in starter production, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Common Starter Materials?
1. Steel
Steel is a widely used material in starter construction due to its strength and durability. It is capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for the harsh conditions within an engine compartment. Steel also offers good corrosion resistance when treated with coatings.
Pros:
– High tensile strength and durability.
– Cost-effective and readily available.
– Can be easily machined and fabricated.
Cons:
– Heavier compared to alternatives like aluminum.
– Susceptible to rust if not properly coated.
– Requires more energy for manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
Steel starters are robust and can handle the mechanical stresses of frequent starting cycles. However, their weight may affect performance in applications where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel must comply with regional standards such as ASTM in the U.S. and DIN in Germany. Buyers should ensure that the steel used is sourced from reputable suppliers to guarantee quality.
Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
2. Aluminum
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in starter housings and components where weight reduction is essential.
Pros:
– Lightweight, which can improve vehicle efficiency.
– Excellent corrosion resistance.
– Good thermal conductivity.
Cons:
– Generally more expensive than steel.
– Lower tensile strength, which may require thicker components.
– More complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum starters can enhance fuel efficiency due to their reduced weight, but they may not be suitable for all applications, especially in heavy-duty vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Aluminum parts should meet JIS standards in Japan or equivalent certifications in other regions. Buyers should also consider the recycling potential of aluminum, which is a significant factor in sustainable sourcing.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
3. Copper
Copper is primarily used in starter electrical components, such as windings and connections, due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
Pros:
– Superior electrical conductivity.
– High resistance to corrosion.
– Ductile and easy to work with.
Cons:
– More expensive than aluminum and steel.
– Heavier than aluminum, which may affect overall weight.
– Prone to oxidation if not properly treated.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
Impact on Application:
Copper components are essential for efficient electrical performance in starters. However, the cost can be a limiting factor for budget-conscious buyers.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Copper sourcing must comply with international trade regulations, especially in regions with strict mining and environmental laws. Buyers should verify the ethical sourcing of copper to avoid supply chain issues.
4. Plastic Composites
Plastic composites are increasingly used in non-structural components of starters due to their lightweight and insulating properties.
Pros:
– Lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
– Can be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity.
– Cost-effective for mass production.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
Cons:
– Lower thermal resistance compared to metals.
– May not withstand high mechanical loads.
– Limited lifespan in high-heat environments.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites can be ideal for insulating components, but their use in structural parts should be limited to applications where mechanical strength is not a primary concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastics is crucial, especially in Europe where regulations like REACH apply. Buyers should also consider the recyclability of plastic materials.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Replacement Costs
| Material | Typical Use Case for average cost to replace starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components and housings | High strength and durability | Heavier, rust potential | Medium |
| Aluminum | Housings and lightweight components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | Electrical windings and connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | Expensive, oxidation risk | High |
| Plastic Composites | Insulating components and non-structural parts | Lightweight and moldable | Lower thermal resistance, limited lifespan | Low |
This guide provides insights into material selection for automotive starters, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regulatory compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for average cost to replace starter
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Automotive Starters?
The manufacturing process for automotive starters involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the production of reliable and efficient components. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers and their capabilities.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Starter Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Typically, automotive starters are made from a combination of metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper. These materials are chosen for their strength, conductivity, and resistance to wear.
During this stage, raw materials are subjected to various treatments, such as heat treatment and surface finishing, to enhance their durability and performance. For instance, steel components may be treated to prevent corrosion, while copper wiring is often insulated to prevent electrical shorting.
How Is Forming Achieved in Starter Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping the raw materials into the required components of the starter. Key techniques include:
- Casting: Used for creating complex shapes like the starter housing, casting involves pouring molten metal into molds.
- Machining: Precision machining is employed to create finely-tuned components, such as the armature and solenoid. This process ensures that parts fit together seamlessly.
- Stamping and Forging: These methods are used to create durable parts, such as the starter drive gear, which must withstand significant mechanical stress.
Each forming technique is selected based on the design requirements and the specific properties needed in the final product.
What Does the Assembly Process Look Like for Starters?
The assembly stage is where all the individual components come together to create the final starter unit. This process often involves:
- Manual and Automated Assembly: Depending on the manufacturer, assembly may be performed by skilled workers or automated systems. Automation can enhance efficiency and consistency, particularly in high-volume production settings.
- Integration of Components: During assembly, components such as the electromagnetic coils, armature, solenoid, and drive gear are meticulously integrated. Each part must be positioned correctly to ensure optimal functionality.
- Quality Control Checks: As parts are assembled, they undergo initial quality control checks to catch any defects early in the process.
This stage is crucial because any misalignment or assembly error can lead to product failure in the field.
How Is Finishing Handled in Starter Production?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, where the assembled starters are treated to enhance their performance and longevity. This may include:
- Coating: Starters may receive a protective coating to resist corrosion and wear. Common coatings include powder coating and galvanization.
- Final Inspection: Each starter undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets all specifications. This step often includes visual inspections and dimensional checks to verify that the product conforms to design standards.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that automotive starters meet both safety and performance standards. Various international standards guide this process:
How Does ISO 9001 Influence Starter Manufacturing Quality?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for consistent quality in products and services. Manufacturers that adhere to ISO 9001 implement a quality management system that focuses on customer satisfaction, continuous improvement, and process efficiency.
This certification is particularly important for B2B buyers, as it signifies that the supplier is committed to maintaining high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
What Are Other Relevant Standards, Such as CE and API?
In addition to ISO 9001, automotive starters may also need to comply with other industry-specific standards, such as:
- CE Marking: In Europe, the CE mark indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
- API Standards: For starters used in specific applications, such as heavy-duty trucks, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary to ensure performance under demanding conditions.
These certifications help B2B buyers verify that the products they source are reliable and safe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is vital at multiple stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that defects are caught and corrected promptly. Key checkpoints include:
What Is Incoming Quality Control (IQC)?
Incoming Quality Control (IQC) involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This step ensures that all materials meet the specified standards before they are used in production.
Suppliers may conduct tests for material composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy to prevent defective materials from entering the manufacturing process.
How Is In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) Conducted?
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) occurs during the manufacturing stages, where operators perform checks at various points in the production line. Techniques may include:
- Visual Inspections: Checking for visible defects, such as cracks or misalignments.
- Dimensional Measurements: Using tools like calipers and gauges to verify that components meet design specifications.
This ongoing monitoring helps identify issues early, reducing the likelihood of defective products reaching the final inspection stage.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
What Does Final Quality Control (FQC) Involve?
Final Quality Control (FQC) is the last line of defense before products are shipped to customers. This stage typically involves comprehensive testing of the completed starters, including:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying that the starter operates correctly under various electrical loads.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting starters to simulated use conditions to ensure they can withstand real-world stresses.
FQC ensures that only products meeting all quality standards are delivered to clients.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is crucial to ensure reliable sourcing. Here are key methods to consider:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Evaluation?
Regular audits of suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing and quality assurance processes. Buyers should look for:
- Third-Party Audits: Engaging independent auditors to evaluate a supplier’s compliance with international standards like ISO 9001.
- Quality Reports: Requesting documentation that outlines the supplier’s quality control processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
These reports can help buyers assess the reliability and performance of the supplier’s manufacturing processes.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Buyer Confidence?
Third-party inspections involve hiring external organizations to evaluate a supplier’s products and processes. This can include:
- Factory Inspections: Assessing manufacturing facilities for compliance with safety and quality standards.
- Product Testing: Conducting independent tests on samples to verify performance metrics.
Such inspections can provide additional assurance that the products sourced are of high quality and meet international standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
When sourcing automotive starters internationally, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of specific nuances:
- Local Regulations: Different countries may have varying regulations that impact quality standards. Understanding these can help buyers ensure compliance.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Recognizing that quality expectations may differ across regions can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers.
- Logistical Challenges: Consider the impact of logistics on product quality, especially regarding transportation and storage conditions.
By understanding these nuances, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality assurance requirements and business objectives.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘average cost to replace starter’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement process for automotive parts, particularly starter replacements, requires careful consideration and informed decision-making. This guide provides B2B buyers with a step-by-step checklist to effectively assess costs, suppliers, and technical specifications, ensuring a seamless purchasing experience for starter replacements.
Step 1: Assess Your Vehicle’s Requirements
Understanding the specific starter requirements for your vehicle is crucial. Different makes and models have varied starter specifications, which can influence both cost and availability. Consult your vehicle’s manual or technical documentation to identify the correct starter model, part numbers, and any unique installation requirements.
- Key Considerations:
- Verify the make, model, and year of your vehicle.
- Check for any manufacturer-specific recommendations or constraints.
Step 2: Research Average Replacement Costs
Before approaching suppliers, familiarize yourself with the average costs associated with starter replacements in your market. This knowledge will empower you to negotiate better pricing and evaluate supplier offers more effectively.
- What to Look For:
- Gather data on the cost range for both new and rebuilt starters.
- Consider labor costs associated with installation, as these can significantly impact the total expense.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Identifying reliable suppliers is essential for ensuring quality and service. Investigate potential partners by reviewing their company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies, particularly those relevant to your industry and region.
- Important Steps:
- Request references from businesses that have previously sourced starters from them.
- Look for suppliers with experience in your vehicle type and region to ensure they understand local requirements and standards.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirming that your suppliers adhere to industry standards is vital for quality assurance. Look for certifications that indicate compliance with international automotive standards, such as ISO 9001 or specific automotive quality certifications.
- Why This Matters:
- Certifications can reflect the supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability.
- It can also impact warranty terms and the overall lifecycle of the starter.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
When you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations. A comprehensive quote should outline not just the price but also include terms of sale, warranties, and delivery timelines.
- Checklist for Quotations:
- Ensure the quote includes all costs, including shipping and handling.
- Review warranty terms to understand the coverage for parts and labor.
Step 6: Consider Warranty and Support Options
A robust warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment. Evaluate the warranty terms offered by suppliers and consider the availability of after-sales support.
- Key Questions:
- What is the duration of the warranty, and what does it cover?
- Is there a dedicated support team available for troubleshooting and installation assistance?
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve evaluated all factors, finalize your purchase agreement. Ensure all terms discussed are documented clearly to avoid any misunderstandings.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
- What to Confirm:
- Delivery timelines and logistics.
- Payment terms and conditions.
By following this practical checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter replacements, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for average cost to replace starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Replacing a Starter?
The average cost to replace a starter can vary widely, influenced by several key components. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of starter units themselves can range from $50 for remanufactured parts to over $350 for brand-new components. Factors like the starter’s size, type (e.g., standard vs. high-performance), and the vehicle’s make and model significantly impact material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs for installation typically range from $150 to over $1,100, depending on the complexity of the job. More accessible starters, such as those in standard sedans, generally incur lower labor costs, while starters in luxury vehicles or larger trucks may require additional disassembly and specialized skills.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with the production of starters, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary by region and manufacturing facility, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tools required for starter production can influence prices, particularly for custom or high-performance starters.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each starter meets strict quality standards incurs additional costs. Certifications and testing, especially for high-performance or OEM parts, can elevate prices but provide assurance of reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, especially for international orders, can add significantly to the overall cost. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties in the buyer’s country can also affect pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin based on the total cost structure. This margin can vary significantly depending on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Starter Replacement Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starters, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in bulk can lead to cost savings. Many suppliers offer discounts for large orders, allowing buyers to negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom starters designed for specific vehicles or applications may incur higher costs. Buyers should assess whether off-the-shelf products meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The quality of materials used can dramatically affect price. Higher-quality materials may lead to increased longevity and better performance, providing value in the long run.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that have undergone stringent testing and certification may come at a premium. However, they often guarantee better performance and reliability, reducing the risk of future failures.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, impacting the final price.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency in Starter Replacement?
To optimize costs when replacing a starter, international B2B buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to explore bulk discounts or favorable terms. Building a strong relationship can lead to long-term savings.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the entire lifecycle cost of the starter, including installation, maintenance, and potential failure costs. Investing in higher-quality starters may yield lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and additional costs associated with international shipping, such as tariffs and customs fees. This knowledge can aid in budgeting accurately.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on various suppliers. Comparing quotes and understanding the differences in materials, quality, and service can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Local Regulations and Compliance: Familiarize yourself with local automotive regulations and compliance standards in your region to avoid potential fines or additional costs related to non-compliance.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including geographical location, market conditions, and specific vehicle requirements. Always consult multiple suppliers and perform due diligence to ensure the best pricing and quality for your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing average cost to replace starter With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Starter Replacement
When faced with the need to replace a vehicle’s starter, B2B buyers must consider various alternatives that may provide similar functionality or address the underlying issues causing starter failure. The replacement of a starter can be costly, and exploring alternative solutions can help businesses optimize their maintenance budgets and operational efficiency. In this analysis, we will compare the average cost to replace a starter with two viable alternatives: starter repair and utilizing a jump start as a temporary solution.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
Comparison Table of Starter Replacement Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Average Cost To Replace Starter | Starter Repair | Jump Start as Temporary Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores full functionality | May restore functionality but not always reliable | Allows for immediate operation but not a permanent fix |
| Cost | $150 – $1,100 | $50 – $300 | Minimal (cost of jumper cables) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional service | Can be DIY or professional | Very easy; requires minimal tools |
| Maintenance | Long-term solution | Requires monitoring of starter condition | No maintenance but depends on battery health |
| Best Use Case | Long-term vehicle operation | Cost-effective for minor issues | Emergency situations to start vehicle |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Starter Repair
Starter repair involves diagnosing and fixing specific components of the starter rather than replacing it entirely. This option can be cost-effective, particularly for minor issues like worn brushes or a faulty solenoid. However, it requires a good understanding of the starter’s mechanics and can be time-consuming. If the starter has multiple issues or is significantly worn, repair may not be a viable long-term solution, potentially leading to repeated repairs and additional costs down the line.
Jump Start as a Temporary Solution
Using a jump start can be an effective short-term solution to get a vehicle running when the starter is malfunctioning. This method can be particularly useful in emergency situations where immediate operation is necessary. The cost is minimal, mainly involving the purchase of jumper cables if not already owned. However, this is not a permanent fix; if the starter is faulty, the vehicle will require further attention. Moreover, reliance on this method can lead to operational disruptions if not addressed promptly.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When determining the most suitable solution for starter issues, B2B buyers should weigh the costs and benefits of each alternative based on their specific operational requirements. If long-term reliability and performance are paramount, investing in a full starter replacement may be the best route. However, if the issues are minor, starter repair could be a cost-effective solution. For immediate operational needs, a jump start may suffice temporarily, but it should prompt a more thorough investigation into the vehicle’s starting system. Ultimately, understanding the vehicle’s condition, budget constraints, and operational demands will guide buyers in making an informed decision that aligns with their maintenance strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for average cost to replace starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties Affecting the Average Cost to Replace a Starter?
Understanding the technical properties of starters is essential for B2B buyers when evaluating replacement costs. Here are several critical specifications that play a significant role in determining the overall price.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a starter often includes metals such as aluminum and steel, which influence durability and performance. Higher-grade materials can increase the longevity of the starter, reducing the frequency of replacements and thereby lowering long-term costs. For international buyers, selecting starters made from high-grade materials can also mean better performance in varying climatic conditions across regions.
2. Electrical Specifications
Key electrical specifications, such as voltage (typically 12V for automotive starters) and amperage ratings, determine how well the starter can perform under different loads. Higher amperage starters can deliver more power, which is crucial for larger engines or vehicles operating in demanding conditions. B2B buyers should consider these specs to ensure compatibility with their fleet or equipment, avoiding potential failures that could lead to costly downtime.
3. Torque Rating
The torque rating of a starter indicates its ability to crank an engine. This specification is critical for larger vehicles or those with high-performance engines. Understanding torque requirements helps buyers select the right starter, ensuring efficient operation and reducing the risk of premature failure.
4. OEM vs. Aftermarket Components
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) starters are designed to meet the exact specifications of the vehicle manufacturer, often resulting in higher prices due to brand assurance and warranty coverage. In contrast, aftermarket starters may offer lower prices but can vary in quality. B2B buyers must weigh the cost savings against potential risks associated with aftermarket parts, making informed decisions based on their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to average cost to replace starter
5. Installation Complexity
The complexity of installation can significantly affect labor costs associated with starter replacement. Some starters are easily accessible and can be replaced quickly, while others may require extensive disassembly of engine components, increasing labor time and costs. Understanding the installation requirements is crucial for budgeting and operational planning.
6. Warranty and Support
Warranties vary widely between manufacturers and can influence the total cost of ownership. A starter with a longer warranty period may come at a higher upfront cost but can provide peace of mind and cost savings in the long run. B2B buyers should consider warranty terms and customer support availability, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Replacement Costs?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon can streamline negotiations and purchasing processes. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the vehicle’s manufacturer, ensuring compatibility and reliability. These parts typically come with a higher price tag but offer peace of mind regarding performance and warranty.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and avoid overstocking, particularly for replacement parts like starters.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. Crafting an effective RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing for starter replacements while ensuring all technical specifications are met.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping, including who pays for shipping, insurance, and import duties. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers avoid unexpected costs and ensures smooth transactions across borders.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes for an order to be fulfilled, from placement to delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to plan for inventory needs and avoid operational disruptions.
6. Aftermarket
Aftermarket parts are those made by third-party manufacturers and are not sourced from the original vehicle manufacturer. While often more affordable, the quality can vary, making it essential for buyers to evaluate the reliability of aftermarket options.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions regarding starter replacements, optimizing costs while ensuring quality and reliability in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the average cost to replace starter Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Average Cost to Replace Starters?
The market for automotive starters is influenced by several global drivers, including the increasing demand for vehicles, rising disposable incomes in developing regions, and advancements in automotive technology. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models, which often feature more complex starting systems. This trend is driving up the demand for high-quality starter components, as buyers seek to ensure reliability and performance in their fleets.
Additionally, the availability of aftermarket parts is enhancing competition, leading to a wider range of pricing options for buyers. Technological advancements, such as smart diagnostics and integration with telematics, are also shaping sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also value-added services like real-time data on component performance and predictive maintenance solutions.
Moreover, fluctuating raw material prices and supply chain disruptions—exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic—have made it crucial for international buyers to adopt agile sourcing strategies. By diversifying their supplier base and investing in long-term partnerships, companies can mitigate risks associated with cost volatility and ensure a steady supply of components.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Average Cost to Replace Starters?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming pivotal in the automotive industry, influencing the average cost to replace starters. As environmental concerns rise, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials that are recycled or have lower environmental impacts, thus leading to a growing market for “green” starter components. Suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or those who utilize recycled metals in their products can provide a competitive edge.
Furthermore, the push for corporate social responsibility (CSR) is reshaping supplier selection criteria. Buyers are keen on partnering with manufacturers who ensure ethical labor practices and maintain transparency in their supply chains. By choosing ethically sourced components, companies can enhance their brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, which is particularly important in European markets where regulations around sustainability are stringent.
However, ethical sourcing may come with higher upfront costs. Buyers need to balance these costs with the long-term benefits of sustainability, such as reduced waste and improved brand loyalty. By investing in suppliers committed to ethical practices, companies can also minimize risks associated with supply chain disruptions, thereby ensuring more stable pricing for replacements.
What Is the Historical Context of the Automotive Starter Industry?
The automotive starter industry has evolved significantly since the introduction of the first electric starters in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles relied on hand-cranked starters, which posed safety risks and required significant physical effort. The first electric starter was patented in 1912, revolutionizing the automotive sector by making vehicle operation more accessible and user-friendly.
Over the decades, advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient and compact starter designs, including the introduction of gear reduction starters in the 1980s, which improved cranking power while reducing weight. In recent years, the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles has further transformed the industry, requiring manufacturers to innovate and adapt to new starting technologies.
Today, the focus is not only on performance but also on sustainability and ethical sourcing, marking a significant shift in how B2B buyers evaluate their options in the starter market. As the automotive landscape continues to change, understanding this evolution helps buyers make informed decisions regarding sourcing and partnerships.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of average cost to replace starter
-
How do I determine if I need a starter replacement?
To ascertain if a starter replacement is necessary, start by checking for symptoms such as erratic cranking, no response when turning the key, or unusual sounds during engine start. Inspect the battery and connections, as a weak battery can mimic starter issues. If these preliminary checks do not resolve the problem, consult a qualified mechanic to perform a thorough diagnostic, ensuring you identify the root cause effectively before committing to a replacement. -
What is the average cost range for starter replacement?
The cost of replacing a starter typically ranges from $150 to $1,100, depending on the vehicle make, model, and year. For parts, rebuilding a starter can cost between $50 and $350, while a new starter can range from $80 to over $350. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the installation, particularly for vehicles where the starter is less accessible. Always obtain multiple quotes from suppliers or mechanics to gauge a fair market price. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for starters?
To find reliable suppliers for starters, start by researching manufacturers and distributors with a strong reputation in the automotive industry. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or local trade fairs to connect with potential vendors. Request samples and check reviews or testimonials from previous customers to assess quality. Additionally, ensure the suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications, to guarantee the reliability of their products. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter replacements?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, automotive parts suppliers may have an MOQ ranging from 10 to 100 units, depending on the part type and supplier policies. For bulk purchases, negotiating lower MOQs can be possible, especially if you establish a long-term relationship with the supplier. Always clarify MOQ terms before placing an order to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starters internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common payment options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance payment before shipment. International buyers should inquire about payment methods such as letters of credit, PayPal, or bank transfers. It’s crucial to understand the terms fully, including any fees associated with currency conversion or international transactions, to avoid surprises. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for starters?
To ensure quality assurance for starters, request detailed product specifications and quality certifications from your supplier. Consider conducting third-party inspections before shipment to verify product integrity. Implement a quality control process that includes receiving inspections upon arrival, and maintain a feedback loop with your supplier to address any quality concerns promptly. Establishing clear communication about your quality expectations is vital for maintaining standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starters?
When importing starters, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery times. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness based on your timeline and budget. Familiarize yourself with the import duties and taxes applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Work with a reliable freight forwarder who can guide you through the import process and ensure compliance with all regulations. -
Can I customize starters to fit specific vehicle models?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for starters to fit specific vehicle models. Customization can include modifications in size, electrical specifications, or mounting configurations. When discussing customization with suppliers, provide detailed vehicle specifications and requirements. However, be aware that custom orders may come with longer lead times and higher costs, so factor these into your planning.
Top 5 Average Cost To Replace Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Facebook – Auto Repair Costs
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: cost to get car to the shop and replace starter
2. AAA – Starter Replacement Costs and Options
Domain: aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: Average cost for starter replacement: $700 – $1,200; Replacement part cost: under $100 to over $400; Labor cost: $100 – $250 per hour; Types of starters: Gear reduction (more efficient, more expensive) and Direct drive (less efficient, cheaper); Common symptoms of starter issues: slow cranking, car won’t start, clicking/grinding sounds, starter running after engine starts, smoke from engine, dashb…
3. Car Talk – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cost to replace a starter: $600 to $900 for common vehicles, $900 to $1,400 for luxury models. Symptoms of a failing starter include a click when trying to start, screeching sounds, and intermittent functionality. Starters can be remanufactured or rebuilt, often used in repairs. Modern vehicles with stop-start systems have redesigned starters that are robust and not prone to premature failure.
4. Denso – Starter Replacement
Domain: tundras.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Starter replacement cost: $1500 (labor: $900, part: $650). Part number: Denso 428000-4640. Vehicle: 2007 Toyota Tundra CrewMax with 174k miles.
5. CarBuzz – Starter Motor Replacement Costs
Domain: carbuzz.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Starter motor replacement cost ranges from $450 to $600 on average. Specific models like the Toyota Tundra (2000-2005) with a V8 engine can cost between $650 and $900 due to labor-intensive removal of the intake manifold. The Honda Civic’s replacement cost is estimated between $490 and $760. Factors affecting costs include labor time (1.5 to 2.5 hours for most starters, up to 4 hours for valley-mo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for average cost to replace starter
In summary, understanding the average cost to replace a starter is crucial for international B2B buyers navigating the automotive parts market. Costs can vary significantly based on vehicle make, model, and regional factors, with replacement parts ranging from $50 to over $350 and labor potentially exceeding $1,100. Strategic sourcing enables businesses to identify reliable suppliers and assess total cost implications, ensuring that decisions are data-driven and value-oriented.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local supplier networks and considering bulk purchasing options can lead to significant cost savings. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer warranties and quality assurances can further mitigate risks associated with part replacements.
As the automotive market continues to evolve, staying informed about sourcing trends and cost fluctuations is essential. By fostering strong supplier relationships and employing strategic sourcing techniques, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and drive profitability. Moving forward, consider evaluating your sourcing strategies to capitalize on opportunities that align with your operational needs and market dynamics.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.