Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for altenator
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing reliable alternators can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With various types, specifications, and applications available, making informed purchasing decisions is crucial, especially in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the essential knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the alternator market, ensuring you choose the right solutions that meet your business needs.
Throughout this guide, you will discover an in-depth analysis of different alternator types, including their amperage ratings, voltage specifications, and suitability for various applications—from automotive to industrial uses. We will also delve into critical aspects of supplier vetting, highlighting key criteria that ensure quality and reliability in your sourcing process. Understanding cost implications and potential savings will further empower you to make strategic purchasing decisions.
By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Vietnam and Nigeria, can confidently approach the alternator market, reducing the risks associated with procurement. This resource is designed to streamline your purchasing journey, ensuring you secure high-quality products that enhance your operational efficiency and drive business growth.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Altenator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for altenator
- Understanding altenator Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of altenator
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘altenator’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for altenator
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for altenator
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘altenator’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for altenator Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing altenator With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for altenator
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the altenator Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of altenator
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for altenator
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding altenator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Regulator Alternator | Voltage regulation integrated within the alternator unit. | Automotive, Heavy Machinery | Pros: Compact design, easier installation. Cons: Limited to specific voltage ranges. |
| External Regulator Alternator | Uses a separate component for voltage regulation. | Industrial Equipment, Custom Builds | Pros: Greater flexibility in voltage settings. Cons: More complex installation and maintenance. |
| Brushless Alternator | Lacks brushes, reducing wear and maintenance needs. | Renewable Energy, Marine | Pros: Longer lifespan, higher efficiency. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed to deliver higher amperage for demanding applications. | Performance Vehicles, Racing | Pros: Supports additional electrical loads. Cons: Requires careful compatibility checks with existing systems. |
| Remanufactured Alternator | Refurbished to meet original specifications. | Cost-sensitive applications | Pros: Cost-effective, environmentally friendly. Cons: Potential variability in quality. |
What are Internal Regulator Alternators and Their Key Features?
Internal regulator alternators are designed with the voltage regulation mechanism built into the alternator itself. This compact design simplifies installation and is commonly used in automotive applications and heavy machinery. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific voltage requirements of their systems, as these alternators typically operate within limited voltage ranges. Their ease of use makes them a popular choice for standard vehicle electrical systems.
How Do External Regulator Alternators Differ?
External regulator alternators utilize a separate voltage regulator, providing flexibility in voltage settings. This feature is particularly beneficial for industrial applications and custom-built machinery where varying voltage is required. Buyers should assess compatibility with their existing systems, as the added complexity in installation may require more technical expertise. This type is ideal for businesses needing tailored electrical solutions.
What Advantages Do Brushless Alternators Offer?
Brushless alternators eliminate the need for brushes, which reduces wear and maintenance requirements, making them suitable for renewable energy applications and marine environments. Their longer lifespan and higher efficiency appeal to businesses looking for durable solutions. While the initial investment is higher, the long-term savings on maintenance and replacements can justify the cost, particularly for high-demand applications.
What Makes High-Output Alternators Essential?
High-output alternators are engineered to provide increased amperage, making them essential for performance vehicles and racing applications where additional electrical loads are common. When considering a high-output alternator, it’s crucial for buyers to verify compatibility with their vehicle’s electrical systems to avoid issues. While these alternators can support extensive electrical systems, they may also require more robust mounting solutions.
Why Consider Remanufactured Alternators?
Remanufactured alternators are refurbished to meet original specifications, offering a cost-effective alternative for businesses with budget constraints. They are particularly appealing for cost-sensitive applications where new units may exceed budget limits. However, buyers should be aware of potential variability in quality and should source from reputable suppliers to ensure reliability. Remanufactured units also contribute to sustainability by reducing waste.
Key Industrial Applications of altenator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Alternator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Power generation for vehicle electrical systems | Ensures reliable operation of vehicle electronics | Quality certifications, compatibility with various models |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in wind turbines and solar power systems | Enhances energy efficiency and reliability | Voltage specifications, durability in harsh environments |
| Marine and Shipping | Auxiliary power supply for ships and boats | Provides essential power for navigation and safety | Corrosion resistance, compliance with marine standards |
| Construction | Powering heavy machinery and equipment | Maximizes productivity and reduces downtime | Amperage requirements, ruggedness for tough environments |
| Agriculture | Used in irrigation systems and farm equipment | Supports efficient operations and reduces energy costs | Energy efficiency, adaptability to different power sources |
How is the Alternator Used in the Automotive Manufacturing Sector?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, alternators are critical for generating electrical power for vehicles. They ensure that all electronic components, such as lights, infotainment systems, and safety features, function properly. Reliable performance is paramount, as any failure can lead to costly downtime or safety issues. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the alternators meet stringent quality certifications and are compatible with various vehicle models to optimize production efficiency.

Illustrative image related to altenator
What Role Does the Alternator Play in Renewable Energy Solutions?
Alternators are increasingly integrated into renewable energy systems, particularly in wind turbines and solar power setups. They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, enhancing the overall efficiency of energy generation. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs. Buyers should consider voltage specifications and the alternator’s durability, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
How is the Alternator Essential for Marine and Shipping Industries?
In the marine and shipping industries, alternators provide auxiliary power for ships and boats, powering essential systems like navigation, communication, and safety equipment. A reliable alternator ensures that these systems remain operational, which is critical for safety at sea. Buyers should prioritize sourcing alternators with corrosion resistance and compliance with marine standards to withstand harsh maritime environments.
What is the Importance of Alternators in Construction Equipment?
In construction, alternators are vital for powering heavy machinery and equipment, such as excavators and cranes. They ensure that these machines can operate efficiently, maximizing productivity on job sites. For businesses in this sector, sourcing alternators that meet specific amperage requirements and are rugged enough to endure tough working conditions is crucial to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
How Do Alternators Benefit Agricultural Operations?
Alternators are used in agricultural applications, particularly in powering irrigation systems and various farm equipment. They help in maintaining efficient operations and can significantly reduce energy costs associated with farming activities. Buyers should focus on the energy efficiency of the alternators and their adaptability to different power sources, ensuring that they can meet the unique demands of agricultural operations in diverse environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘altenator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Concerns in Alternator Sourcing
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to sourcing high-quality alternators. This is particularly true in regions with less established supply chains, such as parts of Africa and South America. The risk of receiving subpar or counterfeit products can lead to increased operational downtime, higher maintenance costs, and ultimately, a loss of customer trust. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the vast array of brands and specifications, unsure which products will meet their performance needs without compromising quality.
The Solution: To navigate these quality concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who offer transparent product sourcing information. Conduct thorough due diligence by checking supplier certifications and reviews, and ask for detailed specifications of the alternators, including amperage ratings, voltage compatibility, and warranty details. When possible, request samples or start with a small order to evaluate performance before committing to larger purchases. Additionally, consider utilizing suppliers who provide remanufactured alternators with a proven track record, as these can often offer a balance between cost-effectiveness and reliability. Establishing a clear communication line with the supplier can also facilitate quicker resolution of any issues that arise.
Scenario 2: Understanding Technical Specifications for Diverse Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to understand the technical specifications associated with alternators, particularly when dealing with various applications across different vehicle types and industries. Misinterpreting specifications such as voltage ratings, amperage, or pulley configurations can lead to compatibility issues, resulting in costly errors and delays in project timelines. This challenge is often exacerbated in regions where technical expertise may be limited, leaving buyers feeling frustrated and uncertain.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest time in training or workshops focused on alternator specifications and applications. Engaging with manufacturers or technical experts can provide valuable insights into how to match alternators with specific vehicle requirements. Furthermore, creating a checklist that outlines key specifications for each application can streamline the selection process. For instance, buyers should document the voltage requirements, the type of pulley system in use, and any specific amperage needs. Utilizing online resources, such as product datasheets or instructional videos from reputable brands, can also enhance understanding. This proactive approach not only minimizes errors but also empowers buyers to make informed decisions confidently.
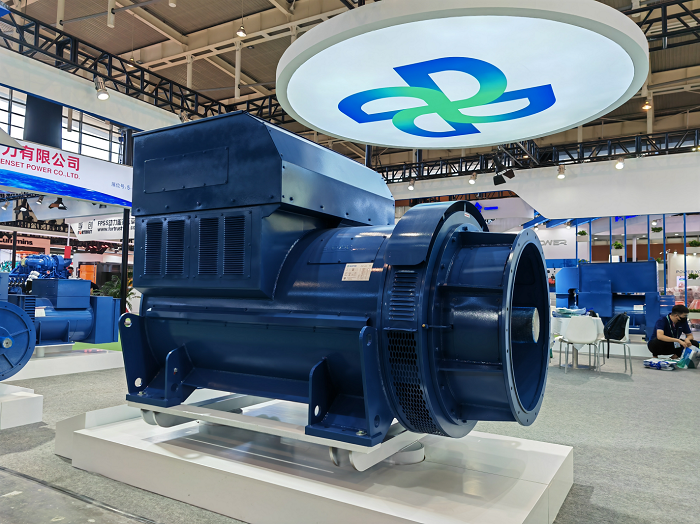

Illustrative image related to altenator
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions and Lead Times
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions are a common pain point for B2B buyers, particularly in the current global landscape. Delays in alternator shipments can halt production lines, delay vehicle repairs, or disrupt other critical operations. Buyers may find themselves facing extended lead times, especially when sourcing from international suppliers, leading to frustration and financial strain. The unpredictability of supply chains can make it challenging to maintain adequate stock levels, further compounding these issues.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions, buyers should develop a robust inventory management strategy that includes safety stock levels for alternators based on historical demand. Collaborating with multiple suppliers can also provide a backup option in case of delays from a primary source. Buyers should establish clear communication with suppliers regarding lead times and potential disruptions, fostering a partnership that encourages transparency. Additionally, utilizing technology, such as inventory management software, can help track stock levels and forecast demand more accurately, allowing for proactive ordering and reducing the risk of shortages. In regions with unstable supply chains, establishing local partnerships or exploring regional manufacturers can provide more reliable access to alternators and enhance overall supply chain resilience.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for altenator
What Are the Key Materials Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
When it comes to the manufacturing of alternators, the choice of materials significantly influences performance, durability, and cost. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Alternator Performance?
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used materials in alternator construction, particularly for housings and rotor components. Its key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent thermal conductivity, and good corrosion resistance. These characteristics allow aluminum alternators to operate efficiently under varying temperatures and conditions.
Pros and Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles, making it a popular choice. However, it can be more expensive than other materials like steel, and while it offers good resistance to corrosion, it may not be suitable for extremely harsh environments without additional protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media and its ability to withstand high temperatures make it suitable for automotive applications. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM for material specifications.
What Role Does Copper Play in Alternators?
Copper is another critical material, primarily used for windings in alternators. It boasts excellent electrical conductivity, which is vital for efficient energy conversion and performance.
Pros and Cons: The high conductivity of copper ensures minimal energy loss, enhancing overall performance. However, copper is relatively expensive and can be prone to corrosion if not properly insulated. This makes it essential for manufacturers to apply protective coatings, particularly in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Impact on Application: For B2B buyers, especially in coastal regions, understanding the corrosion resistance of copper is crucial. Compliance with international standards regarding electrical components is also a consideration.
How Does Steel Compare in Terms of Durability for Alternators?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is often used in alternator components that require high strength and durability, such as the frame and mounting brackets. Its key properties include high tensile strength and excellent resistance to wear and deformation.
Pros and Cons: The durability of steel makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, but it is heavier than aluminum, which may affect overall vehicle performance. Additionally, while stainless steel offers corrosion resistance, it can be more expensive than standard carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Buyers in regions with high mechanical stress or extreme temperatures may prefer steel components for their robustness. Compliance with standards such as DIN can guide material selection.
What About Composite Materials in Alternator Manufacturing?
Composite materials are increasingly being used in alternators for components that require a combination of strength and lightweight properties. These materials often include carbon fiber or fiberglass reinforced plastics.
Pros and Cons: Composites can provide excellent weight savings and corrosion resistance, enhancing the overall efficiency of the alternator. However, they can be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, especially in technologically advanced markets, the use of composite materials can be a selling point. Compliance with specific industry standards for composites is essential to ensure quality and performance.
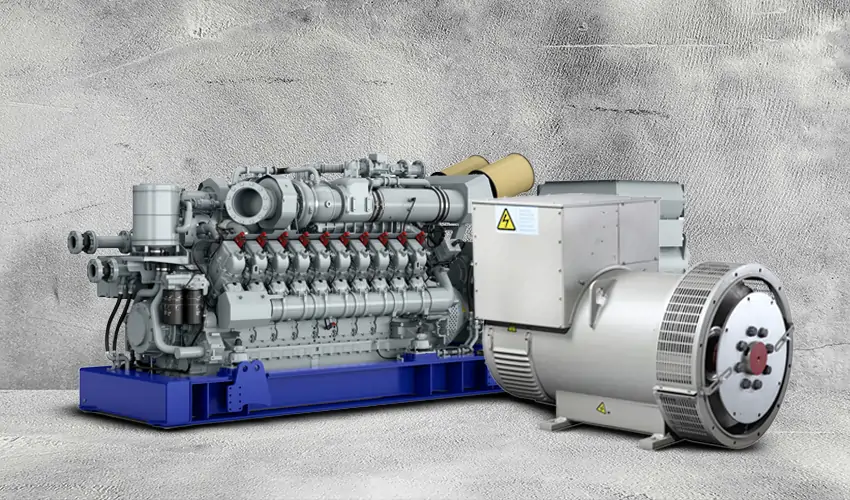
Illustrative image related to altenator
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for Alternator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housings and rotor components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | More expensive than steel | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical windings | Excellent electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Steel | Frame and mounting brackets | High tensile strength | Heavier, may rust without treatment | Medium |
| Composite | Lightweight components | Weight savings and corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for alternators, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for altenator
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Alternators?
The manufacturing of alternators is a complex process that involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance and reliability standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality materials, typically copper for windings, silicon steel for the stator and rotor cores, and aluminum or iron for housings. The materials must be free of contaminants and meet specified grades to ensure efficiency and durability. Suppliers often conduct material testing to verify compliance with international standards.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the required components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and machining are commonly used. For example, stator and rotor cores are stamped from silicon steel sheets, while housings are cast or machined to precise specifications. Advanced methods like CNC machining enhance precision, which is crucial for the performance of the alternator.
-
Assembly: The assembly process involves integrating the various components into a functional unit. Key tasks include winding the coils, inserting them into the stator, and assembling the rotor with bearings and other moving parts. This stage often utilizes automated systems for efficiency and accuracy. Skilled technicians perform critical tasks to ensure that each component is fitted correctly and operates smoothly.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes applying protective coatings, conducting surface treatments, and performing final assembly checks. Finishing processes like anodizing or painting protect the alternator from environmental factors. Additionally, this stage may involve the installation of electronic components such as voltage regulators, which are essential for the alternator’s performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the alternator manufacturing process, ensuring that each unit meets strict performance and safety standards. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes.
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard signifies that a company has established processes for consistent quality and continuous improvement.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are crucial for products intended for specific markets. These certifications indicate that the product meets essential safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Alternator Production?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each alternator meets specified quality standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival. This includes verifying material specifications and conducting tests to check for defects or inconsistencies.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor processes and identify any deviations from standards. This includes checking assembly tolerances and conducting functional tests on components as they are assembled.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed alternator undergoes a comprehensive inspection that includes functional testing, electrical performance checks, and visual inspections for any cosmetic defects. This stage is crucial for ensuring the product is ready for the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Alternator Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the performance and reliability of alternators. These include:
-
Electrical Testing: This involves measuring output voltage, current, and ripple to ensure the alternator performs within specified limits. Testing may include load testing to simulate operational conditions.
-
Mechanical Testing: Mechanical integrity is assessed through vibration analysis, thermal cycling, and torque tests. These tests help identify potential points of failure under operational conditions.
-
Environmental Testing: Products are often subjected to environmental tests, including humidity, temperature extremes, and corrosion resistance tests, to ensure they can withstand harsh operating conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensuring product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. Audits should focus on their quality management systems, employee training, and equipment maintenance.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request documentation of quality control processes, including inspection reports and testing results. This documentation can offer proof of compliance with industry standards and highlight the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can help verify the quality of products before shipment. These services can conduct independent testing and provide certifications that assure buyers of the product’s quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate several nuances related to quality control when sourcing alternators from different regions. Factors include:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural practices related to quality and manufacturing can influence how quality is perceived and executed. Buyers should be aware of regional manufacturing practices and quality expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and performance. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations, which may differ from international standards.
-
Logistical Considerations: Quality control processes may be impacted by shipping and handling practices. It’s important for buyers to discuss how products will be packaged and transported to minimize damage during transit.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alternators, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘altenator’
Introduction
When sourcing alternators for your business, a structured approach can significantly streamline the procurement process. This guide provides a practical checklist to ensure that you select the right alternators that meet your technical requirements and business objectives. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, following these steps will help you make informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to altenator
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications you need for your alternators, including voltage, amperage, and pulley types. This step is crucial because it ensures compatibility with your existing systems. Identify whether you require new or remanufactured units based on your budget and operational needs.
- Voltage Requirements: Determine if you need 12V, 24V, or higher.
- Amperage Needs: Assess the power requirements of the equipment the alternators will support.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in alternators. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the market and positive reviews from previous clients. This step is essential for establishing a reliable supply chain.
- Supplier Profiles: Review the company’s history, product range, and client testimonials.
- Industry Presence: Check if they have experience supplying to businesses in your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with international quality standards. This is vital for ensuring product reliability and safety.
- Quality Assurance: Look for ISO certifications or equivalent.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure they meet local and international standards relevant to your market.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before placing a bulk order, request samples or prototypes of the alternators. This allows you to evaluate the product quality firsthand, ensuring it meets your specifications and performance expectations.
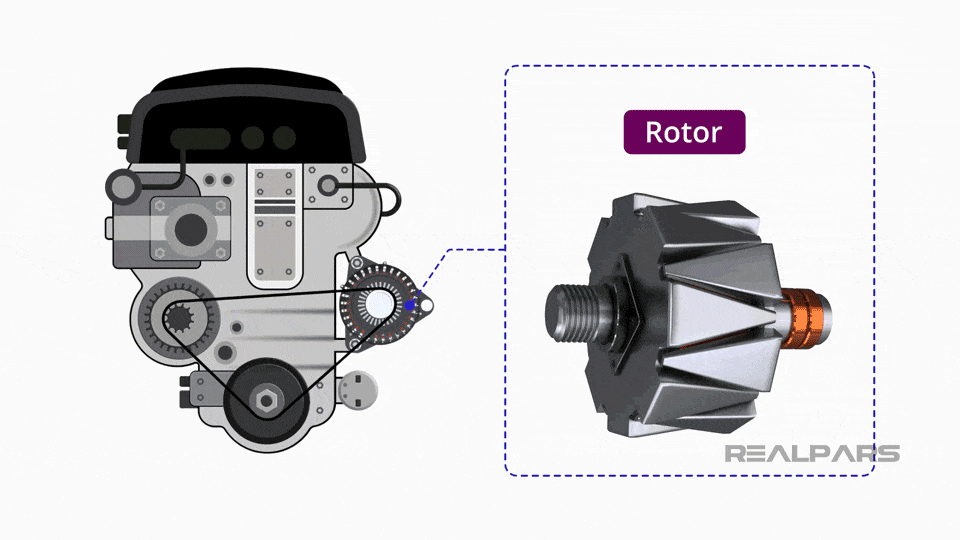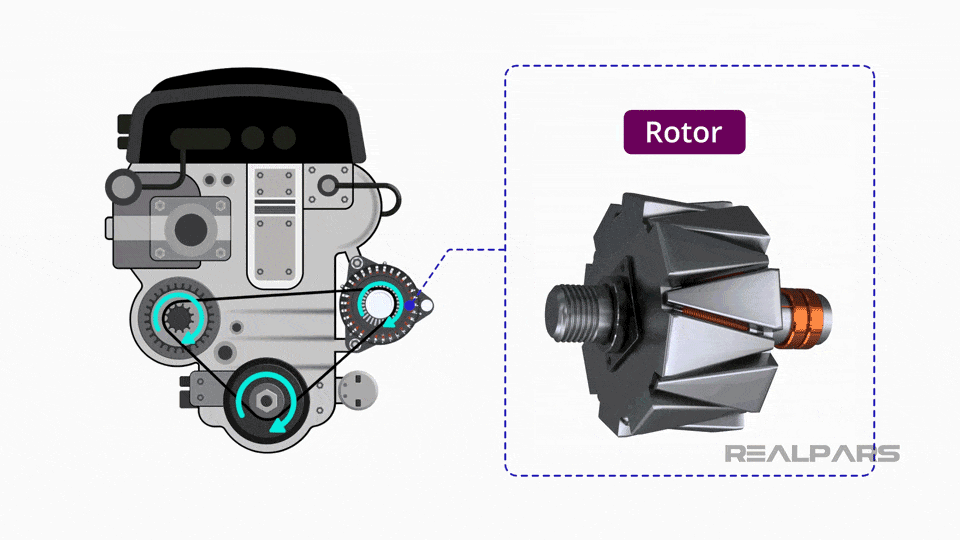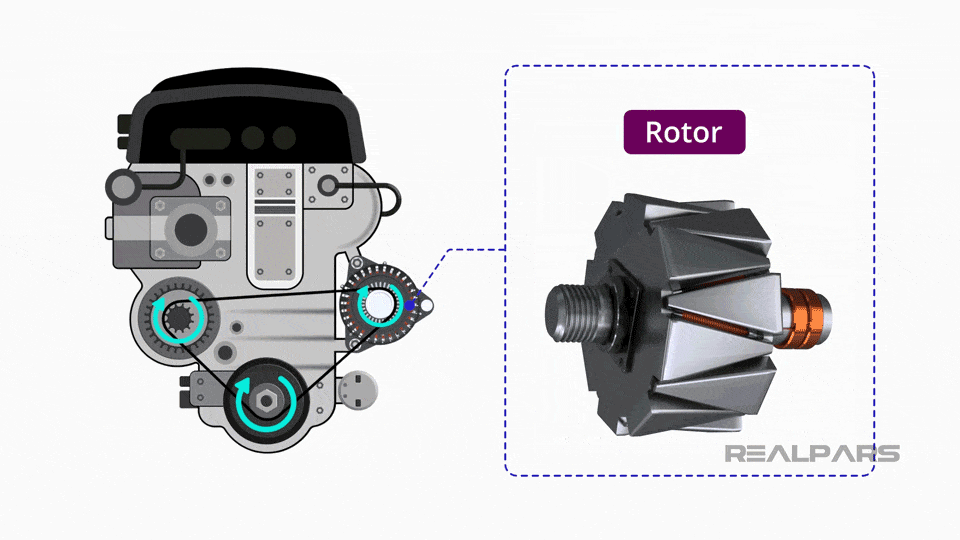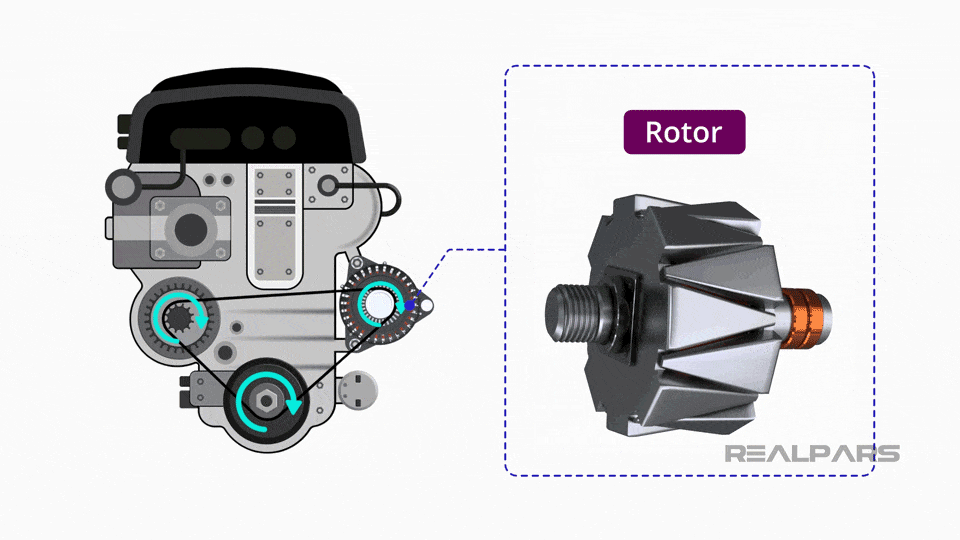
Illustrative image related to altenator
- Testing Performance: Check for efficiency, durability, and compatibility with your equipment.
- Feedback from Technicians: Involve your technical team in the evaluation process for professional insights.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and payment terms. Understanding your budget constraints while also aiming for competitive pricing is crucial for maintaining profitability.
- Bulk Order Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment options that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Establish a Communication Channel
Set up a clear communication channel with your chosen supplier to facilitate ongoing dialogue regarding order updates, technical support, and potential issues. Effective communication can prevent misunderstandings and enhance cooperation.
- Regular Updates: Schedule periodic check-ins to discuss order status and resolve any concerns.
- Point of Contact: Designate a specific representative from both sides for streamlined communication.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support
Ensure that your supplier offers robust after-sales support, including warranties, return policies, and technical assistance. This is important for addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase and maintaining operational efficiency.
- Warranty Coverage: Understand the terms of warranties for the alternators.
- Technical Support: Confirm availability of support for installation and troubleshooting.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the procurement process more effectively, ensuring that you acquire high-quality alternators that meet your operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for altenator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Alternator Sourcing?
When sourcing alternators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in alternator production significantly impact costs. Common materials include copper for windings, aluminum for housings, and various plastics for insulation. Higher quality materials may lead to increased durability and performance but also elevate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can significantly influence the overall price of alternators. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, the manufacturing price may be higher compared to regions like Vietnam or Nigeria, where labor costs are generally lower.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help reduce these overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tools and machinery for alternator production can be substantial. Custom tooling for specialized designs can further increase costs but may be necessary for specific client requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each alternator meets quality standards involves additional costs. This includes testing and inspection processes that may vary depending on the certifications required by different markets.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can fluctuate based on the origin and destination of the alternators. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and current fuel prices play a significant role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their business expenses and risks. Understanding the typical margin within the industry can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Alternator Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing for alternators that international B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing. Larger orders often qualify for bulk discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials, tooling, and production processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can raise costs but may provide significant long-term benefits in performance and reliability. Buyers must weigh the initial costs against potential savings from reduced failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for calculating total landed costs. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can significantly impact pricing based on shipping methods and insurance.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers When Sourcing Alternators?
International B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies by considering the following tips:
-
Negotiation Skills: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Buyers should prepare by researching market rates and understanding the supplier’s cost structure.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than only considering the initial purchase price, buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, warranty, and operational costs over the product’s lifespan.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying pricing structures influenced by local economic conditions, tariffs, and import duties. Buyers should be aware of these factors and consider them when negotiating.
-
Conduct Market Research: Staying informed about market trends, competitor pricing, and new technologies can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best suppliers.
-
Request Sample Products: Before placing large orders, requesting samples can help assess quality and performance, ensuring that the chosen supplier meets expectations.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and practical tips, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in their alternator sourcing process, ultimately leading to more effective procurement strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing altenator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to ‘Altenator’
In the competitive landscape of industrial power generation and automotive applications, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional alternators. Evaluating these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to enhance performance, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency. Below, we compare ‘altenator’ with two viable alternatives: DC Generators and Battery Systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Altenator | DC Generator | Battery Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, reliable output | Moderate efficiency, variable output | Limited output, dependent on capacity |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, long-term savings | Higher initial costs, variable maintenance | High upfront costs, lifecycle savings possible |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy to install and integrate | More complex installation and setup | Simple installation, requires management of charge cycles |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, periodic checks required | Higher maintenance needs, regular servicing | Minimal maintenance, requires monitoring system |
| Best Use Case | Automotive applications, renewable energy systems | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Emergency power supply, off-grid systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
DC Generators
DC generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy and are particularly effective in industrial settings. They are well-suited for applications requiring a stable voltage output under varying loads.
Pros:
– Reliable performance in heavy-duty applications.
– Robust and can handle significant electrical loads.
– Ideal for industrial setups with fluctuating power demands.
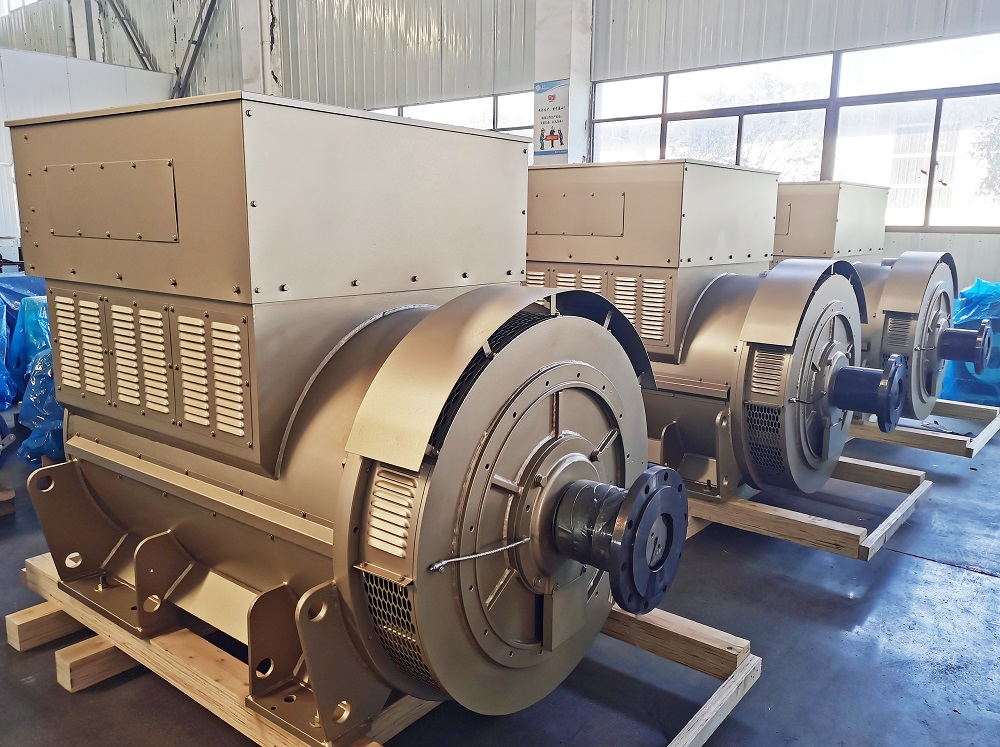

Illustrative image related to altenator
Cons:
– Generally higher initial costs than alternators.
– More complex installation and maintenance requirements, which can lead to increased operational downtime.
– Efficiency can drop under lower load conditions, making them less ideal for applications with constant low demand.
Battery Systems
Battery systems provide a portable and efficient power solution, especially useful for applications where grid access is limited. They store energy for later use, making them suitable for off-grid scenarios.
Pros:
– Flexibility in usage, allowing for mobile applications.
– Minimal maintenance compared to mechanical systems.
– Can be paired with renewable sources (solar, wind) for sustainable energy solutions.
Cons:
– Limited power output based on the battery capacity.
– High upfront costs, particularly for large-scale installations.
– Dependence on charge cycles can lead to downtime if not managed effectively.
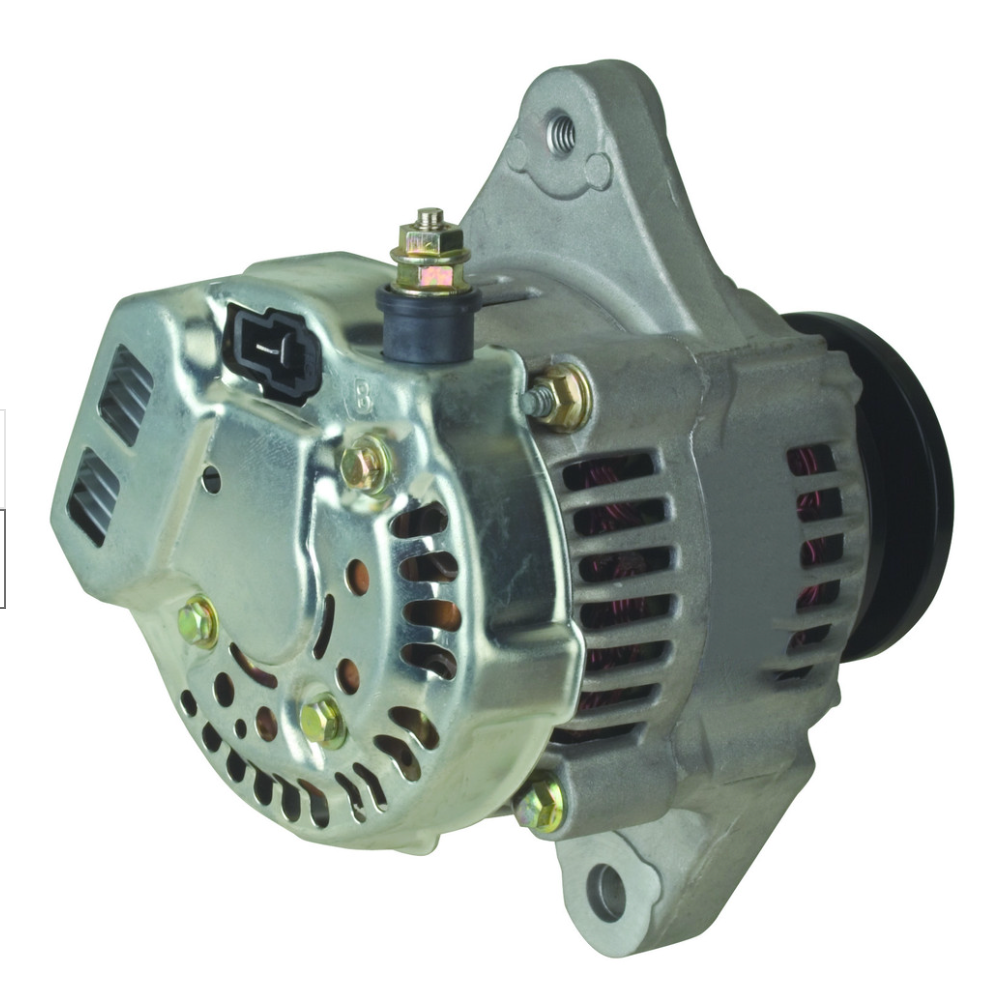

Illustrative image related to altenator
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the most appropriate power solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. While alternators are ideal for consistent automotive applications and renewable energy setups, DC generators excel in heavy-duty industrial applications, and battery systems offer flexibility for off-grid and emergency scenarios. By carefully assessing these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and financial strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for altenator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Alternator for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical properties of an alternator is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications that influence performance and compatibility:
-
Amperage (A)
This specification indicates the electrical current output of the alternator, typically ranging from 90 to over 300 amps. Amperage is vital because it determines the alternator’s ability to charge the battery and power electrical components in vehicles or machinery. Buyers should assess their specific power requirements to ensure the selected alternator meets operational demands. -
Voltage (V)
Alternators generally operate at either 12V or 24V, with some specialized versions available for higher voltages. The voltage rating affects compatibility with the electrical system of the vehicle or equipment. Selecting the correct voltage is essential to prevent damage to electrical components and ensure optimal performance. -
Pulley Type and Diameter
The pulley is a critical component that connects the alternator to the engine. Common types include conventional and clutch pulleys. The diameter of the pulley also impacts the rotational speed and, subsequently, the output of the alternator. Buyers must match the pulley specifications with their engine requirements to ensure effective power transmission. -
Regulator Type
Alternators can feature either internal or external voltage regulators. The regulator maintains the output voltage within a specified range, ensuring consistent performance. Understanding the type of regulator is important for maintenance and replacement, as it affects the alternator’s efficiency and longevity. -
Cooling Method
Alternators can utilize air or liquid cooling methods. The cooling method impacts the alternator’s efficiency and operational lifespan, especially in high-demand applications. Buyers should consider the cooling needs based on the expected workload and environmental conditions. -
Rotational Direction
Most alternators are designed to rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. This specification is crucial for compatibility with the engine design. Incorrect rotational direction can lead to installation issues and operational failures.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Alternator Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of vehicles or machinery. OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality. B2B buyers should consider whether they require OEM parts or if aftermarket options suffice for their needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is important for budgeting and inventory planning. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs and financial capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. This process helps buyers compare costs and services from multiple vendors. Properly crafting an RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps mitigate risks and ensures clarity in shipping agreements. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for supply chain management, particularly for buyers operating in industries with tight schedules. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the performance and reliability of the alternator. It outlines the terms of service and conditions under which repairs or replacements will be provided. Buyers should carefully review warranty terms to understand their rights and protections.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right alternator for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the altenator Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Global Alternator Market?
The global alternator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by a surge in demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in automotive technology. The transition to EVs is reshaping sourcing dynamics, as manufacturers seek lightweight and high-efficiency alternators to support battery systems. In regions like Africa and South America, the rising middle class is boosting vehicle ownership, increasing the need for reliable alternators across various automobile segments. Furthermore, the Middle East and Europe are seeing a shift towards hybrid and electric models, prompting suppliers to innovate and adapt their product offerings.
Emerging technologies such as IoT and AI are also influencing sourcing trends. These technologies enable predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of alternators, enhancing performance and reducing downtime. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide integrated solutions that combine traditional alternator manufacturing with advanced technological capabilities. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers, as they navigate diverse market needs and regulatory environments.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Alternator Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the alternator supply chain, with increasing pressure on manufacturers to minimize environmental impacts. The sourcing of raw materials, particularly metals used in alternators, is under scrutiny for its ecological footprint. Ethical sourcing practices, including responsible mining and recycling of components, are gaining traction among B2B buyers who prioritize environmental stewardship.
Buyers are also looking for suppliers that adhere to ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, which ensures effective environmental management systems. Using eco-friendly materials and processes not only helps in reducing carbon footprints but also enhances brand reputation. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, businesses that demonstrate commitment to sustainability can differentiate themselves in the competitive alternator market.
What Is the Evolution of the Alternator in the Automotive Industry?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles relied on DC generators, which were less efficient and required more maintenance. The introduction of the alternator marked a pivotal shift, providing greater efficiency and reliability in power generation for automotive electrical systems.
In the 1970s and 1980s, advancements in materials and design led to the development of high-output alternators, which became essential for vehicles equipped with additional electrical accessories. Today, the focus is on lightweight, high-efficiency models that can support the growing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles. This evolution is crucial for B2B buyers, as they must stay informed about technological advancements that impact product performance and sourcing strategies.
Conclusion
Navigating the alternator market requires an understanding of global trends, sustainability practices, and the historical context of the industry. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, aligning sourcing strategies with these dynamics is essential for maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring long-term success. By focusing on innovative technologies and ethical practices, businesses can meet the demands of modern consumers while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of altenator
-
How do I choose the right alternator for my application?
Selecting the right alternator involves understanding your specific power requirements, vehicle specifications, and the type of electrical systems you intend to support. Consider factors such as amperage output, voltage ratings, and whether you need a new or remanufactured unit. Research the compatibility of the alternator with your existing systems, and consult with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and recommendations tailored to your needs. -
What is the best alternator brand for heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty applications, brands like Bosch, Denso, and Powermaster Performance are renowned for their reliability and performance. These manufacturers offer high-output options designed to withstand the rigors of demanding environments. When selecting a brand, look for features such as robust construction, high amperage ratings, and positive customer reviews regarding performance and durability. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering alternators internationally?
Lead times for international orders of alternators can vary widely based on the supplier, shipping method, and destination. Typically, expect 2-4 weeks for standard shipments, but expedited options may reduce this time. It’s crucial to discuss timelines with your supplier upfront to ensure alignment with your project schedules and to account for potential customs delays. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators?
Minimum order quantities for alternators often depend on the supplier and the type of alternator being purchased. Generally, MOQs can range from 10 to 100 units. For large-scale purchases, negotiating MOQs is possible, especially if you establish a long-term partnership with your supplier. Always clarify MOQs during initial discussions to avoid surprises later. -
How can I ensure the quality of alternators I’m sourcing?
To ensure quality, request certifications and quality assurance documentation from your suppliers. Look for products that meet international standards such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider ordering samples for testing before making bulk purchases. Establishing a clear quality control process with your supplier can further mitigate risks associated with defective products. -
What payment terms are typically offered by alternator suppliers?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common terms include payment in full upon order placement, net 30/60 days, or a combination of a deposit with the remainder due upon shipment. Discuss and negotiate terms that work best for your cash flow while ensuring the supplier is comfortable with the arrangement. -
What customs regulations should I be aware of when importing alternators?
When importing alternators, it’s essential to understand the customs regulations specific to your country. This includes tariffs, import duties, and documentation requirements. Research the Harmonized System (HS) codes applicable to alternators and prepare necessary paperwork such as commercial invoices and packing lists. Consulting with a customs broker can streamline the process and ensure compliance. -
How do I vet potential alternator suppliers?
Vetting potential suppliers involves evaluating their business history, customer reviews, and product quality. Request references and check their reputation through online reviews or industry forums. Additionally, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Conducting a site visit or requesting a virtual tour can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality controls.
Top 2 Altenator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HowStuffWorks – Alternator Insights
Domain: auto.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The alternator is a crucial component in a vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for charging the battery and powering electrical systems when the engine is running. Symptoms of a failing alternator include dimming headlights, flickering dashboard lights, and loss of power to accessories such as the radio and heater. A malfunctioning alternator can lead to a dead battery and engine failure, lea…
2. Advance Auto Parts – Alternator
Domain: shop.advanceautoparts.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Alternator – Advance Auto Parts; 15% OFF ORDERS $35+ | 20% OFF $100+ | ONLINE ONLY USE CODE BLACKFRIDAY; OEM-quality alternators from brands like Carquest, ACDelco, and Bosch; Free testing of old alternator at local Advance Auto Parts; Categories: Alternator (3510), Performance Alternator or Generators (6), Generator (1); Price Range: $25 – $49.99 (2), $50 – $99.99 (41), $100 and up (3467); Limite…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for altenator
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in the Alternator Market?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of alternators is crucial for ensuring reliability and cost-effectiveness in supply chains. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable manufacturers who offer both new and remanufactured options, allowing for flexibility in meeting diverse operational needs. Understanding specifications such as amperage, voltage, and pulley types is essential to align purchases with vehicle requirements and performance expectations.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Emphasizing strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also fosters long-term relationships with suppliers, ultimately leading to better pricing and service agreements. By leveraging data and market insights, businesses can negotiate favorable terms that enhance profitability.
What Does the Future Hold for International B2B Buyers?
As global demand for reliable automotive components continues to rise, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is imperative for buyers to stay ahead of market trends. Embrace innovation and sustainability in sourcing practices to ensure your business remains competitive. Engage with suppliers today to secure your supply chain’s future and drive growth in the dynamic alternator market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.