Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what does and alternator do
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, understanding the role of an alternator is crucial for international B2B buyers navigating the complexities of vehicle maintenance and parts procurement. An alternator is not merely a component; it is a vital generator that transforms mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, ensuring that vehicles operate smoothly by powering essential systems and recharging the battery. This guide delves into the intricacies of what an alternator does, exploring its various types, applications across different vehicle models, and the implications of sourcing quality components from reliable suppliers.
With an emphasis on empowering decision-makers, this comprehensive resource addresses key challenges faced by buyers in diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, specifically in countries like Brazil and Germany. By examining factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the impact of alternator performance on vehicle reliability, this guide equips international buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. As you navigate the global market for automotive parts, understanding the critical function of alternators will enhance your ability to source quality products that meet your operational demands and maintain vehicle efficiency. Whether you are involved in fleet management, automotive repair, or parts distribution, this guide is designed to serve as your go-to reference for all things related to alternators.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 What Does And Alternator Do Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what does and alternator do
- Understanding what does and alternator do Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what does and alternator do
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what does and alternator do’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what does and alternator do
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what does and alternator do
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what does and alternator do’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what does and alternator do Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what does and alternator do With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what does and alternator do
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what does and alternator do Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what does and alternator do
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what does and alternator do
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what does and alternator do Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Alternator | Utilizes a rotor and stator to generate AC, then converts to DC | Automotive manufacturing and repair | Pros: Widely available, cost-effective. Cons: Limited efficiency under high loads. |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed to provide greater electrical output for high-demand vehicles | Performance vehicles, commercial fleets | Pros: Supports heavy electrical loads. Cons: Higher cost and potential for overheating. |
| Brushless Alternator | Uses electromagnetic induction, eliminating brushes for longevity | Industrial machinery, generators | Pros: Longer lifespan, reduced maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Smart Alternator | Incorporates advanced electronics for optimized charging and efficiency | Hybrid and electric vehicles | Pros: Improves fuel efficiency, reduces emissions. Cons: Complexity may require specialized knowledge for repairs. |
| Regenerative Alternator | Captures energy during braking to recharge the battery | Electric and hybrid vehicle systems | Pros: Enhances energy efficiency, extends battery life. Cons: More complex, may increase vehicle weight. |
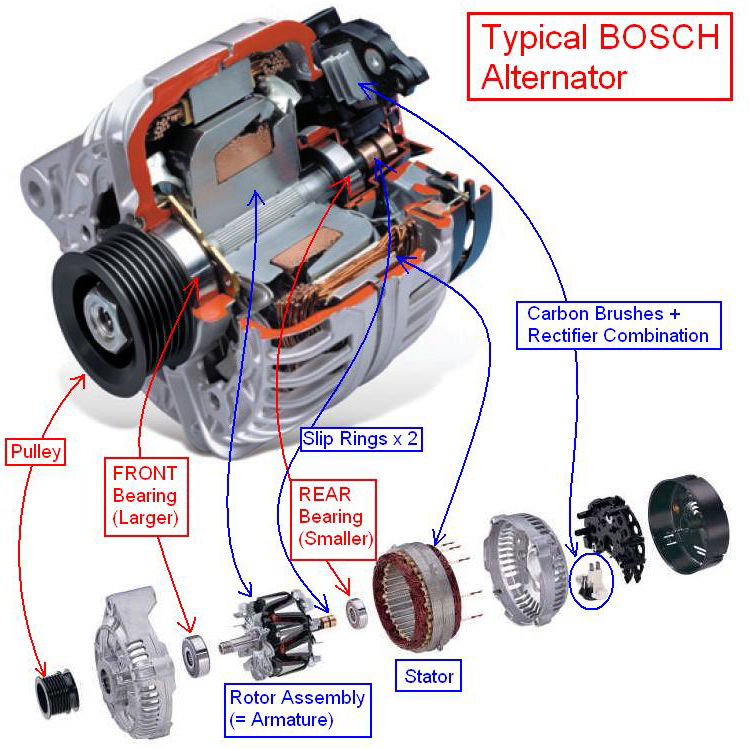
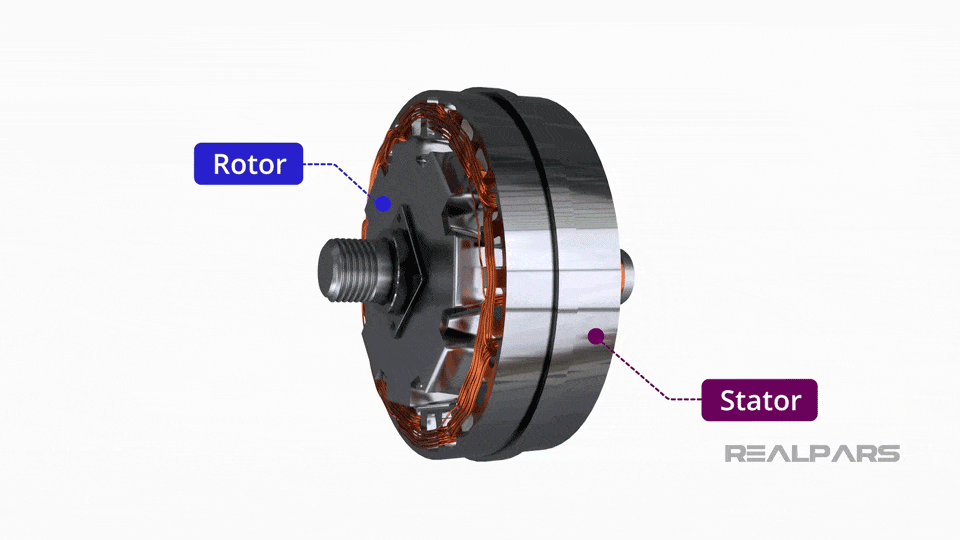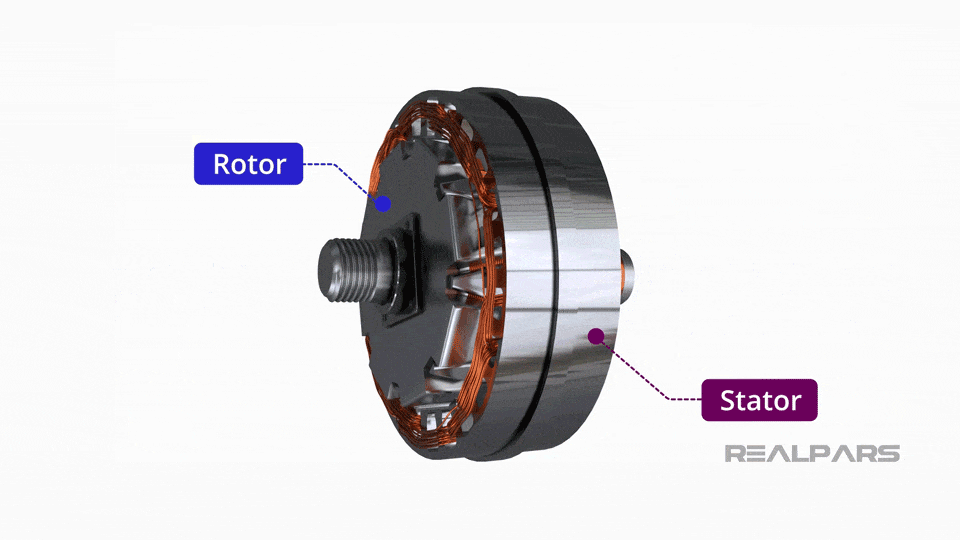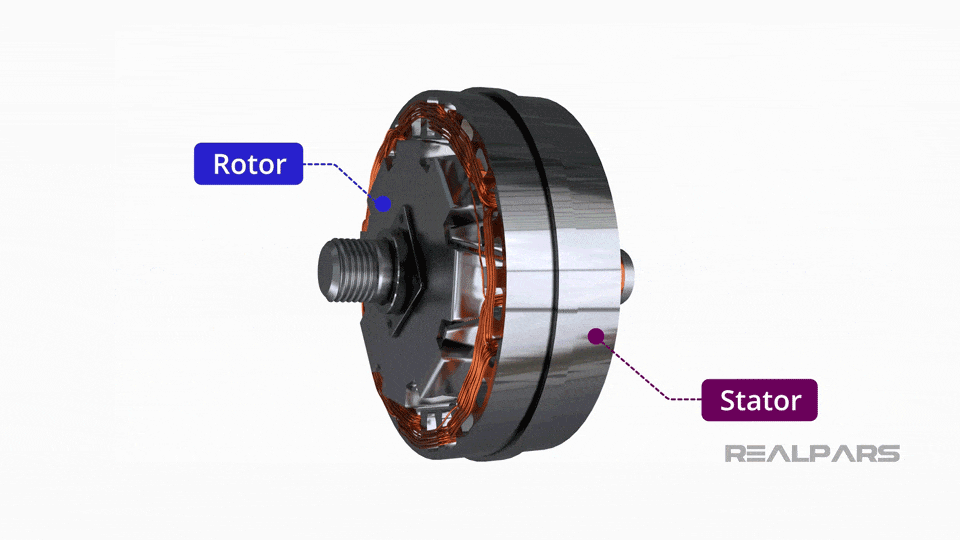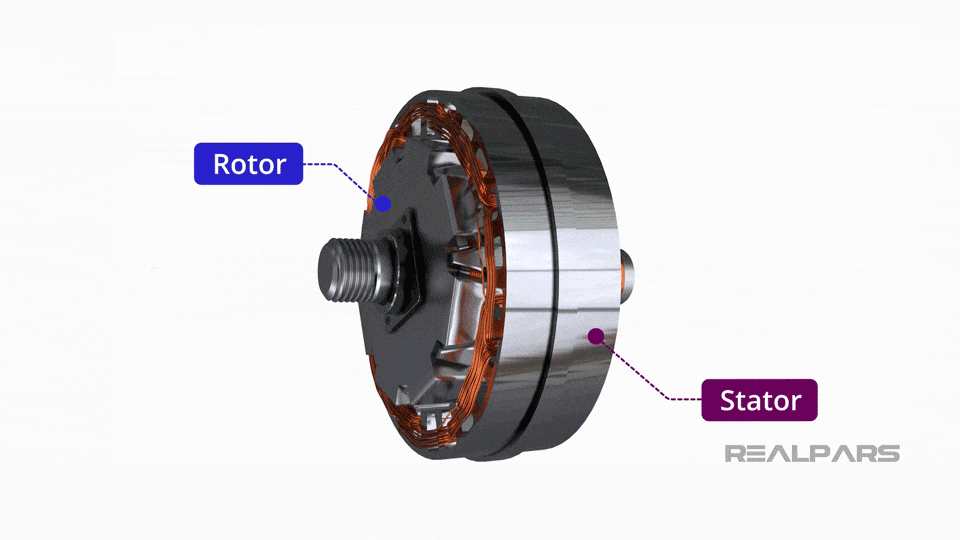
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Alternators?
Conventional alternators are the most common type used in standard vehicles. They operate by converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy through a rotating magnetic field. This type is suitable for general automotive applications where standard electrical loads are expected. When purchasing, buyers should consider the alternator’s output rating and compatibility with their vehicle model, as well as its installation requirements.
How Do High-Output Alternators Differ from Standard Models?
High-output alternators are specifically engineered to handle increased electrical demands, making them ideal for performance vehicles and commercial fleets that operate numerous electrical accessories. These alternators are characterized by their ability to produce higher amperage, ensuring that all electronic components function optimally. Buyers should evaluate their vehicle’s electrical needs and consider the alternator’s heat management capabilities to prevent overheating during heavy use.
What Advantages Do Brushless Alternators Offer?
Brushless alternators utilize electromagnetic induction instead of brushes, which reduces wear and tear, leading to a longer lifespan. They are commonly used in industrial applications where reliability is paramount. When considering a brushless alternator, buyers should assess the initial investment against long-term maintenance savings, as well as compatibility with existing machinery or vehicles.
Why Are Smart Alternators Important for Modern Vehicles?
Smart alternators are equipped with advanced electronic control systems that optimize charging based on real-time energy demands. This makes them particularly suitable for hybrid and electric vehicles, where efficiency is crucial. Buyers must consider the complexity of these systems, as they may require specialized knowledge for installation and repairs, but the long-term fuel savings and reduced emissions can justify the investment.
How Do Regenerative Alternators Enhance Vehicle Efficiency?
Regenerative alternators are designed to capture kinetic energy during braking, converting it back into electrical energy to recharge the vehicle’s battery. This technology is particularly beneficial in electric and hybrid vehicles, where maximizing energy efficiency is essential. Buyers should evaluate the system’s integration with their vehicle’s overall energy management strategy, as well as the potential for increased weight due to additional components.
Key Industrial Applications of what does and alternator do
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what does an alternator do | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Power generation in vehicle assembly lines | Ensures consistent power supply for automated machinery, enhancing productivity | Quality and reliability of alternators, compliance with industry standards |
| Renewable Energy | Hybrid vehicles and electric car systems | Supports efficient energy conversion, optimizing battery performance | Compatibility with various battery technologies, sourcing from reputable manufacturers |
| Agriculture | Powering agricultural machinery and equipment | Enhances operational efficiency by ensuring reliable power for essential equipment | Durability in harsh environments, local availability of parts and service |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet vehicles’ electrical systems | Reduces downtime by ensuring reliable vehicle operation, improving delivery schedules | Cost-effectiveness and warranty terms, local support for maintenance |
| Construction | Powering heavy machinery and tools | Increases productivity by ensuring uninterrupted power for construction activities | Sourcing alternators that meet specific voltage and power requirements |
How is an Alternator Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, alternators play a critical role in powering assembly line machinery. These machines require a steady and reliable power supply to operate efficiently, ensuring that production schedules are met. By converting mechanical energy from the production line into electrical energy, alternators help maintain the operational integrity of tools and equipment. Businesses must consider the quality and reliability of alternators, ensuring they comply with industry standards to avoid production delays.
What Role Does an Alternator Play in Renewable Energy Applications?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in hybrid vehicles and electric car systems, alternators are crucial for energy conversion. They help manage the transition from mechanical energy to electrical energy, optimizing battery performance and extending vehicle range. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, it’s essential to source alternators that are compatible with various battery technologies and can withstand diverse climatic conditions. This ensures that vehicles operate efficiently and sustainably.
How Do Alternators Enhance Agricultural Operations?
Agricultural machinery relies heavily on alternators to power essential equipment such as tractors and harvesters. A reliable alternator ensures that these machines operate without interruption, enhancing productivity in the field. For B2B buyers in agriculture, sourcing durable alternators that can withstand harsh environments is vital. Additionally, having local availability of parts and service can significantly reduce downtime during critical harvesting periods.
Why are Alternators Important for Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics industry, fleet vehicles depend on alternators to maintain their electrical systems. A well-functioning alternator ensures that vehicles can operate reliably, reducing downtime and improving delivery schedules. For businesses, cost-effectiveness and favorable warranty terms are key considerations when sourcing alternators. Additionally, having local support for maintenance can help keep fleets running smoothly, especially in regions with challenging logistics.
What is the Significance of Alternators in Construction?
Construction sites often utilize heavy machinery that requires consistent power for tools and equipment. Alternators are essential in providing this power, thereby increasing productivity on-site. Businesses need to source alternators that meet specific voltage and power requirements to ensure compatibility with their machinery. Additionally, understanding the local market for parts and service can help mitigate risks associated with equipment failure in remote construction areas.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what does and alternator do’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Alternator Functions for Fleet Management
The Problem: For fleet managers operating in diverse environments, ensuring that every vehicle in their fleet is running efficiently is paramount. Many managers may struggle to understand the dual role of the battery and alternator in their vehicles. They often face challenges related to unexpected vehicle downtime due to alternator failures, which can result in operational disruptions and increased maintenance costs. Misunderstanding the alternator’s function can lead to inadequate preventative maintenance, ultimately affecting productivity and revenue.
The Solution: To effectively manage this issue, fleet managers should invest in comprehensive training for their maintenance teams about how alternators work and their importance in vehicle operations. It is crucial to create a checklist for routine inspections that includes alternator health. Regularly checking for signs such as dim dashboard lights or unusual noises can help identify problems early. Additionally, implementing a proactive replacement schedule based on the average lifespan of alternators—typically between 80,000 to 150,000 miles—can prevent unexpected failures. Utilizing telematics systems to monitor vehicle performance can also assist in tracking alternator functionality, ensuring that any issues are addressed before they lead to vehicle breakdowns.
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Alternators for International Markets
The Problem: International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, often face challenges when sourcing quality alternators for their automotive needs. They may encounter difficulties related to inconsistent quality among suppliers, leading to premature failures and increased costs associated with replacements and repairs. This challenge is compounded by the need for compliance with local regulations and standards, making it crucial for buyers to ensure they are sourcing from reputable manufacturers.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should prioritize building relationships with established suppliers known for their quality and reliability. Conducting thorough research and seeking out reviews or testimonials from other businesses in the region can provide insights into supplier performance. Additionally, buyers should consider engaging with manufacturers who offer warranties and detailed product specifications, ensuring that the alternators meet local automotive standards. Attending international trade shows or automotive expos can also be beneficial, allowing buyers to evaluate products firsthand and establish direct communication with manufacturers. This proactive approach not only secures high-quality alternators but also fosters long-term partnerships.
Scenario 3: Troubleshooting Alternator Problems in Remote Areas
The Problem: In remote areas, technicians may face significant challenges when diagnosing and repairing alternator issues due to limited access to specialized tools and parts. This situation can lead to prolonged vehicle downtime, affecting service delivery and customer satisfaction. B2B buyers in sectors like logistics or public transport may experience frustration when trying to maintain their fleets without immediate access to qualified service centers or replacement parts.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should invest in equipping their technicians with mobile diagnostic tools that can quickly identify alternator issues. Providing training on basic troubleshooting techniques can empower local teams to perform on-site repairs, reducing downtime significantly. Moreover, establishing agreements with local parts suppliers to ensure quick access to alternators and necessary components is essential. Implementing a mobile service solution, where technicians can travel to remote sites with essential tools and parts, can also enhance operational efficiency. By creating a robust support system for technicians, businesses can minimize disruptions and ensure that their operations run smoothly, even in the most challenging environments.
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what does and alternator do
What Are the Key Materials Used in Alternators and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for alternators, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of alternators: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Alternators?
Aluminum is widely used in alternator housings due to its lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and lightweight, which contributes to better fuel efficiency in vehicles. It also offers good resistance to oxidation, ensuring longevity.
Cons: While aluminum is relatively cost-effective, it may not withstand high-stress applications as effectively as other metals. Additionally, its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized techniques to ensure structural integrity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and its ability to dissipate heat effectively make it a preferred choice for alternator casings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and ISO, particularly concerning environmental regulations.
How Does Copper Enhance Performance in Alternators?
Copper is primarily used in the windings of alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity, which is crucial for efficient energy transfer. Its temperature rating can reach up to 200°C, and it is resistant to corrosion when properly coated.
Pros: The high conductivity of copper allows for efficient energy transfer, enhancing the overall performance of the alternator. It is also highly durable and can withstand significant mechanical stress.
Cons: The main drawback of copper is its relatively high cost compared to aluminum and its susceptibility to oxidation, which can affect performance if not adequately protected.
Impact on Application: Copper’s superior conductivity makes it ideal for applications requiring high electrical efficiency, ensuring that the alternator can meet the demands of modern vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN and JIS is essential, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is critical.
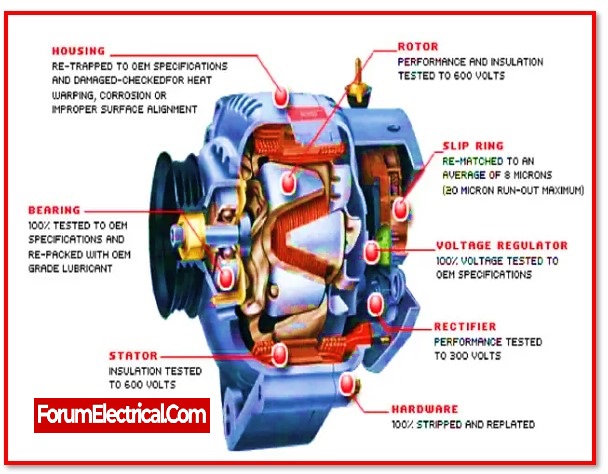
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
What Role Does Steel Play in Alternator Construction?
Steel is often used for the structural components of alternators, including the rotor and stator. It has a high tensile strength and can withstand significant mechanical loads, with a temperature rating of approximately 300°C.
Pros: Steel’s strength and durability make it suitable for high-stress applications, ensuring that the alternator can function effectively under various conditions.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of steel is its weight, which can impact fuel efficiency. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s robustness makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, particularly in commercial vehicles that require reliable performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Steel components must meet specific quality standards, and buyers should be aware of corrosion resistance requirements, especially in humid or coastal regions.
How Is Plastic Utilized in Alternators?
Plastic is commonly used for non-structural components in alternators, such as covers and insulators. It is lightweight and can be engineered to withstand various temperatures, typically rated up to 120°C.
Pros: Plastic is cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, making it versatile for various applications. It also provides good insulation properties.
Cons: While plastic is lightweight, it may not offer the same level of durability as metals, making it less suitable for high-stress areas. It can also degrade over time when exposed to high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic components can help reduce the overall weight of the alternator, contributing to improved vehicle efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with international safety standards, particularly in Europe, where regulations regarding materials are stringent.

Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for what does and alternator do | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housings and casings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less effective under high stress | Medium |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | High electrical conductivity | High cost and oxidation susceptibility | High |
| Steel | Structural components like rotor and stator | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Covers and insulators | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable under stress and heat | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in alternators, facilitating informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific regional and operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what does and alternator do
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Alternators?
The manufacturing process of alternators involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Alternator Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Raw materials typically include high-grade aluminum for the housing, copper for the windings, and various steel components for the rotor and stator. Suppliers must be vetted to ensure they provide materials that meet specific technical requirements. This often involves checking certifications such as ISO 9001 to ensure consistency in quality. Additionally, some manufacturers might employ advanced material analysis techniques to verify the integrity of the materials before they are used in production.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Alternators?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves several key techniques such as die casting and stamping. Die casting is commonly used for producing the aluminum housing of the alternator, as it allows for precise shaping and a smooth finish. Stamping is typically used to create the rotor and stator components from sheets of steel. The forming process must be closely monitored to maintain tolerances, as even slight deviations can affect the alternator’s performance. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are often employed to enhance precision during this phase.
How Are Alternators Assembled?
After the components are formed, the assembly stage takes place. This is where the rotor, stator, voltage regulator, and other parts are put together. Assembly lines are commonly used, where skilled technicians follow strict protocols to ensure each alternator is assembled correctly. Automation is increasingly being integrated into assembly processes to improve efficiency and reduce human error. Every step in this process is documented to facilitate traceability, which is essential for quality assurance.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Alternators?
The finishing stage involves several processes aimed at improving the alternator’s durability and performance. This may include surface treatment processes like anodizing or powder coating to prevent corrosion and enhance aesthetic appeal. Additionally, electrical testing is conducted to ensure the alternator meets performance specifications. Manufacturers often use automated testing equipment to simulate operational conditions and verify electrical output, ensuring that the alternators can handle the demands of various vehicle types.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of alternator manufacturing, ensuring that each unit meets international standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically involves adherence to several relevant international standards and checkpoints throughout the production cycle.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For alternator manufacturing, compliance with ISO 9001 is crucial as it outlines the requirements for a quality management system. This certification assures buyers that the manufacturer consistently provides products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, CE marking is important for products sold in Europe, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in specific industries, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may also be relevant.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is typically segmented into three main checkpoints: Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- IQC involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This ensures that materials meet the specified standards before they enter the production line.
- IPQC takes place during the manufacturing process. This includes monitoring production parameters and conducting random inspections to ensure that the assembly and forming processes are being executed correctly.
- FQC is the final inspection stage, where finished alternators undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance metrics, such as voltage output and efficiency. Only products that pass these tests are released for sale.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This can be achieved through several means:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Suppliers?
-
Conduct Audits: Buyers can perform on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in place. This provides firsthand insight into how a supplier operates and the standards they adhere to.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should be willing to provide documentation regarding their quality control processes, including test reports, certifications, and compliance records. This documentation should be thoroughly reviewed to ensure it meets the required standards.
-
Utilize Third-party Inspection Services: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can conduct inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process and provide comprehensive reports.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Different regions may have varying standards and regulatory requirements, which can impact the quality of the alternators being sourced.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Control?
-
Africa and South America: Buyers from these regions should ensure that suppliers not only meet local standards but also adhere to international certifications to facilitate smoother trade and compliance with importing regulations.
-
Middle East and Europe: In these markets, strict adherence to CE marking and ISO standards is crucial for market entry. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven compliance to avoid delays and ensure product acceptance.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alternators are complex and multifaceted, requiring diligent attention to detail and adherence to international standards. B2B buyers must actively engage in verifying supplier practices to ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs. Understanding these processes will empower buyers to make informed decisions when selecting alternator suppliers in the global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what does and alternator do’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, understanding the functionality and importance of alternators is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide aims to provide a structured checklist for international buyers seeking to procure alternators, ensuring you have the necessary information to evaluate your options effectively.
Step 1: Identify Your Application Requirements
Understanding the specific application of the alternator is essential. Consider factors such as the type of vehicle or machinery, the electrical load requirements, and environmental conditions. This will help in determining the appropriate alternator specifications needed for optimal performance.
- Key Considerations:
- Vehicle type (e.g., passenger cars, commercial vehicles)
- Electrical demands (e.g., lighting, audio systems, HVAC)
Step 2: Define Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications required for your alternator. This includes voltage output, amperage rating, and type of current (AC vs. DC). Having precise specifications helps ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
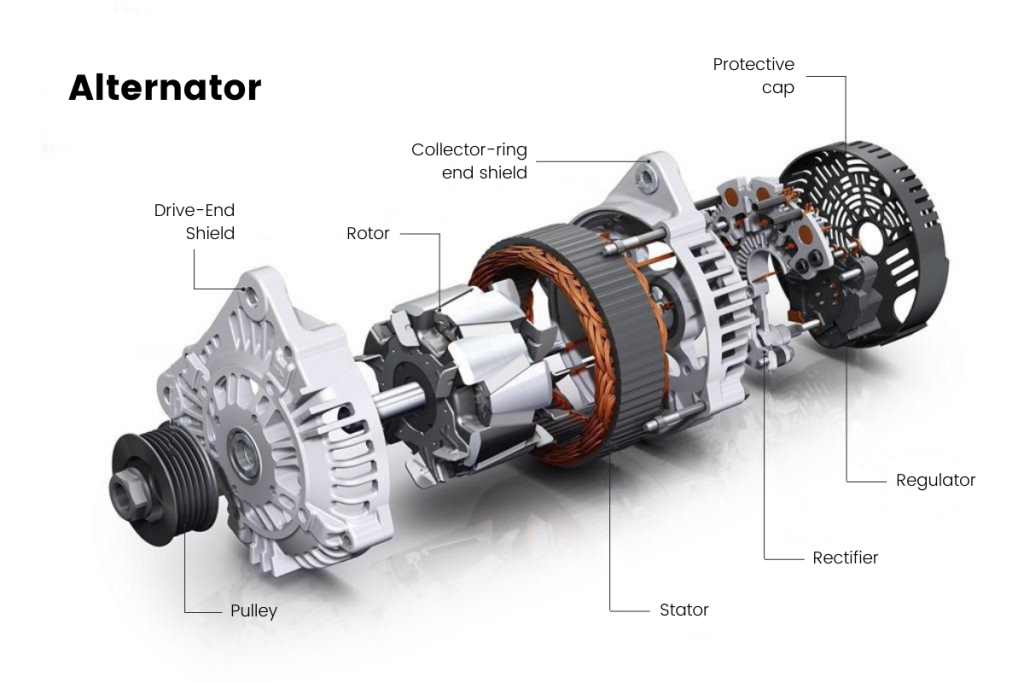
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
- Important Details:
- Voltage range (e.g., 12V, 24V)
- Amperage capacity (consider peak and continuous loads)
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry, particularly those that specialize in automotive or heavy machinery components. A diverse supplier base can provide you with various options.
- Action Items:
- Check supplier reviews and testimonials
- Evaluate their experience in your specific market region
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications that comply with international standards. This can include ISO certifications, quality control measures, and safety standards. Compliance with these standards indicates reliability and quality assurance.
- What to Look For:
- Relevant industry certifications (e.g., ISO 9001)
- Compliance with regional regulations, especially in your target markets (e.g., EU standards)
Step 5: Request Product Samples and Technical Documentation
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples or technical documentation from your shortlisted suppliers. This enables you to evaluate the quality and performance of the alternators firsthand, ensuring they meet your specifications.
- Documentation to Request:
- Product datasheets and specifications
- Installation and maintenance guidelines
Step 6: Evaluate Pricing and Terms of Purchase
Analyze pricing structures and payment terms from your potential suppliers. Compare quotes to ensure you’re getting competitive pricing while considering the total cost of ownership, including warranties and after-sales support.
- Pricing Considerations:
- Bulk purchase discounts
- Warranty terms and conditions
Step 7: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Options
Strong after-sales support is critical for minimizing downtime in your operations. Investigate the warranty options provided by suppliers and their responsiveness to service inquiries.
- Support Elements to Evaluate:
- Duration and coverage of the warranty
- Availability of technical support and spare parts
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring alternators, ensuring they select the right product and supplier to meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what does and alternator do Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing an Alternator?
When sourcing an alternator, several key cost components must be considered to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the overall expenditure. The primary components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as copper for windings and various metals for casing and components, significantly influences the overall price. The quality and source of these materials can vary widely, impacting both performance and cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, might offer competitive pricing, but this can affect quality and delivery timelines.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers in regions with higher operational costs will reflect this in their pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial. If custom designs or modifications are needed, tooling costs will rise, necessitating a higher upfront investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that alternators meet international standards involves rigorous testing and inspection processes, which can add to the overall cost. Certifications for quality assurance can also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and handling fees, are crucial, especially for international buyers. Incoterms will dictate responsibilities and costs related to transportation, insurance, and delivery.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition and perceived value.
What Price Influencers Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Several factors can influence the price of alternators beyond the direct cost components. Understanding these price influencers can empower B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Many manufacturers offer tiered pricing based on the minimum order quantity (MOQ), so negotiating for higher volumes can be beneficial.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications or custom features may increase costs. Buyers should carefully consider their needs and whether standard models can suffice.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or components that meet specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) typically come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to proven quality and service, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. These terms define who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Alternator Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing alternators.
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in thorough negotiations with suppliers. Understanding market trends and competitor pricing can provide leverage in discussions.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, lifespan, and efficiency. Sometimes, a higher upfront cost can lead to lower long-term expenses due to durability and reliability.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying price structures due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and market demand. For example, while sourcing from Germany may involve higher base prices, the quality and longevity of the product could justify the investment.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Whenever possible, look for local suppliers to minimize shipping costs and lead times. This can also simplify logistics and customs processes.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Pricing for alternators can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and material costs. It’s advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct periodic reviews to ensure competitive pricing.
By understanding these components, influencers, and strategies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing alternators effectively, ensuring they achieve both quality and value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what does and alternator do With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Alternators
In the automotive industry, the alternator plays a critical role in powering the electrical systems of vehicles by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. However, there are alternative technologies and solutions that can serve similar functions, particularly in specific contexts or applications. This section will compare the traditional alternator with alternative energy solutions, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Does An Alternator Do | Alternative 1 Name: DC Generators | Alternative 2 Name: Battery Management Systems (BMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy efficiently; supports vehicle electrical systems. | Provides reliable electrical output; often used in stationary applications. | Manages battery charge and discharge cycles; optimizes battery life and performance. |
| Cost | Typically ranges from $100 to $500, depending on vehicle make and model. | Costs vary widely; typically cheaper for stationary setups but can be more expensive for mobile applications. | Can range from $50 to several thousand dollars based on complexity and features. |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in most vehicles; requires basic mechanical knowledge. | Requires knowledge of electrical systems; installation complexity varies. | Generally requires specialized knowledge for setup and integration with existing systems. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; usually lasts 7-10 years. | Requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance; lifespan varies. | Minimal maintenance; highly dependent on battery health and usage patterns. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for all conventional vehicles and hybrid systems. | Best suited for generators and industrial applications. | Perfect for electric vehicles and advanced energy storage systems. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: DC Generators
DC generators convert mechanical energy into direct current electricity, similar to alternators, but they are generally used in stationary applications, such as backup power systems or industrial machinery. Pros of DC generators include their simplicity and reliability in providing a steady electrical output. However, their performance can decline over time, requiring more maintenance than alternators. Additionally, they are less suitable for mobile applications due to their bulkiness and weight.
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
Alternative 2: Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Battery Management Systems are essential for electric vehicles and energy storage solutions. They monitor and manage the charging and discharging of batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. BMS can enhance battery safety and efficiency, making them crucial for modern electric mobility solutions. However, they can be complex to implement and require specialized knowledge. Additionally, BMS systems do not generate power themselves; they rely on external charging sources, which may limit their standalone effectiveness compared to alternators.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating alternatives to alternators, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications. Traditional alternators remain the most efficient solution for conventional and hybrid vehicles due to their straightforward implementation and low maintenance needs. However, for stationary applications, DC generators may provide a cost-effective alternative, while Battery Management Systems are essential for optimizing electric vehicle performance. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each solution, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and long-term goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what does and alternator do
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Alternator in Automotive Applications?
Understanding the essential technical properties of an alternator is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing parts for automotive manufacturing or repairs. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Output Voltage
The standard output voltage for automotive alternators is typically 12 volts, but it can vary based on the vehicle’s electrical demands. This specification is vital because it directly affects the charging of the vehicle’s battery and the operation of electrical components. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems can prevent electrical failures and enhance vehicle performance. -
Ampere Rating
The ampere rating indicates the maximum electrical current the alternator can produce. Common ratings range from 40 to 150 amps for standard vehicles, while high-performance models may exceed 200 amps. This rating is essential for B2B buyers as it determines whether the alternator can support additional electrical accessories such as sound systems or lighting, which is increasingly popular in various markets. -
Efficiency Rating
Alternator efficiency is typically expressed as a percentage, indicating how effectively it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. A higher efficiency rating (above 70%) means less wasted energy and better performance. For manufacturers, this property impacts fuel economy and overall vehicle reliability, making it a critical consideration in procurement decisions. -
Lifespan
The average lifespan of an alternator ranges between 80,000 to 150,000 miles or approximately 7 to 10 years. Factors such as driving conditions and maintenance frequency can influence this lifespan. Understanding the expected lifespan helps businesses plan for replacement schedules and reduce downtime, which is particularly important in fleet operations. -
Material Composition
Alternators are typically made from aluminum and copper, with varying grades affecting weight, durability, and cost. The choice of materials can influence the alternator’s performance and longevity. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is crucial for maintaining product quality and ensuring compliance with international standards. -
Regulation System
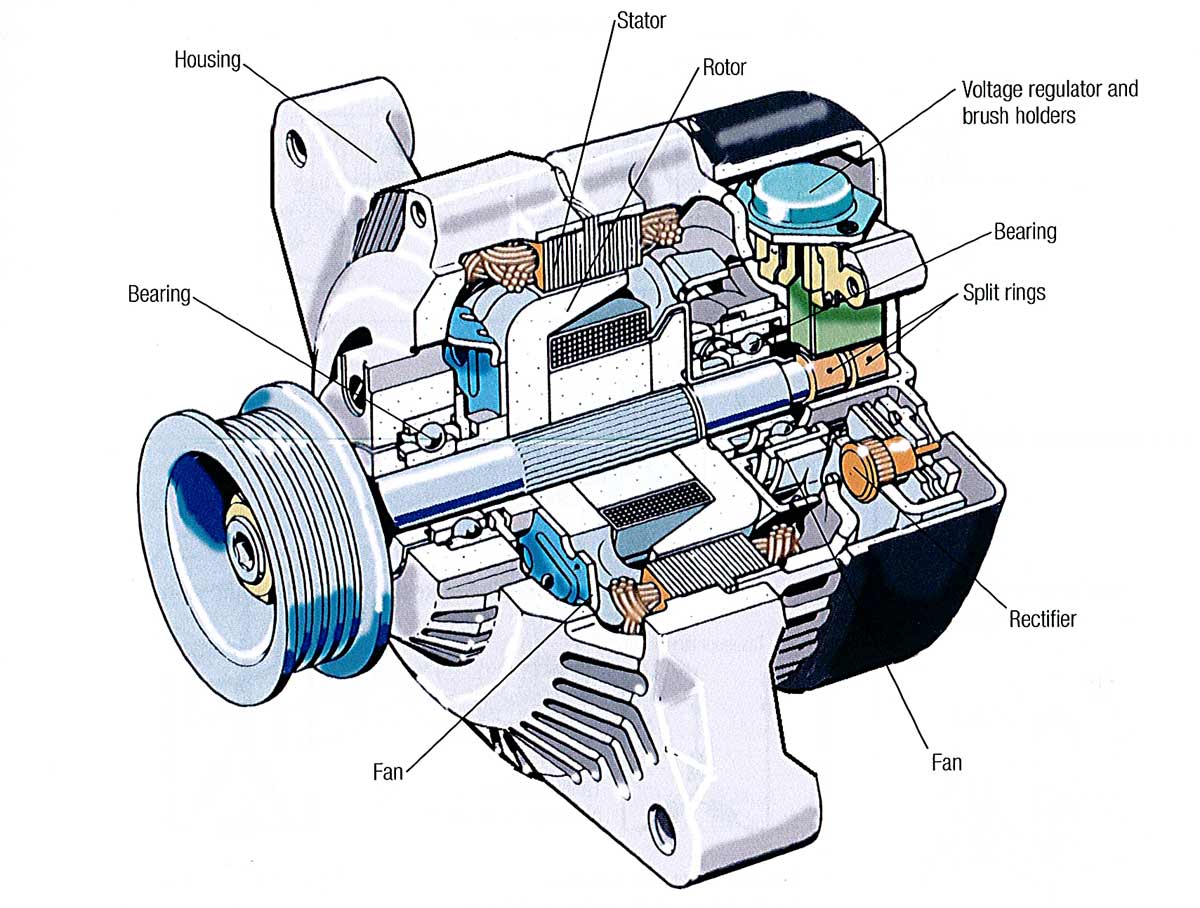
Most modern alternators feature an internal voltage regulator that controls the output voltage. This component is critical for preventing overcharging, which can damage the battery and electrical systems. Understanding the regulation system can help buyers make informed decisions about compatibility and maintenance needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Alternators?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the procurement process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the vehicle manufacturer or their authorized suppliers. These components are designed to meet the specific requirements of the vehicle, ensuring compatibility and reliability. For B2B buyers, sourcing OEM alternators can provide assurance of quality and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for businesses to ensure they can meet their operational needs without overcommitting to inventory. This term is particularly relevant for international buyers who may be dealing with varying supplier policies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price quotes on specific products. It’s an essential part of the procurement process, allowing businesses to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers efficiently. For B2B buyers, a well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and service agreements. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and logistics. Understanding these terms is vital for international transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for costs, risks, and insurance during transport. Proper knowledge of Incoterms can prevent misunderstandings and financial losses. -
Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to the secondary market for vehicle parts and accessories. This sector often includes replacement parts that may not be OEM, providing cost-effective alternatives. For businesses, engaging with the aftermarket can offer opportunities for savings and customization. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the goods. In automotive manufacturing, understanding lead times is essential for inventory management and production scheduling. This knowledge helps businesses maintain smooth operations and meet customer demands effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what does and alternator do Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Global Alternator Market?
The global alternator market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several factors. The increasing demand for vehicles, particularly in developing regions such as Africa and South America, is a primary driver. As urbanization accelerates, more consumers are seeking reliable transportation, which in turn fuels the need for efficient vehicle components like alternators. Additionally, the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles is reshaping the market landscape, as these vehicles require advanced alternators that cater to their unique power needs.
Emerging technologies, such as smart alternators equipped with IoT capabilities, are also gaining traction. These innovations enhance efficiency and provide real-time diagnostics, appealing to B2B buyers looking for advanced solutions. Furthermore, the trend towards automotive electrification is leading to increased investments in research and development, enabling manufacturers to produce more efficient and durable alternators.
International buyers should also note the growing importance of supply chain resilience. The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities, prompting businesses to diversify their sourcing strategies. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe and the Middle East, where buyers are increasingly looking for local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Alternator Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern business practices, influencing sourcing decisions in the alternator market. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This includes sourcing materials that minimize environmental impact and ensuring that manufacturing processes adhere to eco-friendly standards.
The use of recycled materials in alternator production is gaining momentum, reducing the carbon footprint associated with new component manufacturing. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who possess ‘green’ certifications, which verify their commitment to environmentally responsible practices. Furthermore, transparency in the supply chain is critical; B2B buyers want assurance that their suppliers uphold ethical labor practices and contribute positively to their communities.
For those operating in regions like Africa and South America, where resource management can be challenging, aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals not only enhances brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. Investing in sustainable practices is not just an ethical choice; it is becoming a competitive necessity in the global market.
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
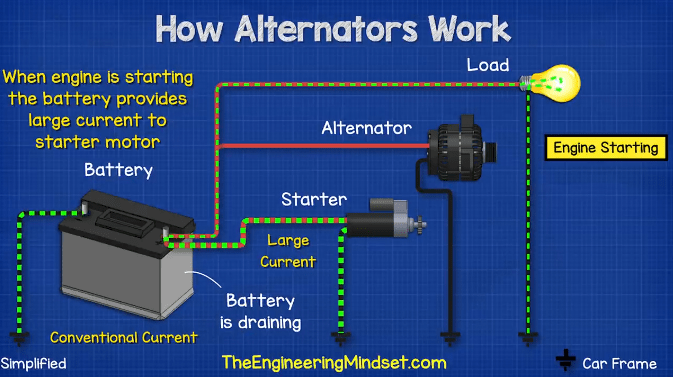
What Is the Historical Context of Alternators in the Automotive Industry?
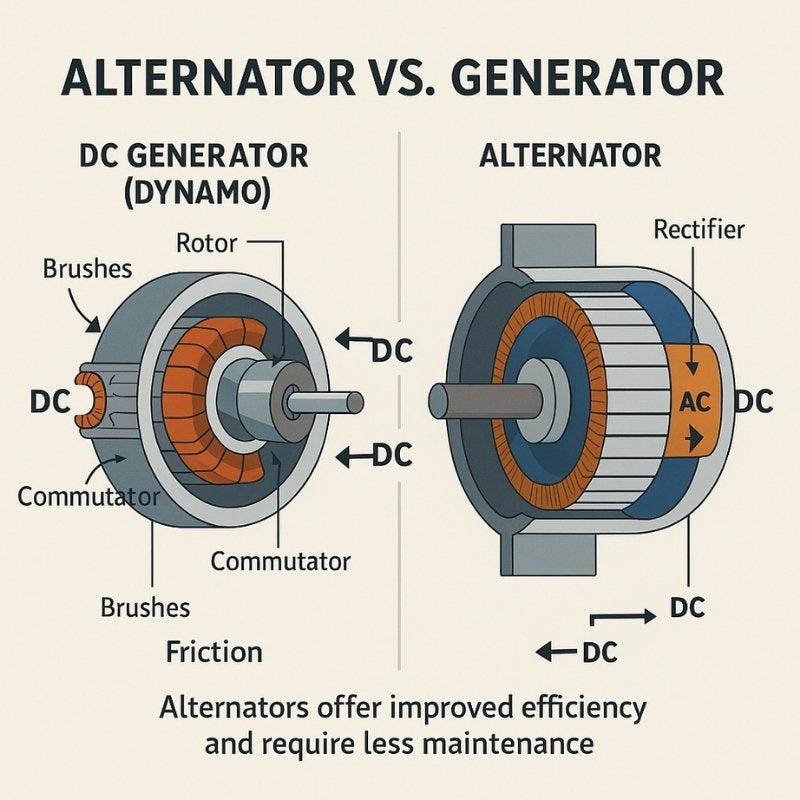
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles relied on direct current (DC) generators, which were less efficient and required more maintenance. The introduction of the alternator in the 1960s marked a turning point, as it offered higher efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements.
As automotive technology progressed, so did the design and functionality of alternators. Modern alternators are equipped with sophisticated voltage regulators and rectifiers that enhance performance and reliability. This evolution reflects the automotive industry’s broader trend towards electrification and efficiency, driven by consumer demand for more reliable and environmentally friendly vehicles.
For international B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of alternators is essential. It not only highlights the technological advancements in the sector but also informs sourcing decisions by illustrating the long-term reliability and performance evolution of these components. Investing in high-quality alternators from reputable suppliers can lead to significant operational efficiencies and customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what does and alternator do
-
How do I identify if an alternator is malfunctioning?
To determine if an alternator is malfunctioning, look for several key symptoms. Common signs include dimming headlights, dashboard warning lights, or difficulty starting the vehicle. If the car requires frequent jump-starts, or if electrical accessories are performing poorly, these may also indicate a failing alternator. Regular maintenance checks can help catch these issues early, ensuring that your operations remain smooth and minimizing downtime in your fleet. -
What is the average lifespan of an alternator in commercial vehicles?
The average lifespan of an alternator typically ranges from 80,000 to 150,000 miles or around 7 to 10 years, depending on driving conditions and vehicle maintenance. Factors such as rough terrain, high electrical demand, and poor-quality components can shorten this lifespan. Understanding these variables can assist B2B buyers in selecting the right alternators that suit their fleet’s operational needs. -
What are the key features to look for in a high-quality alternator?
When sourcing alternators, prioritize features like durability, efficiency, and compatibility with your vehicle models. Look for units with high amperage output to handle additional electrical loads, such as advanced lighting systems or infotainment setups. Additionally, ensure that the alternator comes with a warranty and is manufactured by reputable suppliers, which can provide peace of mind and reduce the risk of premature failure. -
How do I vet suppliers for alternators in international trade?
Vetting suppliers involves several steps: check their certifications, production capabilities, and customer reviews. Request samples or prototypes to assess quality firsthand. Utilize trade platforms and industry networks to gather information about potential suppliers’ reputations. For international buyers, it’s also crucial to understand local regulations and compliance standards that could affect the importation of alternators. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for alternators when sourcing internationally?
The MOQ for alternators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of alternator required. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs between 50 to 200 units. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may be flexible with lower quantities for first-time orders or pilot projects. Understanding MOQ helps in budgeting and planning your inventory effectively. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with alternator suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms, consider options like net 30 or net 60 days to allow time for product evaluation upon delivery. For larger orders, a partial upfront payment followed by balance payment upon delivery may be advantageous. Ensure that payment methods are secure and offer buyer protection, especially in international transactions where risk factors are higher. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for the alternators I purchase?
Implement a comprehensive QA process by requesting certifications such as ISO or TS16949 from your suppliers. Conduct regular audits and inspections of production facilities, and consider third-party testing for critical components. Establish clear quality standards and communicate these with your suppliers to ensure that the alternators meet your specifications consistently. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing alternators?
Logistics for importing alternators involves understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose reliable freight forwarders familiar with automotive parts to streamline the process. Plan for additional time for customs clearance, and ensure that all documentation is complete to avoid delays. Proper logistics planning can significantly impact your overall operational efficiency and cost management.
Top 2 What Does And Alternator Do Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Car Alternator Explained
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Car Alternator Explained, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Kia – Alternator
Domain: kia.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: An alternator is an integral part of every combustion engine vehicle, responsible for converting chemical energy to electrical energy to charge and replenish the battery and power other electrical components in the car. It works as part of the vehicle’s charging system, which includes the car battery, voltage regulator, and alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what does and alternator do
What Are the Key Benefits of Understanding Alternators for B2B Buyers?
In summary, understanding the role of alternators is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in the automotive sector. The alternator serves as a pivotal component that converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, powering essential vehicle systems and ensuring reliable performance. Key takeaways include the importance of sourcing high-quality alternators that can withstand varying operational conditions, particularly in regions with challenging environments like Africa and South America.
Strategic sourcing of alternators not only enhances vehicle reliability but also reduces long-term maintenance costs, which is essential for businesses managing fleets. By prioritizing quality and durability, buyers can ensure that their vehicles remain operational, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
As the automotive landscape evolves with advancements in technology and sustainability, it is imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed about emerging trends in alternator design and functionality. Engage with reputable suppliers to explore innovative solutions that can meet your business’s specific needs. By investing in quality alternators today, you position your business for success in an increasingly competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to what does and alternator do
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.