Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter solenoid test
Navigating the complexities of sourcing reliable starter solenoid tests can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The starter solenoid is a critical component in automotive systems, directly influencing vehicle performance and reliability. Ensuring that you have access to accurate testing solutions is paramount to maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of starter solenoid tests available, their applications across different vehicle models, and best practices for supplier vetting.
In addition to outlining key testing methodologies, this resource explores the factors influencing costs, helping you make informed decisions that align with your budget and operational needs. We will also discuss how to identify trustworthy suppliers, focusing on quality assurance and compliance with international standards.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical guidance, this guide empowers organizations to navigate the global market effectively. Whether you are in Brazil, Vietnam, or elsewhere, understanding the nuances of starter solenoid testing will help you procure the right solutions that enhance your business’s automotive service capabilities and contribute to long-term success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Starter Solenoid Test Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter solenoid test
- Understanding starter solenoid test Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter solenoid test
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter solenoid test’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter solenoid test
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter solenoid test
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter solenoid test’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter solenoid test Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter solenoid test With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter solenoid test
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter solenoid test Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter solenoid test
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter solenoid test
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter solenoid test Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Quick assessment of solenoid condition through observation. | Automotive repair shops, fleet management. | Pros: Fast and cost-effective. Cons: May miss internal faults. |
| Electrical Testing | Measures voltage and current flow to assess functionality. | Vehicle maintenance services, diagnostics. | Pros: Accurate performance analysis. Cons: Requires specialized tools. |
| Resistance Testing | Checks for continuity and resistance in the solenoid circuit. | Quality control in manufacturing, repairs. | Pros: Identifies specific faults. Cons: Time-consuming. |
| Load Testing | Evaluates solenoid under operational conditions. | Heavy machinery, commercial vehicle repairs. | Pros: Real-world performance insights. Cons: Requires additional equipment. |
| Component Replacement Testing | Involves swapping out solenoids to confirm issues. | Parts suppliers, automotive service centers. | Pros: Definitive diagnosis. Cons: Higher labor costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Visual Inspection for Starter Solenoid Testing?
Visual inspection is the most straightforward method for assessing the condition of a starter solenoid. Technicians look for visible signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. This method is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and fleet management, where quick assessments can save time. While it is cost-effective and rapid, buyers should note that it may not detect internal faults, potentially leading to overlooked issues.
How Does Electrical Testing Enhance Starter Solenoid Diagnostics?
Electrical testing involves measuring voltage and current flow to determine the solenoid’s functionality. This method is essential for vehicle maintenance services and diagnostic centers, as it provides accurate insights into electrical performance. The primary advantage is its precision, allowing for targeted repairs. However, it requires specialized tools, which may increase upfront costs for businesses.
Why Is Resistance Testing Important for Quality Control?
Resistance testing checks for continuity and measures resistance within the solenoid circuit, making it crucial for quality control in manufacturing and repair environments. This method helps identify specific faults that may not be evident through visual inspection. While it offers detailed insights, the process can be time-consuming, requiring a balance between thoroughness and operational efficiency for businesses.
What Are the Benefits of Load Testing in Real-World Scenarios?
Load testing evaluates a starter solenoid’s performance under actual operating conditions, making it particularly relevant in heavy machinery and commercial vehicle repairs. This method provides valuable data on how the solenoid performs when engaged, helping businesses make informed decisions about repairs or replacements. However, it necessitates additional equipment, which can represent a higher investment for B2B buyers.
How Does Component Replacement Testing Confirm Issues Effectively?
Component replacement testing involves swapping out suspected faulty solenoids to confirm whether they are the source of the problem. This method is commonly used by parts suppliers and automotive service centers as it offers a definitive diagnosis. While it effectively resolves ambiguity in troubleshooting, it can lead to higher labor costs, making it essential for businesses to consider the potential return on investment when implementing this testing approach.
Key Industrial Applications of starter solenoid test
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of starter solenoid test | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in assembly lines | Ensures reliable starter systems, reducing warranty claims and increasing customer satisfaction. | Availability of testing equipment and trained personnel. |
| Heavy Machinery | Maintenance of construction equipment | Prevents downtime by ensuring solenoids function properly, enhancing operational efficiency. | Compatibility with various machinery models and robust testing protocols. |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet vehicle maintenance | Improves vehicle reliability and reduces operational costs by avoiding unexpected breakdowns. | Access to parts and expertise for diverse vehicle types. |
| Marine Industry | Testing of marine engines | Enhances safety and performance by ensuring engine reliability in critical environments. | Compliance with marine regulations and environmental standards. |
| Agricultural Equipment | Servicing of tractors and harvesters | Increases productivity by minimizing equipment failure during peak seasons. | Understanding of specific agricultural equipment needs and supply chain logistics. |
How is ‘starter solenoid test’ utilized in automotive manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, the starter solenoid test is a critical part of quality control during the assembly process. By testing solenoids before installation, manufacturers can ensure that the electrical connections are reliable, which directly impacts the vehicle’s starting performance. This proactive approach helps in reducing warranty claims and enhancing customer satisfaction. For international buyers, sourcing testing equipment that meets local safety and quality standards is essential, as well as ensuring that staff are adequately trained to perform these tests.
What role does ‘starter solenoid test’ play in the heavy machinery sector?
In heavy machinery, particularly construction equipment, the starter solenoid test is vital for maintenance practices. Regular testing can identify potential failures before they lead to equipment downtime, which can be costly. This application is particularly important in regions with harsh working conditions, where equipment reliability is paramount. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing durable testing equipment that can withstand tough environments and ensure that they have access to skilled technicians familiar with various machinery models.
How does ‘starter solenoid test’ benefit transportation and logistics?
For transportation and logistics companies, maintaining a fleet of vehicles is crucial for operational efficiency. The starter solenoid test plays a significant role in fleet maintenance by ensuring that vehicles start reliably, thereby reducing unexpected breakdowns. This reliability translates to lower operational costs and improved service delivery. Buyers in this industry should focus on sourcing parts that are compatible with diverse vehicle types and ensure that they have a robust maintenance schedule to keep their fleet running smoothly.
Why is ‘starter solenoid test’ important in the marine industry?
In the marine industry, the reliability of engine systems is critical for safety and performance. The starter solenoid test helps ensure that marine engines start reliably, particularly in emergency situations. Given the stringent regulations governing marine operations, buyers must source testing equipment that complies with industry standards and environmental regulations. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of marine engines can facilitate better sourcing decisions and enhance overall operational safety.
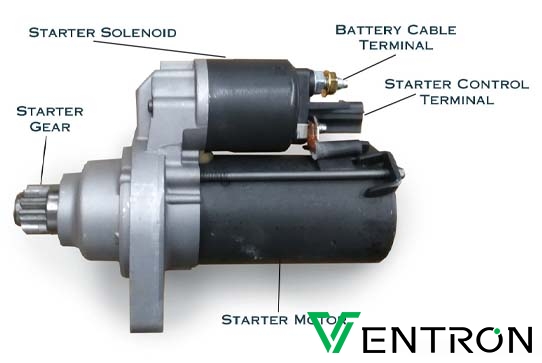
Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
How does ‘starter solenoid test’ support agricultural equipment maintenance?
In agriculture, the starter solenoid test is essential for servicing tractors and harvesters, especially during peak seasons when equipment reliability is crucial. Ensuring that these machines start without issues can significantly impact productivity and operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing testing solutions that are tailored to the specific needs of agricultural equipment and consider logistics for timely repairs and maintenance to avoid delays during critical farming periods.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter solenoid test’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Diagnosing Starter Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those in the automotive repair and maintenance sectors, encounter significant challenges when diagnosing whether the starter solenoid is the culprit behind a vehicle’s failure to start. Confusion often arises from the overlapping symptoms of a faulty starter solenoid, battery issues, or problems with the starter itself. Without a systematic approach to testing, businesses risk misdiagnosing the problem, leading to wasted time and unnecessary expenses in parts and labor.
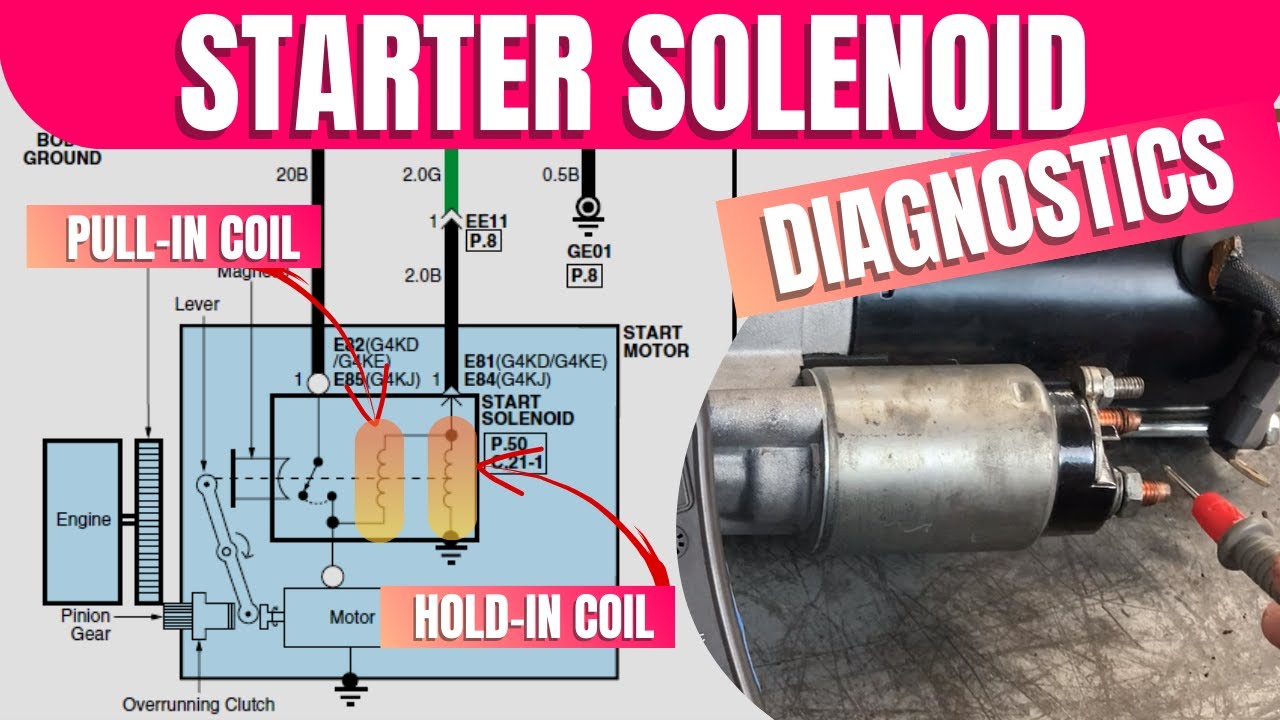
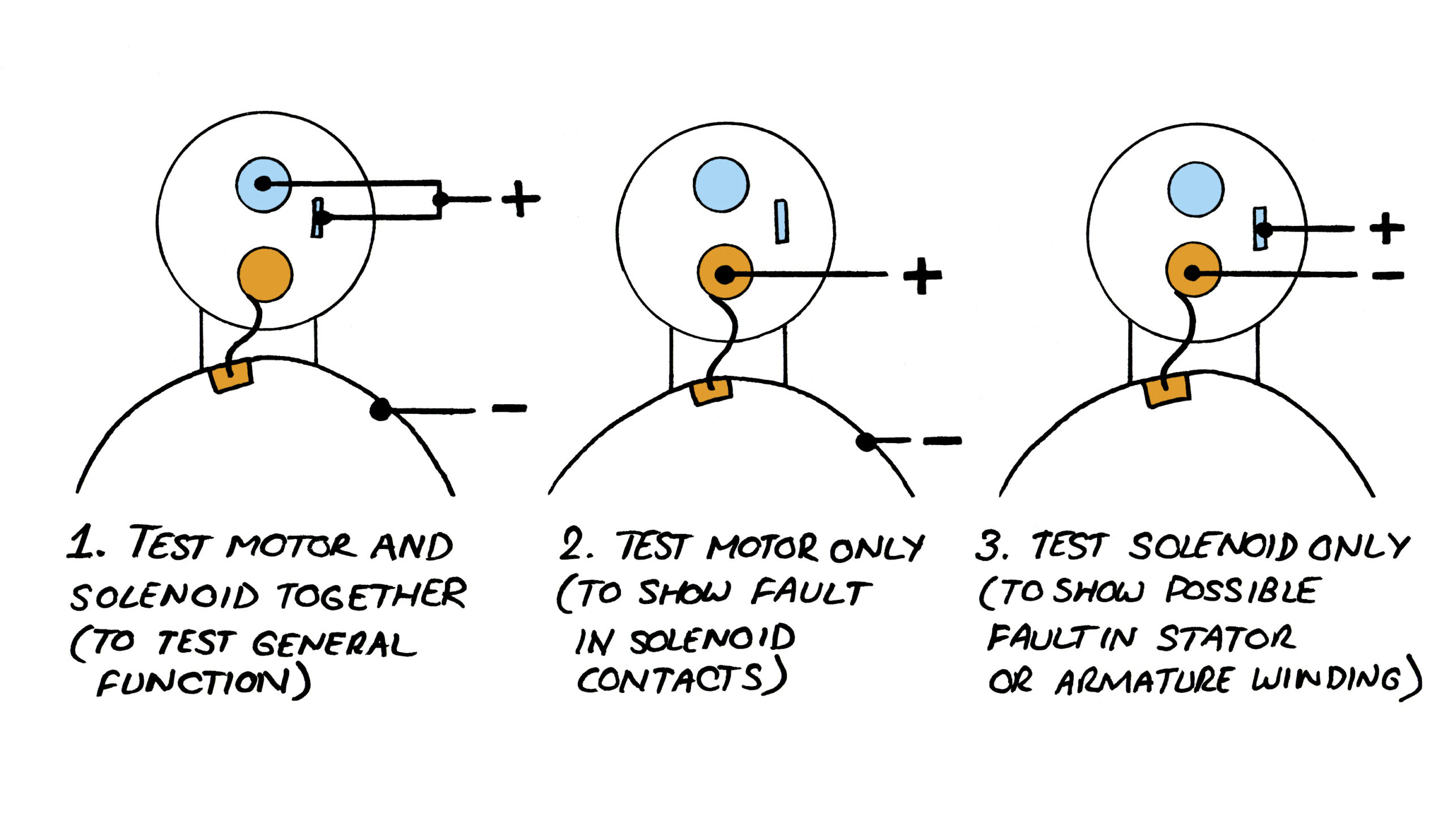
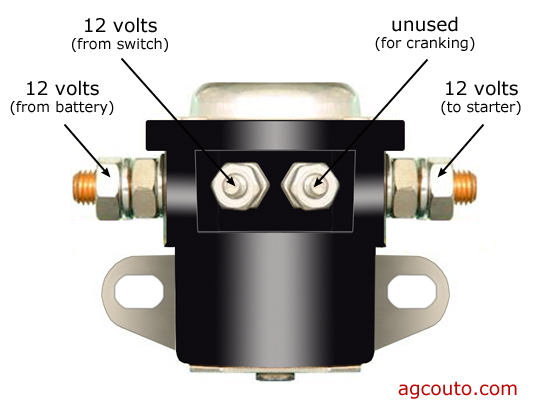
The Solution: To streamline the diagnostic process, it is crucial to implement a structured testing protocol. Start by ensuring that the battery is functioning correctly, as a low charge can often masquerade as a solenoid issue. Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage; it should ideally read around 12 volts. Next, carefully test the starter solenoid by following a step-by-step procedure. Begin by connecting a test light to the output terminal of the solenoid. Have a colleague turn the ignition while you observe the light. If it illuminates, power is reaching the solenoid, indicating that the issue may lie with the starter itself rather than the solenoid. This method not only saves time but also enhances customer satisfaction by reducing misdiagnosis.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Replacement Parts
The Problem: Sourcing reliable replacement parts for starter solenoids can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly in regions with limited access to quality automotive components. Many businesses struggle with the inconsistency in part quality, leading to frequent failures and customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, understanding the correct specifications for various vehicle models adds another layer of complexity, often resulting in incorrect orders and wasted resources.
The Solution: Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in automotive parts is essential. Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong track record of quality and reliability. Utilize platforms that offer comprehensive catalogs, allowing you to filter by vehicle make, model, and year. Additionally, consider investing in an inventory management system that tracks the performance of sourced parts. By analyzing failure rates and customer feedback, you can refine your sourcing strategy over time, ensuring that your business consistently stocks high-quality replacement parts that meet the needs of your clientele.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Testing Procedures
The Problem: In many automotive repair shops, the testing procedures for starter solenoids are often inefficient and time-consuming. Technicians may rely on outdated methods or lack proper tools, which can lead to extended downtimes and increased labor costs. This inefficiency not only impacts profitability but also affects customer trust and retention, as clients expect quick and effective service.
The Solution: To optimize testing procedures, consider investing in modern diagnostic tools that provide accurate readings with minimal effort. Tools such as digital multimeters and specialized starter solenoid testers can significantly enhance the efficiency of your testing process. Train your technicians on the latest testing techniques, emphasizing the importance of systematic approaches to diagnostics. Regularly review and refine your testing protocols based on performance metrics and feedback from your team. By streamlining your testing process, your shop can reduce labor costs, improve turnaround times, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction, positioning your business for long-term success in a competitive market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter solenoid test
What Are the Key Materials for Starter Solenoid Testing?
When selecting materials for starter solenoid testing, understanding the properties and performance characteristics of each material is essential. This guide analyzes four common materials used in this context: copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic composites.
How Does Copper Perform in Starter Solenoid Tests?
Copper is widely used in electrical applications due to its excellent conductivity and thermal properties. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and can withstand significant electrical loads, making it ideal for starter solenoids.
Pros: Copper’s primary advantage is its superior electrical conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer. It is also relatively easy to work with, allowing for straightforward manufacturing processes.
Cons: However, copper is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments, which can affect its longevity and performance. Additionally, it is relatively expensive compared to other metals.
Impact on Application: In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions may vary significantly, the corrosion resistance of copper can be a concern. International buyers should consider protective coatings to enhance durability.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Starter Solenoid Testing?
Aluminum is another popular choice due to its lightweight nature and good conductivity, though not as high as copper. It has a melting point of around 1,221°F (660°C) and offers decent resistance to corrosion, especially when anodized.

Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its weight, which can reduce overall component weight in automotive applications. Additionally, it is less expensive than copper, making it a cost-effective option.
Cons: The downside is that aluminum has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which may lead to efficiency losses in power transfer. It is also less durable under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East where high temperatures can affect material performance, aluminum’s thermal properties may be beneficial. However, buyers should ensure that the aluminum used meets relevant standards for conductivity and strength.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Starter Solenoid Testing?
Stainless steel is often selected for its durability and corrosion resistance. With a melting point of approximately 2,500°F (1,370°C), it can withstand extreme conditions, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Stainless steel’s resistance to rust and corrosion makes it ideal for environments with high moisture or exposure to chemicals. It also offers good mechanical strength.
Cons: The main disadvantage is its higher cost compared to aluminum and copper, along with more complex manufacturing processes due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: For B2B buyers in Europe, where compliance with strict material standards is common, stainless steel can provide peace of mind regarding durability and safety. Buyers should confirm that the stainless steel used complies with ASTM or DIN standards.
How Do Plastic Composites Fit into Starter Solenoid Testing?
Plastic composites are increasingly used in automotive applications due to their lightweight and insulating properties. They can withstand temperatures up to around 300°F (150°C) depending on the specific type of plastic.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and electrical insulation, which can enhance safety in electrical applications.
Cons: However, they may not offer the same mechanical strength as metals, making them less suitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, their thermal stability can be a concern in extreme environments.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, especially in regions like Brazil and Vietnam, where cost and weight are critical factors, plastic composites can be an attractive option. However, buyers must ensure that the materials meet relevant safety and performance standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Solenoid Testing
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter solenoid test | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections in solenoids | Superior electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components in solenoids | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Durable housings and components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic Composites | Insulating components in solenoids | Corrosion-resistant and lightweight | Less mechanical strength | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in starter solenoid testing, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter solenoid test
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Solenoids?
The manufacturing of starter solenoids involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards.
Material Preparation
The process begins with careful selection and preparation of materials. The primary components of a starter solenoid include copper for electrical connections, various alloys for the housing, and insulating materials. Suppliers often undergo rigorous testing to guarantee that materials comply with international standards like ISO 9001. This stage may involve cleaning, cutting, and shaping materials into appropriate sizes for subsequent processes.
Forming Techniques Utilized in Starter Solenoid Production
Forming techniques play a vital role in shaping the solenoid components. Common methods include stamping, machining, and die casting. Stamping is typically used for creating metal parts, while machining allows for precise shaping of components like the solenoid housing. Die casting is particularly beneficial for producing complex shapes and is often employed for parts that require high levels of durability and precision. Each of these methods must be executed under strict tolerances to ensure optimal functionality.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Starter Solenoids?
The assembly of starter solenoids is a meticulous process that combines various components into a fully functional unit. This stage usually involves:
- Winding the Coil: Copper wire is wound around a core to create the electromagnetic coil, which is essential for the solenoid’s operation.
- Integration of Components: The wound coil is then integrated with other components, including the housing, terminals, and plunger.
- Soldering and Fastening: Connections are soldered or fastened to ensure a secure electrical connection. This step is crucial for the solenoid’s performance and reliability.
Each assembly step must be performed in a clean environment to prevent contamination, which could lead to malfunctions.

Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used for Starter Solenoids?
Finishing processes are essential to enhance the solenoid’s durability and aesthetic appeal. Common techniques include:
- Electroplating: This process is often used to apply a protective layer to metal components, preventing corrosion and enhancing conductivity.
- Painting or Coating: Various coatings are applied to the outer housing to protect against environmental factors and improve appearance.
- Final Inspection: Before packaging, solenoids undergo final inspections to confirm that they meet all specifications and quality standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Starter Solenoids?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that starter solenoids perform reliably in their applications.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards like ISO 9001 are pivotal for manufacturers, as they outline the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards assures B2B buyers that the manufacturer has established effective processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for automotive applications may also apply.
How Are QC Checkpoints Structured in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Inspections during the manufacturing process help identify issues as they occur. Techniques such as visual inspections, measurements, and functional tests are employed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough examination is conducted to verify that the finished product meets all design specifications and quality benchmarks.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Starter Solenoids?
Testing methods are critical for assessing the performance and reliability of starter solenoids. Common approaches include:
- Electrical Testing: Solenoids are subjected to tests that measure electrical resistance and current flow. This ensures that they can handle operational demands.
- Functional Testing: Each solenoid is activated to confirm proper engagement and disengagement, simulating real-world conditions.
- Durability Testing: Solenoids may undergo stress testing to evaluate their performance under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or vibrations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. This can be accomplished through:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality assurance systems in place. This firsthand observation can provide invaluable insights into a supplier’s capabilities.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand testing methodologies, results, and any corrective actions taken to address issues.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an impartial assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can confirm compliance with international standards and industry-specific certifications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, necessitating thorough research to ensure compliance.
Moreover, cultural differences in business practices can impact negotiations and supplier relationships. Understanding local standards and expectations can help buyers establish trust and ensure a successful partnership.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for starter solenoids are intricate and require meticulous attention to detail. By understanding these processes and implementing robust verification strategies, B2B buyers can ensure they procure reliable and high-quality products for their applications.
Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter solenoid test’
To ensure a successful procurement process for starter solenoid testing equipment and services, this practical sourcing guide outlines key steps for B2B buyers. This checklist will help you assess your needs and identify reliable suppliers that meet your specifications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, clearly outline the technical specifications required for the starter solenoid tests. Consider the types of vehicles or machinery the tests will be conducted on, as well as the specific testing methods you will utilize.
– Key considerations: Voltage requirements, compatibility with various starter solenoids, and measurement accuracy.
– Impact: Clear specifications help in communicating your needs to suppliers, ensuring they can provide the right solutions.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in automotive testing equipment, particularly for starter solenoids. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of potential vendors.
– Sources: Industry publications, supplier databases, and recommendations from industry peers.
– Outcome: A well-researched supplier list increases the likelihood of finding vendors with the necessary expertise and product range.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making any commitments, verify that your potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality standards. Look for ISO certifications or other relevant industry standards that demonstrate their commitment to quality.
– Why it matters: Certifications ensure that the products you receive will meet safety and performance standards, reducing the risk of equipment failure.
– What to ask for: Request copies of certifications and inquire about their quality assurance processes.
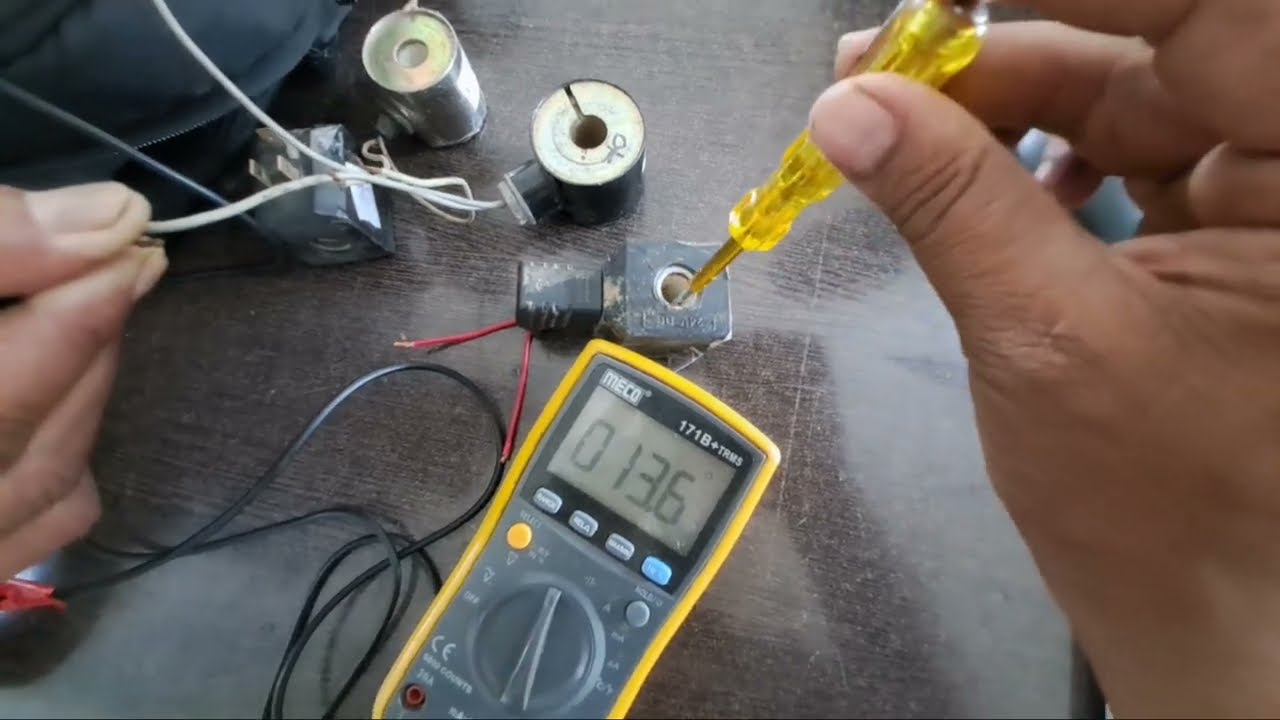

Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of their testing equipment to evaluate performance and compatibility with your specific needs. Testing the equipment firsthand allows you to assess quality and usability.
– How to proceed: Clearly communicate your requirements when requesting samples.
– Benefits: Hands-on evaluation helps mitigate risks associated with purchasing equipment that may not meet your expectations.
Step 5: Inquire About After-Sales Support
Assess the level of after-sales support provided by each supplier. Strong technical support and warranty offerings are crucial for maintaining testing equipment over time.
– What to look for: Availability of technical assistance, ease of contacting support, and warranty terms.
– Importance: Reliable after-sales service can significantly reduce downtime and ensure ongoing operational efficiency.
Step 6: Compare Pricing Structures
Analyze the pricing models of different suppliers, taking into account the total cost of ownership, which includes purchase price, maintenance costs, and potential shipping fees.
– How to approach: Request detailed quotes that break down costs to better understand pricing structures.
– Reasoning: A comprehensive understanding of costs will help you budget effectively and identify the best overall value.
Step 7: Check Customer Reviews and References
Before finalizing your decision, review customer feedback and request references from previous clients. Positive testimonials and case studies can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and product performance.
– What to ask: Inquire about the experiences of similar businesses or industries with the supplier.
– Benefits: Real-world experiences can illuminate potential issues or advantages that may not be apparent through formal channels.
Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
By following this sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding starter solenoid testing equipment, ultimately ensuring efficient operations and reliable testing outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter solenoid test Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Starter Solenoid Tests?
When sourcing starter solenoid tests, understanding the cost structure is crucial for informed decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing starter solenoids can significantly affect costs. Common materials include copper for electrical components and durable plastics or metals for housing. Sourcing high-quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to better performance and longevity, ultimately reducing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the expertise required. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, you might see increased pricing. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can reduce expenses, though it may also impact quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Understanding the manufacturing environment can help buyers evaluate the overall cost-effectiveness of a supplier.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling required for producing starter solenoids can be a significant initial investment. For custom designs, tooling costs can be substantial, and these costs are often amortized over production volumes.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet specifications and safety standards. While this may add to costs, it can prevent costly defects and returns, making it an essential investment for reliable sourcing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on distance, shipping method, and the mode of transport. International buyers must consider customs duties and import taxes, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and supplier negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions for Starter Solenoid Tests?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starter solenoid tests, particularly for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Higher volume orders often yield better per-unit pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their inventory capabilities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications or unique requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges and ensure that the supplier can meet their needs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry certifications or quality standards may command higher prices. However, investing in certified products can enhance reliability and reduce the risk of failures.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better quality assurance and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for international transactions. Different Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact overall costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices for Starter Solenoid Tests?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to significant savings.
-
Research Market Prices: Conduct thorough market research to understand the average prices for starter solenoid tests. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations and helps identify fair pricing.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate with buyers they view as long-term partners.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating costs, consider not just the purchase price but also factors like maintenance, warranty, and potential downtime costs. A slightly higher initial investment in quality may result in lower long-term expenses.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicate your needs and expectations to suppliers. Transparency can foster trust and lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Solicit quotes from multiple suppliers to create a competitive bidding environment. This can encourage suppliers to offer their best prices.
Conclusion
Sourcing starter solenoid tests involves a comprehensive understanding of cost components and pricing influencers. By strategically negotiating and considering the Total Cost of Ownership, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals. Always keep in mind that prices can vary based on market conditions and supplier dynamics, so continuous monitoring and relationship management are key to optimizing sourcing strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter solenoid test With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Starter Solenoid Test
In the realm of automotive diagnostics, the starter solenoid test is a common method for identifying issues related to vehicle starting systems. However, various alternative solutions exist that can also diagnose or address similar problems. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers in different regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Solenoid Test | Digital Multimeter Test | Relay Bypass Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy in diagnosing solenoid issues | Versatile for various electrical diagnostics | Quick indication of relay functionality |
| Cost | Low (basic tools needed) | Moderate (cost of multimeter) | Low (minimal tools required) |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate (requires some technical knowledge) | Moderate (requires understanding of electrical systems) | Easy (simple connections) |
| Maintenance | Minimal (occasional tool upkeep) | Moderate (calibration may be needed) | Low (no maintenance required) |
| Best Use Case | Identifying solenoid failures in starting systems | General electrical troubleshooting | Quick tests for relay functionality |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of a Digital Multimeter Test?
The digital multimeter test offers a versatile approach to diagnosing electrical problems in automotive systems. It measures voltage, current, and resistance, making it applicable for a wide range of issues beyond just the starter solenoid. The primary advantage of this method is its comprehensive nature, allowing technicians to troubleshoot various components simultaneously. However, it requires a certain level of expertise and understanding of electrical systems, which may pose a challenge for less experienced personnel. Additionally, while the initial cost of a multimeter is moderate, the need for calibration or advanced models can increase expenses.
How Does the Relay Bypass Test Compare?
The relay bypass test is an alternative method specifically designed to check the functionality of relays in starting systems. This technique involves bypassing the relay to see if the starter engages, providing a quick indication of whether the relay is the source of the problem. Its primary benefits include ease of implementation and low cost, as it often requires minimal tools and can be performed quickly. However, this method lacks the depth of diagnostics that a starter solenoid test or multimeter test provides, making it less suitable for comprehensive troubleshooting.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding on a diagnostic method for starter solenoid issues, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific needs, resources, and expertise. The starter solenoid test is ideal for accurate diagnosis of solenoid failures, while the digital multimeter test offers broader electrical troubleshooting capabilities. The relay bypass test serves well for quick checks but may not replace more detailed diagnostics. Ultimately, selecting the right solution will depend on the unique circumstances of the business, the technical skills of the staff, and the urgency of the diagnostic needs. By weighing these factors, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce downtime in their automotive service processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter solenoid test
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Testing a Starter Solenoid?
When assessing starter solenoids, understanding critical technical specifications is essential for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility and performance. Below are some key properties that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of starter solenoids is crucial for durability and performance. Common materials include high-grade steel and copper, which provide excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Selecting the right material grade ensures longevity and reliability, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance costs. -
Coil Resistance
Coil resistance is measured in ohms and indicates how much electrical resistance the solenoid coil has when energized. Typical values range from 0.5 to 3 ohms. Understanding the coil resistance is vital because it affects the solenoid’s ability to engage the starter motor effectively. A solenoid with too high resistance may not activate properly, leading to starting issues. -
Operating Voltage
Most automotive starter solenoids are designed to operate at 12 volts, although some applications may require 24 volts. It’s crucial for B2B buyers to match the operating voltage of the solenoid to the vehicle’s electrical system to prevent failures. Mismatched voltages can lead to overheating or inadequate performance. -
Torque Rating
The torque rating indicates the amount of rotational force the solenoid can exert to engage the starter motor. This rating is often measured in inch-pounds (in-lbs) or Newton-meters (Nm). A higher torque rating ensures that the solenoid can handle the demands of different engine sizes and conditions, which is important for buyers in diverse markets. -
Temperature Range
The temperature range specifies the environmental conditions under which the solenoid can operate effectively. It is typically expressed in degrees Celsius (°C). Buyers should ensure that the solenoid can withstand the temperature extremes common in their geographical markets, such as high heat in Africa or cold climates in Europe.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Associated with Starter Solenoid Testing?
Familiarity with industry terminology helps facilitate smoother transactions and better understanding between suppliers and buyers. Here are some essential trade terms related to starter solenoid testing:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to products made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle or component. For buyers, purchasing OEM starter solenoids ensures compatibility and adherence to quality standards, which can be particularly important for warranty considerations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or understocking, particularly in markets with variable demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing and other details for specific products. This process helps B2B buyers compare options and negotiate better terms, ensuring they get the best value for starter solenoids. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and obligations, which is crucial for successful cross-border trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead time is vital for planning inventory and ensuring that production schedules are met, especially in industries where downtime can be costly.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability in their respective markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter solenoid test Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting the Starter Solenoid Test Sector?
The starter solenoid test sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. Global drivers include an increased focus on vehicle reliability and performance, leading to a growing need for efficient diagnostic tools and testing methods. As automotive technology becomes more complex, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are seeking advanced testing solutions that can accurately diagnose issues with starter solenoids and related components. This trend is particularly evident in countries like Brazil and Vietnam, where the automotive market is rapidly evolving.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled diagnostic tools and mobile applications for real-time testing are gaining traction. These innovations facilitate remote diagnostics, allowing technicians to perform tests more efficiently and reduce downtime. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning in diagnostic equipment is enhancing the accuracy and speed of testing, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to improve operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
Moreover, global supply chain dynamics are affecting sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only high-quality products but also timely delivery and competitive pricing. As the demand for starter solenoid testing rises, suppliers that can adapt to these market dynamics will be better positioned to capture market share.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Starter Solenoid Test Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the starter solenoid test sector. As environmental concerns grow, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental impact. This involves sourcing materials that are not only high-quality but also environmentally friendly. For instance, manufacturers are exploring the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes to create starter solenoids and related testing equipment.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are seeking assurance that their suppliers uphold labor rights and environmental standards throughout their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade for ethical sourcing are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. These certifications not only enhance a supplier’s credibility but also align with the values of socially responsible businesses.
The adoption of green practices in manufacturing and sourcing not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to a growing segment of consumers who prioritize sustainability. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are increasingly stringent regarding environmental impact and sustainability practices.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Starter Solenoid Test Sector?
The starter solenoid test sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, testing methods were rudimentary, often relying on manual checks and basic electrical tests. However, as automotive technology advanced, so too did the methods for testing starter solenoids. The introduction of digital multimeters and specialized diagnostic tools revolutionized the testing process, allowing for more precise measurements and quicker diagnostics.
In recent years, the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT and AI has transformed the landscape further. These innovations enable real-time monitoring and predictive diagnostics, significantly enhancing the efficiency of the testing process. As the automotive industry continues to innovate, the starter solenoid test sector will likely see continued advancements, catering to the needs of increasingly sophisticated vehicles and demanding consumers.
Illustrative image related to starter solenoid test
As international B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and the historical context of the starter solenoid test sector will be crucial in making informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter solenoid test
-
How do I troubleshoot a faulty starter solenoid?
To troubleshoot a faulty starter solenoid, begin by checking the battery’s voltage to ensure it’s adequately charged (around 12 volts). Next, locate the starter solenoid on your vehicle, usually near the starter motor. Listen for a clicking sound when attempting to start the vehicle; if there is no sound, the solenoid may not be engaging. Use a test light to check for current at the solenoid terminals; if power is present but the starter doesn’t engage, the solenoid is likely defective and may need replacement. -
What is the best method to test a starter solenoid?
The most effective method to test a starter solenoid involves using a multimeter or test light. First, check for voltage at the solenoid terminals when the ignition key is turned. If there’s voltage at the input terminal but not at the output terminal when the key is turned, the solenoid is likely faulty. Additionally, you can perform a resistance test by checking the continuity between the terminals; a lack of continuity indicates a failed solenoid. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing starter solenoids internationally?
When sourcing starter solenoids internationally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, product quality certifications, and compliance with local regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s experience in the automotive industry and their ability to provide after-sales support. Additionally, understand the logistics involved, including shipping times and costs, customs duties, and potential tariffs that may apply when importing parts into your region. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter solenoids?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter solenoids can vary significantly depending on the supplier and their production capabilities. Generally, MOQs can range from 50 to 500 units for standard models. It’s advisable to negotiate with suppliers, especially if you are looking to source a smaller quantity for testing or pilot projects. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for established business relationships or bulk orders. -
How can I ensure the quality of starter solenoids from my supplier?
To ensure the quality of starter solenoids, request samples before placing a bulk order and conduct thorough testing for functionality and durability. Verify the supplier’s quality assurance processes, such as ISO certifications or adherence to industry standards. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or utilizing third-party inspection services to assess production practices and product quality prior to shipment. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter solenoids?
Payment terms when sourcing starter solenoids can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and the relationship established. Common payment structures include a deposit (typically 30%) upfront with the balance due upon shipment. Some suppliers may offer net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) for established customers. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment methods, whether by bank transfer, letter of credit, or other secure options to mitigate financial risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter solenoids?
When importing starter solenoids, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance processes. Determine whether air freight or sea freight is more cost-effective for your needs. Also, familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including necessary documentation such as bills of lading, invoices, and certificates of origin. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process and ensure compliance with local laws. -
Can starter solenoids be customized to fit specific vehicle models?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for starter solenoids to fit specific vehicle models or performance requirements. Customization may involve modifications to size, electrical specifications, or mounting configurations. When considering customized solenoids, communicate clearly with your supplier about your requirements and ensure they can meet the necessary specifications. Be prepared for longer lead times and potentially higher costs associated with custom manufacturing.
Top 3 Starter Solenoid Test Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. LinkedIn – Starter Solenoid
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when the ignition key is turned to the ‘start’ position. It controls the high current needed to operate the starter motor safely, ensuring clean engagement and disengagement to reduce wear and tear. Symptoms of a bad starter solenoid include clicking noises, failure to crank, difficulty starting the engine, decreased acce…
2. WikiHow – Starter Solenoid Guide
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The starter solenoid is a mechanism that transmits electrical current from the battery to the starter, engaging the starter motor to start the engine when the key is turned. It is typically located near the engine and transmission, attached to the starter, and has two terminals. A clicking sound when the key is turned indicates the solenoid is engaging, while no sound may suggest a malfunction. Te…
3. Del City – Essential Tools for Electrical Work
Domain: blog.delcity.net
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Solenoid, Multimeter, Jumper Cables (optional), Protective Eyewear and Gloves (recommended)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter solenoid test
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in the Starter Solenoid Market?
In the ever-evolving automotive sector, understanding the intricacies of starter solenoid testing is crucial for international B2B buyers. Effective strategic sourcing not only ensures the procurement of high-quality components but also enhances operational efficiency. By leveraging reliable suppliers and engaging in thorough testing methods, businesses can mitigate risks associated with faulty solenoids, ultimately reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Investing in strategic sourcing for starter solenoids fosters long-term partnerships with trusted manufacturers and suppliers. This approach not only secures better pricing and availability but also promotes access to innovative technologies that can improve product performance. As the demand for reliable automotive components continues to grow across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, aligning your sourcing strategy with quality standards will position your business for success.
What Should B2B Buyers Do Next?
As you move forward, consider evaluating your current supply chain and identifying opportunities for improvement. Engage with reputable suppliers who understand your regional market dynamics and can provide tailored solutions. By prioritizing strategic sourcing in your procurement strategy, you will not only enhance product reliability but also drive your business growth in the competitive automotive landscape. Embrace this opportunity to optimize your operations and ensure your business is well-prepared for the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.