Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does it cost to change a starter
In the dynamic landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding how much it costs to change a starter is crucial for international B2B buyers. Whether you are a supplier, a mechanic, or a fleet manager, sourcing reliable starter replacements can be a significant challenge, especially when navigating diverse markets like those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide delves into the intricacies of starter replacement costs, providing an in-depth analysis of various factors influencing pricing, such as vehicle type, labor costs, and regional market conditions.
By exploring the different types of starters, their applications across various vehicles, and the nuances of supplier vetting, this comprehensive resource equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. We will also highlight the importance of understanding local regulations and market trends that can impact the availability and pricing of starter components.
With actionable insights and a clear framework, this guide empowers businesses to efficiently navigate the global market for starter replacements. From assessing repair versus replacement options to identifying cost-effective suppliers, you will gain valuable strategies that can enhance your operational efficiency and reduce unexpected expenses. Ultimately, this resource is designed to streamline your sourcing process and bolster your purchasing power in a competitive environment.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 How Much Does It Cost To Change A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how much does it cost to change a starter
- Understanding how much does it cost to change a starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how much does it cost to change a starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does it cost to change a starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does it cost to change a starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does it cost to change a starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does it cost to change a starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does it cost to change a starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does it cost to change a starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does it cost to change a starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does it cost to change a starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does it cost to change a starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does it cost to change a starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how much does it cost to change a starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Replacement | Cost-effective, uses OEM or aftermarket parts. | General automotive repair shops. | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Limited warranty. |
| Remanufactured Starter | Refurbished parts, often with a warranty. | Fleet maintenance, budget-conscious shops. | Pros: Environmentally friendly; Cons: Quality can vary. |
| High-Performance Starter | Enhanced durability and performance for demanding applications. | Racing teams, heavy-duty vehicles. | Pros: Improved reliability; Cons: Higher cost. |
| Integrated Starter/Alternator | Combines starter and alternator functions in one unit. | Electric vehicles, hybrids. | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Complex installation. |
| DIY Starter Kits | Includes all necessary components for self-replacement. | Automotive enthusiasts, small repair shops. | Pros: Cost-saving; Cons: Requires technical skill. |
What Are the Characteristics of a Standard Replacement Starter?
A standard replacement starter is typically the most budget-friendly option for B2B buyers. These starters utilize either original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts or aftermarket components that meet OEM specifications. They are suitable for general automotive repair shops that prioritize cost efficiency. Buyers should consider the warranty offered, as it can vary significantly, impacting long-term value.
How Do Remanufactured Starters Benefit B2B Buyers?
Remanufactured starters are refurbished components that often come with a warranty, making them a popular choice among fleet maintenance services and budget-conscious repair shops. These starters undergo rigorous testing and rebuilding processes to ensure reliability. B2B buyers should evaluate the reputation of the remanufacturer to ensure they are receiving quality parts, as the quality can vary across suppliers.
What Makes High-Performance Starters Ideal for Specific Applications?
High-performance starters are designed for demanding applications, such as racing or heavy-duty vehicles. These starters feature enhanced durability and are built to withstand extreme conditions. They are primarily used by racing teams and businesses that operate heavy machinery. While they offer improved reliability, B2B buyers must be prepared for a higher upfront cost and ensure that the performance benefits justify this investment.
Why Choose an Integrated Starter/Alternator for Modern Vehicles?
Integrated starter/alternator units combine the functions of both components, providing a space-saving solution for electric and hybrid vehicles. This design simplifies installation and reduces the number of parts needed, making it appealing for manufacturers and repair shops specializing in modern vehicle technologies. However, the complexity of installation can be a drawback, so B2B buyers should ensure their technicians have the necessary expertise.
What Are the Advantages of DIY Starter Kits for Small Shops?
DIY starter kits are designed for automotive enthusiasts and small repair shops looking to save on labor costs. These kits include all necessary components for a complete starter replacement, allowing buyers to take control of the repair process. However, the requirement for technical skill can be a limiting factor for some buyers. Assessing the skill level of available personnel is crucial when considering this option.
Key Industrial Applications of how much does it cost to change a starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how much does it cost to change a starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Estimating costs for starter replacements in service centers | Enables accurate budgeting and pricing for repair services | Availability of parts, labor costs, and local market rates |
| Fleet Management | Budgeting for starter replacements across a fleet of vehicles | Reduces downtime and ensures operational efficiency | Bulk purchasing options, warranty terms, and service agreements |
| Construction Equipment | Managing starter replacement costs for heavy machinery | Minimizes equipment failure and enhances project timelines | Equipment compatibility, supplier reliability, and service support |
| Transportation Logistics | Assessing starter replacement costs for delivery vehicles | Ensures timely deliveries and maintains customer satisfaction | Geographic availability of parts, local labor costs, and repair times |
| Agriculture | Evaluating starter replacement costs for farming machinery | Enhances productivity and reduces crop loss due to machinery failure | Seasonal demand considerations, sourcing from local suppliers, and part compatibility |
How Can Automotive Repair Shops Benefit from Understanding Starter Replacement Costs?
Automotive repair shops must accurately estimate the costs associated with starter replacements to provide competitive pricing. By understanding the range of costs, from parts to labor, repair shops can better manage customer expectations and maintain profitability. This is especially critical in regions where economic conditions may affect consumer spending. Furthermore, sourcing quality starter components that offer reliability can enhance the shop’s reputation and customer loyalty.
What Are the Implications for Fleet Management?
For fleet management, knowing the costs of changing starters is essential for effective budgeting and maintenance planning. Fleet operators can calculate the total cost of ownership, factoring in the frequency of starter replacements and associated labor costs. By proactively managing these expenses, businesses can reduce vehicle downtime, ensuring that logistics operations run smoothly. Additionally, establishing relationships with suppliers for bulk parts can lead to cost savings and improved service agreements.
How Does Understanding Costs Aid Construction Equipment Management?
In the construction sector, heavy machinery often relies on starters for optimal performance. Understanding the costs involved in replacing starters allows project managers to allocate budgets effectively and avoid project delays due to equipment failure. Timely maintenance and replacement of starters can prevent costly downtime, ensuring that projects are completed on schedule. Buyers should consider sourcing from local suppliers to minimize lead times and ensure compatibility with specific machinery.
Why Is Cost Assessment Critical for Transportation Logistics?
In transportation logistics, the reliability of delivery vehicles is paramount. Assessing the costs of starter replacements helps logistics companies maintain their fleets efficiently, ensuring that deliveries are made on time. This is crucial for customer satisfaction and retention. Companies should evaluate local labor costs and the geographic availability of parts to minimize delays. Establishing strong relationships with trusted suppliers can also provide insights into cost-saving opportunities.
How Does Cost Awareness Impact Agricultural Machinery Operations?
In agriculture, the efficiency of farming machinery is directly tied to productivity. Understanding the costs associated with changing starters helps farmers plan for maintenance and avoid unexpected machinery failures during critical planting or harvesting seasons. By sourcing parts from local suppliers, farmers can ensure timely repairs, which is vital for minimizing crop loss. Additionally, awareness of seasonal demand for parts can inform purchasing strategies, allowing farmers to secure the best prices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how much does it cost to change a starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Unpredictable Costs in Starter Replacement
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in automotive repair or fleet management, often face the challenge of unpredictable costs associated with starter replacements. The price can vary significantly based on the make and model of the vehicle, availability of parts, and labor costs in different regions. For instance, a simple starter replacement for a common sedan might cost less than one for a luxury SUV, leading to frustration when budgeting for repairs. Additionally, fluctuating exchange rates and tariffs can impact the overall expense, making it difficult for businesses to predict their operational costs accurately.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
The Solution: To effectively manage and mitigate these unpredictable costs, B2B buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers and service providers. By comparing prices across various vendors, businesses can identify the most cost-effective options. It’s also beneficial to create a standardized parts list based on the types of vehicles in your fleet, which can help in negotiating bulk purchase discounts. Utilizing technology, such as inventory management systems, can assist in tracking part availability and pricing trends, thus enabling more informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, consider investing in training programs for in-house mechanics to handle common starter issues, which can reduce labor costs and enhance operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Identifying the True Cause of Starter Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties in diagnosing the root cause of starting issues. A vehicle may exhibit symptoms that suggest a faulty starter, but in reality, the problem could stem from other components, such as the battery or ignition system. This misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary replacement costs and extended downtime, which is particularly detrimental for businesses relying on a fleet for operational activities. The inability to accurately pinpoint the issue can result in wasted resources and frustration.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should implement a systematic troubleshooting process before committing to a starter replacement. This involves conducting thorough checks of the battery, fuses, and electrical connections to rule out other potential issues. Providing training for technicians on how to use diagnostic tools effectively can further enhance the accuracy of assessments. Additionally, investing in high-quality diagnostic equipment can facilitate quicker and more reliable evaluations, ensuring that businesses only replace what is genuinely faulty. By adopting these practices, companies can save on unnecessary expenditures and reduce vehicle downtime.
Scenario 3: Managing Labor Costs for Starter Replacements
The Problem: Labor costs can be a significant factor when replacing starters, especially for complex vehicles that require extensive disassembly for access. B2B buyers in the automotive service industry may find that skilled labor is not only scarce but also increasingly expensive. This can create challenges in maintaining profitability while offering competitive pricing for starter replacement services. Consequently, businesses may struggle to balance cost efficiency with the quality of service provided.
The Solution: One effective strategy for managing labor costs is to streamline the starter replacement process through standardized procedures and training programs. Developing detailed service manuals and checklists can help technicians perform replacements more efficiently. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as service scheduling software, can optimize workflow and reduce idle time. By analyzing the time taken for various starter replacements across different vehicle types, businesses can identify best practices and improve efficiency. Furthermore, consider fostering partnerships with technical training institutions to ensure a steady pipeline of skilled technicians. This proactive approach not only helps control labor costs but also enhances service quality and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how much does it cost to change a starter
When considering the cost of changing a starter, material selection plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance, durability, and suitability of the starter components. Below is an analysis of common materials used in starter construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Starters?
1. Steel
Steel is often used for the housing and structural components of starters due to its strength and durability.
- Key Properties: High tensile strength, good fatigue resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance when treated.
- Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive, widely available, and can be easily machined to precise specifications. It provides excellent structural integrity, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
- Cons: Steel can be prone to rust if not properly coated or treated, which can affect longevity. It is also heavier compared to some alternatives, which may impact overall vehicle weight.
- Impact on Application: Steel starters can handle a wide range of temperatures but may not perform well in highly corrosive environments without protective coatings.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM or DIN is essential, especially in regions with varying environmental conditions, such as Africa and South America.
2. Aluminum
Aluminum is commonly used for starter components where weight savings are critical.
- Key Properties: Lightweight, good corrosion resistance, and decent thermal conductivity.
- Pros: Aluminum is lighter than steel, which can improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. It also resists corrosion, making it suitable for humid or coastal environments.
- Cons: Aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may not offer the same level of strength under high-stress conditions. It is also more challenging to machine precisely.
- Impact on Application: Aluminum starters can perform well in moderate temperature ranges but may be less effective in extreme heat compared to steel.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards for automotive applications, particularly in regions like the Middle East where heat resistance is crucial.
3. Copper
Copper is often used in electrical components of starters, such as wiring and contacts.
- Key Properties: Excellent electrical conductivity, good thermal conductivity, and moderate corrosion resistance.
- Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient electrical performance, which is critical for starter operation. It is also relatively easy to work with and can be formed into various shapes.
- Cons: Copper can be expensive and may corrode if not properly treated or insulated. It is also heavier than some alternatives.
- Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for electrical connections but may require protective coatings to prevent oxidation, especially in humid environments.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with electrical standards is vital, and buyers should be aware of the varying quality of copper used in different regions.
4. Plastic Composites
Plastic composites are increasingly being used for non-structural components of starters, such as housings and insulators.
- Key Properties: Lightweight, good insulation properties, and resistance to corrosion.
- Pros: Plastic composites are highly resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity. They are also lighter than metals, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction.
- Cons: They may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals and can be less durable under mechanical stress.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for applications where insulation and weight are prioritized, but not ideal for high-stress components.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the thermal and mechanical properties of plastics to ensure they meet the demands of specific environments, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starters
| Material | Typical Use Case for how much does it cost to change a starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components and housing for starters | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Aluminum | Lightweight starter components for fuel efficiency | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and lower strength | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical connections and contacts in starters | Superior electrical conductivity | Expensive and prone to corrosion | High |
| Plastic Composites | Non-structural components like housings and insulators | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower temperature tolerance | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in starter construction, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how much does it cost to change a starter
What Are the Key Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Automotive Starters?
The manufacturing of automotive starters involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets the necessary performance and reliability standards. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved in the manufacturing process:
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality raw materials are essential for producing durable starters. Typically, manufacturers use materials such as steel for the housing, copper for windings, and high-grade plastics for certain components. These materials undergo rigorous testing to confirm their mechanical properties and electrical conductivity.
Once selected, the materials are cut and shaped according to specific design requirements. This may involve techniques such as laser cutting or stamping to ensure precision. Quality assurance begins here, as initial inspections (Incoming Quality Control, IQC) are conducted to verify that materials meet specifications.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Starter Production?
After material preparation, the next stage involves forming the components. Common techniques include:
Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
- Die Casting: This is often used for the starter housing, allowing for complex shapes and superior surface finishes.
- Injection Molding: Used for plastic components, ensuring they are produced with high precision and consistency.
- Machining: Critical for creating components like the armature and solenoid, where tight tolerances are crucial for performance.
Each of these forming techniques requires careful monitoring to maintain quality. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) checkpoints are established to inspect the forming processes, ensuring that any deviations from specifications are addressed immediately.
How Are Starter Components Assembled?
The assembly stage involves combining all the individual components into a functional starter. This is typically performed in a clean, controlled environment to prevent contamination. Key steps in the assembly process include:
- Component Integration: Each part, such as the solenoid, armature, and drive gear, is carefully fitted together. Precision is vital here; misalignment can lead to failure.
- Wiring and Connections: Electrical connections are made with care to ensure reliable performance. This involves soldering and crimping wires to the appropriate terminals.
- Final Assembly Checks: Before moving to the next stage, each starter undergoes a preliminary inspection to ensure that all components are correctly installed and secured.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Starters?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and performance of starters. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear. This may involve electroplating or powder coating, depending on the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Final Testing: Starters are subjected to various tests, including electrical testing to ensure proper functionality and mechanical testing to confirm durability under load.
Final Quality Control (FQC) checks are conducted at this stage, verifying that each starter meets international and industry-specific standards before it is packaged for distribution.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Starter Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the automotive industry, especially for components like starters that are critical to vehicle operation. Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
In addition to ISO standards, automotive components may also need to comply with specific industry standards like:
- CE Marking: This indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for components used in specific applications, ensuring that products meet the performance criteria set by the American Petroleum Institute.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all specifications.
Common testing methods employed include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that the starter operates correctly under various conditions.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the durability and reliability of the starter under operational stresses.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers looking to source automotive starters should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are some actionable insights:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Look for adherence to ISO 9001 and other relevant standards during these audits.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from testing and inspections. Review these reports to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly beneficial for international buyers who may face challenges in verifying local suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of certain nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements for automotive components. Ensure that the supplier understands and complies with the regulations specific to your market.
- Cultural Differences: Variations in quality perception and practices can exist across cultures. Establish clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Understanding the complete supply chain can help identify potential quality issues early. Request information about the sourcing of materials and any subcontractors involved in the manufacturing process.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing automotive starters and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how much does it cost to change a starter’
To assist B2B buyers in understanding the costs associated with changing a starter, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure informed procurement decisions. By following this checklist, buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of starter replacement, whether they are sourcing parts or hiring services.
Step 1: Assess Your Vehicle’s Requirements
Understanding the specific make, model, and year of your vehicle is crucial for accurate cost estimation. Different vehicles have varying starter designs, accessibility, and associated labor costs. Gather detailed vehicle specifications to facilitate accurate comparisons and avoid miscommunications with suppliers.
Step 2: Define Your Budget
Establish a clear budget for both parts and labor. Starter replacement costs can range significantly, with parts averaging from $50 to over $350 and labor potentially exceeding $1,100. Identifying your financial limits helps narrow down options and ensures you remain within budget throughout the procurement process.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Options
Before selecting a supplier, conduct thorough research on potential vendors. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation in the automotive parts industry and positive reviews from previous customers. This evaluation can include:
– Requesting references from other businesses in your region or industry.
– Reviewing case studies that demonstrate the supplier’s reliability and quality of service.
Step 4: Verify Quality and Certification Standards
Ensure that the starters and replacement parts meet industry standards and certifications. Quality parts are essential for performance and longevity, preventing future issues. Ask suppliers for documentation that proves compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO or other automotive certifications.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to compare costs effectively. Ensure that each quote includes:
– Breakdown of costs for parts and labor.
– Warranties or guarantees on parts, which can provide added security in your investment.
Evaluating quotes helps identify the best overall value rather than just the lowest price.
Step 6: Consider Labor Costs and Expertise
If hiring a mechanic, assess their experience and expertise with your specific vehicle model. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and the mechanic’s qualifications. Ensure the mechanic can provide a detailed estimate that includes time and any additional services that may be required.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Testing
Once you’ve procured the starter, plan for its installation and subsequent testing. Ensure that the mechanic or technician follows proper installation procedures to avoid further issues. After installation, conduct thorough testing to confirm the starter operates correctly and resolves the initial starting problem.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding the costs of changing a starter, ensuring a smoother procurement process and reliable vehicle performance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how much does it cost to change a starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Changing a Starter?
When assessing the costs associated with changing a starter, several key components contribute to the overall expense. Primarily, the materials involved, which include the starter itself, wiring, and any other necessary components, can range significantly based on the vehicle’s make and model. For instance, a standard starter may cost between $80 to $350, while specialized or luxury vehicle starters could exceed $500.
Labor costs are another significant component. The complexity of the installation can vary widely; simpler jobs may take less than an hour, while more intricate installations could require several hours, leading to labor costs that can range from $150 to over $1,100. This variance is crucial for international buyers to understand, as labor rates differ greatly across regions, particularly in Africa and South America.
Additional costs include manufacturing overhead, which encompasses the general expenses a supplier incurs while producing a starter. This could involve costs related to factory operations, employee salaries, and utilities. Moreover, tooling costs may apply if specialized tools are needed for installation or repair.
Quality assurance (QC) processes also influence pricing. Suppliers that invest in rigorous QC measures to ensure reliability and safety may charge more, but they often provide better long-term value. Logistics costs, including shipping and handling, must also be factored in, especially for international transactions where tariffs and customs duties can apply.
What Influences the Price of Starter Replacement?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starter replacement. Volume or Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) plays a crucial role; bulk purchases can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate these terms, particularly when sourcing from suppliers in different countries, to maximize cost efficiency.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
Specifications and customization also affect pricing. Custom starters designed for specific vehicle models may incur additional costs compared to standard replacements. Furthermore, the choice of materials can impact durability and performance, with high-quality components generally commanding higher prices.
The supplier’s reputation and certifications also come into play. Suppliers with established quality standards and certifications may charge more, but they often provide a reliable product that can reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over time. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers; these terms dictate responsibility for shipping costs and risks, which can significantly influence the final price.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs When Changing a Starter?
International B2B buyers should adopt several strategies to optimize costs when changing a starter. First, conducting thorough negotiations with suppliers can lead to better pricing, especially when discussing bulk orders or long-term partnerships. Establishing clear communication regarding expectations can enhance supplier relationships and potentially yield discounts.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
Buyers should also consider the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the upfront costs. Investing in higher-quality starters may lead to fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs over time. Additionally, understanding regional market dynamics can provide insights into labor and material costs, helping buyers make informed decisions.
Lastly, awareness of pricing nuances specific to their regions—such as currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local labor rates—can significantly impact overall costs. For instance, buyers in Brazil or Nigeria should be cognizant of local economic conditions that could affect pricing and availability.
Disclaimer on Pricing Estimates
It is important to note that the prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on multiple factors, including market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific vehicle requirements. Therefore, it is advisable for buyers to conduct their own research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how much does it cost to change a starter With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Starter Replacement Costs
When evaluating the financial implications of changing a starter, it’s essential to consider various alternatives that can serve similar functions. This analysis will focus on comparing the costs associated with replacing a starter against two viable alternatives: repairing the existing starter and utilizing a jump-starting solution. Each option has unique benefits and drawbacks, which can significantly impact the total cost of ownership and operational efficiency for businesses.
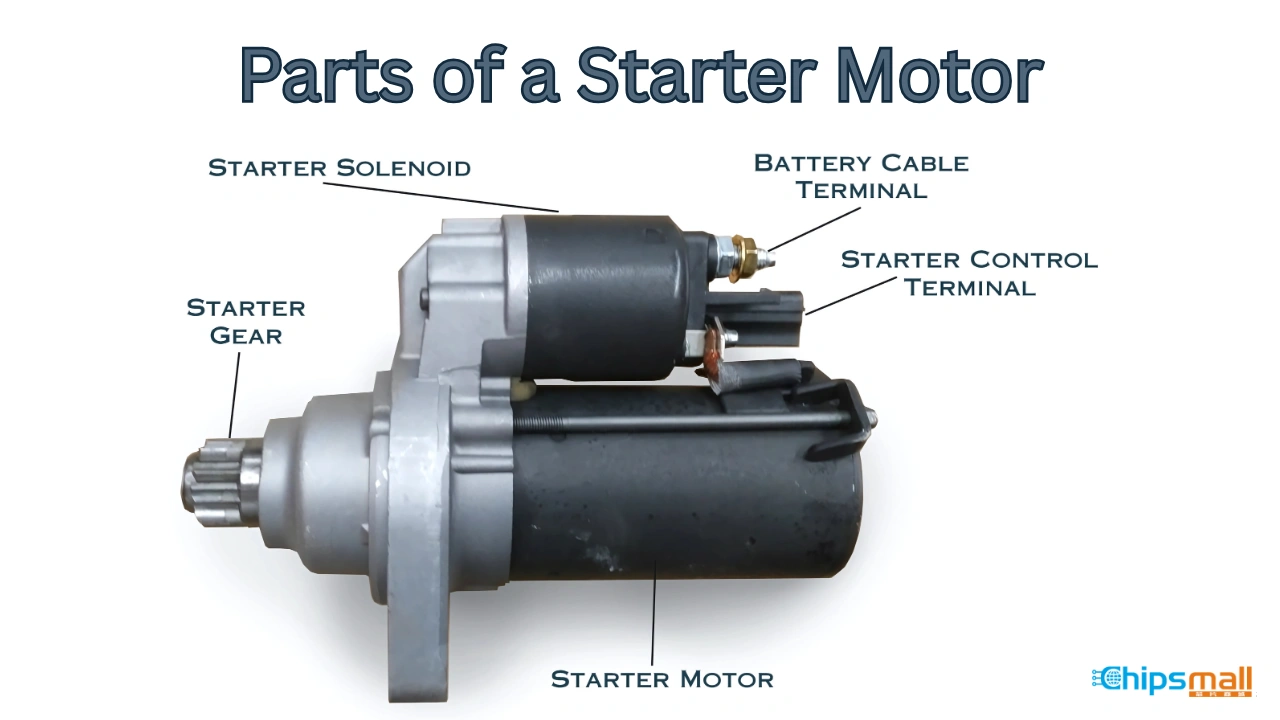
Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
| Comparison Aspect | How Much Does It Cost To Change A Starter | Repair Existing Starter | Jump-Starting Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Restores full functionality | May restore partial functionality | Temporary solution for immediate start |
| Cost | $150 – $1,100 (including parts and labor) | $50 – $350 (parts only) | $20 – $50 (for jump cables) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional mechanic | DIY possible with tools | Very easy, requires minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Minimal once replaced | Ongoing checks needed | None; only use when needed |
| Best Use Case | Long-term reliability for vehicles | Cost-effective for minor issues | Emergency starts or temporary fixes |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Repairing an Existing Starter?
Repairing an existing starter can be a cost-effective solution for minor issues. The average cost for repairs typically ranges from $50 to $350, depending on the extent of the damage. This approach is beneficial for businesses looking to minimize upfront costs while still addressing starter problems. However, repairs may not always restore full functionality, leading to potential recurring issues. Moreover, if the starter has multiple internal failures, the cost and time involved in repairs may exceed that of a full replacement.
How Does a Jump-Starting Solution Compare?
Jump-starting a vehicle can be an immediate, low-cost alternative for getting a vehicle operational without replacing or repairing the starter. The cost of jump-starting equipment, such as jumper cables, is generally between $20 and $50. This method is particularly useful in emergency situations or when the vehicle’s battery is suspected to be the main issue. However, jump-starting does not resolve underlying issues with the starter, and repeated reliance on this method could lead to further complications down the line. Additionally, using a jump-start may not be feasible in all scenarios, especially if the vehicle is in a location that makes access difficult.
How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Decision?
When choosing the most suitable solution for starter issues, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational needs, the frequency of vehicle use, and the potential for future starter problems. For companies with a fleet of vehicles, investing in new starters may offer long-term reliability and reduced downtime. Conversely, for businesses with occasional use vehicles, repairs or jump-starting solutions may provide a more cost-effective approach without the commitment of a full replacement. Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs associated with each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their budgetary and operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how much does it cost to change a starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties Related to Starter Replacement Costs?
Understanding the technical properties associated with starter replacements is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a starter motor can significantly influence its durability and performance. Common materials include high-grade steel for housing and copper for windings. Higher-grade materials generally lead to better heat resistance and longevity, which is essential for minimizing replacement frequency and costs in the long run. -
Torque Specifications
Torque specifications refer to the exact amount of force needed to secure the starter to the engine. Adhering to OEM torque specifications is critical for ensuring optimal performance and avoiding damage. Incorrect torque can lead to starter failure, necessitating costly repairs or replacements, which can disrupt operations for businesses relying on their vehicles. -
Compatibility and Fitment
Compatibility with specific vehicle makes and models is a vital property. Starters designed to fit various vehicles must meet stringent size and connection requirements. Understanding fitment ensures that businesses do not face delays or additional costs due to incorrect parts being ordered. -
Electrical Ratings
This includes the voltage and amperage ratings of the starter motor. Starters typically operate at 12V, but understanding the amperage requirements is essential for ensuring compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. Mismatched ratings can lead to starter failure or inefficient operation, impacting overall vehicle performance. -
Service Life Expectancy
The expected lifespan of a starter, often measured in miles or years, is another critical property. A starter with a longer service life can justify a higher initial investment, as it reduces the frequency of replacements and associated labor costs. Businesses should weigh the service life against the purchase price to determine the best value.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Relevant to Starter Replacement Costs?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common terms related to starter replacement costs:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM parts are made by the same manufacturer that produced the original parts for a vehicle. While they tend to be more expensive, they offer guaranteed compatibility and reliability, which can be crucial for businesses seeking to minimize downtime. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers, especially those managing inventory, as it can affect cash flow and stock levels. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production costs and market demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing information for specific products. This term is essential for B2B buyers who want to compare costs and negotiate better deals. Providing detailed specifications can lead to more accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping costs and risk management. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for companies involved in cross-border trade, ensuring clarity in logistics and reducing potential disputes. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates the time frame during which a manufacturer will cover repairs or replacements for defects. A longer warranty can enhance buyer confidence and provide financial protection against unforeseen starter failures. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are produced by third-party manufacturers rather than the original equipment manufacturer. These parts are typically less expensive but may vary in quality. B2B buyers must assess the trade-off between cost savings and potential risks associated with aftermarket components.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and ultimately optimize their operations when it comes to starter replacements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how much does it cost to change a starter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Starter Replacement Costs?
The market for starter replacements is influenced by several global drivers, particularly the increasing complexity of automotive technology and the rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs). As more vehicles incorporate advanced starter systems, including those used in hybrid and electric models, international B2B buyers must stay abreast of the evolving components and technologies that affect replacement costs. Additionally, fluctuations in raw material prices due to global supply chain disruptions can lead to increased costs for starter components, making it essential for buyers to engage in proactive sourcing strategies.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as the use of digital platforms for parts procurement and the integration of supply chain management software, are reshaping how businesses source starter parts. These technologies facilitate better inventory management, allowing companies to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands. Moreover, the rise of data analytics enables businesses to predict trends and optimize pricing strategies, enhancing their competitive edge.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics is crucial. Factors such as regional vehicle preferences, import tariffs, and local labor costs significantly influence the overall cost of starter replacements. Establishing strong relationships with local suppliers can also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and ensure timely delivery of components.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Starter Replacement Market?
As sustainability becomes a focal point in global business practices, the automotive sector is witnessing a shift toward more environmentally responsible sourcing. The impact of starter production on the environment, including the extraction and processing of raw materials, is prompting B2B buyers to prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials with lower environmental footprints and utilizing processes that minimize waste.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important, especially for companies looking to enhance their brand reputation. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who hold certifications for sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or other ‘green’ certifications that demonstrate a commitment to reducing ecological impact. Choosing suppliers that utilize recycled materials in starter production can also contribute to sustainability goals while potentially reducing costs.
In addition, engaging with suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing practices can foster trust and build long-term partnerships. By aligning with ethical suppliers, B2B buyers can not only ensure compliance with regulatory standards but also appeal to a growing customer base that values corporate social responsibility.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
How Has the Starter Replacement Market Evolved Over Time?
The automotive starter replacement market has seen significant evolution, particularly with the introduction of electronic ignition systems and advanced starter technologies. In the past, starters were relatively simple mechanical devices, but as vehicles have become more sophisticated, so too have the starters that power them.
The move towards electric and hybrid vehicles has further transformed the market, necessitating more specialized starters capable of supporting these innovative technologies. As a result, the cost of starter replacements has also fluctuated, influenced by the need for higher-quality components and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of sourcing quality parts that meet the demands of modern vehicles. As the industry continues to innovate, staying informed about technological advancements and their implications on costs will be crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how much does it cost to change a starter
-
How do I determine the cost of changing a starter for my fleet vehicles?
To estimate the cost of changing a starter for fleet vehicles, consider factors such as the make and model of each vehicle, labor rates in your region, and the availability of replacement parts. Generally, starter replacement costs can range from $150 to over $1,100, depending on these variables. It’s advisable to obtain quotes from multiple local mechanics or service providers, and factor in the cost of parts, labor, and any additional diagnostics that may be required. -
What are the signs that a starter needs replacement in commercial vehicles?
Common signs that a starter needs replacement in commercial vehicles include erratic engine cranking, no response when turning the ignition key, and unusual noises like grinding or clicking sounds. If your drivers report these issues, it’s crucial to conduct timely inspections to prevent vehicle downtime. Regular maintenance checks can also help identify starter problems early, allowing for scheduled replacements that minimize operational disruptions. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for starter replacement parts internationally?
To find reliable suppliers for starter replacement parts, start by researching manufacturers and distributors that specialize in automotive components. Utilize B2B platforms such as Alibaba, Global Sources, or local trade directories. Check for certifications, customer reviews, and the supplier’s track record in fulfilling international orders. Engaging with suppliers who have experience in your target markets (e.g., Africa, South America) can also ensure smoother transactions and compliance with local regulations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter parts when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Many manufacturers set MOQs based on production costs and shipping logistics. To negotiate favorable terms, inquire with multiple suppliers and express your specific needs. If you are starting with a smaller fleet, consider suppliers that offer lower MOQs or are willing to provide sample orders to build a relationship before committing to larger purchases. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing starter parts internationally?
When sourcing starter parts internationally, consider payment terms that protect your business while ensuring supplier trust. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, or escrow services. Evaluate the supplier’s payment flexibility and any potential risks associated with each method. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure timely delivery of parts. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for starter parts sourced from overseas?
To ensure quality assurance for starter parts sourced internationally, implement a rigorous vetting process for suppliers. Request product samples, check for industry certifications, and review quality control measures they have in place. Additionally, consider third-party inspection services to evaluate product quality before shipment. Building strong relationships with suppliers can also facilitate open communication about quality expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter parts?
Logistics considerations for importing starter parts include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the intricacies of international shipping and can navigate customs processes efficiently. Understand the lead times involved in shipping and allow for potential delays. Proper documentation and compliance with local import regulations are essential to avoid costly disruptions. -
Can I customize starter parts for specific vehicle models?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for starter parts to fit specific vehicle models. When engaging with suppliers, discuss your customization requirements, including dimensions, voltage specifications, and any unique features needed for your application. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and possibly engage in prototype testing to ensure the customized parts meet your operational standards. Customization can enhance performance and reliability in your fleet operations.
Top 3 How Much Does It Cost To Change A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Facebook – Car Repair Cost Guide
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: cost to get car to the shop and replace starter
2. Last Chance Auto Repairs – Starter Replacement Costs
Domain: lastchanceautorepairs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Starter Replacement Cost: Economy starters: $75 – $200, OEM starters: $150 – $400, High-performance starters: $300 – $1000+. Labor costs: Basic vehicle starter replacement: $100 – $250, Complex installations: $300 – $600+. Factors affecting cost: Vehicle type & model, New vs Re-Manufactured starters, Additional repairs. DIY costs: Parts only: $100 – $400, Time investment: 2-6 hours. Professional r…
3. CarTalk – Starter Replacement Guide
Domain: cartalk.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cost to replace a starter: $600 to $900 for common vehicles, $900 to $1,400 for luxury models. Symptoms of a bad starter include clicking sounds, screeching, and intermittent functionality. Repairing a starter is often not cost-effective; replacement is preferred. New starters are rare; remanufactured starters are commonly used with warranties of 30 days to a year. Modern vehicles with stop-start …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how much does it cost to change a starter
In summary, the cost of changing a starter can vary widely based on vehicle type, part accessibility, and labor complexity. For B2B buyers, understanding these factors is crucial for effective budgeting and cost management. By leveraging strategic sourcing, companies can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they secure quality parts at competitive prices, ultimately driving down maintenance costs.
As you consider replacement options, it’s essential to evaluate both new and rebuilt starters, along with the associated labor costs. This can lead to significant savings, especially when sourcing from reliable suppliers who understand the unique demands of your region, whether in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Looking ahead, fostering relationships with trustworthy suppliers can enhance your operational efficiency and reduce downtime. As you navigate the complexities of starter replacements, consider implementing a strategic sourcing framework that aligns with your business goals. This proactive approach will not only help you manage costs effectively but also position your company for sustained growth in an increasingly competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to how much does it cost to change a starter
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.