Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator components diagram
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality alternator components diagram is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, as well as established regions in Europe and the Middle East. As the demand for reliable automotive parts escalates, understanding the intricate workings of alternators and their components becomes essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of alternator components, their specific applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
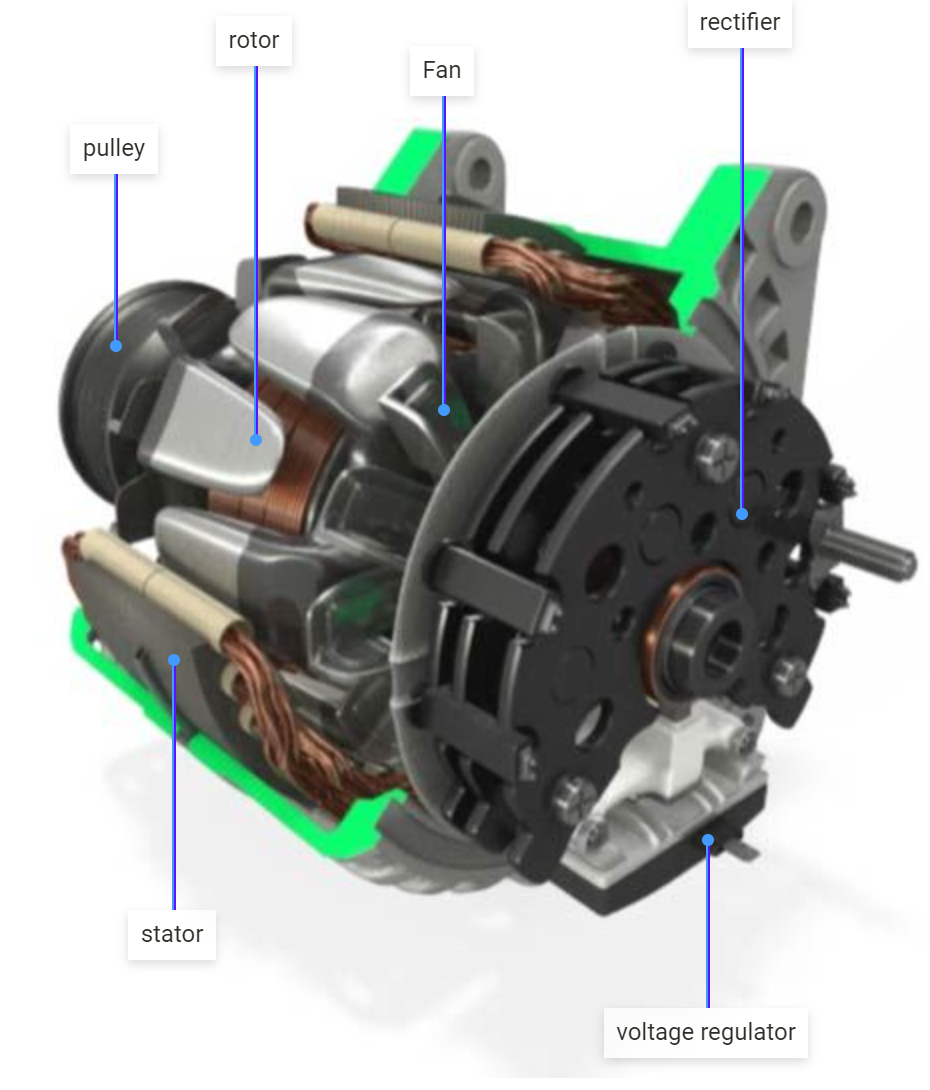
From understanding the roles of the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator to exploring the nuances of pricing and quality assurance, this guide equips B2B buyers with actionable insights. By breaking down complex diagrams and processes, it demystifies the alternator’s functionality, enabling businesses to select the right components that ensure operational efficiency and longevity in their vehicles.
Moreover, this guide emphasizes the importance of supplier vetting, offering criteria that international buyers can use to assess potential partners. With an eye on cost-effectiveness without compromising quality, businesses can navigate the global market landscape more effectively. Ultimately, this resource aims to empower B2B buyers with the knowledge they need to make confident decisions, fostering successful partnerships that drive growth in their respective markets.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Alternator Components Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alternator components diagram
- Understanding alternator components diagram Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of alternator components diagram
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator components diagram’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator components diagram
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator components diagram
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator components diagram’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator components diagram Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator components diagram With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator components diagram
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator components diagram Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator components diagram
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator components diagram
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding alternator components diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schematic Diagram | Simplified representation of electrical flow | Educational materials, training | Pros: Easy to understand; Cons: Lacks detailed components. |
| Component Layout Diagram | Detailed view of individual parts | Manufacturing, assembly line | Pros: Comprehensive; Cons: Can be complex for beginners. |
| Functional Block Diagram | Shows functional relationships between components | Systems engineering, diagnostics | Pros: Highlights interactions; Cons: May oversimplify. |
| Electrical Connection Diagram | Focuses on wiring and connections | Installation, troubleshooting | Pros: Essential for installation; Cons: Can be overwhelming. |
| 3D Exploded View Diagram | Three-dimensional representation of components | Marketing, product development | Pros: Visually engaging; Cons: Requires advanced software. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Schematic Diagrams in B2B Applications?
Schematic diagrams serve as a foundational tool in understanding alternator functionality. They simplify the representation of electrical flow, making it ideal for educational purposes or training sessions. B2B buyers in the automotive education sector or technical training institutes benefit from these diagrams as they facilitate easier comprehension of complex concepts. However, while they are user-friendly, they may not provide the intricate details necessary for advanced troubleshooting.
How Do Component Layout Diagrams Support Manufacturing and Assembly?
Component layout diagrams offer a detailed view of individual alternator parts, making them essential for manufacturing and assembly line operations. These diagrams help engineers and technicians visualize how components fit together and function as a unit. Buyers in the automotive manufacturing sector can leverage these diagrams for quality control and assembly efficiency. However, the complexity of these diagrams may pose challenges for those unfamiliar with alternator components, requiring additional training or resources.
Why are Functional Block Diagrams Important for Systems Engineering?
Functional block diagrams illustrate the functional relationships among alternator components, which is crucial for systems engineering and diagnostics. They enable engineers to see how various parts interact, aiding in the design and optimization of alternators. For B2B buyers involved in engineering, these diagrams provide a high-level overview that is beneficial in early design stages. However, the potential for oversimplification means that users must complement these diagrams with more detailed information for in-depth analysis.
What Role Do Electrical Connection Diagrams Play in Installation and Troubleshooting?
Electrical connection diagrams focus on the wiring and connections within an alternator, making them indispensable for installation and troubleshooting. These diagrams guide technicians in correctly connecting components, ensuring optimal functionality. B2B buyers in the automotive repair and maintenance sectors rely on these diagrams to minimize installation errors. However, the detailed nature of these diagrams can be overwhelming for inexperienced technicians, necessitating proper training.
How Can 3D Exploded View Diagrams Enhance Marketing and Product Development?
3D exploded view diagrams provide a visually engaging representation of alternator components, which is particularly useful in marketing and product development. They allow potential buyers to appreciate the complexity and craftsmanship of the product, enhancing customer engagement. B2B marketers in the automotive industry can utilize these diagrams to showcase their products effectively. However, the need for specialized software to create these diagrams can be a barrier for some businesses, limiting their accessibility.
Key Industrial Applications of alternator components diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alternator components diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Design and assembly of vehicle alternators | Enhanced vehicle reliability and performance | Quality standards, compatibility with existing systems |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in wind and solar power systems | Efficient energy conversion and storage | Durability, efficiency ratings, and environmental compliance |
| Marine Engineering | Power generation for ships and offshore platforms | Reliable onboard power supply for navigation and safety | Corrosion resistance, size constraints, and certification |
| Mining and Heavy Equipment | Power supply for machinery and equipment | Continuous operation in remote locations | Robustness, maintenance requirements, and service support |
| Telecommunications | Backup power systems for communication towers | Ensures uninterrupted service during outages | Reliability, scalability, and integration capabilities |
How is the alternator components diagram utilized in the automotive manufacturing sector?
In the automotive manufacturing industry, the alternator components diagram is crucial for the design and assembly of vehicle alternators. This diagram helps engineers visualize the interaction between various components such as the rotor, stator, and rectifier, ensuring that the alternator efficiently converts mechanical energy to electrical power. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality components that meet stringent automotive standards is vital to enhance vehicle reliability and performance. Buyers must consider compatibility with existing systems and adherence to local regulations.
What role does the alternator components diagram play in renewable energy applications?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind and solar power systems, the alternator components diagram is instrumental in integrating alternators for efficient energy conversion and storage. It allows engineers to design systems that can convert mechanical energy from turbines or solar trackers into usable electrical energy. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East where solar energy is a significant focus, sourcing durable and efficient components that comply with environmental standards is essential. The ability to withstand harsh conditions and maintain efficiency is a key consideration.
How does the alternator components diagram benefit marine engineering?
Marine engineering relies heavily on alternators for power generation on ships and offshore platforms. The alternator components diagram assists in designing systems that ensure a reliable onboard power supply for navigation, communication, and safety systems. For businesses in this sector, particularly those operating in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing alternators with corrosion resistance and compact designs is critical. These components must meet specific maritime certification standards to ensure safety and reliability in challenging environments.
In what ways does the alternator components diagram support mining and heavy equipment operations?
In the mining and heavy equipment industry, the alternator components diagram is utilized to ensure continuous power supply for machinery operating in remote locations. This is crucial for maintaining productivity and safety. For international buyers, particularly in South America, it’s important to source robust alternators that can withstand extreme conditions and require minimal maintenance. Key considerations include the operational environment and the availability of service support to minimize downtime.
How is the alternator components diagram relevant to telecommunications?
Telecommunications companies utilize the alternator components diagram for backup power systems in communication towers. This ensures uninterrupted service during power outages, which is critical for maintaining connectivity. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions prone to power instability, sourcing reliable and scalable alternators is essential. Buyers should focus on the integration capabilities of these components with existing power systems to ensure seamless operation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘alternator components diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Alternator Functionality
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties when trying to explain the functionality of alternators to their teams or clients, especially when the audience lacks technical expertise. This gap in understanding can lead to miscommunication regarding component specifications, ultimately affecting product selection and performance. When buyers cannot clearly illustrate how alternator components interact—such as the roles of the rotor, stator, and rectifier—they may struggle to make informed decisions on sourcing, installation, or maintenance.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should utilize comprehensive alternator components diagrams that not only illustrate each component’s role but also detail the operational flow of electricity within the alternator. Look for diagrams that include annotations or labels that clarify the function of each part. Educational resources or training modules that incorporate these diagrams can further enhance understanding. Buyers should also consider hosting workshops or training sessions that leverage visual aids, allowing team members to engage directly with the material. This will help cultivate a knowledgeable team capable of making confident, informed decisions about alternator components.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Specification for Diverse Applications
The Problem: Another common pain point arises when B2B buyers need to source alternator components for a variety of applications, from automotive to industrial uses. Each application may require different specifications, such as varying voltage outputs or physical dimensions. Without a clear understanding of these requirements, buyers risk ordering incorrect components, leading to project delays and increased costs due to returns and reorders.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should develop a comprehensive checklist of specifications based on the intended application of the alternator. This checklist should include parameters such as voltage requirements, physical dimensions, and compatibility with other systems. Utilizing detailed alternator components diagrams can aid in visualizing how these specifications translate into real-world applications. Furthermore, establishing relationships with suppliers who offer customizable or tailored components can provide additional flexibility. Buyers should also consider leveraging simulation software that allows them to model different configurations, ensuring that they select the correct components before purchase.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently face difficulties during maintenance and troubleshooting of alternators due to a lack of clear diagrams that illustrate the interconnectivity of components. This can result in extended downtime when issues arise, as technicians may not have a clear reference for identifying faults or performing repairs. Compounding this issue is the fact that many technical documents are too complex or poorly illustrated, which can further confuse maintenance personnel.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance challenges, buyers should invest in high-quality, detailed alternator components diagrams that are specifically designed for troubleshooting and repair scenarios. These diagrams should not only depict component locations but also include common failure points and indicators of potential issues. Buyers can also create a maintenance manual that combines these diagrams with step-by-step troubleshooting guides. Regular training sessions for maintenance personnel, utilizing these resources, can ensure that teams are prepared to address issues swiftly. By fostering an environment of continuous learning and providing accessible resources, businesses can minimize downtime and enhance the efficiency of their operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alternator components diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Alternator Components?
When selecting materials for alternator components, several factors must be considered, including thermal properties, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. The choice of material can significantly influence the performance, durability, and overall efficiency of the alternator. Below, we analyze four common materials used in alternator components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Alternator Components?
Aluminum is widely used for the outer housing of alternators due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It has a high corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments, including humid and coastal areas. The typical temperature rating for aluminum components can reach up to 150°C, which is adequate for most automotive applications.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for complex shapes and designs. Its lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it may not withstand extreme mechanical stress as well as some other metals. Additionally, it can be more susceptible to wear over time compared to tougher materials.
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and its non-magnetic properties make it ideal for housing components that require heat dissipation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial when sourcing aluminum components. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers meet local regulations regarding material quality and environmental impact.
Why Is Copper Essential for Electrical Connections in Alternators?
Copper is the preferred material for electrical connections and windings within alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It operates effectively at high temperatures (up to 200°C) and has good corrosion resistance when properly coated.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity allows for efficient power transmission, reducing energy losses. It is also relatively easy to work with, making manufacturing processes straightforward.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which can be significantly higher than that of aluminum. Additionally, copper is heavier, which may not be ideal for all applications.
Impact on Application: Copper is essential for components that require reliable electrical performance, such as rotor windings and connections, which must handle high currents.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for copper quality across different regions. Compliance with international standards like JIS is essential, especially in markets like the Middle East and Europe.
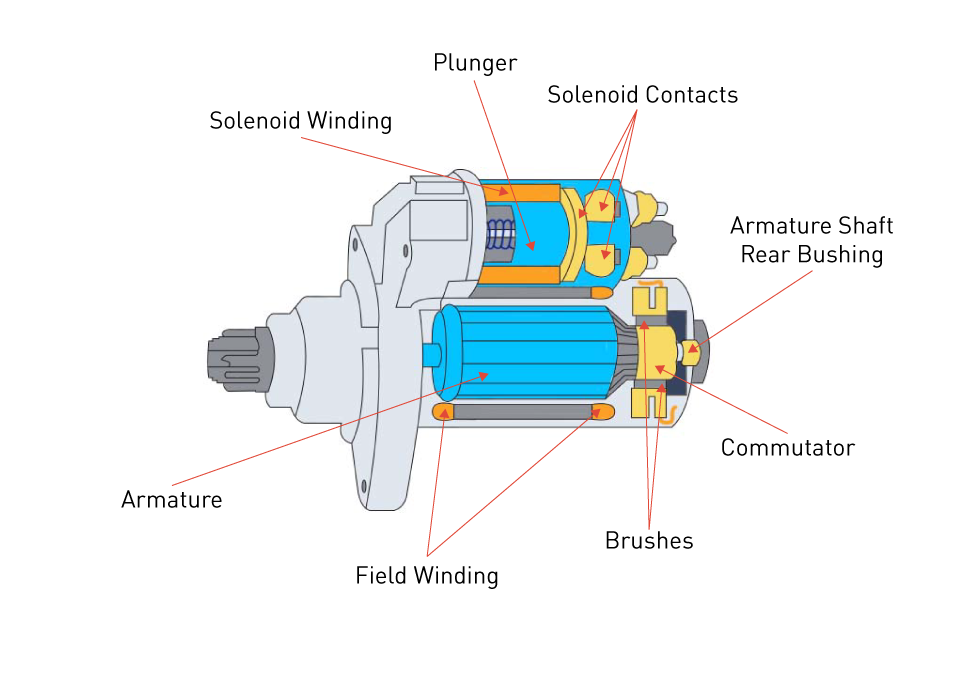
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
How Does Steel Contribute to the Durability of Alternator Components?
Steel is often used in components that require high strength and durability, such as the rotor shaft and brackets. It can withstand high mechanical stresses and has a temperature rating of around 300°C, making it suitable for intense operational environments.
Pros: Steel’s strength and durability make it ideal for components that experience significant wear and tear. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to premature failure in harsh environments. Additionally, it is heavier than aluminum, which may affect overall vehicle weight.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for components that must endure high mechanical loads, but care must be taken to ensure adequate corrosion protection.
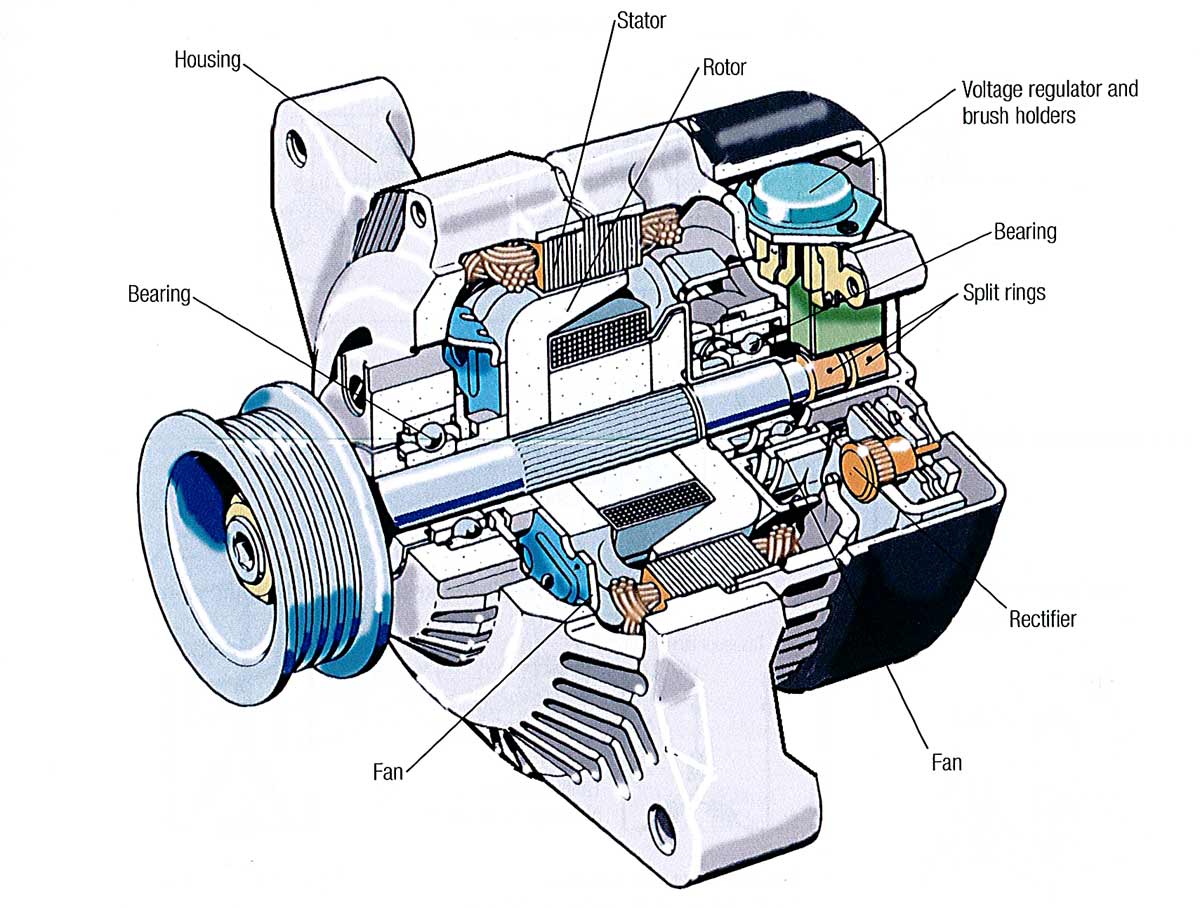
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the local availability of treated steel that meets ASTM or DIN standards. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality steel can be challenging, and buyers should verify supplier certifications.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Alternator Component Design?
Plastic materials, particularly thermoplastics, are increasingly used in non-structural components of alternators, such as housings for electrical connectors and insulation parts. They offer good electrical insulation properties and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for versatile designs. They are also resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
Cons: Plastics may not be suitable for high-stress applications and can degrade over time when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are ideal for lightweight applications where electrical insulation is crucial, but they should be used judiciously in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for plastics, such as those set by ISO, is essential. Buyers should ensure that the materials used are suitable for the specific environmental conditions in their regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternator Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for alternator components diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Outer housing | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under extreme stress | Low |
| Copper | Electrical windings and connections | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Steel | Rotor shaft and brackets | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Med |
| Plastic | Non-structural components | Lightweight and versatile | Not suitable for high-stress applications | Low |
This material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers looking to optimize their alternator component designs while considering performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alternator components diagram
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Alternator Components?
Manufacturing alternator components involves several crucial stages, each designed to ensure the efficiency and reliability of the final product. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Alternator Components?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality materials are essential for the performance and durability of alternators. Common materials include aluminum for the housing due to its lightweight and non-magnetizing properties, as well as copper for windings and steel for the rotor.
This stage involves selecting materials based on specifications, cutting them into appropriate sizes, and treating them to enhance their properties, such as corrosion resistance. Techniques like anodizing or powder coating may be employed to improve surface durability, especially for components exposed to harsh environments.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in the Production of Alternator Components?
Once materials are prepared, forming techniques are utilized to shape the components. Common methods include:
- Die Casting: Used primarily for the aluminum housing, this method allows for complex shapes while minimizing waste.
- Stamping: Employed for creating the stator and rotor components, stamping ensures high precision and uniformity in production.
- Machining: Components like the rotor shaft may undergo machining processes to achieve exact dimensions and tolerances.
Each forming technique is selected based on the specific component’s requirements, balancing production efficiency with quality assurance.
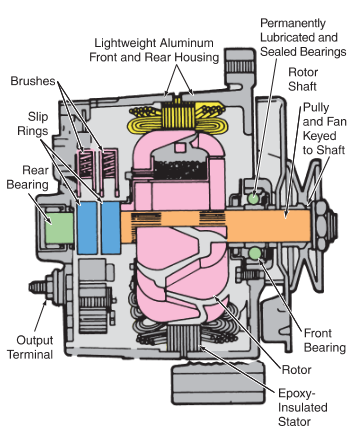
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
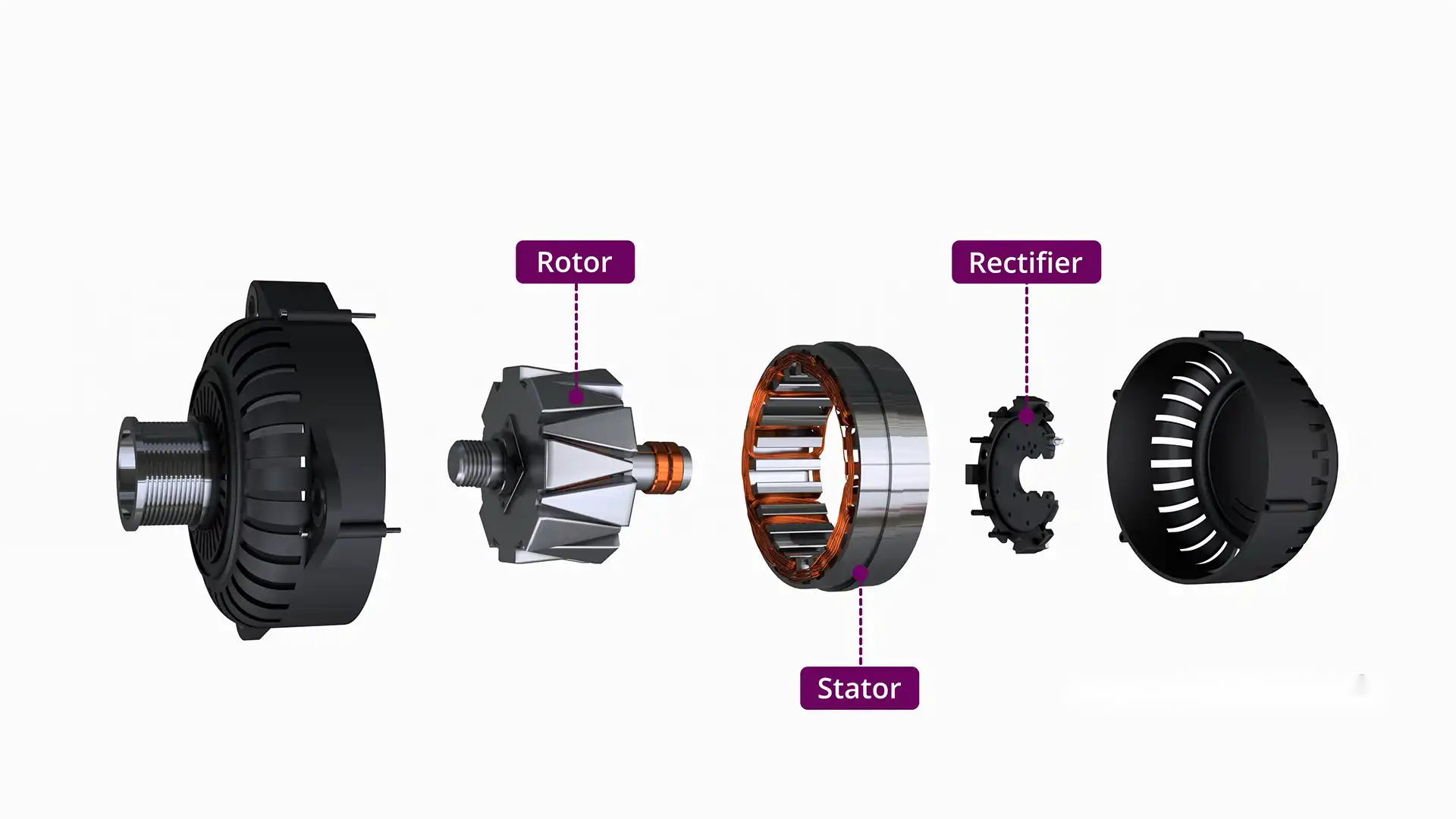
How Are Alternator Components Assembled?
Assembly is a critical phase where individual components come together to form the alternator. This process typically involves:
- Initial Assembly: The rotor is inserted into the stator, ensuring proper alignment.
- Electrical Connections: Connections are established for the rectifier, voltage regulator, and other electronic components.
- Final Assembly: The housing is closed, and the drive pulley is attached.
This phase often requires skilled labor and precise tooling to ensure that components fit together seamlessly, contributing to the overall functionality of the alternator.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Ensure Quality?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of alternator components. Typical finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing and powder coating protect against corrosion and wear.
- Quality Inspection: Visual inspections and measurements are conducted to ensure that components meet specified tolerances and quality standards.
Finishing is essential not only for appearance but also for the longevity of the alternator in various operational conditions.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital for ensuring that alternator components meet global standards. Key international standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is fundamental for manufacturers to demonstrate consistent quality.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection legislation.
- API Standards: Relevant for automotive components, ensuring they meet specific performance criteria.
Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers maintain a competitive edge in international markets, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors production processes to catch defects early, preventing costly rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts comprehensive testing of finished products to verify performance and compliance with standards.
Each checkpoint serves to identify and rectify potential issues, ensuring that only high-quality components proceed to the next stage.

Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Alternator Components?
Testing methods are essential to validate the functionality and reliability of alternator components. Common testing techniques include:
- Electrical Testing: Measures output voltage and current to ensure the alternator operates within specified parameters.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluates the performance of components under varying temperature conditions to ensure durability.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the structural integrity of components, including stress and fatigue tests.
These tests provide critical data that can be used to improve manufacturing processes and product design.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial. Buyers can take several steps, including:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site inspections of manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Asking suppliers for detailed QC reports that outline testing methods and results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent agencies to evaluate supplier quality and adherence to international standards.
These strategies help mitigate risks associated with sourcing components from different regions, ensuring that buyers receive reliable and high-quality products.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
Quality certification can vary significantly across different regions and industries. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these nuances is essential. Key considerations include:
- Regional Standards: Familiarity with local regulations and standards that may differ from international guidelines.
- Certification Validity: Ensuring that certifications are current and recognized in the buyer’s market.
- Cultural Differences: Being aware of variations in business practices and quality expectations that may affect supplier relationships.
By navigating these complexities, B2B buyers can establish more effective partnerships and ensure that they receive components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘alternator components diagram’
When sourcing alternator components diagrams, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to ensure you acquire high-quality diagrams that accurately represent the components and functions of alternators. This guide will help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for the alternator components diagram is crucial. Determine what details need to be included, such as the layout of components like the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator. This clarity will guide your search and help ensure the diagrams meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding trustworthy suppliers is key to obtaining accurate and high-quality diagrams. Research companies that specialize in automotive components or electrical engineering resources. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing technical diagrams and customer testimonials that vouch for their reliability.
- Tip: Use platforms like LinkedIn or industry-specific forums to gather insights about potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your supplier, verify their certifications and industry affiliations. Certifications ensure that the supplier adheres to industry standards for quality and safety. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems.
- Tip: Request documentation that proves their compliance with international standards, especially if you are sourcing from different regions like Africa or South America.
Step 4: Review Sample Diagrams
Request sample diagrams from your shortlisted suppliers to evaluate their quality and accuracy. Assess whether the diagrams include essential components and follow industry-standard notations. This step is critical to ensure that the diagrams are not only informative but also usable for your technical teams.
Step 5: Inquire About Customization Options
Different projects may require specific adaptations of standard diagrams. Discuss customization options with your suppliers to see if they can modify existing diagrams or create new ones tailored to your specifications. Customization can enhance the usability of the diagrams in your specific applications.
- Tip: Ask for examples of previous custom work to gauge the supplier’s capability in meeting unique demands.
Step 6: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing can vary significantly among suppliers, so it’s important to compare costs while considering the quality of the diagrams. Request detailed quotes that outline what is included in the price. Additionally, clarify payment terms and conditions to avoid any misunderstandings later.
- Tip: Look for flexible payment options, especially if you are purchasing in bulk or require ongoing support.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Channel
Establish clear lines of communication with your supplier to facilitate ongoing discussions and updates. Effective communication is vital for resolving any issues that may arise during the procurement process. Ensure that your supplier is responsive and open to feedback.

Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
- Tip: Use project management tools to streamline communication and track the progress of your order.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure a thorough and efficient sourcing process for alternator components diagrams, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alternator components diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Alternator Components Diagrams?
When sourcing alternator components diagrams, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials for alternator components include aluminum for housing due to its lightweight properties and excellent heat dissipation, and copper for windings, which is essential for efficient electrical conductivity.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the expertise required for manufacturing. Skilled labor is often necessary for assembling complex components like rectifiers and voltage regulators.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower these costs and improve competitiveness.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for customized components. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs when requesting quotes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that components meet specific standards is crucial, especially for international buyers who may face stricter regulations. Investing in robust QC processes can mitigate long-term risks associated with defective products.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs, influenced by the distance and method of transport, play a critical role in the total cost. Incoterms will also affect the logistics costs and responsibilities between buyer and seller.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the market rates can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for Alternator Components Diagrams?
Several factors influence the pricing of alternator components diagrams:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in larger volumes often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. However, buyers must balance their inventory needs with cash flow considerations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized components that meet specific requirements typically incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO) can raise costs but are often necessary for compliance and reliability. Buyers must weigh the benefits of quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality and service, but at a premium. It’s important to evaluate the trade-offs.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the cost and risk distribution between buyer and seller. Understanding these terms can lead to more favorable shipping arrangements and cost savings.
What Are Some Effective Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic negotiation can lead to significant savings:
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Consider long-term partnerships that benefit both parties.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating suppliers, consider not just the initial purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs. This approach can justify higher upfront costs for better quality components.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs that can affect total costs. Understanding these factors can help in budgeting and negotiations.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Don’t settle for the first price. Obtaining multiple quotes can give you leverage in negotiations and help identify the market rate for components.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Please note that the prices for alternator components diagrams can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure the best pricing for your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing alternator components diagram With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Alternator Solutions
In the realm of automotive and industrial applications, understanding the intricacies of alternator components is vital. However, there are alternative solutions that can fulfill similar functions, often with varying degrees of effectiveness, cost, and implementation ease. This section compares the ‘alternator components diagram’ with two viable alternatives: the DC Generator and the Battery Management System (BMS). Each alternative presents unique advantages and drawbacks, making it essential for B2B buyers to assess which solution best aligns with their operational needs.
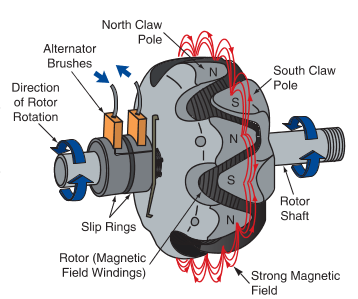
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
| Comparison Aspect | Alternator Components Diagram | DC Generator | Battery Management System (BMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in AC generation | Moderate efficiency, primarily for DC | High efficiency in energy management |
| Cost | Typically low-cost for diagrams | Higher initial investment for equipment | Varies based on complexity and features |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to understand and implement | Requires skilled installation | Complex installation and setup required |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; visual aid only | Moderate; requires periodic checks | High; software updates and hardware checks needed |
| Best Use Case | Educational and design applications | Standalone power generation in remote areas | Efficient energy management in battery systems |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a DC Generator?
DC generators convert mechanical energy into direct current electrical energy, making them a traditional choice for applications requiring stable DC power. They are particularly beneficial in remote locations where AC power is unavailable. However, they can be more expensive than an alternator in terms of initial investment and maintenance, as they typically require regular servicing to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, the efficiency of DC generators is generally lower compared to alternators, especially when it comes to larger power requirements.
How Does a Battery Management System (BMS) Compare?
A Battery Management System (BMS) is designed to monitor and manage battery performance, ensuring optimal charging and discharging cycles. It excels in applications where energy efficiency and battery longevity are critical, such as in electric vehicles or renewable energy systems. However, BMSs can be complex to implement, often requiring specialized knowledge for installation and regular maintenance to update software and hardware. The initial costs may also be higher, depending on the system’s complexity and features.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating the ‘alternator components diagram’ against alternatives like DC generators and Battery Management Systems, it’s essential to consider specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. For educational purposes and design visualization, the alternator components diagram is unmatched in simplicity and effectiveness. However, for applications necessitating direct current output or advanced energy management, DC generators and BMSs may provide better long-term solutions. Ultimately, B2B buyers should align their choice with their operational goals, weighing performance, cost, and maintenance needs to select the most suitable solution for their specific context.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alternator components diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Alternator Components?
When sourcing alternator components, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade:
Alternators are typically constructed from aluminum and other non-magnetic materials. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and excellent heat dissipation properties. Understanding the material grade can help buyers assess durability, weight, and thermal management, which are vital for efficient performance. -
Tolerance Levels:
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For alternator components, tight tolerances are essential to ensure proper fit and function, particularly between the rotor and stator. This precision affects the alternator’s efficiency, longevity, and overall performance. Buyers should inquire about the tolerance specifications to ensure quality and reliability. -
Cooling Efficiency:
An alternator’s ability to manage heat generated during operation is critical. Buyers should look for components designed with advanced cooling technologies, such as integrated cooling fans or optimized vent designs. Efficient cooling extends the lifespan of the alternator and enhances performance, making it a vital property to consider. -
Electrical Output Rating:
The electrical output rating, measured in amperes (A), indicates the alternator’s capacity to supply power. This rating is crucial for ensuring that the alternator meets the electrical demands of the vehicle or machinery it serves. Buyers must match the output rating to their specific needs to avoid underperformance or damage. -
Voltage Regulation:
Voltage regulation is vital for maintaining a consistent voltage output to prevent damage to electrical components. Buyers should ensure that the alternator comes equipped with a reliable voltage regulator to optimize performance and protect sensitive electronic systems.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Alternator Components Industry?
Navigating the alternator components market requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are several essential terms that B2B buyers should understand:
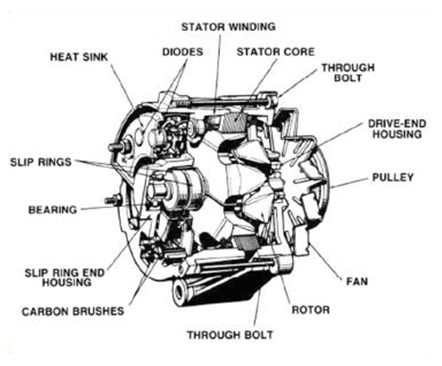
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
OEM refers to components made by the same manufacturer that produces the original product. When sourcing alternators, buyers often prefer OEM parts for their guaranteed compatibility and performance reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their procurement strategies, especially when dealing with international suppliers, where minimum orders may vary significantly. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This is a critical step for buyers looking to compare prices and negotiate terms. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline the purchasing process and ensure the best possible pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Understanding these terms is essential for managing logistics, including who bears the risk during transit and who is responsible for shipping costs. Familiarity with Incoterms can prevent misunderstandings and financial disputes. -
Lead Time:
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For B2B buyers, knowing the lead time is essential for inventory management and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays. -
Certification Standards:
Certification standards, such as ISO or SAE, indicate compliance with international quality and safety standards. Buyers should verify that alternator components meet relevant certification standards to ensure reliability and performance.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing alternator components, ultimately ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the alternator components diagram Sector
What are the Global Drivers Influencing the Alternator Components Diagram Market?
The alternator components diagram market is experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. One of the primary global drivers is the automotive industry’s shift towards electrification and hybrid technology. As manufacturers increasingly adopt electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids, the need for efficient alternator systems that can effectively manage electrical energy is paramount. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where stringent emissions regulations are pushing for cleaner technologies.
Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping sourcing strategies in the alternator components sector. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms and data analytics to streamline procurement processes, ensuring they can source high-quality components at competitive prices. This is especially relevant in emerging markets such as Brazil and South Africa, where the automotive sector is rapidly growing.
Furthermore, global supply chain dynamics are shifting due to geopolitical factors and the recent disruptions caused by the pandemic. Buyers must now navigate these complexities by adopting flexible sourcing strategies, which may include diversifying suppliers and investing in local manufacturing capabilities to mitigate risks associated with international shipping.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Alternator Components Diagram Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become crucial considerations for international B2B buyers in the alternator components market. The automotive industry is increasingly scrutinizing its environmental impact, prompting manufacturers to seek components that adhere to sustainable practices. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who implement eco-friendly production methods, utilize recyclable materials, and ensure minimal waste generation during manufacturing processes.
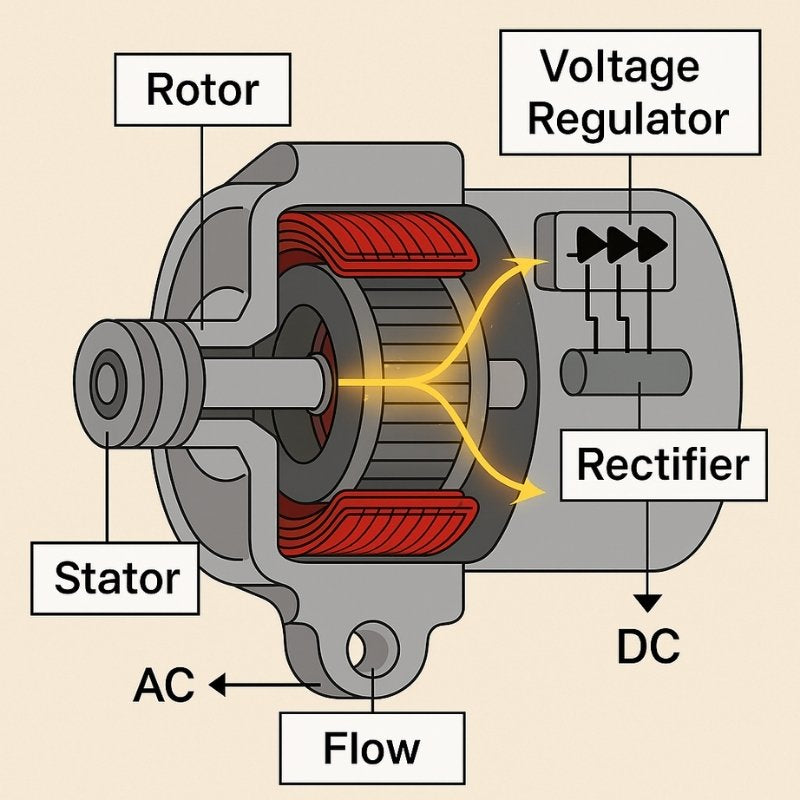
Illustrative image related to alternator components diagram
Ethical supply chains are also gaining prominence, particularly as consumers become more environmentally conscious. B2B buyers in regions such as the Middle East and Africa are more likely to partner with suppliers who have transparent supply chains and demonstrate a commitment to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In addition, the adoption of ‘green’ materials, such as those with lower carbon footprints or that are sourced responsibly, is reshaping the components utilized in alternators. As buyers increasingly demand eco-friendly options, suppliers are innovating to provide components that not only meet performance standards but also align with the growing trend toward sustainability.
What is the Brief Evolution of the Alternator Components Diagram Market?
The evolution of the alternator components diagram market has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in consumer preferences. Initially, traditional mechanical generators dominated the automotive landscape, but with the rise of electrical systems in vehicles during the mid-20th century, alternators began to replace them due to their efficiency and reliability.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the introduction of more sophisticated electronic voltage regulators, improving the efficiency of alternators significantly. As the automotive industry began to embrace the importance of electrical systems, the design and functionality of alternators became more complex, integrating features such as intelligent voltage regulation and cooling systems.
In recent years, the demand for lightweight and compact designs has driven innovation in materials and manufacturing processes. Advanced materials, such as aluminum and composite plastics, have become standard in alternator construction, allowing for better heat dissipation and improved performance. This evolution continues as the industry adapts to the needs of modern vehicles, particularly with the increasing focus on electric and hybrid models, shaping the future of alternator components and their diagrams.
As B2B buyers navigate this dynamic landscape, understanding these trends and their implications will be crucial in making informed sourcing decisions that align with both current market needs and future developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alternator components diagram
-
How do I determine the quality of alternator components from suppliers?
To ensure high-quality alternator components, conduct thorough supplier assessments. Request certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Evaluate samples of components for physical quality and performance specifications. Additionally, consider suppliers with a proven track record and positive reviews from previous clients. Engaging in audits or site visits can further enhance trust in the supplier’s manufacturing process and quality control measures. -
What is the best way to customize alternator components for specific applications?
Customization of alternator components begins with clear communication of your requirements to the supplier. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics needed for your application. Collaborate with the supplier’s engineering team to explore feasible design alterations. Additionally, requesting prototypes can help in assessing functionality before mass production, ensuring that the components meet your specific operational needs. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternator components?
Minimum order quantities for alternator components can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the components. Generally, MOQs may range from 100 to 1,000 units. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and inventory management strategies. Some suppliers may offer flexible options for smaller orders, especially for customized or high-demand components. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternator components internationally?
International payment terms typically include options such as letters of credit, wire transfers, or payment in advance. Many suppliers prefer a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment. Ensure you clarify the terms in the contract to avoid disputes. Additionally, consider using escrow services for added security, especially when working with new suppliers, to safeguard your investment during the transaction. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of alternator components?
To ensure timely delivery, establish clear timelines and deadlines with your supplier at the outset. Consider using suppliers who have a robust logistics network and experience in international shipping. Inquire about their shipping methods, average lead times, and any potential customs delays. It may also be beneficial to build in buffer time to account for unforeseen delays, particularly when sourcing from regions with less predictable logistics. -
What quality assurance processes should be in place for alternator components?
A comprehensive quality assurance process should include regular inspections at various stages of production, from raw material sourcing to final assembly. Implement testing protocols for performance metrics like electrical output and thermal resistance. Additionally, consider third-party quality inspections before shipment to verify that components meet specified standards. Maintaining open communication with your supplier about QA practices can enhance product reliability. -
What are the common challenges when sourcing alternator components from different regions?
Sourcing alternator components internationally may present challenges such as language barriers, varying quality standards, and differing regulations. Additionally, logistical issues like customs clearance and shipping delays can impact timelines. To mitigate these challenges, partner with suppliers who have experience in your target markets and are familiar with local regulations. Establishing strong relationships and communication channels can also help navigate potential difficulties. -
How can I assess the technical support provided by suppliers of alternator components?
Evaluating technical support from suppliers can be done by reviewing their responsiveness to inquiries and the availability of technical documentation, such as installation guides and diagrams. Inquire about after-sales support, including warranty terms and return policies. A supplier that offers comprehensive technical assistance, including training or troubleshooting services, can significantly enhance your operational efficiency and reduce downtime in case of issues with components.
Top 5 Alternator Components Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electude – Automotive Alternator
Domain: electude.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: An alternator is a crucial automotive component that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, generating power for the vehicle’s electrical consumer units and battery. Key components include:
1. Pulley: Transfers mechanical energy from the engine.
2. Rotor: Creates the magnetic field for generating alternating current.
3. Stator: The static part where voltage is generated.
4. Rectifi…
2. HowStuffWorks – Alternators
Domain: auto.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Alternators are small and lightweight, roughly the size of a coconut, constructed with an aluminum outer housing for heat dissipation and non-magnetization. Key components include:
– Drive pulley attached to the rotor shaft, converting mechanical energy to electrical power.
– Terminals: S terminal (senses battery voltage), IG terminal (ignition switch for voltage regulator), L terminal (closes c…
3. Facebook – Car Alternator Diagram
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: A detailed diagram showing the internal structure of a car alternator, with labeled components such as the rotor, stator windings, brushes, rectifier.
4. Pinterest – Exploded View of an Alternator
5. AutoElectro – Alternators
Domain: autoelectro.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Alternators generate energy to feed the electrical system and charge the battery in a vehicle. They work by converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. Key components include: 1. Regulator: Controls power distribution to the battery. 2. Rectifier: Converts AC to DC. 3. Rotor: Spinning mass that acts as an electromagnet. 4. Slip Rings: Provide direct current to the rotor. 5…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alternator components diagram
In today’s dynamic automotive landscape, understanding the intricacies of alternator components is paramount for B2B buyers. The alternator, as a crucial power generator, comprises essential components such as the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator. Each part plays a vital role in converting mechanical energy into reliable electrical power, ensuring optimal vehicle performance. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, businesses can enhance their procurement processes, ensuring they partner with reputable suppliers who provide high-quality components that meet international standards.
As global markets expand, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for efficient alternator systems is set to rise. Buyers should focus on cultivating relationships with manufacturers that offer innovative solutions and robust support. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, organizations can not only reduce costs but also enhance their supply chain resilience.
Looking ahead, it is essential to stay informed about emerging technologies and trends in alternator design and functionality. Engage with suppliers who are committed to sustainability and innovation to maintain a competitive edge in the evolving automotive industry. Take action now to secure your supply chain and ensure your business is equipped for future challenges.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.