Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is starting motor
In the complex landscape of global automotive parts, sourcing a reliable starting motor can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. As an essential component that initiates the engine’s operation in internal combustion vehicles, the starter motor plays a critical role in vehicle functionality. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the starting motor, detailing its types, applications across various vehicle models, and essential factors to consider when sourcing. It also provides insights into supplier vetting processes, pricing structures, and maintenance considerations, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
International B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia—will find this guide invaluable. It not only addresses the technical specifications and standards required for different markets but also highlights potential pitfalls in the procurement process. By equipping buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers them to navigate the intricacies of sourcing starter motors effectively. Ultimately, informed purchasing decisions lead to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime, fostering long-term success in the competitive automotive industry.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 What Is Starting Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is starting motor
- Understanding what is starting motor Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is starting motor
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is starting motor’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is starting motor
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is starting motor
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is starting motor’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is starting motor Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is starting motor With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is starting motor
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is starting motor Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is starting motor
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is starting motor
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is starting motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Starter | Uses a solenoid to engage a pinion gear; relies on battery power for operation. | Automotive manufacturing and repair. | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited lifespan under heavy use. |
| Gear Reduction Starter | Features a gear reduction mechanism, providing higher torque with less battery draw. | Heavy machinery, trucks, and commercial vehicles. | Pros: Greater efficiency, improved starting power. Cons: More complex, potentially higher cost. |
| Permanent Magnet Starter | Utilizes permanent magnets for motor operation, enhancing efficiency and reducing size. | Small engines, motorcycles, and compact vehicles. | Pros: Lightweight, compact design. Cons: May be less powerful for larger engines. |
| High-Performance Starter | Designed for racing and high-performance vehicles, offering rapid engagement and high torque. | Motorsports and performance automotive sectors. | Pros: Superior performance, quick starts. Cons: Higher cost, may require specialized installation. |
| Integrated Starter/Generator | Combines starting and generating functions, often used in hybrid vehicles. | Hybrid and electric vehicle manufacturing. | Pros: Space-saving, dual functionality. Cons: Complex system, potential for higher maintenance costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Starters and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Conventional starters are the most widely used type in internal combustion engines. They operate by utilizing a solenoid to engage a pinion gear that meshes with the flywheel, allowing for engine ignition. B2B buyers in the automotive manufacturing and repair industries favor these starters due to their straightforward design and cost-effectiveness. However, they have a limited lifespan, particularly under heavy usage conditions, which may lead buyers to consider alternatives for high-demand applications.
How Do Gear Reduction Starters Enhance Efficiency in Heavy-Duty Applications?
Gear reduction starters incorporate a gearing mechanism that boosts torque while minimizing battery consumption. This makes them ideal for heavy machinery, trucks, and commercial vehicles where starting power is essential. B2B buyers benefit from their efficiency and reliability, especially in environments where frequent starts are necessary. The complexity and higher initial cost may be drawbacks, but the long-term performance often justifies the investment.
What Advantages Do Permanent Magnet Starters Offer for Smaller Engines?
Permanent magnet starters are designed with permanent magnets, allowing for a more compact and efficient motor operation. They are particularly suited for small engines, motorcycles, and compact vehicles. B2B buyers appreciate their lightweight design and reduced size, which can lead to overall vehicle weight savings. However, these starters may lack the power required for larger engines, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
In What Scenarios Are High-Performance Starters Necessary for B2B Buyers?
High-performance starters are tailored for motorsports and high-performance vehicles, providing rapid engagement and high torque. They are essential in environments where quick starts are critical, such as racing. B2B buyers in the motorsports industry value these starters for their superior performance, although the higher cost and specialized installation requirements can be limiting factors for some businesses.
Why Are Integrated Starter/Generator Systems Important for Hybrid Vehicles?
Integrated starter/generator systems combine the functionalities of starting and generating power, making them a vital component in hybrid and electric vehicles. These systems are space-efficient and enhance overall vehicle performance. B2B buyers involved in hybrid vehicle manufacturing find these systems appealing for their dual functionality. However, the complexity of the system may lead to higher maintenance costs, which should be considered in the purchasing decision.
Key Industrial Applications of what is starting motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is starting motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Starting systems in passenger and commercial vehicles | Ensures reliable engine ignition and operational efficiency | Quality standards, compatibility with various vehicle models, and sourcing from reputable manufacturers |
| Agriculture | Starting motors in farm machinery (tractors, harvesters) | Enhances productivity by ensuring machinery starts reliably | Durability for harsh environments, availability of parts, and service support |
| Construction | Heavy machinery (excavators, bulldozers) starting systems | Reduces downtime by enabling quick machinery starts | Robustness, compliance with local regulations, and warranty terms |
| Marine | Starting motors for boats and marine vessels | Ensures safety and reliability in marine operations | Resistance to corrosion, compatibility with various engine types, and availability of marine-grade components |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine systems for starting mechanisms | Facilitates efficient energy generation and operational reliability | Adaptability to varying environmental conditions, certification for energy efficiency, and supplier reliability |
How is the Starting Motor Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, starter motors are crucial for initiating the engine in both passenger cars and commercial vehicles. They provide the necessary torque to turn the engine over, ensuring a reliable start every time. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions with diverse climates like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing high-quality starter motors that can withstand extreme temperatures is essential. Buyers must consider compatibility with various vehicle models and the availability of replacement parts to minimize downtime.
What Role Does the Starting Motor Play in Agriculture?
Starting motors are integral to agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, enabling them to operate efficiently. Reliable starting mechanisms are vital for maintaining productivity during critical planting and harvesting seasons. Buyers in South America, where agriculture is a significant industry, should focus on sourcing durable starter motors that can endure harsh conditions, including dust and moisture. Additionally, access to local service and parts support can significantly enhance operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to what is starting motor
How is the Starting Motor Essential in Construction Machinery?
In construction, starting motors are used in heavy machinery like excavators and bulldozers, where reliable engine ignition is paramount for project timelines. A malfunctioning starter motor can lead to costly delays. B2B buyers in Europe, particularly in Germany, should prioritize sourcing robust starter motors that meet stringent safety and performance standards. Furthermore, understanding warranty terms and after-sales support can help mitigate risks associated with machinery downtime.
Why are Starting Motors Important in Marine Applications?
Marine vessels rely on starter motors to ensure safe and reliable engine starts, which is critical for both safety and operational efficiency. The harsh marine environment demands starter motors that resist corrosion and can operate effectively in varying conditions. Buyers in the Middle East, where marine activities are prevalent, should focus on sourcing marine-grade starter motors with proven performance records. Compatibility with different engine types and reliable supplier relationships are key considerations.
How Do Starting Motors Contribute to Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbine systems, starting motors play a vital role in initiating turbine operation. Efficient starting mechanisms contribute to optimal energy generation and system reliability. International buyers must consider the adaptability of these motors to varying environmental conditions, especially in regions prone to high winds and fluctuating temperatures. Certification for energy efficiency and the reliability of the supplier are crucial factors for ensuring long-term operational success.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is starting motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying Starter Motor Issues in Vehicles
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly fleet managers or automotive repair shop owners, often face challenges in diagnosing starter motor issues. In many cases, vehicles exhibit symptoms like slow cranking or clicking sounds when attempting to start. However, these symptoms can also indicate battery problems or faulty wiring, leading to confusion and potential misdiagnosis. This uncertainty not only wastes time but can also lead to unnecessary replacement of components, increasing repair costs and downtime for vehicles.
The Solution:
To effectively diagnose starter motor issues, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive diagnostic tools. These tools should include multimeters and battery testers that can help identify whether the starter motor is receiving adequate power from the battery. Additionally, training staff to understand the specific electrical systems of different vehicle models will enhance their ability to pinpoint issues accurately. Providing clear guidelines for troubleshooting—such as checking battery connections and testing the solenoid—can streamline the diagnosis process and ensure that the right components are replaced. Establishing a partnership with reputable suppliers of starter motors and related diagnostic tools can also facilitate access to quality parts and support.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Reliable Starter Motors for Diverse Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing reliable starter motors that meet the specifications required for various vehicles in their fleet or inventory. With numerous manufacturers and models, it can be challenging to ensure compatibility and quality. Poor-quality starter motors can lead to frequent failures, resulting in increased maintenance costs and decreased trust from customers or end-users.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should develop strong relationships with established manufacturers and distributors that specialize in starter motors. Conducting thorough research to understand the specifications required for different vehicle models will enable buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It’s advisable to request samples or trial orders to evaluate the performance of starter motors before committing to large orders. Additionally, leveraging platforms that aggregate reviews and ratings can help identify trusted suppliers. Buyers should also consider investing in a warranty program with their suppliers to protect against defects and ensure they can replace faulty units without significant financial impact.
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Replacement Costs for Starter Motors
The Problem:
For businesses operating fleets, managing inventory and replacement costs for starter motors can be a daunting task. Frequent vehicle breakdowns due to starter motor failures can lead to unplanned expenses and disrupt operational efficiency. Additionally, maintaining an adequate inventory of starter motors that cater to various vehicle types without overstocking can complicate cash flow management.
The Solution:
Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can significantly alleviate these pain points. By analyzing historical failure rates and seasonal trends, B2B buyers can forecast demand more accurately and adjust their inventory levels accordingly. Establishing contracts with suppliers for regular deliveries based on these forecasts can ensure that the right starter motors are available when needed without tying up too much capital in stock. Furthermore, utilizing inventory management software can provide real-time tracking of stock levels and alert managers when it’s time to reorder. Training staff on preventative maintenance checks can also reduce the likelihood of starter motor failures, thus minimizing unexpected replacements and enhancing overall fleet reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is starting motor
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starter Motors?
When selecting materials for starter motors, several factors must be considered, including performance characteristics, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of starter motors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Starter Motors?
Steel is a widely used material in starter motor components, particularly for the casing and internal gears. It offers excellent tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for high-torque applications. Steel can withstand high temperatures, typically rated up to 300°C, and is resistant to deformation under pressure.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. Its strength ensures longevity and reliability in harsh operating conditions.
Cons: However, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can lead to premature failure in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Illustrative image related to what is starting motor
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media is generally good, but its susceptibility to rust necessitates protective coatings, especially in humid regions like parts of Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for steel grades and consider local regulations regarding material treatment and coatings.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Starter Motor Design?
Aluminum is increasingly used in starter motors due to its lightweight nature and good thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of around 200°C and is less dense than steel, which aids in reducing overall vehicle weight.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its resistance to corrosion, especially when anodized. This makes it suitable for applications in coastal or humid environments.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-torque applications without reinforcement.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various fluids and gases, making it versatile for different starter motor designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards for aluminum alloys is essential, particularly in Japan and other Asian markets. Buyers should also consider the cost implications of using aluminum versus steel.
What Role Does Copper Play in Starter Motors?
Copper is primarily used in starter motors for electrical connections and windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It can handle high currents, which is crucial for the starter’s performance.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity ensures efficient power transfer, reducing energy loss and enhancing the starter motor’s performance.
Cons: The main drawback of copper is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in acidic or saline environments, which can affect its longevity.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with most electrical systems, but its corrosion resistance must be considered, particularly in regions with harsh environmental conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper components meet relevant DIN standards and are properly treated to enhance corrosion resistance.
Why Is Plastic Used in Starter Motor Components?
Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers, are used for insulation and housing components in starter motors. They can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and offer good electrical insulation properties.
Pros: The lightweight nature of plastics can contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction, and they are generally resistant to corrosion.
Cons: However, plastics may not withstand high mechanical stress as well as metals, which can limit their use in critical load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with various chemicals, but their thermal limits must be considered in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for plastics, such as ASTM and ISO, is crucial, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is starting motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Casing and internal gears | High tensile strength | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Housing and lightweight components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical connections and windings | Excellent electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulation and non-load-bearing components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited mechanical strength | Low |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements, environmental conditions, and compliance with relevant standards.
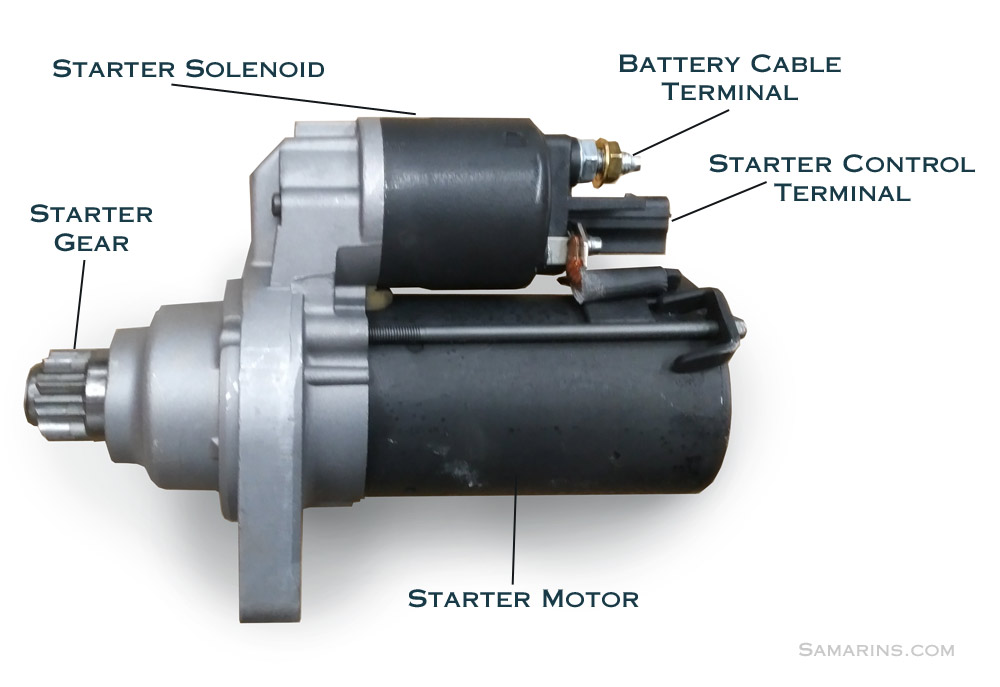
Illustrative image related to what is starting motor
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is starting motor
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Motors?
Manufacturing a starter motor involves several key stages that ensure the final product is reliable and efficient. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Are Materials Prepared for Starter Motor Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of materials. Starter motors typically utilize high-grade steel, copper, and plastic for various components. The selection of materials is crucial as they directly affect the motor’s performance and durability. Suppliers must ensure that raw materials meet specific industry standards, including those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Once materials are sourced, they undergo a quality inspection to verify their specifications. This may involve chemical analysis and physical testing to ensure they can withstand the operational stresses of a starter motor. Buyers should inquire about their suppliers’ material traceability systems to confirm the origins and quality of materials used.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Starter Motor Components?
Forming is a critical stage that shapes the components of the starter motor. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and machining are commonly employed. Stamping is often used for creating metal parts like the housing and brackets, while forging is used for parts requiring higher strength, like the pinion gear.
Precision machining is essential for components such as the armature and commutator, which must meet tight tolerances for optimal performance. Buyers should assess whether their suppliers employ computer numerical control (CNC) machining to enhance precision. Additionally, verifying that suppliers maintain a robust quality control process during forming can prevent defects and ensure consistency across batches.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Starter Motors?
The assembly stage combines all the manufactured components into a complete starter motor. This process typically involves several steps, including:
- Electrical Connections: Wiring is performed, ensuring all connections are secure and correctly insulated.
- Integration of Components: The solenoid, armature, and pinion gear are assembled, ensuring proper alignment and functionality.
- Final Assembly: The starter motor is enclosed in its housing, and all seals and fasteners are checked.
Quality assurance during assembly is vital, as errors can lead to performance issues or complete failure of the starter motor. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly line’s worker training and experience to ensure skilled labor is used in the assembly process.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) in starter motor manufacturing is essential for meeting both international and industry-specific standards. These QA processes can significantly affect the reliability and performance of the final product.
What International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
Most reputable manufacturers comply with international quality management standards such as ISO 9001. This certification indicates a commitment to consistent quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for automotive applications can be crucial.

Illustrative image related to what is starting motor
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers have the necessary certifications and that these are current. Regular audits and reassessments by certifying bodies ensure ongoing compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established at various stages, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various tests and inspections are performed to identify and rectify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the complete starter motor undergoes rigorous testing, including electrical tests and functional assessments, to ensure it meets performance specifications.
These checkpoints help maintain high-quality standards and reduce the likelihood of defective products reaching the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Starter Motors?
To ensure the functionality and reliability of starter motors, various testing methods are employed, including:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying that the motor operates at the correct voltage and current levels.
- Torque Testing: Measuring the torque produced by the motor to ensure it meets specifications.
- Durability Testing: Simulating extended use to assess the motor’s reliability over time.
B2B buyers should request details about the testing methods used by suppliers and the criteria for passing these tests. This can include documented test results and performance data for previous batches.
How Can Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
- Quality Reports: Requesting access to quality reports, including defect rates and compliance with quality standards, can help buyers assess supplier reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide unbiased evaluations of supplier quality practices, especially for international transactions where direct oversight may be limited.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Different regions may have varying expectations and definitions of quality. Understanding these differences can help in negotiations and establishing quality benchmarks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and standards, which may differ significantly from those in the buyer’s home country.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality can be impacted by shipping and handling practices. Buyers should discuss packaging and transportation methods with suppliers to mitigate risks during transit.
By understanding these aspects of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for starter motors, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable and high-quality products for their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is starting motor’
Introduction
In the dynamic world of automotive components, understanding the procurement of starter motors is crucial for B2B buyers. This guide provides a clear checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you acquire high-quality starter motors that meet your operational needs. By following these steps, you can mitigate risks, enhance performance, and optimize your supply chain.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search for starter motors, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider the specific type of vehicle or machinery the starter motor will be used for, including power ratings, torque specifications, and compatibility with existing systems.
– Key Details to Include:
– Engine type (diesel or petrol)
– Voltage requirements (12V or 24V)
– Size and weight constraints
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest trends and technological advancements in starter motors. Understanding market dynamics will help you identify which suppliers offer cutting-edge solutions that could enhance your operations.
– Focus Areas:
– Developments in integrated starter-generator systems
– Innovations in energy efficiency and durability
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers to ensure they align with your quality and service expectations. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to assess their capabilities.
– What to Look For:
– Supplier certifications (ISO, TS16949)
– Customer testimonials and industry reputation
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, always request samples of the starter motors. This step allows you to assess the quality and performance of the products firsthand, ensuring they meet your specifications.
– Testing Criteria:
– Performance under varying conditions
– Durability and lifespan predictions
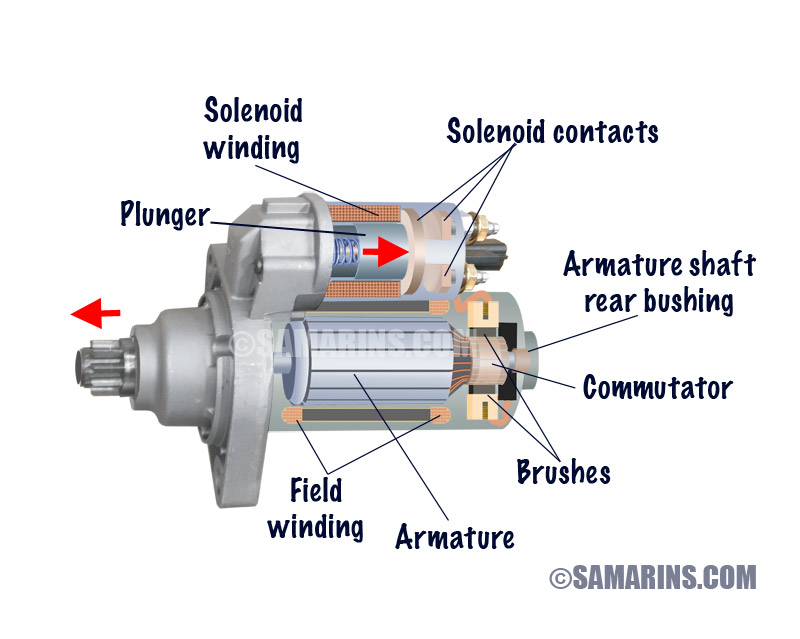
Illustrative image related to what is starting motor
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications that guarantee product quality and compliance with international standards. This verification is vital to avoid any potential liabilities.
– Important Certifications to Check:
– ISO 9001 for quality management
– CE marking for compliance with EU regulations
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms and conditions of the purchase. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, warranty conditions, and after-sales support.
– Key Negotiation Points:
– Bulk purchase discounts
– Return policy and warranty coverage
Step 7: Implement a Quality Control Process
After procurement, establish a quality control process to monitor the performance of the starter motors in real-world applications. This ongoing evaluation helps ensure that the products continue to meet your operational standards over time.
– Quality Control Measures:
– Regular performance assessments
– Feedback loops with maintenance teams
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in sourcing starter motors, ultimately leading to better operational efficiency and reliability in their automotive applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is starting motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starter Motors?
When sourcing starter motors, B2B buyers must consider a variety of cost components that contribute to the overall price. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing starter motors—such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and various alloys—can significantly influence costs. High-performance materials will typically increase the price but may offer better durability and efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region of production. Countries with lower labor costs, such as those in Southeast Asia, may provide competitive pricing, while European manufacturers may have higher labor costs due to stricter labor laws and standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production facilities can lower overhead costs, making the final product more cost-effective.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery can be substantial, especially for custom or high-specification starter motors. These costs are often amortized over large production runs, making high volume orders more economical.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that starter motors meet international standards and certifications can add to the cost. However, rigorous QC processes can prevent costly failures and warranty claims, making this an essential investment.
-
Logistics: The cost of shipping and handling can vary significantly based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, the mode of transport, and any customs duties involved. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial to budgeting for these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply a markup to cover their costs and profit margin. Buyers should compare margins across different suppliers to ensure they are getting a competitive price.
What Factors Influence the Price of Starter Motors?
Several factors play a critical role in determining the pricing of starter motors:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing; larger orders often lead to discounts. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate better terms based on volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications will generally incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected charges later in the sourcing process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) can increase costs but may be necessary for specific applications, especially in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and production capabilities of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears the cost and risk at various points in the shipping process.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Starter Motors?
-
Negotiation: Leverage your position as a buyer to negotiate better pricing and terms. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to more favorable conditions over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. A lower initial price may not always be the best deal if the product has a shorter lifespan or higher failure rate.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local regulations that may impact pricing. For instance, buyers in Europe may face different compliance costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Supplier Due Diligence: Conduct thorough background checks on potential suppliers to assess their reliability and quality. Request references and review past performance to make informed decisions.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and average pricing in different regions. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help identify competitive suppliers.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed in this guide are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer needs. Always conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure you are making the most informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is starting motor With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Starting Motors in Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, the starter motor is a crucial component that allows internal combustion engines to initiate operation. However, various alternative technologies exist that can either replace or complement the traditional starter motor. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and maintenance requirements.
Illustrative image related to what is starting motor
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Starting Motor | Alternative 1 Name: Integrated Starter Generator (ISG) | Alternative 2 Name: Air Start System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque for brief periods | Combines starting and generating functions, efficient | Quick engine start, reliable in cold weather |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront cost, but potential long-term savings | Moderate to high cost, dependent on air system setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in vehicles | Requires integration with electrical systems | Installation complexity varies, may need specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic checks | Generally low maintenance, but electrical issues can arise | Requires regular air supply checks |
| Best Use Case | Conventional internal combustion vehicles | Mild hybrids and electric vehicles | Aviation and heavy machinery applications |
Analyzing Integrated Starter Generators (ISG)
The Integrated Starter Generator (ISG) technology offers a sophisticated solution by merging the starter motor with an alternator. This dual functionality allows for smoother engine starts and greater efficiency, particularly in hybrid and electric vehicles. While the initial cost of ISG systems is generally higher than traditional starter motors, the potential for reduced fuel consumption and improved vehicle performance can result in long-term savings. Moreover, ISG systems typically require less maintenance compared to traditional systems, although they do necessitate a more complex integration with the vehicle’s electrical systems.
Exploring Air Start Systems
Air Start Systems are particularly beneficial in aviation and heavy machinery applications. These systems utilize compressed air to start engines, making them exceptionally reliable, especially in extreme weather conditions. While the performance is commendable, the cost of setting up an air start system can be moderate to high, depending on the complexity of the installation and the need for additional infrastructure to manage the air supply. Maintenance focuses primarily on ensuring the air supply remains reliable, which can be a drawback in environments where air compressors are not readily available.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Starting Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate starting solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application requirements, including performance needs, cost constraints, and maintenance capabilities. For those dealing with conventional internal combustion engines, the starter motor remains a dependable choice. However, for organizations focusing on fuel efficiency and hybrid technology, the Integrated Starter Generator presents a modern alternative. Meanwhile, industries such as aviation may find Air Start Systems to be the most reliable option, despite the potential for higher installation costs. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each solution will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is starting motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Starter Motor?
Understanding the technical specifications of a starter motor is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for automotive applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Torque Rating
Torque is a measure of the rotational force produced by the starter motor. A higher torque rating indicates the starter’s ability to turn over larger engines, making it vital for heavy-duty vehicles. B2B buyers should assess torque requirements based on engine size to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. -
Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of a starter motor, such as steel for the casing and copper for the windings, affect durability and performance. High-grade materials can withstand extreme conditions and prevent wear, which is critical for maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to strict material standards to ensure longevity. -
Current Draw
The amount of current a starter motor draws during operation is another key specification. This is typically measured in amps. Understanding current draw is essential for ensuring that the vehicle’s electrical system can support the starter without issues. B2B purchasers should evaluate the electrical capacity of their systems to avoid potential failures. -
Engagement Mechanism
The engagement mechanism, usually a solenoid, is responsible for connecting the starter motor to the engine’s flywheel. A reliable engagement system ensures quick and effective starting without damaging components. Buyers should consider the design and reliability of this mechanism, as it directly impacts overall performance. -
Temperature Rating
Starter motors are subject to extreme temperatures, both hot and cold. The temperature rating indicates the range within which the motor can operate effectively. Understanding this specification helps buyers select starters that will perform reliably in different climates, particularly in regions like Africa or the Middle East.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Motors?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and procurement in the automotive sector. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the original manufacturer of a vehicle. These parts are designed to meet specific quality and performance standards. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility, particularly in markets demanding high-quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory levels and cost management. Understanding MOQ helps businesses optimize their purchasing strategy and avoid excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. It’s an essential step for B2B procurement as it allows for comparison of costs and conditions. Companies should utilize RFQs to ensure they receive competitive pricing and favorable terms for starter motors. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations associated with the delivery of starter motors. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by companies other than the OEM. While they can be more affordable, their quality and compatibility can vary. B2B buyers should weigh the cost savings against potential risks when considering aftermarket starter motors for their applications. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and ensure timely project completion. Buyers should negotiate lead times with suppliers to align with their operational needs.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter motors, ensuring they meet their specific operational requirements and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is starting motor Sector
What are the Key Market Trends Impacting the Starter Motor Sector?
The starter motor sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by advancements in automotive technology and evolving consumer demands. One of the primary global drivers is the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models. This shift is prompting manufacturers to innovate starter motors that are compatible with integrated systems, such as starter-generator units. As traditional internal combustion engines are phased out in favor of cleaner technologies, the need for efficient and reliable starter motors remains critical.
Additionally, international B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality components that comply with stringent regulatory standards. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are observing a surge in demand for starter motors due to the growing automotive markets and rising vehicle ownership rates. In Europe, particularly in Germany, there is a marked emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, influencing procurement strategies to favor suppliers who demonstrate advanced manufacturing processes.
Emerging technologies, including IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence), are reshaping the sourcing landscape. Manufacturers are leveraging predictive analytics to forecast demand and streamline production, ensuring timely delivery of starter motors. B2B buyers are advised to seek partnerships with suppliers who invest in smart manufacturing technologies, which can enhance product reliability and performance.
How is Sustainability Shaping the Starter Motor Supply Chain?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the starter motor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in resource extraction and production waste, is a growing concern among international B2B buyers. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications into procurement processes is essential for buyers looking to align their operations with global sustainability goals. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 50001 for energy management are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who utilize renewable energy in their manufacturing processes can significantly minimize the environmental impact associated with starter motor production.
Ethical supply chains are also critical, particularly in regions where labor practices may be scrutinized. B2B buyers should conduct due diligence to ensure that their suppliers comply with international labor standards, promoting fair working conditions and responsible sourcing of raw materials. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, companies can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What is the Historical Evolution of the Starter Motor?
The evolution of the starter motor dates back to the early 20th century when Charles Kettering invented the electric starter in 1911. This innovation revolutionized the automotive industry, enabling drivers to start their vehicles with the simple turn of a key, eliminating the need for manual cranking. The design of starter motors has since advanced significantly, with modern versions incorporating sophisticated technologies to improve efficiency and performance.
Throughout the years, the starter motor’s functionality has expanded, especially with the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles. Today’s starter motors are often part of integrated systems that combine the roles of a starter and generator, reflecting the industry’s shift towards multifunctional components. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it underscores the importance of choosing suppliers who are not only aware of the latest technologies but also understand the historical significance of their products in the automotive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is starting motor
-
How do I determine if a starter motor is suitable for my vehicle?
To determine if a starter motor is suitable for your vehicle, verify the specifications such as the voltage, power output, and torque requirements. Cross-reference these with your vehicle’s make and model to ensure compatibility. It’s also advisable to check for any specific mounting configurations or electrical connections that may differ across manufacturers. Additionally, consult the manufacturer’s catalog or technical sheets, which often provide detailed compatibility information for different vehicle models. -
What are the common signs that indicate a starter motor needs replacement?
Common signs that a starter motor may need replacement include difficulty starting the engine, a clicking sound when turning the key, or the engine not cranking at all. If the motor runs intermittently or requires multiple attempts to start, this may indicate wear or internal failure. It’s also essential to rule out battery and electrical connection issues, as they can present similar symptoms. Regular inspections can help identify these issues before they lead to complete failure. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a starter motor internationally?
The lead time for ordering a starter motor internationally can vary based on the supplier, shipping method, and destination. Generally, you can expect a lead time of 2 to 6 weeks. Factors affecting this include production schedules, customs clearance, and the availability of specific models. It’s crucial to discuss timelines with your supplier and consider expedited shipping options if you require faster delivery. -
How can I vet a supplier for starter motors?
To vet a supplier for starter motors, review their industry reputation, certifications, and experience in manufacturing or distributing automotive components. Request references from other clients and check for customer reviews or testimonials. It’s also beneficial to visit their facility if possible, to assess their quality control processes and production capabilities. Ensure they comply with international standards and regulations relevant to your market. -
What customization options are available for starter motors?
Customization options for starter motors may include variations in voltage, torque specifications, mounting configurations, and electrical connectors. Some suppliers may also offer branding options, such as custom logos or specific paint finishes. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier, as they may have the capability to modify existing designs or create a tailored solution to meet your needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starter motors?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for starter motors can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 10 to 100 units. Factors influencing MOQ include production costs, inventory levels, and the specific model of the starter motor. When negotiating with suppliers, consider discussing the possibility of lower MOQs for initial orders or trial runs, especially if you are entering a new market or testing a new product line. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter motors?
Payment terms when sourcing starter motors can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include a deposit upfront (usually 30% to 50%) with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms of 30 to 90 days, especially for established relationships. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letters of credit) and ensure they align with your financial practices. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in starter motors?
When sourcing starter motors, look for suppliers that implement robust quality assurance measures, such as ISO certification, regular testing of components, and adherence to industry standards. Inquire about their testing procedures, including electrical performance, durability, and compliance with safety regulations. A supplier that provides warranties or guarantees on their products can also indicate confidence in their quality and reliability.
Top 5 What Is Starting Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Haynes – Starter Motors
Domain: us.haynes.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Haynes – Starter Motors, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. RAC – Starter Motor
Domain: rac.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Starter Motor: An essential electric component in internal combustion vehicles that initiates engine rotation when the ignition is engaged. It operates by receiving an electrical signal from the ignition system, activating the starter solenoid, which then sends charge to the battery and engages the starter motor to crank the engine. Common causes of failure include broken solenoids, mechanical iss…
3. AutoElectro – Starter Motors
Domain: autoelectro.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Starter motors are essential components that engage the engine during ignition, allowing it to turn over and suck in air and fuel for combustion. Key components include:
– Armature: An electromagnet mounted on the drive shaft, made of laminated soft iron core with conductor windings.
– Commutator: A section of the shaft that conducts electricity via brushes, made of two plates attached to the ar…
4. Reddit – Starter Motor Components
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Starter Motor Components, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. ScienceDirect – Starter Motor
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: A starter motor is a device required to run an internal combustion engine up to a speed sufficient for satisfactory carburation. It engages with the flywheel through a pinion, utilizing inertia-engaged or pre-engaged methods to transmit torque from the motor to the engine. Key features include:
– Mounted on the engine casing with a pinion engaging with the flywheel teeth.
– Gear ratio between pini…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is starting motor
In the realm of automotive components, the starter motor holds a pivotal role, ensuring the reliable initiation of internal combustion engines. As a fundamental part of vehicle functionality, understanding its mechanics, potential failures, and maintenance needs is crucial for B2B buyers. Strategic sourcing of high-quality starter motors not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces long-term costs associated with repairs and replacements.
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in reputable suppliers ensures access to durable and innovative starter motor solutions. Establishing strong partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize quality and reliability can lead to improved supply chain resilience and better service offerings.
Looking ahead, the automotive landscape is evolving with advancements in technology, including electric and hybrid systems that may redefine starter motor applications. Therefore, staying informed about emerging trends and technologies is essential. We encourage you to evaluate your sourcing strategies and consider the long-term benefits of quality components. By doing so, you position your business for success in an increasingly competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.