Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter motor
In today’s dynamic automotive landscape, sourcing reliable starter motors presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The starter motor is a critical component for internal combustion engines, playing an essential role in initiating the vehicle’s operation. As global markets expand, understanding the diverse types of starter motors, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting becomes imperative for businesses looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of starter motors available, from conventional systems to advanced integrated solutions used in modern hybrid vehicles. It addresses key considerations such as performance metrics, compatibility with different engine types, and maintenance requirements. Additionally, we explore the intricacies of cost analysis, helping buyers identify budget-friendly options without compromising on quality.
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—this guide serves as an invaluable resource. It equips decision-makers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the global starter motor market, ensuring that they can select the best products that meet their operational needs while maximizing efficiency and reliability. Empower your purchasing strategy with the insights provided in this guide, and ensure your business stays ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for starter motor
- Understanding starter motor Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of starter motor
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter motor’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter motor
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter motor
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter motor’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter motor Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter motor With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter motor
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter motor Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter motor
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter motor
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding starter motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC Starter Motors | Operate using direct current, typically compact and lightweight | Automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited torque for larger engines. |
| Gear Reduction Motors | Employ gear systems to amplify torque while reducing size | Construction equipment, marine vessels | Pros: High torque output, compact size. Cons: More complex, potentially higher maintenance. |
| Permanent Magnet Motors | Use permanent magnets for efficient operation | Electric vehicles, small machinery | Pros: High efficiency, lightweight. Cons: Higher initial cost, sensitive to heat. |
| Integrated Starter/Alternator | Combines starting and alternator functions | Hybrid and electric vehicles | Pros: Space-saving, improved fuel efficiency. Cons: Higher cost, specialized repair needs. |
| High-Performance Starter Motors | Designed for extreme conditions and high torque | Racing, performance vehicles | Pros: Exceptional durability and power. Cons: Premium pricing, may require specialized installation. |
What Are the Characteristics of DC Starter Motors?
DC starter motors are the most common type found in automotive applications. They utilize direct current to operate, making them straightforward and cost-effective. These motors are ideal for standard vehicles and light machinery where the power requirements are moderate. When purchasing, buyers should consider the motor’s torque rating and compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system to ensure optimal performance.
Why Choose Gear Reduction Motors for Heavy Machinery?
Gear reduction starter motors utilize a gear mechanism to increase torque output while minimizing size. This makes them particularly suitable for heavy machinery and construction equipment, where high torque is necessary to start large engines. B2B buyers should evaluate the gear ratio and overall durability, especially in demanding environments, to ensure they meet operational needs without frequent replacements.
How Do Permanent Magnet Motors Enhance Efficiency?
Permanent magnet motors are known for their high efficiency and lightweight design, making them an excellent choice for electric vehicles and small machinery. Their operation relies on permanent magnets rather than electromagnets, which reduces energy loss. When considering a purchase, buyers should assess the motor’s thermal tolerance and efficiency ratings to ensure it aligns with their energy consumption goals.
What Are the Benefits of Integrated Starter/Alternator Systems?
Integrated starter/alternator systems combine the functions of starting and charging, making them a popular choice for hybrid and electric vehicles. This design not only saves space but also enhances fuel efficiency by optimizing energy use. B2B buyers must consider the system’s compatibility with existing vehicle electronics and potential repair complexities, as these systems may require specialized knowledge for maintenance.
When to Consider High-Performance Starter Motors?
High-performance starter motors are engineered for extreme conditions, providing exceptional torque and durability suited for racing and performance vehicles. These motors are designed to withstand high stress and can significantly improve engine responsiveness. Buyers should weigh the benefits of increased power against the higher costs and potential installation requirements, ensuring they align with their performance goals.
Key Industrial Applications of starter motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Starter Motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Starting systems for vehicles | Ensures reliable engine ignition, enhancing vehicle performance | Quality certifications, compatibility with various models |
| Agriculture | Starting engines of tractors and farm equipment | Increases productivity by minimizing downtime during operations | Durability under harsh conditions, ease of maintenance |
| Construction | Heavy machinery starting systems | Facilitates quick mobilization of equipment on job sites | High torque requirements, resistance to environmental factors |
| Marine | Engine ignition for boats and vessels | Critical for operational efficiency in marine transport | Corrosion resistance, reliability in extreme conditions |
| Mining | Starting motors for heavy-duty mining equipment | Enhances operational efficiency in rugged environments | Robust design, ability to handle high-power demands |
How Are Starter Motors Utilized in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, starter motors are integral to the starting systems of vehicles. They provide the necessary torque to initiate engine operation, ensuring reliable ignition. For businesses in this industry, sourcing high-quality starter motors is crucial, as it directly affects vehicle performance and reliability. Buyers should consider compatibility with various vehicle models and the quality certifications of the motors to ensure they meet industry standards.
What Role Do Starter Motors Play in Agriculture?
Starter motors are essential for tractors and other agricultural equipment, enabling quick and reliable engine starts. This functionality is vital in agricultural operations, where time is of the essence, and delays can lead to significant productivity losses. Buyers in this sector should prioritize starter motors that demonstrate durability under harsh working conditions, as well as ease of maintenance to minimize downtime during critical farming periods.
How Are Starter Motors Applied in Construction Equipment?
In the construction industry, starter motors are used in heavy machinery such as excavators and bulldozers. These motors allow for the rapid mobilization of equipment, which is crucial for maintaining project timelines. Businesses should focus on sourcing starter motors that can deliver high torque, as well as those designed to withstand challenging environmental conditions, ensuring consistent performance on job sites.
Why Are Starter Motors Important in Marine Applications?
Starter motors are vital for the ignition systems of boats and vessels, where they ensure efficient engine operation. For marine businesses, the reliability of starter motors can significantly impact operational efficiency and safety in transport. Buyers should look for motors that offer corrosion resistance and reliability under extreme conditions, as these factors are critical for ensuring the longevity and performance of marine engines.
What Are the Key Considerations for Starter Motors in Mining Equipment?
In the mining industry, starter motors are utilized in heavy-duty equipment such as drills and haul trucks. These motors play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency within rugged environments. Buyers should consider sourcing robust starter motors capable of handling high-power demands and ensuring reliable performance under extreme conditions, which is essential for minimizing equipment failure and maximizing productivity in mining operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘starter motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Diagnosing Starter Motor Issues in Fleet Vehicles
The Problem:
B2B buyers managing fleets often encounter significant downtime due to starter motor failures in their vehicles. When a vehicle fails to start, it can disrupt operations, leading to delayed deliveries and increased costs. Fleet managers may struggle to identify whether the issue lies with the starter motor or if it’s a battery or electrical connection problem. This uncertainty complicates maintenance schedules and can result in unnecessary part replacements, further straining budgets.
The Solution:
To effectively address starter motor issues, fleet managers should implement a systematic diagnostic approach. Begin by ensuring that all vehicles undergo regular preventive maintenance checks, which include testing the starter motor’s performance along with the battery and electrical connections. Investing in diagnostic tools that can read error codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer can provide insight into whether the starter motor is functioning correctly.
When sourcing replacement starter motors, opt for reputable suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and compatibility information for your fleet’s vehicles. Consider purchasing remanufactured starter motors as a cost-effective alternative, ensuring they meet industry standards. Establishing a reliable supplier relationship will facilitate timely replacements and minimize downtime. Additionally, providing training for maintenance staff on how to properly test and install starter motors can further enhance operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Starter Motors for Diverse Applications
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing starter motors for a wide variety of vehicles and machinery, especially in regions with diverse automotive needs, such as Africa and South America. Variability in local market standards and availability of parts can lead to compatibility issues, performance inconsistencies, and ultimately, increased operational costs.
The Solution:
To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify local and international suppliers who specialize in starter motors for different applications, including commercial vehicles, agricultural machinery, and construction equipment. Building a database of suppliers that offer a range of starter motors can streamline the procurement process.
When engaging suppliers, request detailed catalogs that include specifications, compatibility information, and warranty details. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about your specific requirements, including voltage ratings and torque specifications, will help ensure that the parts sourced are suitable for the intended application. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support to assist in the selection of appropriate starter motors.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs Related to Starter Motor Failures
The Problem:
Cost management is a critical concern for B2B buyers, particularly in industries heavily reliant on machinery and vehicles. Starter motor failures can lead to unexpected repair costs and operational delays, affecting the overall budget and profitability. Companies may struggle to balance between purchasing high-quality starter motors and managing their maintenance expenditures effectively.
The Solution:
To manage costs associated with starter motor failures, organizations should adopt a proactive maintenance strategy. Implementing a predictive maintenance program using IoT sensors can help monitor the health of starter motors in real-time, allowing for early detection of potential issues before they lead to complete failures. This approach not only minimizes unexpected downtime but also extends the lifespan of the components.
Additionally, consider bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers for starter motors, which can provide cost savings and ensure a consistent supply of quality parts. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance expenses, rather than just the upfront purchase price, will enable better financial planning. Training staff on proper handling and installation techniques can further reduce the likelihood of starter motor failures, leading to long-term savings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for starter motor
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starter Motors?
When selecting materials for starter motors, several factors must be considered, including performance, durability, cost, and regional compliance standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in starter motors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Steel: A Durable Choice for Starter Motor Components
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it an excellent choice for components that undergo significant stress, such as the housing and mounting brackets of starter motors. It typically withstands high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for automotive applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and resistance to deformation under load. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to premature failure in harsh environments. Additionally, steel components can be heavier than alternatives, potentially impacting overall vehicle efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and its ability to endure high torque make it a reliable choice for starter motors. However, its weight could affect vehicle dynamics, especially in performance-oriented applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that steel components meet local corrosion resistance standards, as environmental conditions can vary widely. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel may also be necessary.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for components that require both strength and reduced weight, such as the starter motor casing.
Pros & Cons: The major advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can enhance fuel efficiency. However, it is generally less durable than steel and may require additional reinforcement for high-stress applications. Manufacturing aluminum parts can also be more complex and costly due to the need for specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance is beneficial in humid or coastal environments, where steel might fail. However, its lower strength may limit its use in high-torque applications without additional design considerations.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards, such as EN 573 for aluminum alloys. Understanding local recycling regulations for aluminum can also influence material selection.
Copper: Essential for Electrical Conductivity
Key Properties: Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a critical material for starter motor windings and connections. It can withstand high temperatures and has good corrosion resistance when properly coated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the efficiency of the starter motor. However, copper is heavier than aluminum and can be more expensive, impacting overall cost-effectiveness.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Impact on Application: Copper’s conductivity ensures that the starter motor operates efficiently, reducing energy loss during the starting process. However, its weight and cost may necessitate careful consideration in design and budget.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM B170 for copper wire may be essential. Buyers should also consider the local availability of copper and potential fluctuations in pricing.
Plastic Composites: Innovative and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Plastic composites are increasingly used in starter motors for non-load-bearing components due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic composites is their low weight and resistance to corrosion. However, they may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, limiting their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites can reduce the overall weight of the starter motor, improving vehicle efficiency. However, their thermal limitations may restrict their use in high-heat environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that plastic materials comply with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Understanding the local market for composite materials, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, can also influence sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for starter motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Housing and mounting brackets | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Casing and lightweight components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | High |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Plastic Composites | Non-load-bearing components | Lightweight and moldable | Limited thermal resistance | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in starter motors, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for starter motor
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Starter Motor?
The manufacturing process of starter motors encompasses several critical stages, each designed to ensure the end product meets the high-performance standards required for automotive applications. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
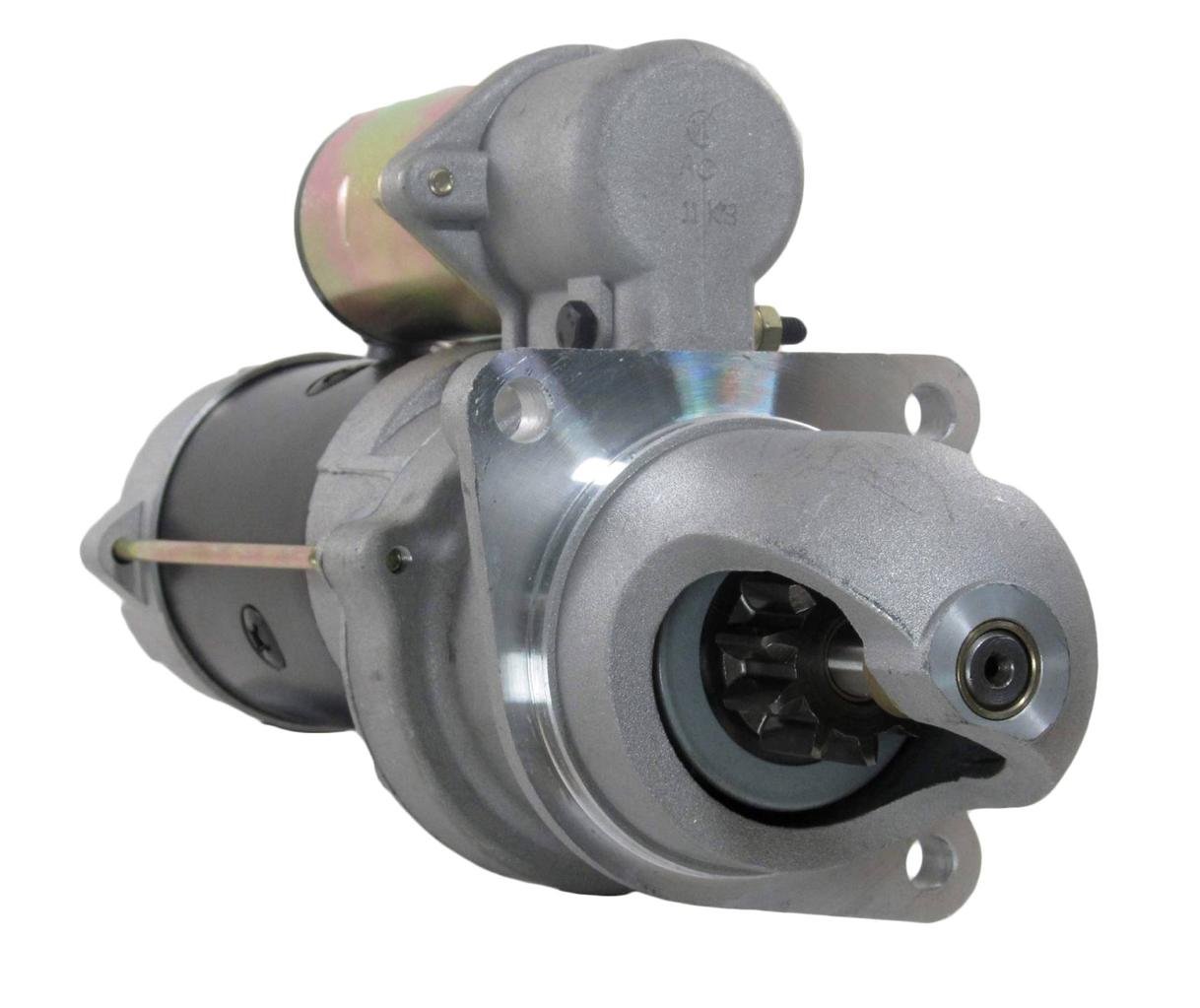

Illustrative image related to starter motor
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Motor Production?
The first step involves sourcing high-quality materials, primarily metals such as steel, copper, and aluminum. These materials are selected based on their mechanical properties, such as strength and conductivity.
- Material Inspection: Incoming materials undergo rigorous inspections to verify compliance with specified standards. This may include checking for chemical composition and physical properties.
- Cutting and Shaping: The materials are then cut and shaped into the required components, such as the casing, rotor, and stator. Techniques such as CNC machining or laser cutting ensure precision and consistency.
What Techniques Are Employed in the Forming Process?
The forming stage is crucial for creating the starter motor’s internal components.
- Stamping: Metal stamping is often used to form parts like the end plates and casing. This process allows for high-volume production with minimal waste.
- Winding: The armature winding is performed with precision. Copper wire is wound around the core to create the necessary electromagnetic field. This step is critical, as the winding quality directly affects the motor’s torque and efficiency.
- Molding: In some cases, plastic components are molded using injection techniques. These may include housing or insulation parts, which contribute to the motor’s durability and performance.
How Are Starter Motors Assembled?
Assembly is a multi-step process that combines all individual components into a fully functional starter motor.
- Initial Assembly: Workers or automated systems place the rotor into the casing, followed by the installation of the stator and other internal components.
- Electromechanical Integration: The solenoid, which is responsible for engaging the motor, is attached. This step requires careful alignment to ensure proper engagement and disengagement with the flywheel.
- Final Assembly: After all components are fitted, the motor is sealed, and any additional features, such as connectors and sensors, are added. Quality checks are conducted throughout this process to detect any issues early.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Starter Motors?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and longevity of starter motors.
- Surface Treatment: Components undergo surface treatments like galvanization or powder coating to prevent corrosion and enhance appearance.
- Final Testing: Each motor is tested for functionality, including torque output and electrical resistance. This ensures that the product meets operational specifications before it leaves the factory.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Starter Motors?
Quality assurance is essential in the manufacturing of starter motors, with several international and industry-specific standards guiding the process.
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance indicates that the manufacturer consistently provides products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking signifies that the starter motor meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers supplying to the automotive sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures compatibility and performance in oil and lubricants.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Motor Production?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process with specific checkpoints designed to catch defects at various stages.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of components as they are produced. This might include dimensional checks and visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final assembly undergoes comprehensive testing to verify performance metrics. This may include functional tests, electrical tests, and durability tests to ensure reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is critical to ensure product reliability.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers helps buyers assess compliance with quality standards. These audits can evaluate processes, equipment, and employee training.
- Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control processes and test results provides insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality. Look for evidence of adherence to ISO standards and other certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly useful for verifying compliance with international standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control and certifications can be challenging for international buyers.
- Regional Compliance: Buyers should be aware of the specific compliance requirements for their region. For instance, the Middle East may have unique standards compared to European markets.
- Documentation: Ensure that all certifications and compliance documents are up-to-date and readily available. This not only aids in verifying quality but also helps in customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
- Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality concerns and compliance issues. Regular feedback loops can help suppliers improve their processes based on buyer experiences.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in starter motor production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘starter motor’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing a reliable starter motor is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency. This guide provides a clear checklist to help international buyers navigate the complexities of purchasing starter motors, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications of the starter motor required for your applications. Consider factors such as voltage, torque rating, and compatibility with specific vehicle models. This step ensures that you communicate precise requirements to potential suppliers and reduces the risk of purchasing an incompatible product.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Invest time in identifying trustworthy suppliers with a proven track record in the automotive parts industry. Look for companies that specialize in starter motors and have experience in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilize platforms like industry trade shows, online directories, and trade associations to gather a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, references, and case studies to gauge their reliability and performance. Pay special attention to suppliers who have successfully serviced businesses in similar regions or industries, as they are likely to understand your unique challenges and requirements.
Step 4: Verify Quality Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering possess relevant quality certifications, such as ISO 9001. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality management systems and can provide assurance regarding the reliability and performance of their products. Additionally, check if the starter motors meet international quality standards specific to your industry.
Step 5: Assess Warranty and Return Policies
A robust warranty and clear return policies are critical when sourcing starter motors. Inquire about the duration of the warranty and what it covers, as this reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in their product. Understand the return process in case the motor does not meet your expectations, as this can save you time and money in the long run.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing any order, request samples of the starter motors for testing. This hands-on evaluation allows you to assess compatibility, performance, and overall quality. Ensure that the samples meet your specifications and operational requirements, as this step can prevent costly errors in bulk orders.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and conditions. Discuss pricing, payment options, lead times, and shipping arrangements to ensure that all aspects of the transaction are clear. A well-negotiated agreement can lead to long-term partnerships that benefit both parties.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for starter motors, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for starter motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Starter Motors?
When considering the sourcing of starter motors, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as copper for windings, steel for the casing, and various plastics for housing and connectors, plays a significant role. Fluctuations in the prices of these materials can directly affect overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and manufacturing practices. Regions with higher wage rates, such as parts of Europe, will have higher labor costs compared to regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these expenses.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized starter motors. Investments in specialized tools and dies are necessary for high-precision components.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and performance of starter motors necessitates robust QC processes, which add to the overall cost. Certifications (like ISO) may also require additional investment.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and handling, can vary significantly based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, as well as the mode of transport used.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin based on their operational costs and market positioning. Understanding the margins in your target market is essential for effective negotiation.
What Influences the Pricing of Starter Motors in International Markets?
Several factors influence the pricing structure for starter motors, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing strategies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications or modifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can drive up costs. Buyers should evaluate the importance of these factors against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products based on perceived quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements. These terms can affect overall landed costs.
What Are Effective Tips for Negotiating Starter Motor Prices?
B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy by employing several negotiation tactics:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When negotiating, consider not just the purchase price but also the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs associated with starter motor failure.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining multiple quotes from different suppliers can provide leverage during negotiations. This practice helps identify competitive pricing and quality options.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Consider negotiating contracts that reward loyalty with discounts.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of regional pricing variations and market conditions. For example, the demand for starter motors in Africa may differ from that in Europe, impacting pricing strategies.
-
Be Prepared for Cultural Differences: When negotiating with suppliers from different regions, be aware of cultural norms that may influence communication styles and negotiation tactics.
Conclusion
In summary, B2B buyers of starter motors must navigate a complex landscape of cost components and pricing influences. By understanding these factors and employing effective negotiation strategies, buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions and achieve favorable outcomes. Keep in mind that indicative prices can fluctuate due to market conditions, and it is advisable to conduct thorough research and maintain flexibility in your sourcing approach.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing starter motor With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Starter Motors: A Comparative Analysis
In the automotive industry, starter motors have long been a standard solution for initiating the operation of internal combustion engines. However, as technology evolves, businesses are increasingly seeking alternatives that may offer enhanced performance, cost efficiency, or unique operational benefits. This section provides a detailed comparison of starter motors against two viable alternatives: Integrated Starter Generator (ISG) and Manual Crank Systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Starter Motor | Integrated Starter Generator (ISG) | Manual Crank System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque for quick engine start | Provides both starting and energy recovery | Requires physical effort and skill |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, affordable | Higher upfront cost, potential savings on fuel | Low cost, minimal investment required |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in most vehicles | Requires compatible engine systems | Simple installation, limited to older models |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed, prone to wear | Low maintenance, integrated design reduces wear | Minimal maintenance, depends on user skill |
| Best Use Case | Conventional vehicles, reliable use | Hybrid and electric vehicles, efficiency-focused | Vintage cars, manual enthusiasts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
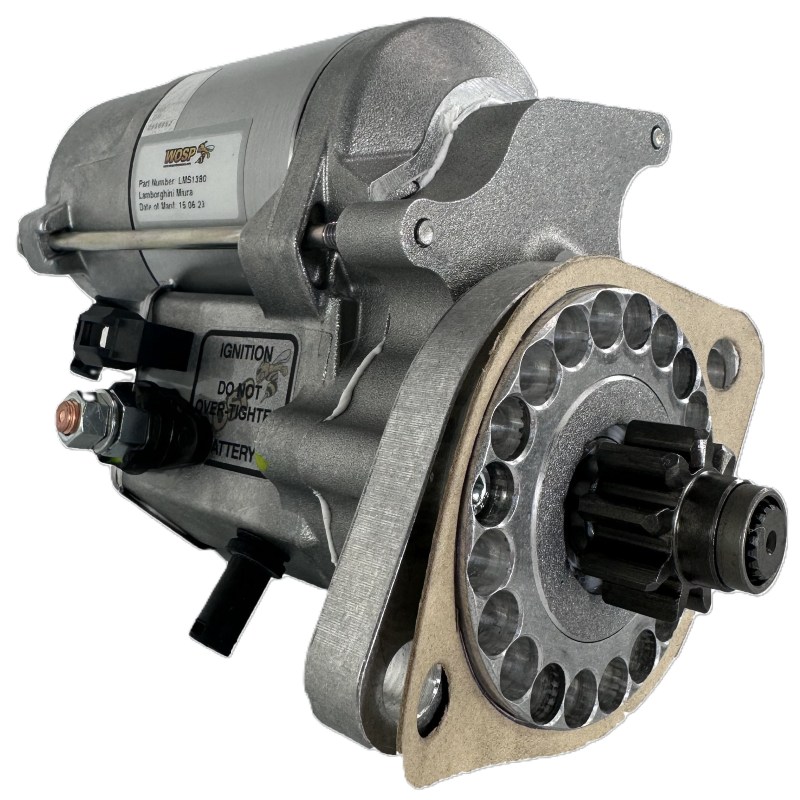
Integrated Starter Generator (ISG)
The Integrated Starter Generator combines the functionalities of a starter motor and an alternator. This system not only starts the engine but also recovers energy during braking, converting it into electricity to recharge the battery. The ISG is particularly advantageous for hybrid vehicles where fuel efficiency is paramount.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Pros: The ISG offers enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, making it ideal for businesses looking to comply with environmental regulations. It also reduces the number of components needed in the engine, potentially lowering overall maintenance costs.
Cons: The initial investment for an ISG system is significantly higher than that of a traditional starter motor. Additionally, its complexity requires specific engineering and design considerations, which may not be feasible for all vehicle types.
Manual Crank System
The manual crank system is a traditional method for starting engines, primarily seen in older vehicles. This system involves physically cranking a lever to start the engine. While largely obsolete in modern vehicles, it remains a viable option for vintage car restorations or in remote areas with limited resources.
Pros: The manual crank system has low initial costs and requires minimal investment in parts. It is straightforward to use and can be a reliable option when modern electrical systems are unavailable.
Cons: This method demands physical effort and skill, which may not be practical for all users. Additionally, its inefficiency and the need for manual operation make it unsuitable for everyday use in most modern contexts.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate starting solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the type of vehicles they operate, budget constraints, and operational requirements. For fleets prioritizing fuel efficiency and sustainability, the Integrated Starter Generator may offer long-term savings despite its higher initial costs. Conversely, for businesses dealing with older models or vintage cars, a starter motor or manual crank system may be more practical and economical. By evaluating these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific operational goals and financial considerations.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for starter motor
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of a Starter Motor?
Understanding the technical properties of starter motors is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing components for automotive applications. Here are several key specifications that impact performance and compatibility.
1. Torque Rating
Torque rating is a critical specification that indicates the rotational force the starter motor can exert to turn the engine over. Typically measured in Newton-meters (Nm) or foot-pounds (ft-lbs), this rating is crucial for ensuring that the starter can handle the engine’s size and compression. Buyers need to consider the torque rating to match the starter motor with specific engine requirements, especially in regions with diverse vehicle types.
2. Voltage Rating
Starter motors are generally designed to operate at specific voltage levels, commonly 12V for most passenger vehicles. Understanding the voltage rating is vital for ensuring compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system. A mismatch can lead to inefficient starting or potential damage to the motor and the vehicle’s battery.
3. Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of a starter motor, such as copper for windings and high-grade steel for the housing, affect durability, efficiency, and performance. High-quality materials can reduce wear and increase the lifespan of the motor, which is particularly important in regions with extreme weather conditions that may impact vehicle performance.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
4. Engagement Mechanism
The engagement mechanism, typically a solenoid, is responsible for connecting the starter motor to the engine’s flywheel. Understanding how this mechanism works is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. Different designs can affect the speed and reliability of engagement, impacting overall vehicle performance.
5. Weight and Dimensions
The weight and physical dimensions of a starter motor are critical for compatibility with the vehicle’s mounting space. Buyers should verify these specifications to ensure a proper fit, especially when replacing or upgrading existing components. Compact designs may be preferred in smaller vehicles, while heavier-duty starters may be necessary for larger engines.
6. Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance indicates how well a starter motor can withstand high temperatures during operation. This property is particularly important in hotter climates, where excessive heat can lead to premature failure. A starter with high thermal resistance will ensure reliable performance and reduce the likelihood of breakdowns.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Motors?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are several common terms relevant to starter motors:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to components produced by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. Sourcing OEM starter motors ensures compatibility and reliability, as these parts are designed to meet the specifications of the vehicle they are intended for. Many buyers prefer OEM parts for their quality assurance and warranty.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they meet supplier requirements. This term is particularly relevant when sourcing starter motors in bulk for fleet maintenance or resale.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. When sourcing starter motors, an RFQ helps buyers compare offers from multiple suppliers, allowing for informed purchasing decisions that can lead to cost savings.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Knowledge of these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving starter motors, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties, thereby minimizing potential disputes.
5. Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to parts and components that are not sourced from the original manufacturer but are made to fit specific vehicles. Many buyers opt for aftermarket starter motors for cost savings, but it’s essential to ensure that these parts meet quality and performance standards.
6. Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the starter motor and its performance over a specific period. Understanding warranty terms is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can impact long-term maintenance costs and product reliability.
These technical properties and trade terms provide essential insights for B2B buyers looking to source starter motors effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the starter motor Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Starter Motor Market?
The global starter motor market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several factors. Firstly, the increasing demand for vehicles, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is a primary driver. As urbanization progresses and disposable incomes rise, more consumers are investing in personal and commercial vehicles, leading to heightened demand for reliable starter motors.
Technological advancements are also shaping the industry. The integration of smart technologies, including IoT and advanced diagnostics, allows for enhanced performance and maintenance monitoring of starter motors. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that provide these innovative features, which can lead to reduced operational downtime and improved vehicle efficiency.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Another trend is the shift toward electric and hybrid vehicles. As manufacturers pivot to meet environmental regulations and consumer preferences for greener options, the demand for starter motors that support these technologies is on the rise. This transition presents opportunities for international B2B buyers to source advanced starter motor solutions that cater to new vehicle types.
Finally, geopolitical factors and trade agreements can impact sourcing strategies. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must stay informed about tariffs, regulations, and trade relationships that could affect the availability and pricing of starter motors.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Starter Motors?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the sourcing of starter motors. The automotive industry is under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, making it essential for B2B buyers to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes that minimize waste and energy consumption.
Ethical sourcing is another vital aspect. Buyers should focus on suppliers that uphold fair labor practices and transparency in their supply chains. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the values of a growing consumer base that favors ethically produced products.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, sourcing starter motors made from recycled materials or those that are designed for easy disassembly and recycling at the end of their lifecycle can further enhance a company’s sustainability profile.
By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also position themselves as leaders in the transition to a more sustainable automotive industry.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Motors for B2B Buyers?
The starter motor has undergone significant evolution since its invention by Charles Kettering in 1911, which revolutionized the automotive industry by eliminating the need for manual cranking. Initially, starter motors were integrated with generators and ignition systems. However, as automotive technology advanced, these components became separate entities, leading to improved performance and reliability.
Over the decades, the design and functionality of starter motors have continually adapted to meet the demands of more sophisticated vehicle engines, including the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles. Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it provides insights into the technological advancements that have shaped current starter motor offerings.
Today, the focus is on enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact, which reflects broader trends in the automotive sector. Buyers should consider suppliers that leverage this historical evolution to offer innovative, high-performance starter motors that align with modern automotive needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of starter motor
-
How do I determine if a starter motor is the right fit for my vehicle?
To ensure compatibility, it’s crucial to verify the specifications of your vehicle’s make and model against the starter motor’s technical details. Key factors include the voltage, torque ratings, and physical dimensions. Request detailed product catalogs or data sheets from suppliers, and consider consulting with a technical expert if needed. Additionally, establishing clear communication with your supplier about your vehicle’s requirements can help prevent mismatches. -
What are the common signs that a starter motor needs replacement?
Frequent symptoms of a failing starter motor include a clicking sound when turning the key, the engine cranking slowly, or complete failure to start. If the starter motor engages intermittently or requires multiple attempts to start, it may also indicate wear. Establish a maintenance schedule to inspect the starter regularly, particularly in regions with extreme weather, which can exacerbate wear and tear. -
What is the typical lead time for sourcing starter motors from international suppliers?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location, production capacity, and shipping methods. Generally, you can expect anywhere from 2 to 12 weeks for delivery. It’s advisable to discuss lead times upfront during negotiations and factor in potential delays, especially during peak seasons or due to customs clearance in international shipping. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter motors?
MOQs can differ widely among suppliers, ranging from a few units to several hundred, depending on their production capabilities and market strategy. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility with MOQs, especially if you are a smaller buyer. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for initial orders or sample purchases. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing starter motors?
Implement a robust QA process by requesting certifications and quality control documentation from your suppliers. Look for products that meet international standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facility or employing third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipment. Regular quality audits can also help maintain standards in ongoing supplier relationships. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter motors internationally?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include upfront payments, letters of credit, or staggered payments based on delivery milestones. Ensure you understand the terms clearly before proceeding, and consider negotiating favorable conditions such as extended payment periods or discounts for early payments. Always assess the financial stability and reputation of the supplier before committing to terms. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing starter motors?
When importing, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international trade regulations in your region. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides accurate shipping documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Planning for potential delays or damages during transit can also mitigate risks. -
How can I vet potential suppliers for starter motors?
Start by researching suppliers through industry directories and trade shows, focusing on their reputation and customer reviews. Request references from other buyers and assess their manufacturing capabilities and certifications. It’s beneficial to conduct background checks or site visits to verify their operations. Establishing a trial order can also help gauge their reliability and product quality before committing to larger purchases.
Top 4 Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Haynes – Ignition System Insights
Domain: us.haynes.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Haynes – Ignition System Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. RAC – Starter Motor
Domain: rac.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Starter Motor: An essential electric component in internal combustion vehicles that initiates engine rotation when the ignition is engaged. It operates by receiving an electrical signal that activates the starter solenoid, sending charge to the battery and engaging the starter motor to crank the engine. Common causes of failure include broken solenoid, mechanical issues, electrical faults, overhea…
3. Auto Electro – Starter Motors
Domain: autoelectro.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Starter motors are responsible for turning the engine over during ignition, allowing air and fuel to enter for combustion. Key components include:
– Armature: An electromagnet mounted on the drive shaft, made of laminated soft iron core with conductor windings.
– Commutator: A section of the shaft with two plates that provide connections for the electromagnet coil.
– Brushes: Conduct electricit…
4. ScienceDirect – Starter Motor
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: A starter motor is a device required to run an internal combustion engine up to a speed sufficient for satisfactory carburation. It engages with the flywheel through a pinion, utilizing inertia-engaged or pre-engaged methods to transmit torque from the motor to the engine. The gear ratio between the pinion and flywheel is about 10:1. The series wound motor is ideal for developing maximum torque at…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for starter motor
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, strategic sourcing of starter motors is pivotal for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of starter motor functionality and the factors influencing their performance can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. With a growing demand for reliable starter motors across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-quality components from reputable suppliers is essential.

Illustrative image related to starter motor
Key considerations include evaluating supplier capabilities, ensuring compliance with regional standards, and leveraging technological advancements in starter motor design. As electric and hybrid vehicles gain traction, the need for innovative starter solutions that integrate seamlessly with modern automotive systems will become increasingly important.
International buyers should prioritize establishing strong relationships with manufacturers who can provide not only product quality but also responsive service and support. By embracing a strategic sourcing approach, businesses can optimize their supply chains, reduce downtime, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the automotive sector will continue to transform, presenting new opportunities for those who adapt quickly. Engage with your suppliers today to secure the best solutions for your starter motor needs and stay ahead in this competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.