Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for que es un alternador
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding the intricacies of automotive components like an alternator is critical for international B2B buyers. The alternator is not merely a part of a vehicle; it plays a pivotal role in powering electrical systems and ensuring that batteries remain charged. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia) seek reliable suppliers, the challenge lies in sourcing high-quality alternators that meet diverse operational needs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of alternators, exploring various types, their applications in different vehicle models, and crucial factors to consider when vetting suppliers. It also addresses cost considerations, maintenance requirements, and troubleshooting common issues associated with alternators. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and data-driven recommendations, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions that can enhance operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
Whether you are looking to upgrade your fleet, ensure compliance with regional automotive standards, or simply understand the alternator’s functionality better, this resource serves as a valuable tool in navigating the global market. Empower your business with the knowledge needed to make sound investments in automotive technology.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Que Es Un Alternador Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for que es un alternador
- Understanding que es un alternador Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of que es un alternador
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘que es un alternador’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for que es un alternador
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for que es un alternador
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘que es un alternador’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for que es un alternador Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing que es un alternador With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for que es un alternador
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the que es un alternador Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of que es un alternador
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for que es un alternador
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding que es un alternador Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt-Driven Alternator | Utilizes a belt and pulley system; common in most vehicles. | Automotive manufacturing and repair | Pros: Widely available, easy to replace. Cons: Belt wear can lead to maintenance issues. |
| Gear-Driven Alternator | Uses gears for power transfer; typically more durable. | Heavy machinery and industrial vehicles | Pros: Robust design, less prone to slippage. Cons: Higher initial cost, more complex installation. |
| High-Output Alternator | Designed to generate more electricity; larger size. | Performance vehicles and custom builds | Pros: Supports high-demand electrical systems. Cons: May require modifications to fit standard mounts. |
| Marine Alternator | Built to withstand harsh marine environments; corrosion-resistant. | Marine vessels and equipment | Pros: Durable, reliable in wet conditions. Cons: Higher cost due to specialized materials. |
| Smart Alternator | Incorporates advanced electronics for efficiency and monitoring. | Electric and hybrid vehicles | Pros: Optimizes power use, increases battery life. Cons: More expensive and requires specialized knowledge for installation. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Belt-Driven Alternators?
Belt-driven alternators are the most common type found in standard vehicles. They operate by connecting to the engine through a belt and pulley system, generating electricity when the engine runs. This type is highly suitable for automotive manufacturing and repair due to its widespread availability and ease of replacement. However, buyers should consider the potential for belt wear, which can necessitate regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
How Do Gear-Driven Alternators Differ from Other Types?
Gear-driven alternators utilize gears instead of belts for power transfer, making them particularly robust and durable. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and industrial vehicles where reliability is paramount. While their sturdiness offers advantages in demanding environments, the initial cost is typically higher, and installation can be more complex, which may deter some buyers.
What Makes High-Output Alternators Suitable for Performance Vehicles?
High-output alternators are designed to produce significantly more electricity than standard models, making them ideal for performance vehicles and custom builds that require additional power for high-demand electrical systems. These alternators can support advanced audio systems, lighting, and other accessories. However, buyers should be aware that they may need to modify their vehicles to accommodate these larger units, potentially increasing installation costs.
Why Are Marine Alternators Essential for Vessels?
Marine alternators are specifically engineered to endure the harsh conditions found in marine environments. They are constructed with corrosion-resistant materials to ensure longevity and reliability on the water. These alternators are essential for marine vessels and equipment, providing dependable power generation. However, their specialized design often comes with a higher price tag, which buyers must factor into their purchasing decisions.
What Advantages Do Smart Alternators Offer in Modern Vehicles?
Smart alternators feature advanced electronics that allow for real-time monitoring and optimization of power generation and distribution. This technology is particularly beneficial in electric and hybrid vehicles, where energy efficiency is crucial. While these alternators can significantly extend battery life and improve overall vehicle performance, they typically come with a higher price point and require specialized knowledge for installation, which may be a consideration for B2B buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of que es un alternador
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of que es un alternador | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Powering vehicle electrical systems | Ensures reliable operation of critical vehicle components | Quality certifications, compatibility with vehicle models, and warranty terms |
| Renewable Energy | Hybrid vehicle systems | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces fuel consumption | Efficiency ratings, integration capabilities, and service support |
| Industrial Equipment | Backup power generation for machinery | Provides uninterrupted power supply during outages | Load capacity, durability, and maintenance requirements |
| Marine Industry | Powering onboard electrical systems in vessels | Supports navigation and safety systems | Compliance with maritime regulations and environmental standards |
| Construction Equipment | Charging systems for heavy machinery | Reduces downtime and ensures operational reliability | Robustness, resistance to harsh environments, and serviceability |
How is que es un alternador utilized in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, alternators play a crucial role in powering the vehicle’s electrical systems, including lights, infotainment, and safety features. As vehicles increasingly rely on electronic components, a reliable alternator ensures that batteries are consistently charged and operational. For international B2B buyers, sourcing alternators that meet quality standards and compatibility with various vehicle models is essential to avoid costly downtimes and maintain customer satisfaction.
What are the applications of que es un alternador in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, alternators are integral to hybrid vehicle systems, where they convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This application not only enhances energy efficiency but also significantly reduces fuel consumption and emissions. B2B buyers in this sector must prioritize alternators with high efficiency ratings and robust integration capabilities to ensure seamless performance with existing systems.
How does que es un alternador support Industrial Equipment?
For industrial equipment, alternators are often employed as backup power generators, ensuring that machinery remains operational during power outages. This application is vital in maintaining production schedules and avoiding financial losses due to downtime. When sourcing alternators for this purpose, businesses should consider factors such as load capacity and durability, ensuring that the equipment can withstand heavy use and harsh conditions.
What is the role of que es un alternador in the Marine Industry?
In the marine industry, alternators are essential for powering onboard electrical systems, including navigation, communication, and safety equipment. A reliable alternator is crucial for the safe operation of vessels, particularly in challenging maritime environments. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing alternators that comply with maritime regulations and environmental standards to ensure safety and sustainability.
How are que es un alternador utilized in Construction Equipment?
Construction equipment frequently relies on alternators to charge batteries and power electrical systems essential for operation. This application is critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring that heavy machinery operates effectively on job sites. When sourcing alternators for construction equipment, businesses should prioritize robustness and resistance to harsh environments, as well as ease of maintenance to maximize operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘que es un alternador’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Importance of Alternators for Vehicle Functionality
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in the automotive repair and maintenance sectors, often struggle to communicate the importance of alternators to their clients. Many vehicle owners believe that the battery alone is responsible for powering the electrical systems of their cars. This misunderstanding can lead to improper vehicle maintenance, where clients neglect alternator issues, resulting in more severe problems such as complete vehicle failure, unexpected breakdowns, and increased repair costs.
The Solution: Educate clients on the critical role of alternators in vehicle functionality. Create informative materials, such as brochures or videos, that clearly explain how alternators work, the consequences of neglecting them, and the signs of potential failure (e.g., dimming lights, strange noises, or warning lights). Furthermore, consider offering workshops or webinars to engage with clients directly. This proactive approach not only empowers clients with knowledge but also positions your business as a trusted resource in their vehicle maintenance journey.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Alternators for Diverse Vehicle Models
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality alternators that are compatible with a wide range of vehicle models. In markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where vehicle diversity is high, finding reliable suppliers who can provide alternators that meet specific quality standards is crucial. Poor-quality alternators can lead to frequent replacements and dissatisfaction among clients, harming the buyer’s reputation.
The Solution: Establish partnerships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who specialize in producing high-quality alternators. Conduct thorough research and due diligence to ensure these suppliers adhere to international quality standards. Additionally, consider implementing a testing protocol for incoming products to verify their performance and compatibility with various vehicle types. By ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality alternators, you can enhance customer satisfaction and build long-term relationships based on trust and reliability.
Scenario 3: Managing Alternator Maintenance and Repair Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the automotive sector struggle with managing the costs associated with alternator maintenance and repairs. This is particularly pressing for businesses operating in regions where labor and parts can be expensive. Clients may be hesitant to invest in proper maintenance or repairs due to perceived high costs, leading to a cycle of reactive rather than proactive maintenance.
The Solution: Develop a comprehensive maintenance plan that emphasizes regular check-ups and timely repairs to prevent more significant issues down the line. Offer tiered service packages that allow clients to choose a level of maintenance that fits their budget while still ensuring their vehicles remain in optimal condition. Educate clients on the long-term savings of preventative maintenance versus the costs associated with emergency repairs. Additionally, consider providing flexible financing options for larger repair jobs to make it easier for clients to commit to necessary services without straining their budgets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for que es un alternador
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Alternators?
When selecting materials for alternators, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and international standards compliance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in alternator construction: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Alternators?
Aluminum is widely used in alternator housings and components due to its favorable properties. It boasts excellent corrosion resistance and is lightweight, which helps in reducing the overall weight of the vehicle. Aluminum can withstand moderate temperature and pressure conditions, making it suitable for automotive applications.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature improves fuel efficiency and handling. It also has good thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat generated during operation.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as well as some other metals. Additionally, it can be more expensive than steel, impacting overall production costs.
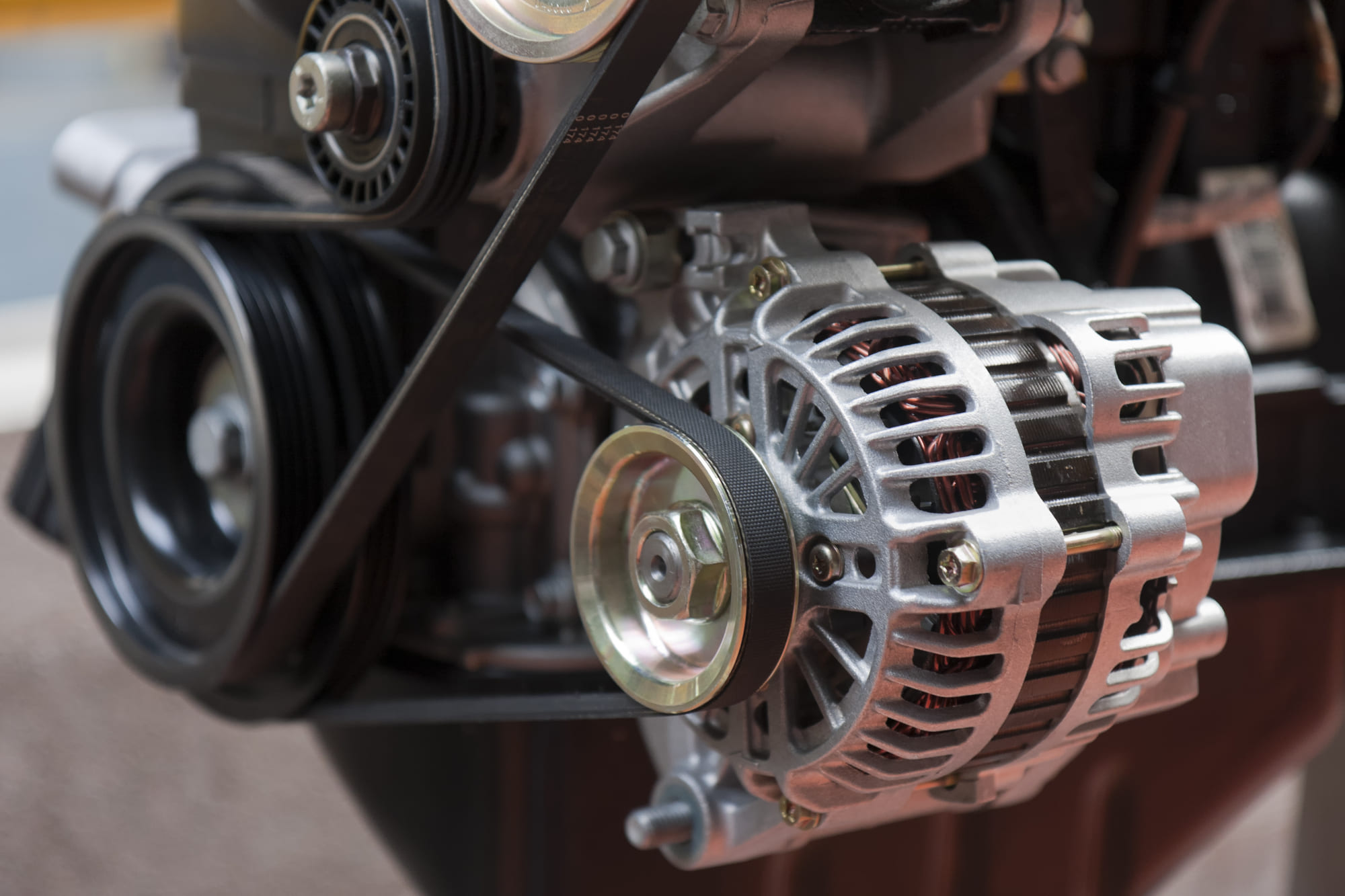
Illustrative image related to que es un alternador
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for vehicles operating in humid or coastal environments, which is particularly relevant for regions like Africa and the Middle East, where such conditions are common.
What Role Does Copper Play in Alternators?
Copper is a critical material in alternators, primarily used in windings and electrical connections. It has excellent electrical conductivity, which is vital for efficient energy transfer from the alternator to the vehicle’s electrical systems.
Pros: The high conductivity of copper ensures minimal energy loss, enhancing the alternator’s efficiency. Copper is also highly durable and resistant to corrosion, contributing to a longer lifespan.
Illustrative image related to que es un alternador
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost; copper is generally more expensive than aluminum or steel. Additionally, it can be heavier, which may affect the overall weight of the alternator.
Impact on Application: Given its high conductivity, copper is essential for high-performance vehicles, especially in markets like Europe, where efficiency standards are stringent.
How Does Steel Contribute to Alternator Durability?
Steel is often used in the structural components of alternators, such as the frame and rotor. Its strength and durability make it suitable for withstanding mechanical stresses during operation.
Pros: Steel’s robustness ensures that alternators can handle high loads and impacts, making them less prone to failure. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to aluminum and copper.
Cons: Steel is heavier than both aluminum and copper, which may negatively impact vehicle performance. Additionally, it is more susceptible to corrosion unless treated or coated.
Impact on Application: In regions like South America, where rugged terrains are common, the durability of steel can be advantageous. However, manufacturers must consider corrosion protection methods to ensure longevity.
What Advantages Does Plastic Offer in Alternator Design?
Plastic is increasingly being used for non-structural components in alternators, such as covers and insulators. It provides insulation and can help reduce weight.

Illustrative image related to que es un alternador
Pros: Plastic is lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. It is also resistant to corrosion and can be produced at a lower cost than metals.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic is its lower thermal resistance compared to metals, which can lead to deformation under high temperatures. Its mechanical strength is also inferior to that of metals.
Impact on Application: For manufacturers targeting cost-sensitive markets in Africa or South America, plastic components can reduce production costs while still meeting basic performance requirements.

Illustrative image related to que es un alternador
Summary Table of Material Selection for Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for que es un alternador | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housings and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost and weight | High |
| Steel | Frames and rotors | High durability and strength | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Non-structural components like covers | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower thermal resistance and strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in alternators, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
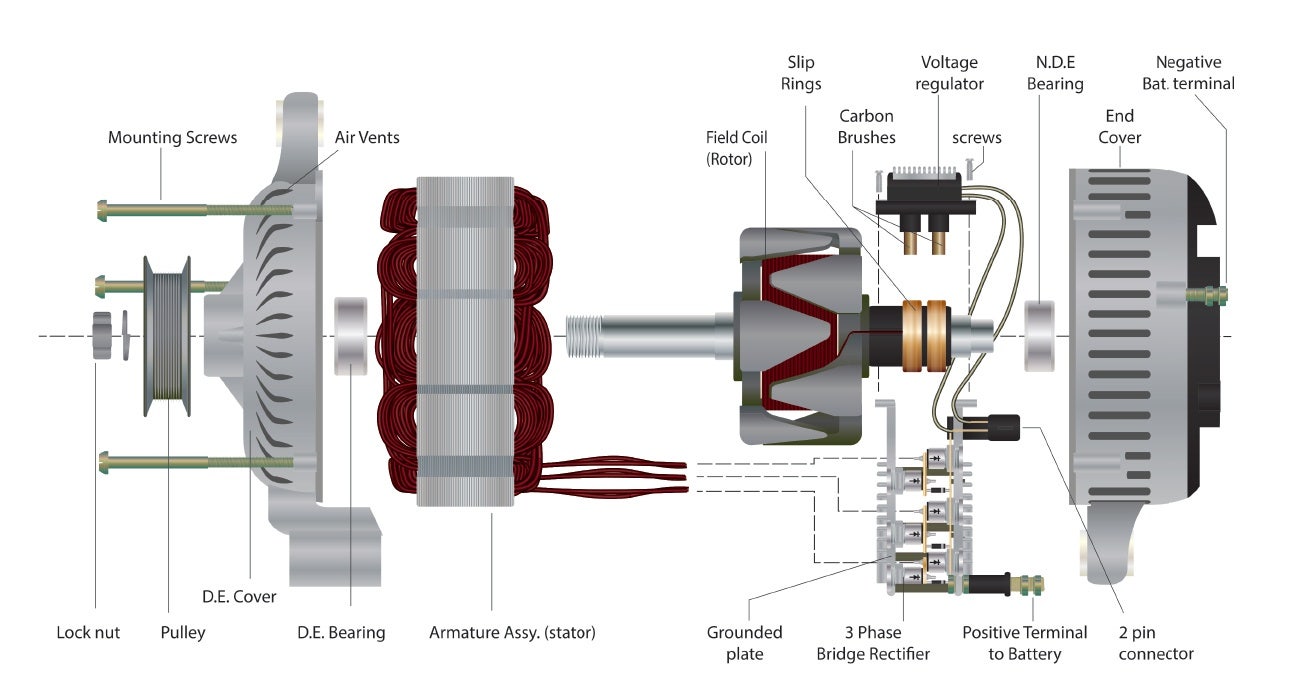
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for que es un alternador
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing an Alternator?
The manufacturing process of an alternator involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Are Materials Prepared for Alternator Production?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the alternator manufacturing process. High-quality materials such as copper for windings, steel for the rotor and stator, and durable plastics for housing are sourced based on industry specifications.
Sourcing requires thorough vetting of suppliers to ensure materials comply with international standards. For instance, copper must meet ASTM standards, while other components should align with ISO guidelines. Once sourced, materials undergo inspection and testing, including chemical composition analysis and physical property checks, to ensure they meet predefined criteria.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Alternator Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage commences, where raw materials are shaped into usable components. Key techniques include:
-
Stamping: This process is used to create the alternator’s casing and other flat components. Stamping machines apply pressure to metal sheets, creating precise shapes that fit together seamlessly.
-
Machining: Components such as the rotor and stator are often produced using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, which ensures high precision in the dimensions of these critical parts.
-
Winding: The copper wire is wound around the stator to create the electromagnetic field necessary for electricity generation. This step must be performed with meticulous attention to detail to ensure optimal performance.
How Is Assembly Carried Out in Alternator Production?
The assembly phase integrates all the formed components into a functioning alternator. It generally follows these steps:
-
Component Integration: The rotor is placed inside the stator, and the rectifier and voltage regulator are added. This assembly must be conducted in a clean environment to prevent contamination.
-
Connection of Electrical Components: The electrical connections between the various components are established, ensuring that they function cohesively. This step often requires skilled technicians to ensure that connections are secure and free from defects.
-
Initial Testing: Before moving to the finishing stage, the assembled alternator undergoes initial electrical testing to verify that it meets operational standards. Any discrepancies are addressed immediately.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Alternator Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of the alternator. Key finishing techniques include:

Illustrative image related to que es un alternador
-
Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear. This step is crucial for ensuring longevity, especially in harsh environments.
-
Final Inspection: Each alternator undergoes a thorough inspection to check for any defects. This includes visual checks, dimensional checks, and performance testing to ensure all specifications are met.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in alternator manufacturing is critical for ensuring reliability and performance. Manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is performed upon receiving materials. Each batch is inspected to confirm compliance with quality standards before being used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular checks are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that components meet specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, each alternator undergoes final testing to verify functionality. This includes electrical performance tests and stress tests to simulate real-world conditions.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Alternators?
Testing methods for alternators can vary but typically include:
-
Electrical Testing: This evaluates the alternator’s output voltage and current under various load conditions.
-
Thermal Testing: This assesses how well the alternator dissipates heat, which is crucial for its longevity.
-
Vibration Testing: This simulates operational conditions to check for stability and durability under typical vehicular dynamics.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to review their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control measures, including inspection reports and testing outcomes. These documents should detail compliance with ISO and other relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to verify the quality of components before shipment. This adds an additional layer of assurance that the products meet specified quality criteria.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating quality certifications can be complex, particularly for international transactions. B2B buyers should be aware of:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific certifications that are recognized locally. For instance, CE marking is essential in Europe, while API certification may be critical for buyers in the oil and gas sector.
-
Documentation Requirements: Ensure that all quality certifications and test results are documented in a language and format that comply with local regulations in the buyer’s country.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context and business practices of suppliers from different regions can facilitate better communication and enhance trust in quality assurance processes.
By gaining insights into the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alternators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable and high-quality products tailored to their market needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘que es un alternador’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing alternators, this guide provides a clear checklist aimed at ensuring a successful procurement process. Understanding the technical and operational aspects of alternators is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, it’s crucial to establish the specific technical requirements for the alternators you need. This includes voltage ratings, amperage output, size, and compatibility with existing systems. Consider the application—whether for automotive use, industrial machinery, or renewable energy systems—as each may have unique demands.
- Key Considerations:
- Voltage output range (e.g., 12V, 24V)
- Maximum amperage requirements
- Physical dimensions and mounting specifications
Step 2: Identify Reputable Suppliers
Research potential suppliers who specialize in manufacturing or distributing alternators. Look for companies with a proven track record, positive customer reviews, and a solid reputation in your industry.
- How to Evaluate:
- Check online reviews and testimonials.
- Seek recommendations from industry peers or trade associations.
Step 3: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing any order, request samples of the alternators to evaluate their performance. Testing samples allows you to assess quality, durability, and compatibility with your systems.
- Testing Criteria:
- Electrical output consistency under load
- Physical durability (e.g., resistance to heat, vibration)
- Noise levels during operation
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications that validate their quality control processes. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific automotive industry standards can indicate adherence to high manufacturing practices.
- Why It Matters:
- Certifications can reduce the risk of defects and ensure compliance with international standards.
- They often reflect a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Step 5: Evaluate Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have narrowed down your suppliers, compare pricing structures. Ensure that the cost reflects the quality and specifications required. Consider the payment terms offered by each supplier, as favorable terms can significantly impact your cash flow.
- Considerations:
- Total cost of ownership, including shipping and tariffs
- Available payment options (e.g., upfront payment, credit terms)
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Look into the after-sales support that suppliers provide. Reliable customer service and warranty options are essential for addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase.
- Key Aspects:
- Duration and coverage of the warranty
- Availability of technical support and replacement parts
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Place the Order
After completing all evaluations, finalize the supplier contract. Ensure all terms, including delivery schedules and penalties for non-compliance, are clearly outlined.
- Important Elements:
- Clear specifications and quantities
- Delivery timelines and penalties for delays
By following these steps, B2B buyers can efficiently navigate the sourcing process for alternators, ensuring they secure high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for que es un alternador Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing an Alternator?
When sourcing alternators, understanding the cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
-
Materials: The quality of materials used in alternators significantly impacts costs. Common components include copper for windings, aluminum for casings, and various plastics. Higher-grade materials can enhance durability and efficiency but will increase the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely based on the region of manufacturing. Countries with lower labor costs, like some in Southeast Asia, may offer more competitive pricing. However, this can sometimes come at the expense of quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with the production process, including utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom alternators. Investing in quality tooling can improve production efficiency and reduce defects, impacting long-term cost-effectiveness.
-
Quality Control: Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential to ensure product reliability, especially for critical components like alternators. While this may increase upfront costs, it can prevent costly failures and recalls.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be a significant factor, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties will influence the final price. Understanding Incoterms is crucial to navigate these logistics effectively.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on the competitive landscape and the uniqueness of the product. Buyers should be aware of the margins typically applied in the industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Alternators?
Several factors can influence the pricing of alternators, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have a MOQ which, if met, can lower the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized alternators tailored to specific vehicle requirements may incur additional costs. Buyers should carefully evaluate whether the benefits of customization outweigh the increased costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality and industry certifications can justify a higher price point. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in certified products that meet international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: Building a relationship with reliable suppliers can facilitate better pricing and terms. Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels are critical considerations.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms can affect pricing structures. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears the costs and risks during shipping, impacting the total landed cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Alternator Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing.
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding current market rates and competitor offerings will empower buyers during negotiations. Gathering insights on pricing trends in different regions can provide leverage.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: While upfront costs are essential, evaluating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) can lead to better long-term savings. This includes maintenance, efficiency, and lifespan of the alternator.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow constraints. Proposing staggered payments or extended terms can be beneficial for both parties.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can foster competition and lead to better pricing. It also provides options in case of supply chain disruptions.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a strong partnership with suppliers can lead to preferential pricing, priority service, and better negotiation outcomes in future transactions.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any purchasing agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing que es un alternador With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to ‘Que Es Un Alternador’
When it comes to powering automotive electrical systems, the alternator is a crucial component. However, businesses looking for alternatives may find various technologies that can fulfill similar roles. Understanding these alternatives is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Comparison Table of Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | ‘Que Es Un Alternador’ | Alternative 1 Name | Alternative 2 Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in converting mechanical energy to electrical energy | Battery Systems (e.g., Lithium-ion) | Fuel Cells (e.g., Hydrogen Fuel Cells) |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, with long-term savings on battery replacements | High initial cost, but lower maintenance | High initial cost, with long-term fuel savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard installation in most vehicles | Requires advanced battery management systems | Requires specialized infrastructure and knowledge |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; typically long lifespan | Moderate maintenance; battery replacements needed | Low maintenance, but fuel sourcing is critical |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for traditional combustion engine vehicles | Best for electric vehicles and hybrid systems | Suitable for zero-emission vehicles and specific industrial applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Battery Systems (Lithium-ion)
Lithium-ion battery systems are increasingly used in electric and hybrid vehicles. They offer a high energy density and can be charged quickly, making them suitable for modern automotive applications. However, the initial cost of lithium-ion batteries can be significantly higher than that of traditional alternators. Additionally, they require a robust battery management system to ensure longevity and performance. Maintenance involves monitoring battery health and eventual replacement, which can lead to increased operational costs over time. Despite these challenges, their efficiency in energy storage makes them a strong contender for vehicles focused on sustainability.
Alternative 2: Fuel Cells (Hydrogen Fuel Cells)
Fuel cells, particularly hydrogen fuel cells, represent a growing technology aimed at reducing emissions in the automotive sector. They generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, providing a clean energy source. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen fuel supply is still limited in many regions, making implementation challenging. The initial investment for fuel cell technology is high, but it can lead to lower operational costs in terms of fuel efficiency. Maintenance is generally low, yet sourcing hydrogen fuel remains a critical aspect. Fuel cells are best suited for businesses looking to invest in cutting-edge technology for zero-emission transportation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting between an alternator, battery systems, or fuel cells, businesses must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. For traditional vehicles, an alternator remains a reliable choice, while electric and hybrid systems may benefit more from advanced battery technologies. Fuel cells present an innovative alternative for businesses aiming for sustainability but come with their own set of challenges. By assessing the performance, cost, implementation ease, and maintenance needs of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for que es un alternador
What are the Key Technical Properties of an Alternator?
Understanding the essential technical properties of an alternator is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive industry, as these specifications impact performance, reliability, and overall value. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Alternators are typically made from high-grade materials such as aluminum and copper. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion, while copper is used in windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity. The choice of material can influence the alternator’s efficiency, longevity, and ability to withstand various environmental conditions, making it vital for buyers to assess material grades when sourcing. -
Output Voltage and Current Rating
Alternators are rated by their output voltage (commonly 12V or 24V) and current output (measured in Amperes). This specification determines how much electrical power can be supplied to the vehicle’s systems and is essential for ensuring that all electrical components function optimally. Understanding these ratings helps buyers match alternators to specific vehicle requirements, ensuring compatibility and performance. -
Efficiency Rating
The efficiency of an alternator is often expressed as a percentage, indicating how effectively it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Higher efficiency ratings lead to less energy wastage, which can enhance vehicle performance and fuel economy. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing alternators with high-efficiency ratings to improve vehicle performance and reduce operational costs. -
Temperature Range
Alternators operate in various thermal environments, and specifications often include a temperature range indicating the optimal operating conditions. Knowing the temperature tolerance is crucial for buyers, especially in regions with extreme climates, as it affects the alternator’s reliability and lifespan. Selecting alternators that can withstand local temperature conditions can prevent premature failures. -
Regulator Type
Alternators may feature different types of voltage regulators, such as internal or external regulators. Internal regulators are typically more compact and integrated, while external regulators can be adjusted for specific applications. Understanding the type of regulator is important for compatibility with vehicle systems and for facilitating easier maintenance or upgrades.
What are the Common Trade Terms Related to Alternators?
Familiarizing oneself with trade terminology is essential for navigating the procurement process effectively. Here are some common terms relevant to the alternator market:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to parts made by the manufacturer of the original vehicle. These parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and quality. B2B buyers must understand the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts to make informed purchasing decisions that meet their quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Understanding MOQ helps businesses negotiate better terms and avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific quantity of products. This process is vital for procurement, allowing buyers to compare offers and select the best supplier based on cost, quality, and delivery terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping contracts. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, which is critical for effective supply chain management. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to receiving the products. This term is essential for planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when sourcing alternators to ensure they meet production schedules and customer demands.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing alternators, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency and product offerings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the que es un alternador Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Trends in the Alternator Sector for B2B Buyers?
The alternator sector is witnessing robust growth driven by several global factors, including the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in automotive technology. As countries push for greener transportation solutions, the shift towards EVs enhances the need for efficient alternators that can support hybrid systems. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics is crucial. In Nigeria, for example, the rising automotive market is creating opportunities for suppliers of high-quality alternators that can withstand varying climatic conditions. Meanwhile, in Saudi Arabia, the focus on diversifying the economy away from oil dependency is driving investments in automotive technologies, including alternators.
Emerging technologies such as smart alternators, which integrate IoT capabilities, are gaining traction. These advancements allow for real-time monitoring and diagnostics, enhancing performance and reliability. B2B buyers should also be aware of the increasing trend towards digital platforms for sourcing. Online marketplaces and supply chain management tools are streamlining procurement processes, making it easier for international buyers to connect with manufacturers and suppliers.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Alternator Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the alternator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of products are under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing waste. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations on emissions and waste management are in place.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, with buyers seeking transparency in their supply chains. This encompasses ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that labor practices comply with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and SA8000 for social accountability are becoming vital indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who can demonstrate compliance with these standards, as this not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation.
What Is the Historical Context of the Alternator’s Evolution in B2B Markets?
The alternator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, vehicles relied on generators, which were less efficient in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The introduction of the alternator marked a pivotal shift, providing a more reliable source of electricity, especially as vehicles became more complex with advanced electrical systems.
Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology have led to the development of more compact and efficient alternators. Today, the integration of digital technology and smart features is setting the stage for the next generation of alternators. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential as it informs sourcing decisions that align with current technological trends and consumer expectations for performance and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of que es un alternador
-
How do I identify a quality alternator supplier for my business?
When sourcing alternators, prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in the automotive industry. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which ensures quality management systems. Assess their experience in international trade, particularly in your target markets, such as Africa or South America. Request references and testimonials from other B2B buyers to gauge reliability. Additionally, evaluate their production capabilities, including technology used and adherence to safety standards, to ensure they can meet your specific requirements. -
What specifications should I consider when purchasing an alternator?
Focus on key specifications such as voltage output, amperage, and compatibility with your vehicle models. Verify the alternator’s type (e.g., internal or external regulator) and check its physical dimensions to ensure a proper fit. Additionally, consider the materials used in construction, as this affects durability and performance. It’s also beneficial to inquire about features like cooling mechanisms and noise levels, which can impact operational efficiency. -
What is the best way to negotiate payment terms with alternator suppliers?
Start by discussing your purchasing volume and frequency, as larger orders may provide leverage for better terms. Request flexible payment options, such as net 30 or net 60 days, to improve cash flow. It’s also wise to inquire about discounts for early payments or bulk orders. Establish clear communication regarding payment methods and any associated fees to avoid misunderstandings. Building a solid relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alternators in international trade?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific alternator model. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from 50 to 500 units, depending on production costs and inventory capabilities. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to see if they can accommodate smaller initial orders, especially if you are testing new products. Be prepared to adjust your order sizes as you build a relationship and assess demand. -
How can I ensure the quality of alternators during shipment?
Implement a quality assurance (QA) process that includes pre-shipment inspections. This can involve third-party inspections to verify that the alternators meet your specifications and industry standards. Additionally, ensure that proper packaging is used to prevent damage during transit. Consider logistics partners with experience in handling automotive components, as they will understand the specific requirements for safe transportation. -
What are the common issues with alternators that I should be aware of?
Common issues with alternators include failing to produce adequate voltage, overheating, and unusual noises such as grinding or squealing. Regular maintenance can help prevent these issues, but it’s also crucial to choose high-quality products from reputable suppliers. Educating your customers about recognizing warning signs, such as dashboard warning lights or electrical failures, can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce return rates. -
How does international shipping affect the cost of sourcing alternators?
International shipping costs can significantly impact your overall sourcing budget. Factors such as shipping method (air vs. sea), distance, and freight charges must be considered. Additionally, customs duties and taxes can vary by country, affecting the final price. Work with logistics experts to estimate these costs accurately and explore options for consolidating shipments to reduce expenses. -
What customization options are available for alternators?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific requirements, such as different voltage outputs, sizes, or connector types. Discuss your particular needs with potential suppliers to determine their flexibility in production. Custom branding or labeling can also be negotiated, which is beneficial for maintaining brand identity in your market. Always confirm the feasibility and additional costs associated with custom orders to ensure they align with your budget and timeline.
Top 5 Que Es Un Alternador Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Infinity Auto – Alternadores
Domain: infinityauto.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
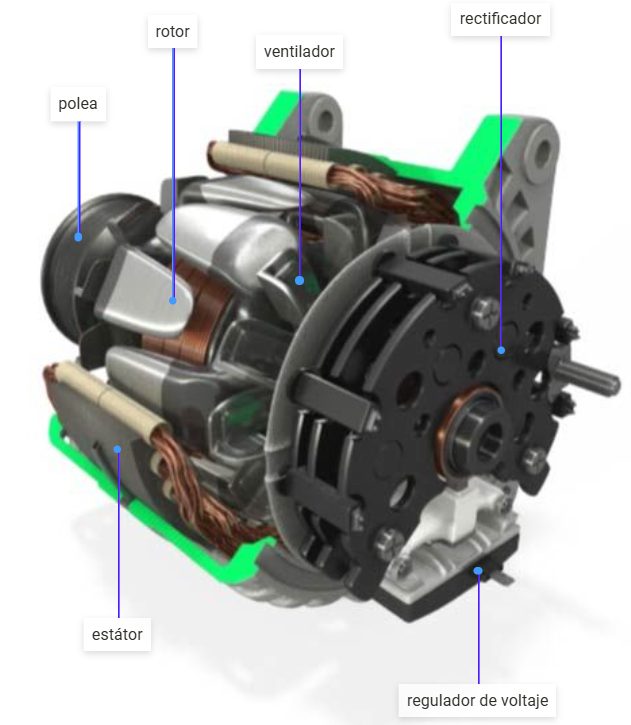
Introduction: El alternador es un generador que distribuye electricidad al auto y recarga la batería. Funciona convirtiendo energía mecánica en energía eléctrica, impulsado por el cigüeñal del motor a través de una correa serpentina. Sus componentes principales incluyen: 1. Rotor: pieza cilíndrica que gira y crea electricidad. 2. Estator: parte fija que trabaja con el rotor para generar electricidad. 3. Rectifi…
2. Sadi Transmisiones – Alternadores Electromecánicos
Domain: saditransmisiones.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Un alternador es un dispositivo electromecánico que convierte energía mecánica en energía eléctrica, fundamental en sistemas eléctricos de vehículos y maquinarias. Consta de un rotor, estator y sistema de excitación. El rotor, impulsado por una correa del motor, gira dentro del estator, induciendo corriente eléctrica en las bobinas. Genera corriente alterna que se rectifica a corriente continua pa…
3. Electude – Alternador Automotriz
Domain: electude.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Un alternador es un componente crucial en los sistemas automotrices que convierte energía mecánica en energía eléctrica. Sus componentes principales incluyen:
1. Polea: Transfiere energía mecánica del motor al alternador.
2. Rotor: Crea el campo magnético para generar corriente alterna.
3. Estator: Parte estática donde se genera la tensión.
4. Rectificador: Convierte corriente alterna en corrient…
4. Kia – Alternador
Domain: kia.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Un alternador es un componente esencial en vehículos con motor de combustión, encargado de convertir energía química en energía eléctrica para cargar la batería y alimentar otros componentes eléctricos. Funciona como parte del sistema de carga, que incluye la batería, el regulador de voltaje y el alternador. El alternador convierte energía mecánica en corriente alterna (CA) mediante un estator y r…
5. Endurance Warranty – Alternador
Domain: endurancewarranty.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Un alternador es un generador eléctrico en el motor de un automóvil que convierte energía mecánica en energía eléctrica. Se encuentra generalmente en la parte delantera del motor y es impulsado por el cinturón serpentino. Los signos de un alternador defectuoso incluyen: luz de batería encendida, faros tenues, batería muerta, ruidos extraños, olor a quemado, pérdida de potencia en accesorios eléctr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for que es un alternador
What Are the Key Benefits of Understanding Alternators for B2B Buyers?
In summary, the alternator is a vital component in vehicles, responsible for generating and supplying electricity, thus ensuring the efficient operation of electrical systems. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of alternators can lead to informed purchasing decisions that enhance vehicle reliability and performance. Strategic sourcing of high-quality alternators not only reduces operational downtime but also contributes to the overall longevity of vehicles, which is crucial for businesses relying on transportation.
As global markets continue to evolve, the demand for reliable automotive components will only increase. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability in their manufacturing processes. By investing in premium alternators and establishing strong supplier relationships, businesses can ensure consistent performance and customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the automotive industry is poised for advancements in technology, including electric and hybrid vehicles, which will further transform the role of alternators. We encourage international B2B buyers to stay proactive, leverage strategic sourcing, and align with forward-thinking suppliers to meet the future demands of the automotive market.
Illustrative image related to que es un alternador
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.