Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test the starter motor
In the competitive landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding how to test the starter motor is crucial for businesses aiming to ensure vehicle reliability and performance. A malfunctioning starter motor can lead to costly downtime and disrupt operations, particularly in regions where reliable transportation is vital. This guide addresses the pressing need for effective testing methods, providing B2B buyers with actionable insights into various testing techniques, applications, and the implications of sourcing quality starter motors.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, you will find detailed methodologies for testing starter motors, including visual inspections, electrical assessments, and bench testing procedures. Each section is designed to empower international buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Vietnam—to make informed purchasing decisions. By evaluating the cost-effectiveness and reliability of starter motors and their components, businesses can optimize their operations and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Moreover, this guide covers essential aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers and distributors that meet your specific needs. With a focus on practical applications and industry best practices, this resource serves as a vital tool for enhancing your automotive service capabilities and maintaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 How To Test The Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test the starter motor
- Understanding how to test the starter motor Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to test the starter motor
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test the starter motor’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test the starter motor
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test the starter motor
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test the starter motor’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test the starter motor Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test the starter motor With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test the starter motor
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test the starter motor Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test the starter motor
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test the starter motor
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to test the starter motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Basic checks for wear, damage, and connections | Automotive repair shops, fleet maintenance | Pros: Quick, no special tools needed. Cons: Limited diagnostic capability. |
| Click Test | Listening for the solenoid engagement sound | Workshops, DIY mechanics | Pros: Simple and fast. Cons: May not identify all issues. |
| Multimeter Voltage Test | Measures battery voltage to rule out issues | Parts suppliers, automotive services | Pros: Accurate battery assessment. Cons: Requires a multimeter. |
| Solenoid Bypass Test | Directly tests the solenoid’s functionality | Automotive service centers | Pros: Isolates solenoid issues. Cons: Risky if not done correctly. |
| Bench Testing | Comprehensive test with starter removed | Parts manufacturers, repair facilities | Pros: Definitive results on starter condition. Cons: Labor-intensive, requires tools. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Visual Inspection for Starter Motor Testing?
Visual inspection is the most fundamental method of assessing a starter motor’s condition. It involves checking for visible signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. This technique is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops and fleet maintenance operations, as it requires no specialized tools and can be performed quickly. However, while it can identify obvious issues, it lacks the diagnostic depth needed for more complex failures, making it less reliable for comprehensive assessments.
How Does the Click Test Help Diagnose Starter Motor Issues?
The click test is a straightforward method that involves listening for a clicking sound when the ignition key is turned. This sound indicates that the starter solenoid is receiving power. It is primarily used in workshops and by DIY mechanics due to its simplicity. While it provides a quick indication of whether the starter motor is attempting to engage, it does not confirm whether the motor is functioning correctly, limiting its diagnostic capabilities.
Why Use a Multimeter Voltage Test for Starter Motor Diagnosis?
The multimeter voltage test is a critical step in diagnosing starter motor issues, as it measures the voltage of the battery. This test is essential for parts suppliers and automotive services to ensure that the battery is functioning properly before concluding that the starter motor is at fault. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts; anything lower indicates a potential battery issue. While this method is accurate, it requires the use of a multimeter and basic electrical knowledge.
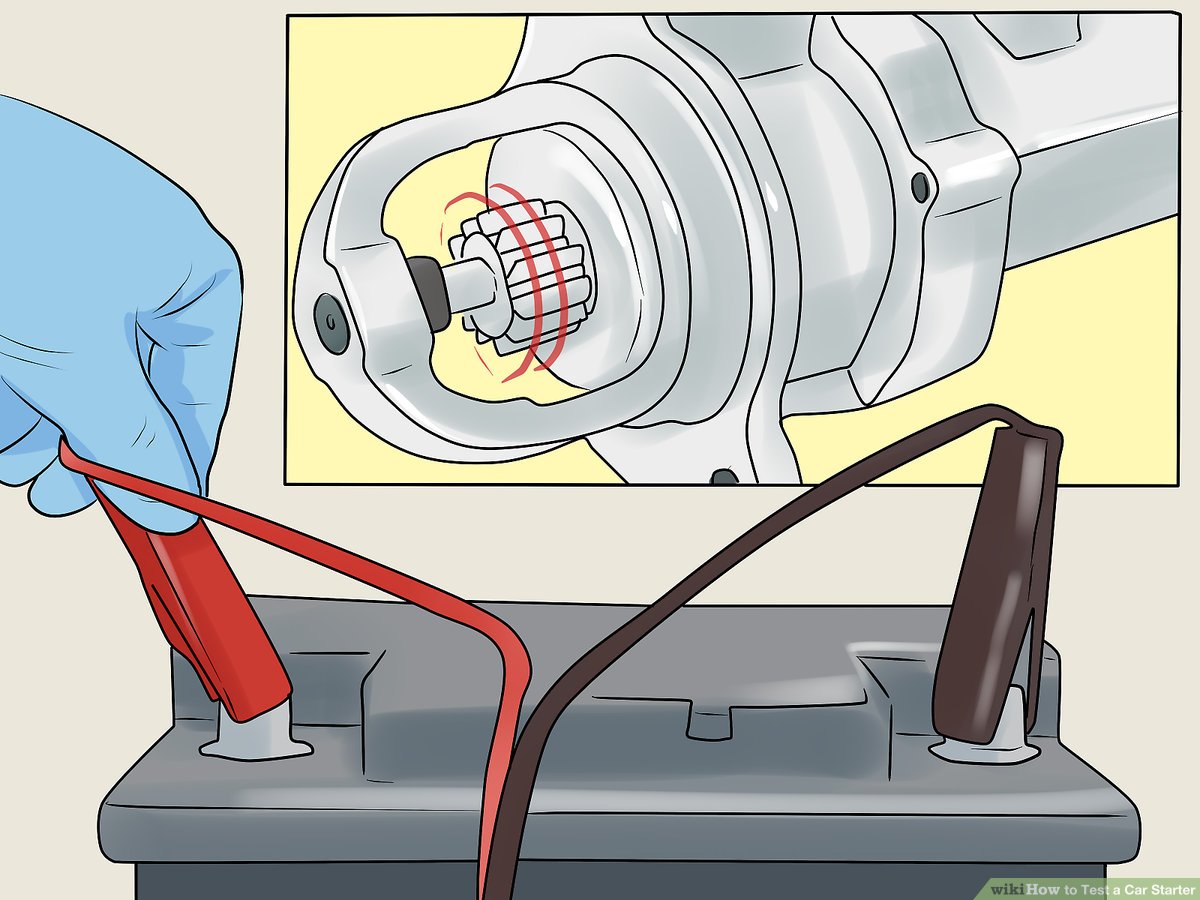
What is the Importance of the Solenoid Bypass Test?
The solenoid bypass test allows technicians to determine if the starter solenoid is functioning correctly by bypassing it with a jumper wire. This test is suitable for automotive service centers and can effectively isolate solenoid-related problems. However, it comes with risks, as improper handling can lead to electrical hazards. Buyers should ensure that their technicians are experienced in performing this test to avoid potential issues.
How Does Bench Testing Provide Definitive Results for Starter Motors?
Bench testing is the most comprehensive method for evaluating a starter motor. This involves removing the starter from the vehicle and connecting it directly to a battery to observe its performance. This method is ideal for parts manufacturers and repair facilities that require definitive results about the starter’s condition. Although it yields accurate insights, it is labor-intensive and requires specific tools, which can increase operational costs. Buyers must consider the trade-off between the accuracy of the results and the resources required for this testing method.
Key Industrial Applications of how to test the starter motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to test the starter motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control testing of starter motors during production | Ensures reliability and performance, reducing warranty claims | Need for precision testing tools and trained personnel for accurate results |
| Fleet Management | Regular maintenance checks on starter motors in commercial vehicles | Minimizes downtime, enhances fleet reliability, and reduces repair costs | Access to diagnostic equipment and skilled technicians for timely assessments |
| Heavy Equipment | Testing starter motors in construction and agricultural machinery | Increases operational efficiency by preventing unexpected breakdowns | Availability of robust testing equipment suited for heavy-duty applications |
| Marine Industry | Verifying starter motor functionality in boats and marine vessels | Enhances safety and reliability during operations in critical environments | Compliance with maritime safety standards and access to specialized tools |
| Transportation & Logistics | Ensuring starter motor reliability in transport vehicles and trailers | Improves logistics efficiency and reduces delays caused by vehicle failures | Need for portable testing solutions and quick access to spare parts in remote locations |
How is ‘how to test the starter motor’ utilized in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, testing starter motors is crucial for quality control. Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure that every starter motor meets performance standards before installation. This proactive approach helps reduce warranty claims and enhances customer satisfaction. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing precision testing tools and ensuring that their workforce is adequately trained to perform these tests effectively.
What role does starter motor testing play in Fleet Management?
Fleet management relies heavily on regular maintenance checks, including testing starter motors. By identifying potential issues early, fleet operators can minimize vehicle downtime and enhance reliability. This practice not only reduces repair costs but also optimizes the overall efficiency of the fleet. B2B buyers in this space must prioritize access to advanced diagnostic equipment and ensure that their technicians are skilled in performing these assessments promptly.
How is starter motor testing applied in Heavy Equipment?
In the heavy equipment sector, testing starter motors is vital for machinery such as excavators and tractors. Regular testing helps prevent unexpected breakdowns that can halt operations on construction sites or farms, leading to significant financial losses. Buyers should ensure they have robust testing equipment capable of withstanding harsh environments and that their personnel are trained to handle heavy-duty applications.
Why is starter motor testing important in the Marine Industry?
In the marine industry, verifying the functionality of starter motors is essential for safety and reliability. Boats and vessels often operate in critical environments where equipment failure can lead to serious consequences. Regular testing ensures that starter motors are in optimal condition, reducing the risk of accidents at sea. Buyers should consider compliance with maritime safety standards and access to specialized testing tools designed for marine applications.
How does testing starter motors benefit Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, ensuring the reliability of starter motors in vehicles and trailers is paramount. Testing helps prevent delays caused by vehicle failures, which can disrupt supply chains and lead to financial penalties. For B2B buyers, sourcing portable testing solutions that can be used in various locations, along with quick access to spare parts, is essential to maintaining operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test the starter motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Diagnosing Starter Motor Issues
The Problem: For B2B buyers in the automotive sector, diagnosing starter motor problems can often lead to confusion and inefficiency. Businesses may face situations where vehicles are not starting, but the cause could be a dead battery, a faulty starter motor, or issues with the ignition system. Without a clear understanding of how to properly test the starter motor, technicians might waste time and resources troubleshooting the wrong components, resulting in unnecessary repairs and extended downtime for vehicles.
The Solution: Implement a systematic approach to diagnosing starter motor issues. Start by training your technicians to conduct a thorough visual inspection of the starter motor and its connections. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose wiring that could impede performance. Following this, use a multimeter to check the battery voltage; a reading below 12.6 volts could indicate a weak battery rather than a faulty starter motor. By establishing a testing protocol that prioritizes battery health and includes a step-by-step guide on how to perform a bench test, businesses can minimize diagnostic errors and enhance overall efficiency in vehicle servicing.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Tools for Effective Testing
The Problem: A common pain point for automotive repair shops and fleet management companies is the lack of proper tools for testing starter motors. Many businesses rely on outdated equipment or do not have the necessary tools, such as multimeters or jumper cables, readily available. This not only slows down the testing process but can also lead to inaccurate results, causing further delays in repairs and increasing labor costs.
The Solution: Invest in high-quality, specialized diagnostic tools that are essential for testing starter motors effectively. Consider sourcing equipment that is robust and designed for frequent use, such as heavy-duty jumper cables and precision multimeters with clear readouts. Provide training for your staff on how to utilize these tools correctly, emphasizing the importance of accurate readings in the diagnostic process. Additionally, establish a maintenance schedule for tools to ensure they remain in good working condition, thus enhancing the reliability of your diagnostics and reducing the likelihood of misdiagnosis.
Scenario 3: High Replacement Costs Due to Misdiagnosis
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant financial implications stemming from misdiagnosing starter motor issues. A faulty diagnosis can lead to unnecessary replacement of starter motors when the real issue lies elsewhere, such as with the battery or wiring. This not only wastes resources but can also damage customer relationships if they perceive a lack of reliability and expertise in your service.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of misdiagnosis, develop a comprehensive training program for your technicians that covers the nuances of starter motor testing. This should include practical workshops on how to perform both visual inspections and bench tests accurately. Encourage technicians to adopt a methodical approach when troubleshooting, ensuring they rule out simpler issues—like battery problems—before concluding that a starter motor needs replacement. Furthermore, consider implementing a standardized checklist that technicians can follow during the testing process to ensure thoroughness and consistency in diagnostics. By investing in education and process improvement, businesses can enhance diagnostic accuracy and significantly reduce costs associated with misdiagnosis.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test the starter motor
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Testing Starter Motors?
When it comes to testing starter motors, selecting the right materials is crucial for ensuring accurate results and durability. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the testing process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Metals Perform in Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Metals such as copper and aluminum are often used in jumper cables and connectors due to their excellent electrical conductivity and strength. Copper, in particular, has a high melting point (approximately 1,984°F or 1,085°C), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: Copper cables are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, ensuring reliable performance over time. However, they can be more expensive compared to aluminum. Aluminum, while lighter and more cost-effective, has lower conductivity and may require larger gauge sizes to match copper’s performance.
Impact on Application: Metals are essential for creating reliable electrical connections during testing. Poor conductivity can lead to inaccurate test results, making it vital to select high-quality materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B187 for copper and ASTM B221 for aluminum is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider local sourcing to minimize costs and ensure material availability.
What Role Do Insulating Materials Play in Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Insulating materials, such as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and silicone, are used for protective coatings and cable insulation. PVC is known for its temperature resistance (up to 158°F or 70°C) and good electrical insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice. However, it may not perform well under extreme temperatures. Silicone, on the other hand, can withstand higher temperatures (up to 500°F or 260°C) and offers excellent flexibility but at a higher cost.
Illustrative image related to how to test the starter motor
Impact on Application: Insulating materials prevent short circuits and electrical failures during testing. Inadequate insulation can lead to safety hazards and inaccurate readings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that materials comply with local regulations and standards, such as IEC 60227 for PVC cables. Understanding regional preferences for insulation types can also guide material selection.
Why Are Testing Equipment Materials Important for Starter Motors?
Key Properties: Testing equipment often incorporates materials like rubber and reinforced plastics. Rubber is valued for its flexibility and grip, while reinforced plastics provide durability and resistance to impact.
Pros & Cons: Rubber is inexpensive and offers excellent shock absorption, making it suitable for handheld testing devices. However, it may degrade over time when exposed to oils and chemicals. Reinforced plastics are more resistant to environmental factors but can be pricier and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: The choice of materials for testing equipment directly affects usability and longevity. Poor-quality materials can lead to equipment failure, resulting in costly downtime.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of these materials in their regions and ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
How Do Conductive Materials Affect Starter Motor Testing?
Key Properties: Conductive materials like carbon and graphite are often used in brushes and contacts within testing equipment. These materials have good electrical conductivity and can withstand wear and tear.
Pros & Cons: Carbon brushes are relatively inexpensive and effective for low-voltage applications. However, they may wear out faster than other materials. Graphite, while more durable, can be more expensive and may require specialized handling.
Impact on Application: The performance of conductive materials can significantly influence the accuracy of test results. Inconsistent conductivity can lead to unreliable data.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding local sourcing options for these materials can help buyers manage costs. Compliance with standards such as ASTM D1505 for graphite materials is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Testing Starter Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to test the starter motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper/Aluminum | Jumper cables and connectors | Excellent electrical conductivity | Copper is expensive; aluminum has lower conductivity | High/Medium |
| PVC/Silicone | Cable insulation and protective coatings | Cost-effective (PVC); high temperature resistance (Silicone) | PVC may degrade; silicone is pricier | Low/High |
| Rubber/Reinforced Plastics | Testing equipment and grips | Flexibility and shock absorption (Rubber) | Rubber degrades; reinforced plastics are complex to manufacture | Low/Medium |
| Carbon/Graphite | Brushes and contacts in testing equipment | Good electrical conductivity | Carbon wears out; graphite is expensive | Low/High |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for testing starter motors, ensuring they can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test the starter motor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Testing Starter Motors?
The manufacturing process for starter motors involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications for performance and reliability. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality starter motors.
Illustrative image related to how to test the starter motor
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Starter Motors?
The first stage of the manufacturing process is material preparation. Starter motors typically utilize a combination of metals, plastics, and electrical components. Common materials include:
- Copper: Used for windings and electrical connections due to its excellent conductivity.
- Steel: Employed in the casing and structural components for durability and strength.
- Plastics: Used for insulation and protective covers, ensuring safety and reducing weight.
Quality control begins at this stage, as the selection of high-grade materials directly impacts the performance and longevity of the starter motor.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted for Starter Motors?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This involves several techniques to shape the components of the starter motor, including:
- Stamping: Used for creating metal parts from sheets, such as the casing and mounting brackets.
- Molding: Essential for producing plastic components like housings and insulators.
- Winding: Copper wire is wound into coils to create the motor’s magnetic field, a critical process that affects motor efficiency.
Precision in forming is vital, as any deviation can lead to assembly issues or performance failures.
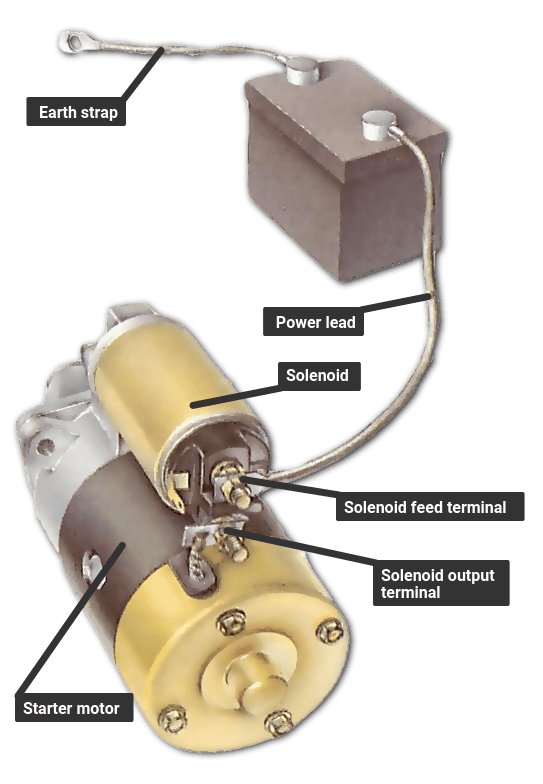
What Happens During the Assembly of Starter Motors?
Assembly is the stage where all the formed components come together. This process typically involves:
- Component Integration: The stator, rotor, and solenoid are assembled, ensuring proper alignment and fit.
- Electrical Connections: Establishing reliable connections between the battery, solenoid, and starter motor is crucial. This involves soldering and crimping techniques to ensure a solid electrical pathway.
- Final Assembly: The completed assembly is encased and sealed to protect against environmental factors.
Each step in assembly requires skilled labor and precise machinery to ensure that the starter motor functions correctly.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Starter Motor Production?
The finishing stage enhances the durability and aesthetics of the starter motor. Common techniques include:
- Painting: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear, especially important for motors exposed to harsh conditions.
- Testing: Every starter motor undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance standards. This includes bench tests and electrical performance checks.
Finishing processes not only improve the product’s appearance but also its lifespan and reliability.
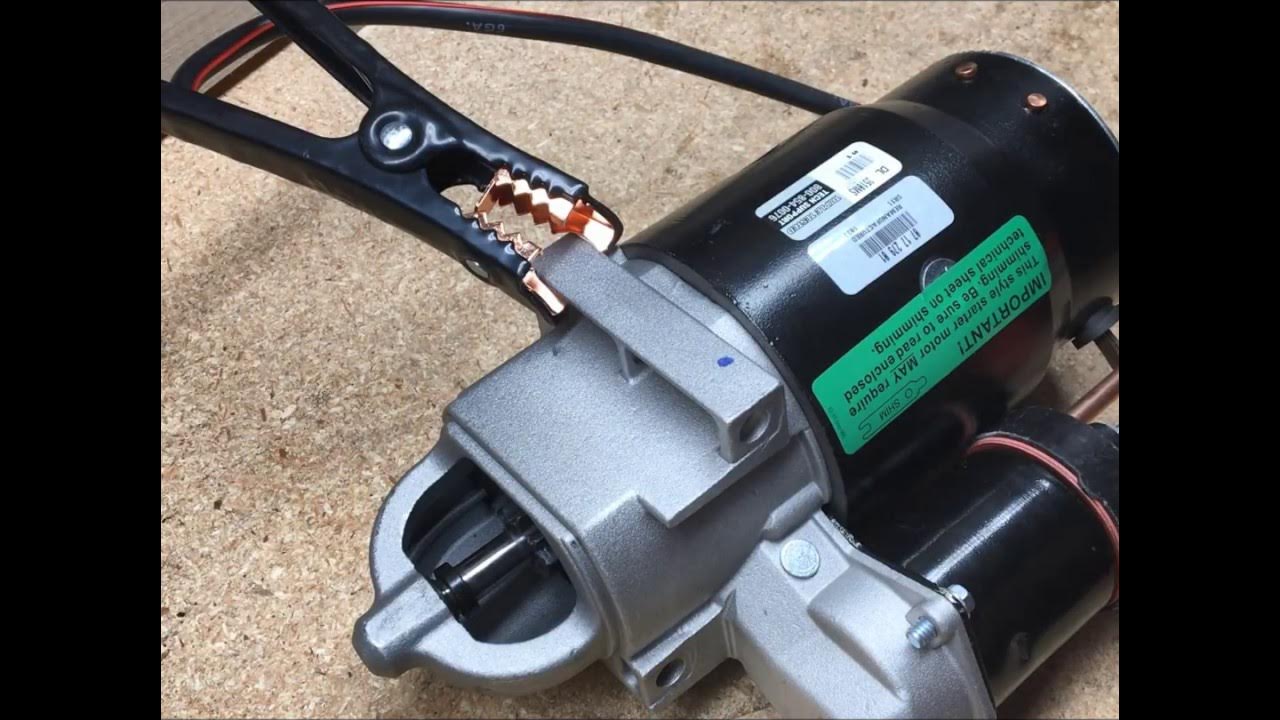

Illustrative image related to how to test the starter motor
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Starter Motors?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of manufacturing starter motors, particularly for B2B buyers. Adhering to international and industry-specific standards is crucial.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards globally. It ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality across their processes. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a company has implemented effective quality management systems.
Additionally, various industry-specific certifications may apply, such as:
- CE Marking: Common in Europe, this certification indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for manufacturers in the oil and gas sector, indicating adherence to quality standards specific to those industries.
These certifications provide assurance to B2B buyers regarding the quality and safety of the products they source.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Motor Production?
The quality control process typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing cycle:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses raw materials for conformity with specifications. It ensures that only high-quality materials enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing stages, this ensures that processes are followed correctly, and any deviations are addressed immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The last step before products are shipped. This includes comprehensive testing of completed starter motors to verify performance and safety standards.
These checkpoints are crucial for identifying and mitigating potential issues early in the manufacturing process.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with standards.
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits involves a systematic review of the manufacturer’s processes, facilities, and quality control measures. Key practices include:
- On-Site Visits: Observing the manufacturing process and quality control measures in action provides valuable insights.
- Document Review: Analyzing quality control documentation, including test reports and compliance certificates, confirms adherence to standards.
- Interviews: Engaging with staff can reveal their understanding of quality control processes and their commitment to maintaining standards.
How Can Buyers Use Third-Party Inspections to Ensure Quality?
In addition to audits, third-party inspections serve as an effective way to verify supplier quality. These independent assessments provide unbiased evaluations of the manufacturer’s processes and products. Buyers can request:
- Inspection Reports: Detailed assessments of the manufacturing process, including any issues identified and corrective actions taken.
- Compliance Certificates: Proof that the manufacturer meets relevant international and industry-specific standards.
Using third-party inspections not only enhances confidence in the supplier but also mitigates risks associated with sourcing.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements and standards that impact the sourcing of starter motors. For example, Europe has stringent CE marking requirements, while countries in Africa may prioritize different certifications based on local regulations.
Understanding these regional nuances is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
What Challenges Do International Buyers Face in Quality Assurance?
International sourcing can pose challenges, including language barriers, cultural differences, and varying standards. Buyers must be proactive in communicating their quality expectations and understanding the supplier’s capabilities.
Investing in strong relationships with suppliers and conducting regular assessments can help mitigate these challenges and ensure a consistent supply of high-quality starter motors.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter motors, ultimately leading to better performance and reliability in their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test the starter motor’
Introduction
Testing a starter motor is crucial for diagnosing starting issues in vehicles, and understanding how to perform these tests can save time and costs for B2B buyers in the automotive industry. This guide provides a practical checklist to help you effectively evaluate the necessary procedures and tools for testing starter motors, ensuring you make informed decisions when sourcing equipment or services.
Step 1: Identify Your Testing Needs
Understanding the specific requirements for testing starter motors is the first step. Determine whether you need to test multiple types of starter motors or focus on a particular brand or model. This clarity will guide your sourcing process and help you choose the right tools and methodologies.
Step 2: Gather Essential Tools
Before proceeding with testing, ensure you have the necessary tools at hand. Common tools include:
– Multimeter for battery testing
– Jumper cables for bench testing
– Screwdriver for solenoid tests
Having these tools ready ensures a smooth testing process and reduces delays during diagnostics.
Step 3: Establish Testing Procedures
Define clear procedures for each testing method you intend to use, such as visual inspections, battery tests, solenoid tests, and bench tests. Document the steps for each method, including:
– Visual Inspection: Check for signs of wear and loose connections.
– Bench Testing: Outline the steps to set up a bench test safely.
A well-documented procedure minimizes errors and ensures consistency across tests.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
When sourcing tools or services, assess potential suppliers based on their expertise in automotive testing equipment. Look for:
– Technical Certifications: Ensure they meet industry standards.
– Product Range: A diverse selection of testing tools that match your needs.
Evaluating suppliers on these criteria can help you secure reliable partners who can provide quality products and support.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Before making a purchase, request demonstrations or trial periods for the equipment you intend to buy. This allows you to:
– Test Usability: Ensure the tools are user-friendly and meet your operational requirements.
– Evaluate Performance: Confirm that the equipment performs as advertised in real-world scenarios.
This step is vital for mitigating risk and ensuring the investment meets your expectations.
Step 6: Consider After-Sales Support
After purchasing, the level of after-sales support can significantly impact your operations. Investigate the following:
– Warranty Policies: Understand the coverage for defects and malfunctions.
– Technical Support: Ensure that the supplier offers robust support for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Reliable after-sales service enhances your ability to maintain and utilize testing equipment effectively.
Step 7: Keep Up with Industry Trends
Finally, stay informed about advancements in starter motor testing technology and methods. Subscribe to industry publications, attend trade shows, and engage with professional networks. This proactive approach will help you adapt to changes and continue to improve your testing processes, ensuring your operations remain competitive.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source the necessary tools and services for testing starter motors, ensuring efficiency and reliability in their automotive operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test the starter motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Starter Motor Testing Equipment?
When sourcing equipment for testing starter motors, understanding the cost structure is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary materials involved are metals, plastics, and electronic components used in tools like multimeters and jumper cables. The quality of these materials can significantly impact both the performance and durability of the testing equipment.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled technicians involved in the production and assembly of testing tools. This is especially relevant for manufacturers that emphasize quality control and precision engineering.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, rent, and administrative expenses related to the production process. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools and machinery used in the production of testing equipment can be substantial. However, these costs can be amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that testing equipment meets industry standards incurs costs related to inspections and certifications. For international buyers, especially from regions with strict regulations, these QC costs are crucial.
-
Logistics: Shipping, handling, and storage costs must be factored into the total cost of ownership. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face additional tariffs and customs fees.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. Understanding the expected margins in your specific market can help in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Starter Motor Testing Equipment?
Several factors can influence the pricing of starter motor testing equipment:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on the quantity ordered, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed testing equipment tailored to specific needs often comes with a premium price. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against their budget.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Equipment made from higher-quality materials or those that meet international certifications (ISO, CE) may cost more but can offer better performance and longevity, impacting the total cost of ownership positively.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record may charge more for their products but offer better customer support and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms will dictate responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, significantly influencing the overall cost. Buyers should understand these terms to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs in Starter Motor Testing Equipment?
-
Negotiation Tactics: Buyers should be prepared to negotiate not just on price but also on payment terms, warranties, and after-sales support. Establishing a relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as maintenance, durability, and potential downtime savings to justify higher initial expenditures.
-
Understanding Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: International buyers must be aware of additional costs such as tariffs, import taxes, and currency fluctuations. Requesting quotes that include all potential costs can help in better budgeting.
-
Local vs. International Suppliers: Weigh the benefits of sourcing from local suppliers versus international ones. While local suppliers may offer faster delivery times, international suppliers might provide more competitive pricing.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on market trends and price points for similar equipment. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help in making informed decisions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for starter motor testing equipment can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct detailed research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing information tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test the starter motor With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Testing Starter Motors
In the automotive industry, ensuring the reliability of starter motors is crucial for operational efficiency. While traditional methods for testing starter motors have their advantages, exploring alternative solutions can provide additional insights and efficiencies. This section compares the conventional approach of testing starter motors with two viable alternatives: using advanced diagnostic tools and outsourcing testing to specialized service providers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Test The Starter Motor | Advanced Diagnostic Tools | Outsourcing to Specialized Service Providers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for basic troubleshooting | High accuracy; can diagnose multiple issues | Expertise ensures accurate diagnostics |
| Cost | Low (basic tools required) | Moderate to high (initial investment needed) | Variable (depends on service provider) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic mechanical skills | Requires training to use effectively | Minimal effort; service provider handles all |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, dependent on tools used | Requires software updates and calibration | No maintenance for the buyer |
| Best Use Case | Quick checks and DIY maintenance | Comprehensive diagnostics for multiple components | When in-house expertise or equipment is lacking |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Starter Motor Testing?
Advanced diagnostic tools, such as automotive scanners and multimeters with specialized functions, offer a modern approach to testing starter motors. These tools can provide detailed insights into the health of the starter and other electrical components.
Pros:
– High accuracy in diagnosing issues not only with the starter motor but also with related systems such as the battery and alternator.
– Ability to store and analyze data over time for better maintenance planning.
Cons:
– Higher upfront investment and may require ongoing costs for software updates.
– Requires technical expertise to interpret results effectively, which may not be available in all organizations.
How Does Outsourcing to Specialized Service Providers Work?
Outsourcing starter motor testing to specialized service providers allows businesses to leverage expert knowledge without investing in tools or training. These providers often have sophisticated equipment and trained personnel who can conduct tests and provide detailed reports.
Pros:
– Saves time and resources by delegating the task to experts.
– Reduces the risk of misdiagnosis that could lead to unnecessary replacements.
Cons:
– Costs can vary significantly based on service provider rates and geographic location.
– May involve longer turnaround times compared to in-house testing if the service provider is not local.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate method for testing starter motors, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, available resources, and expertise. For those seeking cost-effective, quick checks, the traditional testing methods can be sufficient. However, businesses looking for comprehensive diagnostics or those lacking in-house expertise might find greater value in investing in advanced diagnostic tools or outsourcing to specialized service providers. Ultimately, the right choice will align with the organization’s operational goals, budget constraints, and the complexity of the vehicles being serviced.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test the starter motor
What Are the Critical Technical Properties for Testing a Starter Motor?
When assessing the functionality of a starter motor, several technical properties are essential for ensuring accurate testing and optimal performance. Understanding these specifications is crucial for B2B buyers involved in automotive parts procurement and maintenance.
-
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a starter motor typically ranges from 12V to 24V, depending on the vehicle’s electrical system. This specification is vital as it determines the compatibility of the starter with the vehicle’s battery. A mismatch can lead to inadequate performance or even damage to the motor. -
Current Draw
Measured in amperes, the current draw of a starter motor is an important metric that indicates how much electrical current the motor consumes during operation. Knowing the expected current draw helps in diagnosing issues; if the motor draws excessive current, it may indicate internal problems such as short circuits or excessive wear. -
Torque Output
Torque output is crucial for determining the motor’s ability to crank the engine effectively. This specification is usually measured in Newton-meters (Nm) and varies based on the engine size and type. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the starter motor meets the torque requirements of specific engine models is essential for reliable vehicle operation. -
Material Specifications
The materials used in the construction of the starter motor, such as steel or high-grade aluminum, affect durability and performance. Material grade influences the motor’s resistance to heat and wear, thereby extending its lifespan. Understanding these materials can help buyers choose high-quality products that meet industry standards. -
Temperature Range
The operational temperature range of a starter motor indicates the environmental conditions in which it can function effectively. Starter motors designed for extreme temperatures may be necessary for vehicles operating in harsh climates. Knowing this range can assist B2B buyers in selecting appropriate components for specific geographical regions. -
Insulation Class
The insulation class defines the heat resistance of the starter motor’s electrical windings. Common classes include A, B, F, and H, with Class H being the most heat-resistant. Selecting a starter motor with an appropriate insulation class is crucial for ensuring reliability and longevity, particularly in high-heat applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Motor Testing?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for B2B buyers to navigate procurement and technical discussions effectively. Here are several common terms related to starter motor testing and sourcing.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the assembly of vehicles. Purchasing OEM starter motors can ensure compatibility and quality, as these parts are designed to meet the original specifications of the vehicle manufacturer. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers looking to manage inventory costs while ensuring they meet demand without over-purchasing. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Including detailed specifications for starter motors in an RFQ can help ensure accurate and competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms can aid B2B buyers in understanding their obligations and rights during the procurement process. -
Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts are components made by manufacturers other than the original vehicle manufacturer. While often more affordable, they can vary in quality. Understanding the differences between OEM and aftermarket parts is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. -
Testing Standards
Testing standards refer to the protocols and benchmarks established for evaluating the performance of starter motors. Familiarity with these standards helps ensure compliance and quality assurance in sourcing and testing processes.
By understanding both the technical properties and trade terminology associated with starter motor testing, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring the selection of high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test the starter motor Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Starter Motor Testing Sector?
The global starter motor testing market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for reliable vehicle performance across various regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Factors such as rising vehicle ownership, a growing automotive aftermarket, and advancements in automotive technology are shaping this market. In Europe, for instance, the push for electric vehicles (EVs) is creating opportunities for innovative starter motor testing solutions that cater to the unique requirements of hybrid and electric engines.
Emerging technologies are also playing a crucial role in the sector. The integration of digital tools and software solutions for diagnostic testing is becoming commonplace, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of starter motor assessments. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to testing tools and equipment for B2B buyers in remote locations. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from developing markets who are seeking cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality.
Another key trend is the increasing emphasis on training and skills development for automotive technicians. As testing procedures become more complex with the advent of advanced starter motor systems, B2B buyers are looking for suppliers who offer comprehensive training programs. This investment in human capital not only ensures accurate testing but also fosters long-term partnerships between suppliers and buyers.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Starter Motor Testing Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the starter motor testing sector. As businesses globally face mounting pressure to reduce their environmental impact, there is a growing focus on sourcing components and materials that are environmentally friendly. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials in manufacturing starter motors and testing equipment.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now more inclined to partner with manufacturers that demonstrate transparency in their sourcing processes and labor practices. This shift is not only a response to consumer demand for ethical products but also a strategic move to mitigate risks associated with unethical practices in the supply chain.
Illustrative image related to how to test the starter motor
Certifications related to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. These certifications provide assurance that the products meet specific environmental standards, thereby increasing their marketability. In addition, utilizing “green” testing materials and methods can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to a broader customer base.
How Has the Testing of Starter Motors Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of starter motor testing has been significant, reflecting advancements in automotive technology and the growing complexity of vehicle systems. In the early days, testing methods were rudimentary, often relying on basic visual inspections and manual checks. However, as vehicles became more sophisticated, so did the testing processes.
Today, advanced diagnostic tools and electronic testing methods dominate the landscape. The introduction of multimeters, diagnostic software, and bench testing equipment has revolutionized how technicians assess starter motors. These tools not only enhance accuracy but also reduce the time required for testing, allowing for quicker turnaround times in service centers.
Furthermore, the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles has necessitated the development of specialized testing protocols to address the unique characteristics of these engines. As the automotive industry continues to innovate, the methods for testing starter motors will undoubtedly evolve, presenting new challenges and opportunities for B2B buyers in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test the starter motor
-
How do I solve starting issues with my vehicle?
To address starting issues, first check the battery’s voltage with a multimeter; it should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged. Listen for a click sound when turning the ignition, which indicates the starter solenoid is receiving power. Perform a visual inspection for loose connections or corrosion. If these preliminary checks do not resolve the issue, consider testing the starter motor directly or consulting a professional mechanic to ensure a thorough diagnosis. -
What is the best method to test a starter motor?
The most effective way to test a starter motor is through a bench test, where the motor is removed from the vehicle and connected directly to a battery using jumper cables. This method allows for clear results: if the motor spins at normal speed, it’s functioning well; if it clicks or spins slowly, there may be an issue. Always ensure the battery used for testing is fully charged to avoid misdiagnosis. -
What tools do I need to test a starter motor?
To test a starter motor, you will need basic tools including a multimeter, battery jumper cables, a jumper wire, and potentially a vice or a helper to securely hold the motor during testing. Ensuring you have a functioning battery is crucial, as a weak battery can lead to inaccurate test results. -
What should I consider when sourcing starter motors internationally?
When sourcing starter motors internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, quality certifications, and compliance with local regulations. Evaluate their production capabilities and whether they can customize products to meet specific needs. Ensure they have a clear understanding of your market requirements, especially in regions like Africa or South America where standards may vary. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter motors?
MOQs for starter motors can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of motor. Typically, manufacturers may set an MOQ ranging from 50 to 500 units. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements upfront and negotiate terms that suit your business model, especially if you are a smaller buyer looking to minimize inventory costs. -
How do I vet suppliers for starter motors?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their business credentials, customer reviews, and case studies. Request samples to evaluate product quality and assess their ability to meet your specifications. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible or using third-party inspection services to ensure they maintain quality standards and ethical practices. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common arrangements include letters of credit, advance payments, or net terms (30/60/90 days). It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect your cash flow while ensuring the supplier feels secure. Always document these terms clearly in your purchase agreement to avoid disputes later. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my starter motors?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a clear QA process with your supplier, including detailed specifications and testing protocols. Consider implementing third-party quality inspections at various stages of production and prior to shipment. Additionally, ask for warranty terms and after-sales support to address any potential issues that may arise after receiving the products.
Top 2 How To Test The Starter Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Elevate Auto – Starter Motor Testing
Domain: elevateauto.com.au
Introduction: This company, Elevate Auto – Starter Motor Testing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. WikiHow – Car Starter Testing Guide
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The article provides a comprehensive guide on how to test a car starter, detailing three main parts: Checking the Pinion, Testing the Electrical System, and Bench Testing Your Starter. Key steps include checking the pinion for jams, inspecting battery terminals for dirt or corrosion, testing battery voltage with a multimeter, visually inspecting the solenoid and its connections, using a circuit te…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test the starter motor
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Starter Motor Testing Process?
In conclusion, understanding how to effectively test a starter motor is essential for maintaining vehicle reliability and minimizing downtime. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can ensure access to high-quality parts and skilled technicians who can accurately diagnose starter motor issues. This not only reduces the risk of unnecessary replacements but also fosters long-term relationships with trusted suppliers.
Key takeaways for international B2B buyers include the importance of thorough visual inspections, proper testing techniques such as bench testing, and the utilization of diagnostic tools like multimeters. By investing in training and resources to empower your team, you can streamline the testing process and enhance operational efficiency.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritize partnerships that align with your quality standards and technical requirements. Embrace the opportunity to innovate your testing methods and stay ahead of competitors. Explore strategic sourcing options today to ensure your operations remain robust and responsive to market demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.