Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to check a solenoid on a starter
In the dynamic landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding how to check a solenoid on a starter is essential for businesses aiming to optimize vehicle performance and minimize downtime. Many international B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing reliable components and knowledgeable suppliers to ensure their fleets remain operational. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of solenoid testing, including various types, applications, and crucial supplier vetting strategies.
By exploring the intricacies of solenoid functionality, buyers will gain insights into the diagnostic processes necessary to identify potential issues effectively. This knowledge not only empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions but also enhances their ability to negotiate better terms and ensure the quality of components sourced from diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with a focus on countries like Germany and Saudi Arabia.
Furthermore, this guide addresses critical factors such as cost considerations, maintenance practices, and the importance of selecting reputable suppliers. In doing so, it equips B2B buyers with the tools needed to navigate the global market confidently, ensuring their operations are both efficient and economically viable. The ultimate goal is to empower businesses to enhance their service offerings while maintaining a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Table Of Contents
- Top 1 How To Check A Solenoid On A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to check a solenoid on a starter
- Understanding how to check a solenoid on a starter Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to check a solenoid on a starter
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to check a solenoid on a starter’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to check a solenoid on a starter
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to check a solenoid on a starter
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to check a solenoid on a starter’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to check a solenoid on a starter Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to check a solenoid on a starter With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to check a solenoid on a starter
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to check a solenoid on a starter Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to check a solenoid on a starter
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to check a solenoid on a starter
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to check a solenoid on a starter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Check for physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections | Automotive repair shops, fleet services | Pros: Quick and easy; no special tools required. Cons: May miss internal faults. |
| Electrical Testing with a Multimeter | Measures voltage and resistance across terminals | Auto parts suppliers, repair facilities | Pros: Provides precise data; identifies specific issues. Cons: Requires technical knowledge and tools. |
| Test Light Method | Uses a test light to check for power flow | DIY mechanics, small repair shops | Pros: Simple setup; effective for basic diagnostics. Cons: Less detailed than multimeter testing. |
| Bench Testing | Involves removing the solenoid for independent testing | Specialized repair shops, manufacturers | Pros: Thorough testing; isolates solenoid issues. Cons: Labor-intensive; requires more time and tools. |
| Integrated Diagnostic Tools | Uses advanced diagnostic equipment for comprehensive checks | Large-scale repair operations, OEMs | Pros: Highly accurate; can diagnose multiple systems. Cons: High cost; requires training to operate. |
What Are the Characteristics of Visual Inspection for Solenoid Testing?
Visual inspection is the most straightforward method to assess a solenoid’s condition. Technicians look for signs of physical damage, such as cracks or corrosion, and ensure all connections are secure. This method is suitable for automotive repair shops and fleet services where quick diagnostics are crucial. While it offers a rapid assessment, it may overlook internal faults that could cause malfunction.
How Does Electrical Testing with a Multimeter Work?
Using a multimeter to measure voltage and resistance provides a detailed analysis of the solenoid’s functionality. This method is ideal for auto parts suppliers and repair facilities, allowing them to diagnose issues accurately. While this approach is precise, it demands a certain level of technical expertise and the availability of specialized tools, making it less accessible for casual users.
Why Choose the Test Light Method for Solenoid Checks?
The test light method involves connecting a light to the solenoid’s terminals to verify power flow. This approach is particularly popular among DIY mechanics and small repair shops due to its simplicity and minimal setup. Although it effectively indicates whether power is reaching the solenoid, it lacks the depth of analysis provided by multimeter testing, potentially missing nuanced issues.
What Are the Benefits of Bench Testing Solenoids?
Bench testing involves removing the solenoid from the vehicle to conduct a thorough evaluation. This method is often used by specialized repair shops and manufacturers, providing a comprehensive understanding of the solenoid’s performance. While it allows for detailed diagnostics, bench testing is labor-intensive and requires additional tools and time, which may not be practical for all businesses.
How Do Integrated Diagnostic Tools Enhance Solenoid Testing?
Integrated diagnostic tools offer advanced capabilities for testing solenoids, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of multiple vehicle systems. This method is particularly beneficial for large-scale repair operations and OEMs looking for high accuracy. However, the cost of these tools can be prohibitive, and staff may require training to use them effectively, presenting a barrier for smaller operations.
Key Industrial Applications of how to check a solenoid on a starter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to check a solenoid on a starter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Diagnosing starter issues in vehicles | Reduces downtime and repair costs | Availability of quality testing tools and parts |
| Heavy Machinery | Ensuring reliable operation of construction equipment | Enhances equipment uptime and safety | Compliance with local standards and certifications |
| Agriculture Equipment | Maintaining farm machinery for optimal performance | Increases productivity and efficiency | Access to durable parts suitable for harsh conditions |
| Transportation Logistics | Ensuring fleet vehicles start reliably | Minimizes disruptions in logistics | Sourcing from reputable suppliers for quality assurance |
| Renewable Energy | Testing solar-powered vehicles or equipment | Supports sustainability initiatives | Compatibility with diverse energy systems |
How Can Automotive Repair Benefit from Checking a Solenoid on a Starter?
In the automotive repair industry, checking a solenoid on a starter is vital for diagnosing starting issues in vehicles. Technicians can identify whether the problem lies within the solenoid, starter motor, or battery, allowing for targeted repairs. This process saves time and reduces costs for both the repair shop and the customer. B2B buyers in this sector must consider sourcing reliable diagnostic tools and replacement parts to ensure efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What Role Does Solenoid Testing Play in Heavy Machinery Operations?
For heavy machinery, particularly in construction, checking the solenoid on starters is critical for ensuring that equipment operates reliably. Malfunctioning solenoids can lead to equipment failures, resulting in costly project delays. By regularly testing and maintaining solenoids, businesses can improve equipment uptime and safety on job sites. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing components that meet local safety regulations and can withstand rigorous operational conditions.
How Is Solenoid Testing Essential for Agriculture Equipment?
In agriculture, the reliability of machinery is paramount, especially during peak seasons. Checking a solenoid on starters helps maintain the performance of tractors and harvesters, ensuring they start reliably. This process ultimately boosts productivity and efficiency on farms. B2B buyers should seek durable parts that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, as well as suppliers who can offer timely delivery to minimize downtime during critical farming periods.

Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
Why Is Solenoid Checking Important for Transportation Logistics?
In the transportation logistics sector, ensuring that fleet vehicles start reliably is crucial to minimize disruptions. Regularly checking solenoids helps identify potential failures before they affect operations, thereby maintaining a smooth flow of goods. B2B buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who can provide quality assurance and support, as vehicle reliability directly impacts delivery schedules and operational costs.
How Does Solenoid Testing Support Renewable Energy Initiatives?
In the renewable energy sector, especially with the rise of solar-powered vehicles and equipment, checking the solenoid on starters is essential for optimal performance. Ensuring that these systems start efficiently supports sustainability initiatives and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Buyers in this field must focus on sourcing components that are compatible with diverse energy systems and ensure that they meet international quality standards to promote reliability and effectiveness in their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to check a solenoid on a starter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Identifying the Solenoid’s Location
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions with varying automotive technologies, face challenges in locating the starter solenoid within different vehicle models. This issue is compounded by the lack of standardized designs across manufacturers and models, leading to confusion and inefficiency during maintenance or repair tasks. The inability to quickly identify the solenoid can result in extended downtime, increased labor costs, and frustration among technicians who may be unfamiliar with specific vehicle layouts.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, it is essential to invest in comprehensive service manuals or online databases that provide detailed diagrams and descriptions for various vehicle models. Encourage your team to utilize these resources before starting any work. Additionally, consider conducting training sessions to familiarize technicians with common vehicle layouts, focusing on the starter solenoid’s typical positioning. Implementing a systematic approach, such as creating a checklist of common vehicles in your fleet along with their solenoid locations, can streamline the identification process, thus reducing repair time and costs.
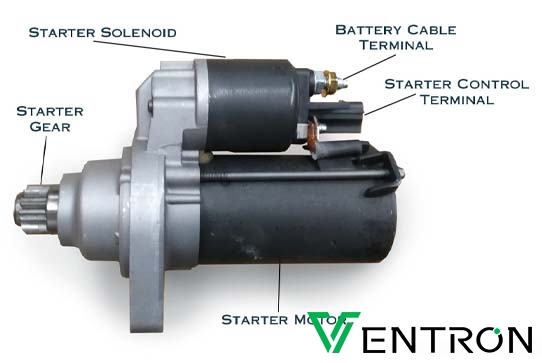
Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Power Supply During Testing
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is experiencing inconsistent power supply readings when testing the solenoid, which may lead to misdiagnosis of issues. This inconsistency often stems from faulty wiring, poor connections, or inadequate testing equipment. Such complications not only waste valuable time but can also result in unnecessary part replacements, inflating repair costs and damaging customer trust.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, ensure your team uses high-quality, calibrated testing equipment such as voltmeters and test lights. Regular maintenance and checks on these tools can prevent inaccuracies during testing. Furthermore, educate technicians on the importance of inspecting wiring and connections for corrosion or damage before conducting tests. Establish a protocol for performing a pre-test checklist, which includes verifying the battery’s voltage and ensuring all connections are secure and clean. By adopting these best practices, you can improve diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Confusion Over Solenoid Failure Symptoms
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with distinguishing between symptoms caused by a failing solenoid and those resulting from other components, such as the starter motor or battery issues. This confusion can lead to delays in repairs, increased costs, and reduced customer satisfaction, especially when technicians jump to conclusions without thorough diagnostics.
The Solution: To tackle this challenge, develop a detailed troubleshooting guide that outlines the specific symptoms associated with solenoid failure versus other potential issues. Incorporate visual aids, such as flowcharts, to help technicians systematically determine the root cause of the problem. Regular training sessions focusing on diagnostic techniques can also enhance your team’s ability to accurately assess issues. Encourage technicians to adopt a methodical approach, verifying each component step-by-step rather than making assumptions. By fostering a culture of thorough diagnostics, your team will be better equipped to handle repairs efficiently, ultimately improving service quality and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to check a solenoid on a starter
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Solenoid Components?
When selecting materials for checking a solenoid on a starter, it is essential to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. The following analysis covers four common materials: copper, aluminum, plastic, and stainless steel, focusing on their relevance to solenoid applications.
How Does Copper Contribute to Solenoid Performance?
Copper is widely used in electrical applications due to its excellent conductivity and thermal properties. It typically has a high-temperature rating and can withstand significant electrical loads, making it ideal for solenoid terminals and wiring connections.
Pros: Copper offers superior electrical conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and can be formed into various shapes, making it suitable for intricate designs.
Cons: However, copper is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments, which can lead to electrical failures over time. Additionally, its cost can be higher than alternative materials, impacting budget considerations for international buyers.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with various electrical media makes it an excellent choice for solenoids, but buyers must consider environmental conditions that may affect its longevity.
Why Choose Aluminum for Solenoid Components?
Aluminum is another popular choice for solenoid components, particularly for housing and structural parts. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has decent electrical conductivity.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its resistance to corrosion, which makes it suitable for outdoor or harsh environments. Its lightweight nature also contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which may affect performance in high-load applications. Furthermore, manufacturing processes can be more complex, leading to increased production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in regions with high humidity or salt exposure, making it a preferred choice for buyers in coastal areas.
How Does Plastic Enhance Solenoid Functionality?
Plastic materials, such as polycarbonate or nylon, are often used for insulating components of solenoids. They provide electrical insulation and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: The key advantage of plastic is its excellent electrical insulating properties, which prevent short circuits. It is also lightweight and generally cost-effective, making it an attractive option for manufacturers.
Cons: However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures as well as metals, potentially leading to deformation or failure in extreme conditions. Additionally, they can be less durable over time compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for non-load-bearing components in solenoids, but buyers must ensure that the selected plastic can withstand the operating environment.
Why Is Stainless Steel a Reliable Choice for Solenoid Applications?
Stainless steel is often used for solenoid housings and structural components due to its strength and corrosion resistance.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for various environments. It also has good mechanical properties, allowing it to withstand physical stress.
Cons: However, stainless steel can be heavier than other materials, which may not be ideal for all applications. Additionally, the cost is typically higher than aluminum or plastic, which could be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s robustness makes it ideal for applications that require high durability, particularly in harsh environments, appealing to international buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Solenoid Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to check a solenoid on a starter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical connections and terminals | Superior electrical conductivity | Prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower electrical conductivity | Medium |
| Plastic | Insulating components | Excellent electrical insulation | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Housings and structural components | High durability and corrosion resistance | Heavier and more expensive | High |
This analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to select the right materials for solenoid applications, considering both performance and environmental factors.

Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to check a solenoid on a starter
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Starter Solenoid?
The manufacturing process of a starter solenoid involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential to ensure that the final product meets performance and quality standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Starter Solenoids?
The first stage, material preparation, begins with selecting high-quality raw materials such as copper for electrical components and durable metals for the solenoid casing. Manufacturers often source materials based on international standards, ensuring they are free from impurities and defects. Quality assurance starts here, as material testing for conductivity and tensile strength is crucial.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo cleaning and treatment processes to enhance performance. This may include electroplating to improve corrosion resistance or applying insulation coatings to electrical components. Proper documentation and traceability of these materials are vital for B2B buyers, ensuring compliance with regulations.

Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
What Techniques Are Used in Forming the Solenoid Components?
The forming stage typically employs techniques like stamping, machining, and molding to create the various components of the solenoid. Stamping is often used for producing metal parts, while precision machining ensures tight tolerances for critical components such as the solenoid’s plunger.
For the coil, winding techniques are essential; manufacturers use automated winding machines to ensure uniformity in the number of turns and tension, which directly affect the solenoid’s efficiency. Each component’s quality is closely monitored through dimensional inspections and functional testing during this stage.
How Are Starter Solenoids Assembled?
The assembly stage involves integrating the individual components into a functional unit. This process may be manual or automated, depending on the scale of production. During assembly, it’s crucial to ensure that connections are secure and that all components fit perfectly to avoid operational failures.
Quality control checks at this stage include visual inspections and electrical testing to confirm that the solenoid operates as intended. Manufacturers often employ specialized tools to verify that the solenoid engages properly when voltage is applied, which is a critical performance metric.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Starter Solenoids?
Finishing processes typically involve applying protective coatings, such as powder coating or painting, to enhance the solenoid’s durability and aesthetics. Additionally, electrical testing is performed to confirm that the solenoid functions correctly under operational conditions.
Final inspections are crucial, where solenoids are tested for continuity, resistance, and operational response. These tests ensure that the solenoid meets the specifications outlined in international standards and customer requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Standards for Starter Solenoids?
Quality assurance in manufacturing starter solenoids is governed by several international and industry-specific standards. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for establishing a quality management system (QMS).
How Do International Standards Like ISO 9001 Affect Quality Control?
ISO 9001 certification indicates that a manufacturer has a robust QMS in place, which is crucial for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers. Compliance with this standard ensures consistent quality, improved customer satisfaction, and a continuous improvement culture.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for automotive components may also apply. These certifications ensure that the solenoids meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Checkpoints in the Quality Control Process?
The quality control process typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards is critical before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections and tests are conducted to monitor quality. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and functional tests on the assembly line.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the solenoids are fully assembled, they undergo final inspections. This includes operational tests to ensure they meet performance criteria and compliance with applicable standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should actively engage in verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This can be achieved through:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards. Auditors can evaluate the effectiveness of the QMS and the implementation of quality control checkpoints.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers provides insights into their testing methodologies, inspection results, and any corrective actions taken. These reports should detail the frequency of inspections and the outcomes of various quality tests.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can cover everything from material quality to final product testing.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional quality control nuances is essential. Different markets may have varying regulatory requirements and standards that suppliers must comply with.
For instance, European buyers must ensure that products meet CE marking requirements, while buyers in the Middle East may prioritize compliance with local regulations. It’s vital for buyers to communicate their specific requirements clearly and verify that suppliers are equipped to meet these standards.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for starter solenoids are complex and require stringent adherence to international standards. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they source high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
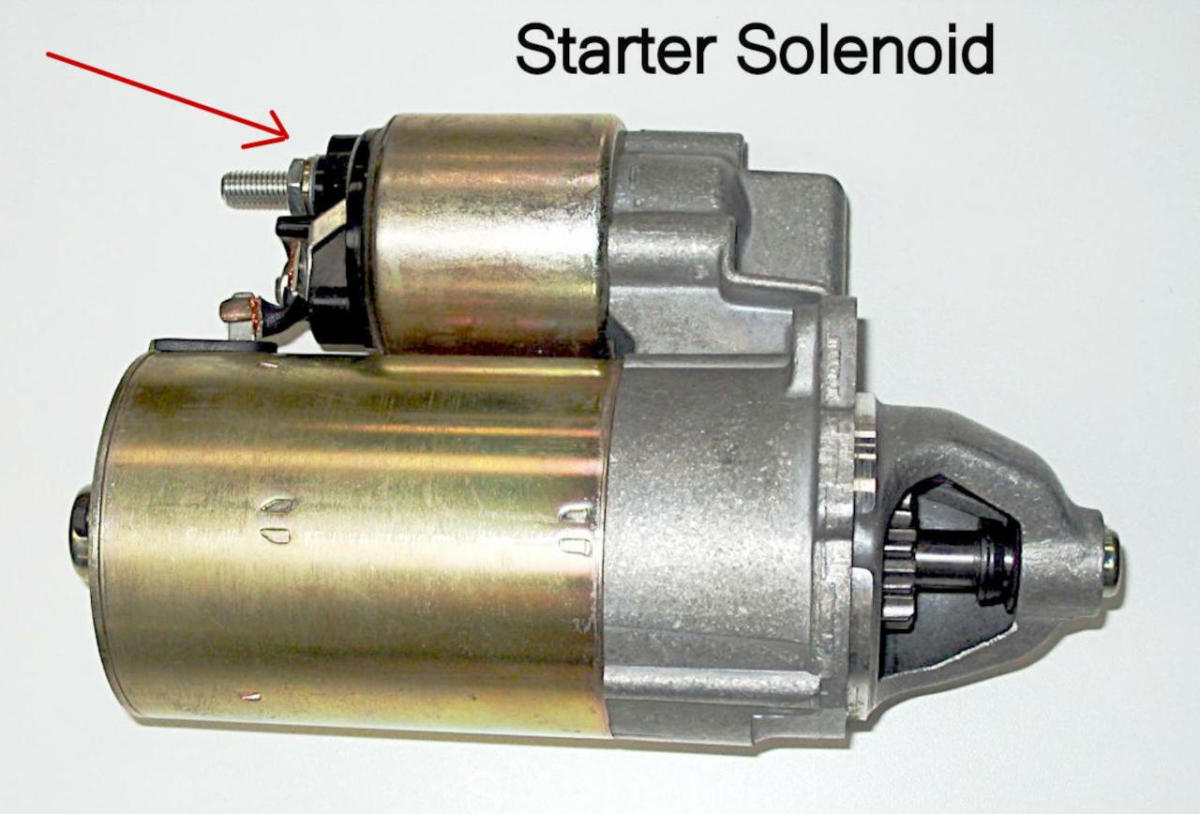
Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to check a solenoid on a starter’
To effectively check a solenoid on a starter, it’s crucial for B2B buyers to have a systematic approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist that will help you ensure you are equipped with the right knowledge and tools to evaluate and procure the necessary components or services.
Step 1: Identify the Application Requirements
Understanding your specific application is the foundation of effective procurement. Determine the type of vehicle or machinery in which the solenoid will be used, as this influences the specifications needed. Consider factors such as voltage requirements, size constraints, and environmental conditions the solenoid must withstand.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for the solenoid. This includes the voltage rating, current capacity, and physical dimensions. Having precise specifications helps in narrowing down supplier options and ensures compatibility with existing equipment.
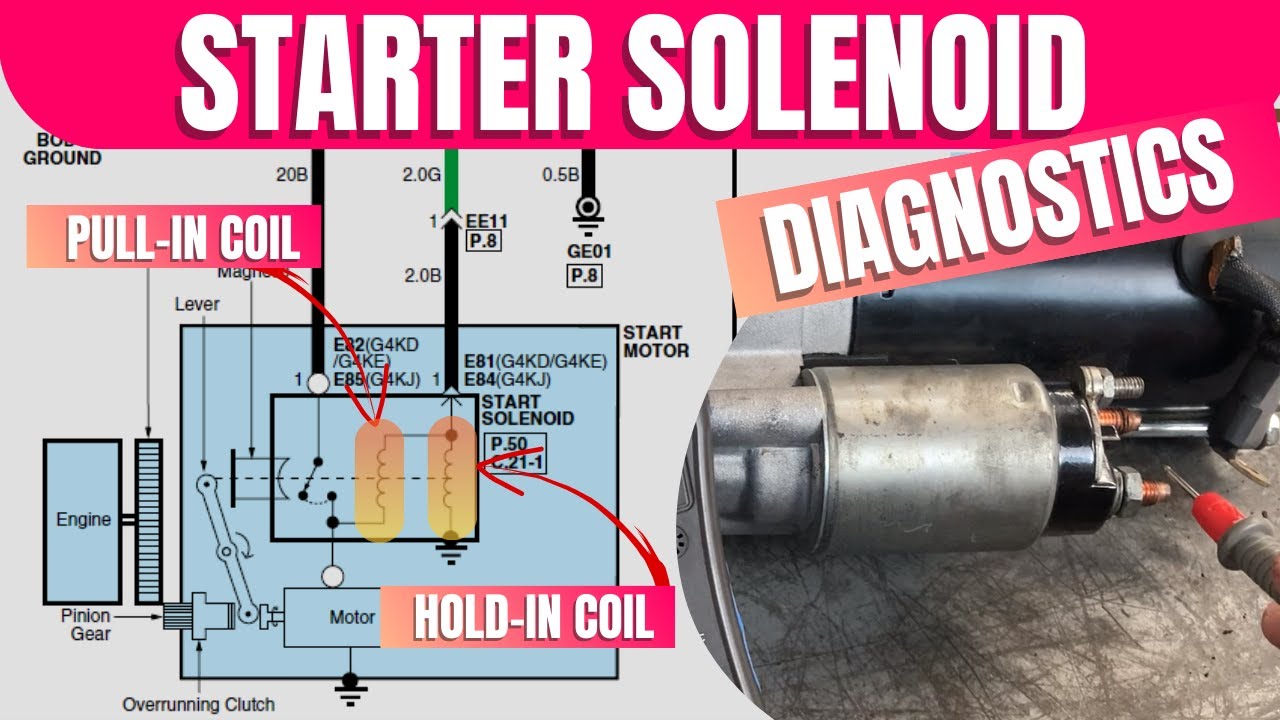
Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Look for companies that specialize in automotive or industrial components, as they are more likely to have the expertise required. Create a shortlist based on their product offerings, market reputation, and geographical location to facilitate easier logistics.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Check for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance marks that demonstrate their commitment to producing reliable products. This step is essential to mitigate risks associated with poor-quality components.
Step 5: Request Detailed Product Information
Engage shortlisted suppliers to provide detailed product catalogs or technical data sheets. This information should include installation guidelines, testing methods, and warranty policies. Understanding these aspects helps in making informed decisions and prepares your team for proper installation and maintenance.
Step 6: Assess Customer Support and Service
Evaluate the level of customer support offered by suppliers. Effective communication and support can significantly impact your procurement process and post-purchase experience. Ensure that the supplier provides adequate resources for troubleshooting, technical assistance, and after-sales service.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate terms of purchase, including pricing, delivery timelines, and payment conditions. Ensure that all agreements are documented to prevent misunderstandings later. A clear agreement fosters a strong business relationship and ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing components for checking a solenoid on a starter with confidence and precision.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to check a solenoid on a starter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Checking a Solenoid on a Starter?
When assessing the cost structure for checking a solenoid on a starter, several components come into play. Materials encompass the solenoid itself, wiring, testing equipment (such as voltmeters and test lights), and any replacement parts needed. Depending on the vehicle’s make and model, prices for these materials can vary significantly.
Labor costs include the time technicians spend diagnosing and testing the solenoid, which may differ based on regional wage standards. Manufacturing overhead covers expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs, often calculated as a percentage of direct labor costs.
Tooling costs are associated with specialized equipment needed for testing and replacing solenoids. This may include specific tools for accessing hard-to-reach areas in vehicles. Quality control (QC) processes ensure that all parts meet safety and performance standards, adding an additional layer of cost. Logistics involves shipping and handling of parts, which can be influenced by the supplier’s location and the chosen shipping method. Lastly, margin represents the profit markup added by suppliers, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Solenoid Testing Costs?
Several factors influence pricing for checking a solenoid on a starter. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) play significant roles; bulk orders may lead to discounted pricing, while smaller quantities could incur higher per-unit costs. Additionally, specifications and customization can impact the price. Custom parts designed for specific vehicle models may be more expensive than standard components.
Materials quality and certifications also affect pricing. High-quality materials that comply with international standards typically come at a premium but can lead to lower failure rates and longer lifespans. Supplier factors, such as reputation, reliability, and geographic location, are crucial; established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
Incoterms are vital for international transactions, determining who bears the risk and cost during shipping. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals, especially when sourcing from diverse regions.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for International B2B Transactions?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing solenoid testing services, buyers should consider several strategies. Negotiation is key; always seek to establish favorable terms, especially regarding price, delivery timelines, and payment conditions.
Focus on cost-efficiency by evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. This holistic view can reveal that cheaper parts may lead to higher long-term expenses if they fail prematurely.
Buyers should also be mindful of pricing nuances specific to their regions. For example, tariffs and import duties may affect the overall cost of parts imported from Europe or North America to regions like Africa and South America.
Understanding regional market dynamics can empower buyers to make informed decisions. Building relationships with suppliers who understand local regulations and market conditions can also facilitate smoother transactions.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Remember About Pricing for Solenoid Testing?
While prices for checking a solenoid on a starter can vary widely, understanding the underlying cost components and price influencers can enable buyers to make strategic decisions. Always consider the total cost of ownership and engage in thorough negotiations to secure the best possible terms. As with any B2B transaction, staying informed and adaptable is essential for achieving cost-effective solutions in international markets.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier rates, and specific buyer requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to check a solenoid on a starter With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives for Checking a Starter Solenoid
When addressing automotive issues, particularly with starter solenoids, it’s vital to explore various methods to ensure efficient diagnostics. Understanding alternative approaches allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions about the best tools and techniques for their operations. This analysis compares the traditional method of checking a solenoid against two viable alternatives: using a multimeter for comprehensive diagnostics and employing a remote starter switch for direct testing.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Check A Solenoid On A Starter | Multimeter Testing | Remote Starter Switch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for basic solenoid checks | Excellent for detailed diagnostics | Good for quick tests |
| Cost | Low (basic tools required) | Moderate (multimeter cost) | Low to moderate (switch cost) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires some technical knowledge | Requires technical knowledge | Simple setup, user-friendly |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Minimal maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Quick checks on solenoid functionality | In-depth electrical diagnostics | Immediate solenoid activation tests |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
How to Check a Solenoid on a Starter
This traditional method involves physically inspecting the solenoid, checking for clicks when the ignition is turned, and using a test light to determine if power is being transferred. While effective for basic checks, it often requires some technical skill and understanding of automotive systems. The primary advantage lies in its low cost; however, it may not provide a comprehensive view of the electrical system’s health.
Multimeter Testing
Using a multimeter allows for a detailed analysis of the electrical system, enabling users to measure voltage, current, and resistance. This method excels in performance, providing insights into not just the solenoid but also the battery and starter motor. While the initial cost is higher due to the investment in a multimeter, the depth of information gained can justify the expense. However, it does require a higher level of technical expertise, making it less accessible for inexperienced users.
Remote Starter Switch
This tool is designed to bypass the ignition system, allowing users to engage the starter directly. It is particularly useful for quickly determining if the starter motor or solenoid is at fault. The setup is straightforward, making it user-friendly for technicians of varying experience levels. The cost is generally low to moderate, depending on the switch’s quality. However, this method may not provide as much diagnostic information as multimeter testing, limiting its use to immediate troubleshooting rather than comprehensive diagnostics.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate method for checking a starter solenoid depends on various factors, including the technical expertise available, the specific diagnostic needs, and budget constraints. For quick checks, the traditional method remains valuable. However, for those requiring detailed diagnostics, investing in a multimeter may offer greater long-term benefits. The remote starter switch serves as an excellent intermediary option for technicians seeking efficiency and ease of use. B2B buyers should evaluate their operational needs and resources before making a decision to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in their automotive diagnostics processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to check a solenoid on a starter
What Are the Key Technical Properties When Checking a Starter Solenoid?
When evaluating a starter solenoid, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Material Grade
The solenoid is typically made from high-grade materials such as copper and durable plastics. Copper is essential for its excellent conductivity, ensuring efficient power transfer from the battery to the starter. The quality of materials impacts longevity and resistance to corrosion, which are vital for vehicles operating in diverse climates. -
Voltage Rating
Starter solenoids generally operate at a voltage rating of 12V or 24V, depending on the vehicle’s system. Selecting a solenoid with the correct voltage rating is critical; using an incorrect voltage can lead to inadequate performance or complete failure of the solenoid, which can result in costly repairs. -
Current Rating
The current rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current the solenoid can handle, usually measured in amperes (A). A solenoid must be able to handle the starter motor’s current draw during operation. Ensuring that the current rating meets or exceeds the starter’s requirements prevents overheating and potential damage. -
Resistance Measurement
Resistance in the solenoid’s coil is measured in ohms. A typical resistance value ensures that the solenoid can engage and disengage effectively. A solenoid with high resistance may fail to operate correctly, leading to starting issues. Regularly checking resistance can identify potential failures before they occur. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the acceptable range of variation in the solenoid’s dimensions and performance parameters. Precise tolerances ensure that the solenoid fits correctly in the vehicle and functions as intended. Poorly manufactured solenoids with inadequate tolerances can lead to mechanical failures or misalignment in the starting system.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Relevant to Solenoid Checks?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and communications between buyers and suppliers. Below are key terms relevant to checking and purchasing starter solenoids.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM parts are components made by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. These parts are generally preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and reliability. B2B buyers often seek OEM solenoids to ensure they meet the vehicle’s specifications and performance standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for businesses to manage inventory effectively. A supplier with a high MOQ may not be suitable for smaller operations or those looking to test a new product line without significant upfront investment. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This is a common practice in B2B transactions and allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal for their solenoids. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines when sourcing solenoids internationally. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Knowing the lead time is essential for planning and inventory management. Delays in lead time can impact business operations, especially in industries reliant on just-in-time inventory systems.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when purchasing solenoids for starters. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right components but also streamlines procurement processes and enhances overall operational efficiency.
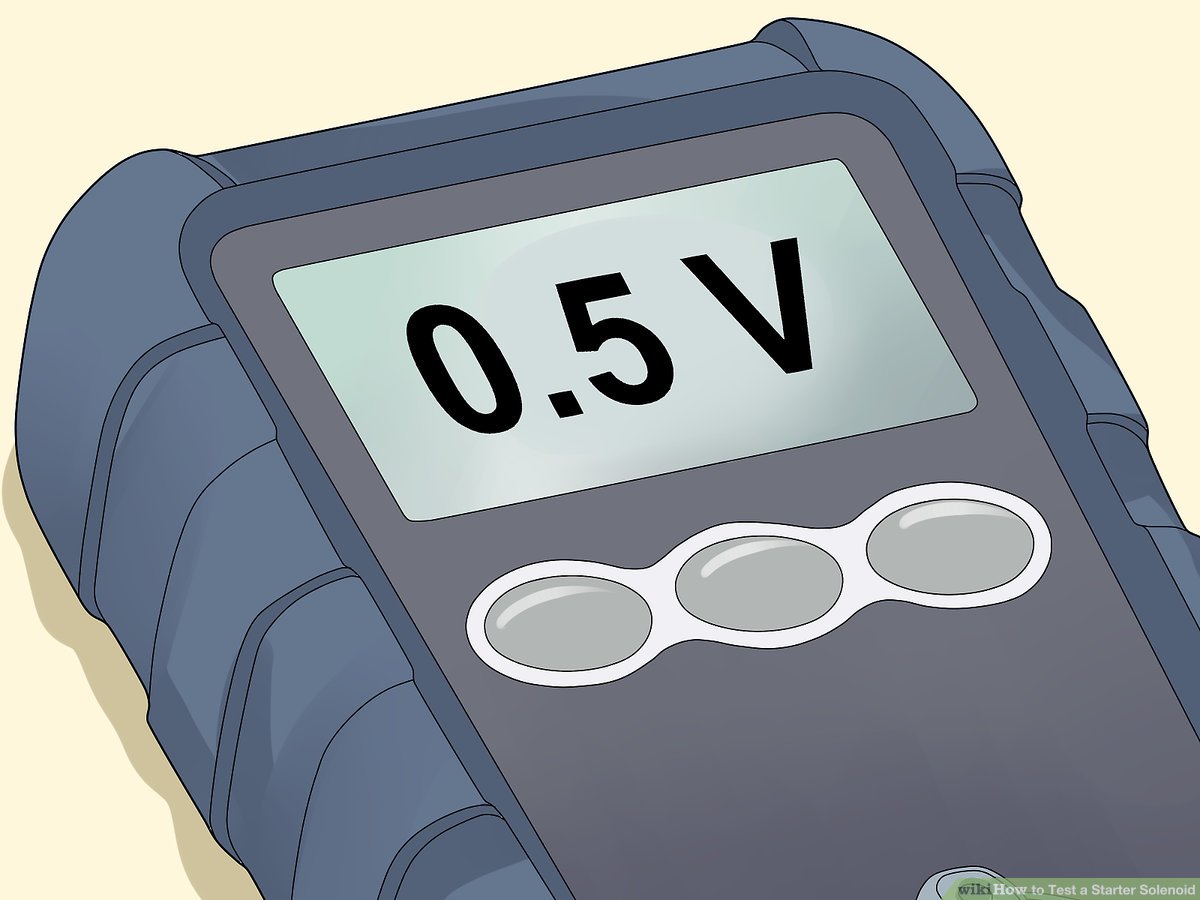
Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to check a solenoid on a starter Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Starter Solenoid Sector?
The market for starter solenoids is influenced by several global drivers, including the increasing demand for reliable automotive components due to the rise in vehicle ownership in emerging markets like Africa and South America. Technological advancements, such as the integration of smart diagnostics in automotive systems, are shaping B2B sourcing strategies. These technologies enable quicker and more accurate assessments of solenoid functionality, thus reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, the automotive industry’s shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles presents new opportunities for suppliers who can adapt their offerings to meet the evolving needs of the market.
International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate flexibility in their sourcing capabilities and can provide high-quality components that meet rigorous industry standards. This is particularly relevant in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where compliance with stringent regulations is non-negotiable. Moreover, the trend toward just-in-time inventory systems is pushing buyers to seek suppliers who can guarantee rapid delivery and consistent quality, ensuring that their operations remain efficient and responsive to market demands.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the Starter Solenoid Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the automotive components industry. The environmental impact of manufacturing practices is under increasing scrutiny, with businesses encouraged to adopt greener methodologies. This includes the use of recyclable materials in starter solenoid production and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing process. As buyers become more conscious of their carbon footprints, the demand for products certified by recognized ‘green’ standards is on the rise.
Suppliers who can demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices not only enhance their appeal to conscientious buyers but also mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the REACH regulation for chemical safety are increasingly becoming prerequisites for successful procurement. Additionally, ethical supply chain practices are crucial; buyers are more likely to collaborate with suppliers who ensure fair labor practices and transparency in sourcing materials, thereby contributing to a more sustainable industry overall.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Solenoid Development?
The starter solenoid has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, solenoids were simple electromagnetic devices that engaged the starter motor directly when the ignition key was turned. Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology have led to more reliable and efficient designs. The introduction of microprocessors and smart technology has allowed for better diagnostics and improved performance monitoring, enabling mechanics and technicians to quickly assess solenoid issues.

Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
In the context of B2B sourcing, understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the technological advancements that can influence product quality and longevity. As manufacturers continue to innovate, B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest developments to ensure they are sourcing the best components for their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to check a solenoid on a starter
-
How do I troubleshoot a non-functioning starter solenoid?
To troubleshoot a non-functioning starter solenoid, start by checking the battery voltage to ensure it has sufficient charge (around 12 volts). Then, locate the solenoid, usually attached to the starter, and listen for a clicking sound when the ignition is turned. If you hear clicking but the starter doesn’t engage, use a test light to check for power at the solenoid’s terminals. If power is present but the starter doesn’t activate, the solenoid may need replacement. Always verify wiring connections for corrosion or damage. -
What is the best way to test a starter solenoid?
The best way to test a starter solenoid involves a few steps. First, confirm there is power to the solenoid by connecting a test light to the input terminal. Then, have a colleague turn the ignition while observing the output terminal. If the test light illuminates, the solenoid is transferring power. If it does not, the solenoid may be defective. Additionally, consider using a multimeter to measure resistance across the solenoid terminals for a more thorough diagnosis. -
How can I source reliable starter solenoids for my business?
Sourcing reliable starter solenoids begins with identifying reputable manufacturers or distributors. Look for suppliers with established track records in automotive parts, preferably those certified by international quality standards like ISO. Request samples to assess quality and performance. Attend trade shows and industry conferences to network with potential suppliers and gather insights. Online marketplaces and industry-specific platforms can also provide valuable reviews and ratings to help you make informed decisions. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter solenoids?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for starter solenoids vary by supplier and manufacturer. Typically, MOQs can range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and the specific model of the solenoid. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs, especially if you are testing a new supplier or product line. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time orders or smaller businesses, allowing you to manage inventory more efficiently. -
What payment terms should I consider when sourcing automotive parts?
When sourcing automotive parts like starter solenoids, consider flexible payment terms that align with your cash flow. Common terms include 30, 60, or 90 days net, which allow you to pay after the goods are received. Also, evaluate options like letters of credit for larger orders, which can provide security for both parties. Ensure clear communication with suppliers regarding payment methods accepted, including bank transfers, credit cards, or escrow services to protect your investment. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for imported starter solenoids?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) for imported starter solenoids, establish a robust inspection process. Request certification documents from suppliers to verify compliance with international standards. Consider hiring third-party inspection services to conduct pre-shipment inspections, ensuring that products meet your specifications. Additionally, set up a return policy for defective items and maintain open communication with suppliers to address any quality concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing automotive parts?
When importing automotive parts, logistics considerations are crucial for timely delivery and cost management. Assess shipping options, such as air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your urgency and budget. Understand customs regulations in your region to avoid delays, and work with experienced freight forwarders to navigate these complexities. Additionally, consider warehousing options close to your market to streamline distribution and reduce lead times. -
How can I customize starter solenoids to meet specific requirements?
Customizing starter solenoids involves collaborating closely with your supplier to define your specific requirements. This can include modifications in size, voltage ratings, or terminal configurations. Be prepared to discuss your application needs, including environmental factors and performance expectations. Most manufacturers will require a minimum order quantity for custom designs, so ensure you have a clear forecast of demand. Prototyping may also be necessary to test functionality before full-scale production.
Top 1 How To Check A Solenoid On A Starter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. LinkedIn – Starter Solenoid
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when the ignition key is turned to the ‘start’ position. It controls the high current needed to operate the starter motor safely and ensures clean engagement and disengagement to reduce wear. Symptoms of a bad starter solenoid include clicking noises, failure to crank, difficulty starting the engine, decreased acceleratio…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to check a solenoid on a starter
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers on Checking a Starter Solenoid?
In summary, understanding how to check a starter solenoid is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive sector, especially when sourcing parts for diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The step-by-step process outlined in this guide not only empowers technicians to diagnose issues effectively but also emphasizes the importance of verifying power supply and resistance, which can save time and reduce costs in repairs.
Strategic sourcing of quality components, such as starter solenoids, can significantly enhance operational efficiency and vehicle reliability. As markets evolve, investing in high-quality, reliable parts will ensure that your business remains competitive and meets the demands of your customers.
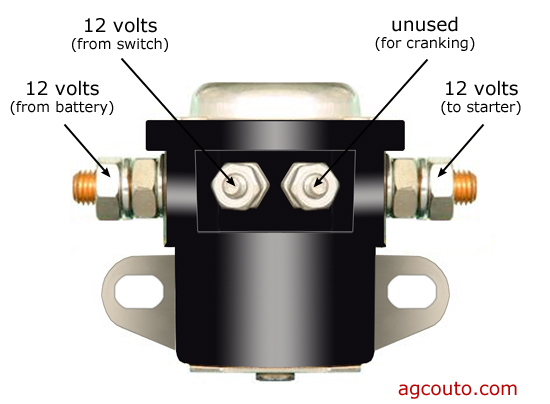
Illustrative image related to how to check a solenoid on a starter
Looking ahead, we encourage international B2B buyers to leverage partnerships with trusted suppliers and manufacturers. By doing so, you can ensure access to top-tier products and technical support, ultimately driving business growth and customer satisfaction. Embrace the future of automotive maintenance with confidence, and make informed sourcing decisions that will benefit your operations and bottom line.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.