Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how does a starter motor work
In the intricate landscape of automotive parts, understanding how a starter motor works is essential for international B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. The starter motor, a critical component that ignites the engine and sets the entire vehicle in motion, plays a pivotal role in ensuring operational efficiency. For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—where diverse vehicle types and market demands exist—grasping the nuances of starter motor functionality can significantly influence sourcing strategies and supplier selection.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of starter motors available, their specific applications across different vehicle models, and essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers. Additionally, it offers insights into pricing structures and market trends that can help buyers optimize their procurement processes. By equipping B2B buyers with a thorough understanding of starter motors, from their mechanical intricacies to their operational significance, this guide empowers businesses to make strategic decisions that enhance performance and reliability.
Navigating the global market for starter motors requires not just knowledge but also the ability to discern quality and value among numerous suppliers. With this guide, buyers will be well-prepared to tackle the challenges of sourcing, ensuring they select the right starter motor solutions that meet their operational needs and budget constraints.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 How Does A Starter Motor Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how does a starter motor work
- Understanding how does a starter motor work Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how does a starter motor work
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how does a starter motor work’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how does a starter motor work
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how does a starter motor work
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how does a starter motor work’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how does a starter motor work Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how does a starter motor work With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how does a starter motor work
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how does a starter motor work Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how does a starter motor work
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how does a starter motor work
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how does a starter motor work Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Starter Motor | Utilizes a solenoid to engage the pinion gear with the flywheel. | Automotive manufacturing and repair | Pros: Reliable, widely available. Cons: Limited efficiency; requires regular maintenance. |
| Permanent Magnet Starter Motor | Employs permanent magnets instead of field coils, leading to a compact design. | Motorcycles, ATVs, and compact vehicles | Pros: Lightweight, energy-efficient. Cons: Less torque compared to conventional types. |
| Gear Reduction Starter Motor | Features a gear reduction mechanism to increase torque output. | Heavy-duty machinery and trucks | Pros: High torque for large engines. Cons: Bulkier design may limit space in small vehicles. |
| High-Performance Starter Motor | Designed for high torque and quick engagement, often used in racing applications. | Performance vehicles and racing teams | Pros: Enhanced performance, quick engagement. Cons: Higher cost, not suitable for everyday vehicles. |
| Integrated Starter/Generator | Combines starter and generator functions into a single unit, often used in hybrid vehicles. | Hybrid and electric vehicle manufacturers | Pros: Space-saving, efficient energy use. Cons: More complex, potential for higher repair costs. |
What are the Characteristics of Conventional Starter Motors?
Conventional starter motors are the most common type, using a solenoid to engage a pinion gear that meshes with the engine’s flywheel. They are well-known for their reliability and availability, making them a standard choice for automotive manufacturing and repair. However, they require regular maintenance, and their efficiency can be limited compared to newer technologies. B2B buyers should consider the availability of parts and service expertise in their region when opting for this type.
How Do Permanent Magnet Starter Motors Differ?
Permanent magnet starter motors utilize magnets instead of field coils, resulting in a more compact and lightweight design. This type is particularly suitable for motorcycles, ATVs, and smaller vehicles where weight reduction is crucial. While they are energy-efficient and provide adequate power for smaller engines, they may lack the torque needed for larger applications. B2B buyers should assess the specific energy requirements of their vehicles to ensure compatibility.
What are the Benefits of Gear Reduction Starter Motors?
Gear reduction starter motors are engineered to deliver high torque output, making them ideal for heavy-duty machinery and large trucks. The gear reduction mechanism allows these motors to start larger engines with ease. However, their bulkier design may limit installation options in smaller vehicles. Buyers in the heavy machinery sector should consider the torque requirements of their applications to determine if this type meets their needs.
What Makes High-Performance Starter Motors Unique?
High-performance starter motors are designed for quick engagement and high torque, catering to the needs of racing vehicles and performance cars. They are built to withstand the rigorous demands of racing, offering enhanced performance compared to standard motors. However, their higher cost and potential incompatibility with everyday vehicles make them a specialized choice. B2B buyers in the automotive performance sector should evaluate the specific performance needs of their applications.
How Do Integrated Starter/Generator Systems Work?
Integrated starter/generator systems combine the functionalities of a starter and a generator into a single unit, primarily used in hybrid and electric vehicles. This design saves space and enhances energy efficiency by allowing the vehicle to recover energy during braking. However, the complexity of these systems may lead to higher repair costs. B2B buyers focused on hybrid technology should consider the long-term benefits of efficiency against potential maintenance challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of how does a starter motor work
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how does a starter motor work | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Integration in vehicle assembly lines | Ensures reliable engine start-up, enhancing production efficiency | Quality control, compatibility with various engine types, supplier reliability |
| Agriculture | Use in farm machinery like tractors | Facilitates quick engine start in harsh conditions, reducing downtime | Durability under extreme conditions, service support, local availability of parts |
| Transportation | Deployment in commercial vehicles | Enhances fleet reliability, minimizing operational disruptions | Compliance with regional regulations, availability of spare parts, warranty terms |
| Mining | Implementation in heavy-duty vehicles | Ensures dependable engine performance in remote locations | Robustness against environmental factors, after-sales support, sourcing from trusted manufacturers |
| Construction | Utilization in construction equipment | Promotes efficient project timelines by ensuring machinery readiness | Compatibility with diverse machinery, maintenance services, supplier responsiveness |
How Does a Starter Motor Work in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, starter motors are integral to assembly lines where vehicles are produced. They ensure that engines start reliably, which is crucial for maintaining production schedules. A failure in the starter motor can lead to significant delays, affecting overall productivity. B2B buyers in this industry must consider sourcing high-quality starter motors that are compatible with various engine types and can withstand the rigors of assembly line operations. Supplier reliability and quality control measures are paramount to ensure consistent performance.
What Role Does a Starter Motor Play in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, starter motors are vital components in farm machinery, particularly tractors. These machines often operate in challenging environments, making the reliability of the starter motor essential for quick engine start-up. This capability minimizes downtime during critical harvesting periods, directly impacting productivity and profitability. Buyers should focus on sourcing durable starter motors that can withstand extreme conditions and offer strong service support. The availability of local parts is also crucial to ensure minimal disruption in operations.
How Are Starter Motors Used in Transportation?
In the transportation industry, starter motors are deployed in commercial vehicles, including trucks and buses. Their ability to provide reliable engine start-up is crucial for fleet operations, as any failure can result in costly delays and service disruptions. B2B buyers in this sector need to ensure that the starter motors comply with regional regulations and are sourced from reputable suppliers that offer warranties and support. The availability of spare parts is also a key consideration to maintain fleet reliability.
What Is the Importance of Starter Motors in Mining Operations?
Starter motors play a critical role in heavy-duty vehicles used in mining operations, where reliable engine performance is necessary in remote locations. These vehicles are often subject to harsh environmental conditions, making the robustness of the starter motor vital for uninterrupted operations. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing starter motors that demonstrate durability and reliability, along with strong after-sales support. Choosing trusted manufacturers can help mitigate risks associated with equipment failure in the field.
How Do Starter Motors Enhance Construction Equipment Efficiency?
In the construction industry, starter motors are utilized in various types of machinery, ensuring that equipment is ready for use at all times. This readiness promotes efficient project timelines, as delays in machinery start-up can lead to significant financial losses. Buyers should look for starter motors that are compatible with a wide range of machinery and provide maintenance services to ensure ongoing operational efficiency. Supplier responsiveness is also essential to address any issues that may arise during project execution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how does a starter motor work’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Starter Motor Functionality for Effective Maintenance
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as automotive repair and fleet management, often struggle with understanding the intricate workings of starter motors. This knowledge gap can lead to misdiagnosing issues, resulting in unnecessary repairs or replacements. For instance, a fleet manager might observe that vehicles are frequently failing to start but may not realize the role of the starter motor in the ignition process, leading to time and resource wastage in troubleshooting.
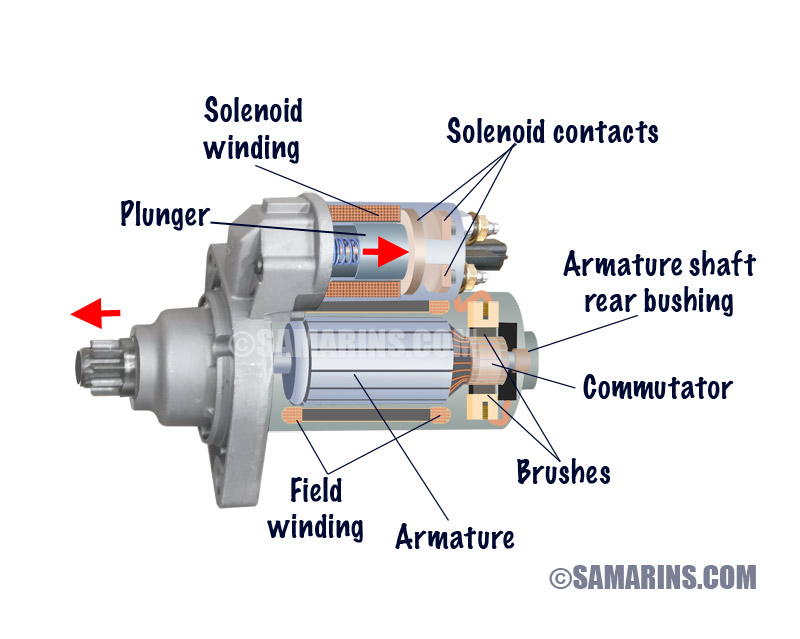
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training resources that explain the operational principles of starter motors. This includes understanding components like the solenoid, pinion, and armature, as well as their interactions during the starting process. Consider sourcing detailed training manuals or workshops that cover not only the theoretical aspects but also practical troubleshooting techniques. For instance, implementing a diagnostic checklist that includes verifying battery health, examining connections, and testing the starter motor’s functionality can streamline maintenance procedures. Additionally, collaborating with manufacturers to access technical support can enhance the team’s understanding, ultimately leading to better maintenance decisions and reduced downtime.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Starter Motors Amidst Diverse Options
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing quality starter motors due to the vast range of products available in the market. In regions like Africa or South America, where supply chains can be inconsistent, it becomes crucial to identify reliable manufacturers and distributors. Poor quality starter motors can lead to frequent failures, increased operational costs, and customer dissatisfaction, affecting the buyer’s reputation and bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, B2B buyers should establish partnerships with reputable suppliers known for their quality products. Conducting thorough research to identify manufacturers with ISO certifications or those that provide warranties can serve as indicators of reliability. Additionally, utilizing platforms that facilitate buyer reviews and ratings can help in assessing supplier credibility. It is also beneficial to engage in direct communication with manufacturers to discuss specifications, quality control processes, and after-sales support. Implementing a pilot testing phase for new suppliers can mitigate risks and ensure that the sourced starter motors meet operational standards before full-scale adoption.
Scenario 3: Managing Starter Motor Failures in Fleet Operations
The Problem: In fleet operations, unanticipated starter motor failures can disrupt service delivery and lead to significant financial losses. Fleet managers may encounter issues such as vehicles not starting due to faulty starter motors, particularly in harsh climates or during peak operational periods. This not only affects vehicle availability but can also lead to costly repair bills and labor hours spent on troubleshooting.
The Solution: To minimize the impact of starter motor failures, fleet managers should implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of starter motors and associated electrical systems. Utilizing telematics to monitor vehicle performance can provide early warnings of potential starter motor issues. Furthermore, establishing relationships with local automotive parts suppliers for quick access to replacement parts can significantly reduce downtime. Fleet managers should also consider investing in training their maintenance staff on recognizing early signs of starter motor wear, such as slow cranking or unusual sounds. By fostering a culture of preventive maintenance and education, fleet operations can enhance reliability and operational efficiency, ultimately leading to better service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how does a starter motor work
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Starter Motors?
When selecting materials for starter motors, several factors influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in the manufacture of starter motors, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Starter Motors?
Steel is widely used in starter motor components, particularly in the housing and gear assembly. Its key properties include high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros and Cons: The durability of steel makes it suitable for high-stress applications, but it can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated. While steel is generally cost-effective, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various automotive environments is a significant advantage, but it requires protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid or saline conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that steel components comply with local standards such as ASTM or JIS to guarantee quality and performance.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Starter Motor Components?
Aluminum is often used in starter motor housings and some internal components due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which contributes to overall vehicle efficiency. However, aluminum has lower tensile strength compared to steel, making it less suitable for high-stress components. Additionally, manufacturing processes for aluminum can be more complex and costly.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for environments where moisture is prevalent. However, it may not withstand extreme mechanical stress as effectively as steel.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, often prefer aluminum for its lightweight properties, aligning with stringent fuel efficiency regulations. Compliance with EU standards for aluminum alloys is essential.
What Role Does Copper Play in Starter Motor Functionality?
Copper is predominantly used in the electrical components of starter motors, such as windings and brushes, due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
Pros and Cons: The high conductivity of copper ensures efficient power transfer, which is crucial for the starter motor’s performance. However, copper is relatively expensive and can be susceptible to corrosion without proper treatment.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with electrical systems is vital, but its cost can be a limiting factor for budget-conscious buyers.
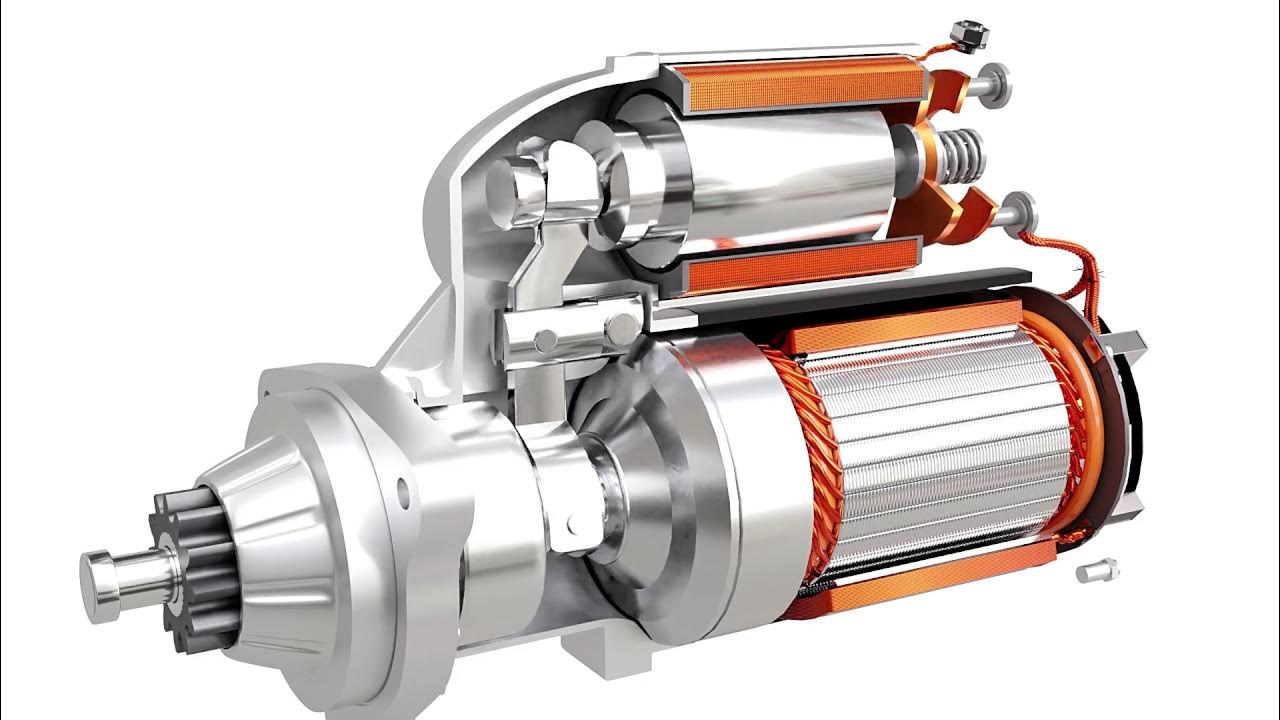

Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should be aware of fluctuations in copper prices and consider sourcing strategies that mitigate these costs while ensuring compliance with local electrical standards.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Starter Motor Design?
Plastics are increasingly used in non-structural components of starter motors, such as insulation and covers, due to their lightweight and insulating properties.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of plastics is their resistance to corrosion and low weight. However, they typically have lower mechanical strength and can degrade under high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for insulating components but may not be appropriate for parts that experience high mechanical stress or heat.
Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used meet relevant international standards for automotive applications, such as DIN in Germany, to ensure safety and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Starter Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for how does a starter motor work | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Housing and gear assembly | High tensile strength and durability | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Aluminum | Motor housing and internal components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength than steel | High |
| Copper | Electrical windings and brushes | Excellent electrical conductivity | Expensive and corrosion-prone | High |
| Plastic | Insulation and non-structural components | Corrosion resistance and lightweight | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in starter motors, equipping international B2B buyers with essential insights for making informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how does a starter motor work
What are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Starter Motor?
The manufacturing of a starter motor involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent performance and quality standards required in the automotive industry. Each stage is integral to producing a reliable starter motor that can withstand the demands of various operating environments.
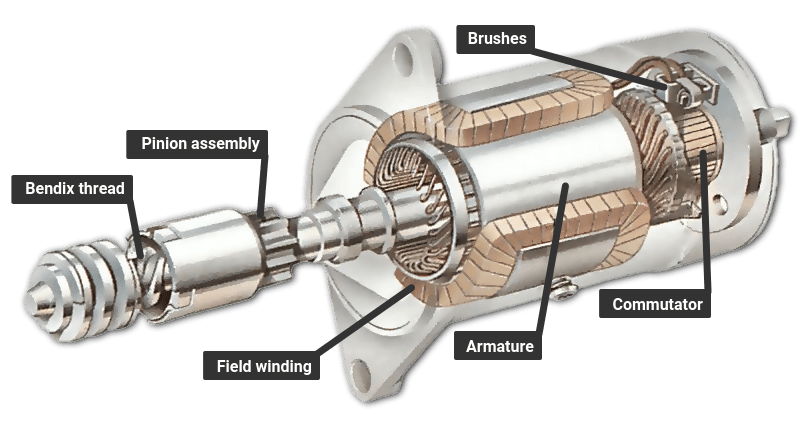
Material Preparation: What Materials are Used in Starter Motor Production?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where raw materials are sourced and prepared for production. Common materials used in starter motors include:
- Copper for electrical windings, due to its excellent conductivity.
- Steel for the housing and other structural components, providing durability and strength.
- Soft iron for the armature, which is essential for creating the magnetic fields necessary for operation.
- Composites and plastics are often used for insulating components.
Quality sourcing of these materials is crucial, as their properties directly affect the performance and longevity of the starter motor.
How is the Forming Process Executed in Starter Motor Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the various components of the starter motor. Key techniques employed during this phase include:
- Machining: Precision machining is used to create the armature and housing, ensuring exact dimensions and fit.
- Winding: The copper wire is meticulously wound around the armature to form the electromagnetic coils. This process must be done with precision to ensure optimal performance.
- Stamping and Die-Casting: Components like the solenoid and pinion gear are often produced using stamping and die-casting methods for consistency and efficiency.
Each component must meet specific tolerances to ensure they will function correctly when assembled.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve for a Starter Motor?
The assembly stage is where all the pre-formed components come together to create the finished starter motor. This stage typically includes:
- Component Integration: The armature, brushes, commutator, solenoid, and other components are carefully assembled. Each part must be installed in a manner that allows for proper engagement and disengagement during operation.
- Electrical Connections: Ensuring that all electrical connections are secure is vital, as poor connections can lead to performance issues or failure.
- Final Assembly: Once all components are integrated, the motor is encased in its housing and prepared for finishing.
Attention to detail during assembly is crucial, as this stage significantly impacts the reliability of the starter motor.
What Finishing Techniques are Applied to Starter Motors?
The finishing stage involves several processes that enhance the durability and aesthetics of the starter motor. Techniques include:
- Painting or Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear, particularly for components exposed to harsh environments.
- Quality Inspections: Visual inspections and measurements are performed to ensure that all components meet the required specifications.
A thorough finishing process ensures that the starter motors can withstand the rigors of automotive applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures are Essential for Starter Motors?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of starter motors, given their critical role in vehicle functionality. B2B buyers should be aware of the standards and processes that ensure product quality.
Which International Standards are Relevant for Starter Motor Quality Assurance?
The automotive industry adheres to several international standards to maintain quality assurance. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- ISO/TS 16949: Specifically tailored for the automotive sector, this standard emphasizes defect prevention and the reduction of variation and waste in the supply chain.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers ensure that their suppliers meet international quality benchmarks.
What are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Starter Motor Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with several critical checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that raw materials meet the specified quality standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various checks are conducted to ensure that components are being produced according to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the completed starter motors undergo rigorous testing to ensure they function as expected. This includes electrical tests, mechanical inspections, and performance testing.
B2B buyers should inquire about these QC checkpoints to understand the thoroughness of their suppliers’ quality assurance processes.
Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
What Testing Methods are Commonly Used for Starter Motors?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality and functionality of starter motors:
- Electrical Testing: This includes checking the resistance and current draw of the motor to ensure it operates efficiently.
- Mechanical Testing: Tests are performed to verify the engagement and disengagement of the pinion gear with the flywheel, assessing the mechanical reliability of the starter motor.
- Durability Testing: Some manufacturers conduct accelerated life tests to simulate extended usage and identify potential failure points.
These tests help ensure that the starter motors meet the performance demands of various automotive applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality assurance reports that document testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices and the performance of their products.
By actively verifying supplier quality control measures, B2B buyers can mitigate risks and ensure they are sourcing high-quality starter motors.
Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
What are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the landscape of quality certification can be complex for international B2B buyers. Specific nuances to consider include:
- Regional Certification Requirements: Different regions may have unique certification requirements. For example, automotive parts sold in Europe must comply with CE marking, while other regions may have different standards.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Buyers should be aware that quality expectations may vary between regions. Understanding these differences can facilitate better communication with suppliers.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that all documentation, including quality reports and certifications, are available in a language that is understood by the buyers to prevent miscommunication.
Being aware of these nuances can enhance the buyer-supplier relationship and ensure a smoother procurement process for starter motors.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for starter motors are critical to ensuring performance and reliability. By understanding these processes and actively engaging with suppliers on quality control, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that benefit their operations and enhance their product offerings.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how does a starter motor work’
To effectively procure information on how a starter motor works, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers, ensuring a thorough understanding of starter motor functionality, specifications, and supplier evaluation.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical specifications of starter motors is crucial for informed procurement. Identify the requirements based on your application, such as voltage, torque ratings, and compatibility with existing systems. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that you select the right product for your needs.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with the relevant industry standards and regulations governing starter motors in your region. Compliance with these standards is vital for safety and performance. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific automotive standards that ensure the reliability and quality of the starter motors you intend to source.
Step 3: Identify Potential Suppliers
Compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in starter motors. Utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry associations to find reputable manufacturers. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as they may have tailored solutions for local conditions.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before making a decision, assess the capabilities of each supplier. Investigate their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and customer service. Inquire about their experience with similar projects and request case studies or references from other clients in your industry. This due diligence will help ensure you partner with a reliable supplier.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have narrowed down your supplier list, request detailed quotations. Ensure that these quotes include all relevant costs, such as shipping, taxes, and warranties. Compare the quotations not only on price but also on the specifications and services offered. This comprehensive evaluation will aid in making a cost-effective decision.
Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Perform a risk assessment to identify potential challenges associated with sourcing starter motors. Consider factors such as supplier reliability, delivery timelines, and geopolitical risks that may affect your procurement. Having a contingency plan will help mitigate risks and ensure a smooth procurement process.
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement
After selecting a supplier, finalize the procurement agreement. Clearly outline the terms of delivery, payment schedules, and warranty conditions. Establish communication protocols for ongoing support and service after the sale. A well-structured agreement will protect your interests and establish a foundation for a successful supplier relationship.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a thorough understanding of starter motors and make informed decisions when sourcing from suppliers, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how does a starter motor work Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Starter Motors?
When sourcing starter motors, several cost components play a crucial role in determining the overall price. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials for starter motors include copper for windings, steel for the housing and pinion gear, and various plastics for insulation. The fluctuating prices of these raw materials can significantly impact the overall cost. Buyers should consider suppliers who offer bulk purchasing options to mitigate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region. In countries with higher wage standards, such as Germany, labor costs may account for a larger percentage of the total price. Conversely, in regions like Nigeria or South America, lower labor costs can provide a competitive advantage.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and salaries of non-production staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, leading to lower prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for starter motor production can be significant. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, especially if custom specifications are required. Sharing these costs across larger orders can lead to savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that starter motors meet international quality standards is crucial. Implementing rigorous QC processes adds to the manufacturing cost but is essential for maintaining reliability and minimizing returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and local tariffs can greatly influence the final price. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers negotiate better logistics terms.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their risks and operational costs. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s reputation.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
Several price influencers can affect the sourcing of starter motors, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their inventory strategies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications may lead to higher costs due to unique tooling or materials. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can affect both performance and price. High-quality materials may increase initial costs but can reduce total cost of ownership by enhancing durability and reducing failure rates.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO, TS16949) may carry a premium but can ensure compliance and reliability, essential for international markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their experience and quality assurance, but they often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and responsibilities can influence overall costs. Buyers should clarify whether they are responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties, as these can add to the final price.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Starter Motors?
To maximize value when sourcing starter motors, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. A good negotiation can lead to reduced costs or added value through improved payment terms or logistics support.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like warranty, service, and expected lifespan to make informed decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and local economic conditions, as these can impact pricing. For buyers in Africa or South America, understanding local supply chains can also lead to better pricing.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough research on multiple suppliers to compare prices and quality. Utilize industry contacts and platforms to gather insights into reputable suppliers.
-
Request Samples: Before placing large orders, request samples to assess quality. This practice can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the product meets your specifications.
By understanding the cost structure and price influencers associated with starter motor sourcing, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that optimize both performance and value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how does a starter motor work With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Starter Motors: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the automotive industry, the starter motor is a crucial component that initiates the engine’s operation. However, several alternative technologies and methods can also achieve similar objectives. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application.
| Comparison Aspect | How Does A Starter Motor Work | Alternative 1: Flywheel Starter | Alternative 2: Integrated Starter-Generator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque for brief intervals, reliable engine cranking. | Moderate performance; relies on mechanical energy. | High efficiency, provides both starting and regenerative braking. |
| Cost | Generally affordable, with a wide range of options available. | Typically lower initial cost, but may require more maintenance. | Higher initial investment, but potential for long-term savings. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation in most vehicles. | Requires more complex integration with drivetrain. | Requires specialized components and design considerations. |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs; common issues are easy to diagnose. | More frequent mechanical wear; requires regular checks. | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts, but requires specialized knowledge. |
| Best Use Case | Standard vehicles and applications needing reliable starting. | Vintage or specialized vehicles where traditional methods are preferred. | Hybrid and electric vehicles aiming for efficiency and reduced emissions. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Flywheel Starter?
The flywheel starter is an alternative method that uses the kinetic energy stored in a flywheel to initiate engine rotation. This system is often employed in applications where space and weight are critical, such as in motorsport or specialized vehicles.
Pros: Flywheel starters tend to be lighter and can offer instant torque, which is beneficial in performance-driven environments. They also have fewer electronic components, reducing the risk of electronic failure.
Cons: However, flywheel starters may not provide the same level of reliability as conventional starter motors, especially in extreme conditions. Their reliance on mechanical energy means they can be less efficient and may require more frequent maintenance.
How Does an Integrated Starter-Generator Compare?
The integrated starter-generator (ISG) represents a modern solution that combines the functionalities of a starter and an alternator into a single unit. This technology is increasingly popular in hybrid and electric vehicles, where efficiency is paramount.
Pros: The ISG system allows for regenerative braking, capturing energy that would otherwise be lost and reusing it to improve fuel efficiency. It also simplifies the vehicle’s electrical architecture, potentially reducing weight and complexity.
Cons: The initial cost of ISG systems is typically higher than traditional starter motors, which can deter some buyers. Additionally, integrating this technology requires specific vehicle designs and expertise, which may complicate installation for some manufacturers.
How Should B2B Buyers Decide on the Best Solution?
When considering alternatives to starter motors, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs and applications. Factors such as vehicle type, operational environment, and budget will influence the decision. For standard vehicles, a traditional starter motor may be the most cost-effective choice. In contrast, those developing hybrid systems might find that the integrated starter-generator offers long-term benefits despite its higher upfront cost. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of performance, maintenance requirements, and implementation ease will guide buyers toward the most suitable solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how does a starter motor work
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Starter Motors?
Understanding the technical properties of starter motors is crucial for B2B buyers in sectors such as automotive manufacturing, repair, and aftermarket services. Here are some critical specifications that define the performance and reliability of starter motors:
1. Material Grade
Starter motors are typically made from high-grade materials such as copper for wiring, steel for the housing, and aluminum for the armature. The choice of material affects durability, weight, and thermal conductivity. For B2B buyers, selecting components made from high-quality materials ensures longevity and performance, minimizing the risk of failures that could lead to costly downtime.
2. Torque Rating
The torque rating indicates the amount of rotational force the starter motor can generate. This is essential for cranking the engine and varies based on engine size and type. Buyers must ensure that the starter motor’s torque rating matches the specifications of the vehicles they service, as insufficient torque can result in inadequate starting performance.
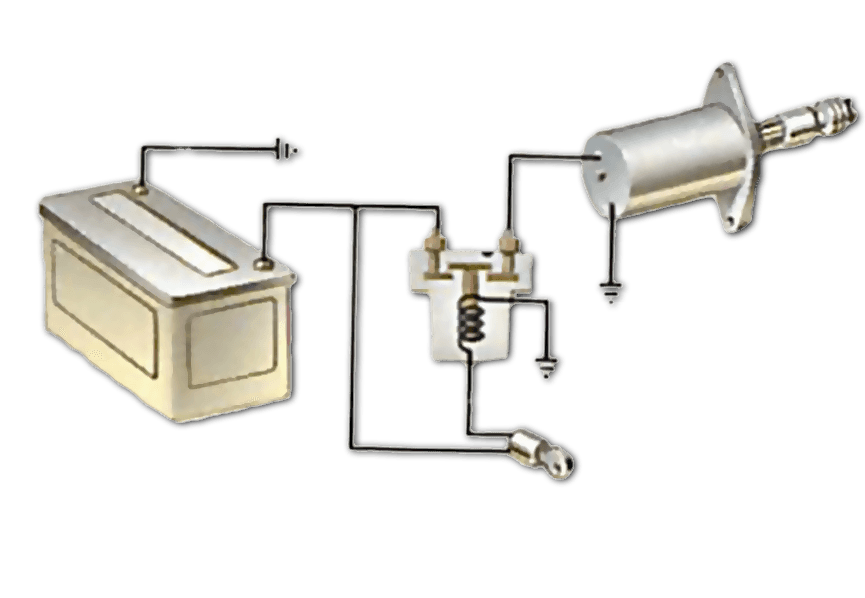
Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
3. Voltage and Current Ratings
Most starter motors operate on a 12V electrical system, but some applications may require 24V systems. The current rating, measured in amperes, indicates the maximum electrical load the motor can handle. Understanding these ratings is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and preventing electrical failures.
4. Gear Ratio
The gear ratio between the starter motor and the flywheel affects the speed and force with which the engine is cranked. A higher gear ratio typically means more torque but slower speed. Buyers should consider the gear ratio to ensure optimal performance in the specific applications they cater to, especially in heavy-duty vehicles.
5. Operating Temperature Range
Starter motors are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges, typically between -40°C to 85°C. Exceeding these temperatures can lead to overheating and premature failure. For B2B buyers, understanding the operating temperature range is essential when sourcing starter motors for diverse climates and applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Starter Motors?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms relevant to starter motors:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of starter motors, OEM parts are designed to meet the exact specifications of the original components. B2B buyers often prefer OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and costs effectively. It can impact pricing and the feasibility of sourcing starter motors, especially for smaller businesses.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for starter motors helps gather competitive pricing and terms, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, ensuring clarity in logistics and cost management.
5. Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to the market for replacement parts and accessories that are not supplied by the original manufacturer. B2B buyers should be aware of the aftermarket landscape for starter motors, as it offers opportunities for sourcing alternative parts that may provide cost savings without sacrificing quality.
Illustrative image related to how does a starter motor work
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing starter motors, ensuring they meet both their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how does a starter motor work Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Starter Motor Market?
The starter motor market is currently shaped by several global drivers that are pivotal for international B2B buyers. Firstly, the increasing demand for fuel-efficient and eco-friendly vehicles is driving innovation in starter motor technology. With the automotive industry leaning towards electric and hybrid vehicles, manufacturers are focusing on developing lightweight and high-efficiency starter motors that can accommodate these new technologies.
Additionally, the expansion of the automotive market in emerging economies, particularly in Africa and South America, is creating a surge in demand for reliable starter motors. Countries like Nigeria are witnessing a rise in vehicle ownership, leading to an increased need for automotive components.
Moreover, the digitization of manufacturing processes, including the integration of IoT and advanced manufacturing technologies, is transforming how starter motors are produced and sourced. This trend enables suppliers to optimize inventory management, reduce lead times, and improve product quality, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the Starter Motor Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the starter motor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning emissions and resource consumption, is prompting companies to adopt greener practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that utilize sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly manufacturing techniques, to reduce their carbon footprint.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming crucial indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers that hold these certifications to ensure compliance and mitigate risks associated with unethical sourcing.
Furthermore, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is prompting innovations in starter motor design, leading to the development of more energy-efficient products. This trend not only aligns with sustainability goals but also enhances the overall performance of vehicles, making it a compelling proposition for B2B buyers looking to meet modern consumer demands.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Motors Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of starter motors is a significant aspect for B2B buyers to understand, especially as they navigate sourcing decisions. The invention of the electric starter motor by Charles Kettering in 1911 revolutionized the automotive industry by eliminating the need for hand-cranking engines. This innovation not only improved vehicle reliability but also set the stage for further advancements in automotive technology.
Over the decades, starter motors have undergone considerable enhancements, including the introduction of solenoid-driven mechanisms that improved engagement and disengagement efficiency. The integration of advanced materials and manufacturing processes has further refined starter motor performance, making them lighter and more durable.
Understanding the historical evolution of starter motors provides B2B buyers with insights into the technological advancements that have shaped the current market. This knowledge enables buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing starter motors that meet modern standards and consumer expectations. As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of these historical developments will be essential for B2B buyers aiming to align with industry trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how does a starter motor work
-
How do I solve starter motor engagement issues?
To address starter motor engagement issues, first ensure that the battery is fully charged and connections are clean and secure. If the starter clicks but does not engage, the solenoid or internal components may be faulty. Testing the starter motor while it’s removed can help identify if the motor or solenoid needs replacement. Additionally, check the ignition switch and wiring for faults, as these can also prevent proper engagement. -
What are the common causes of starter motor failure?
Starter motor failure can be attributed to several factors, including worn internal mechanical parts, such as bearings or brushes, which can increase resistance and reduce efficiency. Over time, insulation on armature windings may degrade, diminishing torque. Corrosion or dirt on terminals can hinder electrical flow, leading to poor performance. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn parts can prevent unexpected failures. -
How can I verify the quality of a starter motor supplier?
To verify the quality of a starter motor supplier, check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples or product specifications to assess quality firsthand. Additionally, review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge reliability. Establishing communication regarding their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols will also help ensure you choose a reputable supplier. -
What customization options are available for starter motors?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for starter motors, including variations in voltage, torque ratings, and housing materials. Depending on your application, you may also request specific pinion gear sizes or mounting configurations. Discussing your unique requirements with suppliers will help them provide tailored solutions that meet your operational needs while ensuring compatibility with your equipment. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter motors?
Minimum order quantities for starter motors can vary significantly between suppliers, often influenced by factors like product type, customization, and market demand. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to several hundred units. It’s advisable to negotiate terms with suppliers, especially if you are a smaller buyer or looking for a trial order. Understanding their production capabilities will also aid in establishing feasible MOQs for your needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing starter motors?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include a percentage upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) for established customers. Always clarify these terms upfront and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How do logistics and shipping impact starter motor sourcing?
Logistics and shipping play a critical role in the sourcing of starter motors, affecting lead times and overall costs. Consider the supplier’s location and their shipping capabilities, as well as the chosen shipping method (air, sea, or land). Be aware of customs regulations and potential tariffs, especially when importing from different regions. Establishing a clear logistics plan can minimize delays and ensure timely delivery of your products. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in starter motors?
Quality assurance measures in starter motors typically include rigorous testing for performance, durability, and safety standards. Look for suppliers who conduct tests such as electrical load testing, thermal cycling, and vibration analysis. Certifications from recognized industry standards, such as TS16949 for automotive components, can also indicate a commitment to quality. Regular audits and inspections during production further enhance confidence in the product’s reliability.
Top 4 How Does A Starter Motor Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Auto Electro – Starter Motors
Domain: autoelectro.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Starter motors are responsible for turning the engine over during ignition, allowing air and fuel to enter for combustion. Key components include:
– Armature: An electromagnet on the drive shaft, wrapped with conductor loops.
– Commutator: A section of the shaft that conducts electricity through brushes.
– Brushes: Conduct electricity by making contact with the commutator.
– Solenoid: Acts as …
2. Haynes – Ignition System Guide
Domain: us.haynes.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Haynes – Ignition System Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Reddit – Starter Components
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Starter Components, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. How A Car Works – Starter System
Domain: howacarworks.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: The starting system includes a pre-engaged starter motor that uses a solenoid to engage a pinion with a gear ring on the engine flywheel. The starter motor requires a heavy electric current from the battery, activated by a large switch controlled by the ignition key. The solenoid operates an electromagnet that closes contacts to complete the circuit. The starter motor has a Bendix gear that engage…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how does a starter motor work
In the intricate world of automotive engineering, understanding how a starter motor works is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. The starter motor is not just a component; it is the heart of the ignition system, providing the necessary torque to initiate the engine’s operation. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, recognizing the importance of quality and reliability in starter motors can significantly influence operational efficiency and vehicle performance.
Strategic sourcing of starter motors involves evaluating suppliers based on product quality, durability, and service support. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a robust understanding of the technology, including the intricate roles of components such as the solenoid, pinion, and armature. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right products but also fosters long-term partnerships with manufacturers who can provide ongoing support and innovation.
As the automotive market evolves, embracing advanced technologies and sustainable practices will be key. We encourage B2B buyers to explore partnerships that offer cutting-edge starter motor solutions, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly changing landscape. Prioritize strategic sourcing today to drive your business forward tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.