Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for diagram alternator parts
In today’s fast-paced automotive industry, sourcing diagram alternator parts poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The intricacies of alternator components, from the rotor to the rectifier, require a deep understanding of their functionalities and applications to ensure compatibility and efficiency in various vehicles. This comprehensive guide is designed to equip buyers with essential knowledge about the diverse types of alternator parts, their specific applications across different markets, and strategies for effectively vetting suppliers.
By delving into cost considerations and the latest industry trends, this resource empowers businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Germany and Nigeria—to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance your product offerings or seeking reliable components for maintenance and repair, understanding the global market for diagram alternator parts is crucial. This guide will not only streamline your sourcing process but also enhance your competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, you can navigate the complexities of alternator parts procurement with confidence.
What Types of Diagram Alternator Parts Should You Consider?
Understanding the various components and their roles will help in making informed decisions.
How Can You Effectively Vet Suppliers of Diagram Alternator Parts?
Learn the key criteria for selecting trustworthy suppliers in the global market.
What Are the Cost Factors Influencing Diagram Alternator Parts?
Explore the economic aspects that affect pricing and value in your purchasing strategy.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Diagram Alternator Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for diagram alternator parts
- Understanding diagram alternator parts Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of diagram alternator parts
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘diagram alternator parts’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for diagram alternator parts
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for diagram alternator parts
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘diagram alternator parts’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for diagram alternator parts Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing diagram alternator parts With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for diagram alternator parts
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the diagram alternator parts Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of diagram alternator parts
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for diagram alternator parts
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding diagram alternator parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Alternator | Basic construction, typically aluminum housing, compact size | Automotive industry, light trucks | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited output for high-demand applications. |
| High-Output Alternator | Enhanced winding and rotor design for increased output | Performance vehicles, heavy machinery | Pros: Greater power capacity, supports advanced electrical systems. Cons: Higher cost, may require modifications for installation. |
| Marine Alternator | Corrosion-resistant materials, designed for harsh environments | Marine applications, boats | Pros: Durable, reliable in marine conditions. Cons: More expensive due to specialized materials. |
| Diesel Alternator | Built for high-load applications, robust design | Commercial vehicles, generators | Pros: High durability and reliability, designed for heavy loads. Cons: Heavier, more complex installation. |
| Smart Alternator | Integrated with electronic controls for optimal performance | Modern vehicles, electric systems | Pros: Efficient voltage regulation, enhances fuel economy. Cons: Higher initial investment, may require specialized knowledge for installation. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Alternators?
Standard alternators are the most common type found in passenger vehicles and light trucks. They typically feature an aluminum housing that dissipates heat effectively and has a compact design for easy installation. These alternators are suitable for basic electrical demands and are widely available, making them a cost-effective option for many businesses. When purchasing, buyers should consider the alternator’s output capacity and compatibility with their vehicle’s electrical system.
How Do High-Output Alternators Differ from Standard Ones?
High-output alternators are designed with enhanced winding and rotor configurations that allow for increased electrical output. They are particularly beneficial for performance vehicles and heavy machinery that require more power to support advanced electrical systems, such as high-end audio systems or additional lighting. Buyers should evaluate the specific power requirements of their applications and whether their vehicles can accommodate the modifications that may be necessary for installation.
What Makes Marine Alternators Unique?
Marine alternators are specifically engineered to withstand harsh marine environments, featuring corrosion-resistant materials and enhanced cooling capabilities. This makes them ideal for boats and other watercraft where exposure to saltwater and humidity can significantly affect performance. When considering a marine alternator, businesses should focus on durability and the ability to maintain performance under challenging conditions, as well as any additional certifications required for marine use.
Why Choose Diesel Alternators for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Diesel alternators are built to handle the high-load demands of commercial vehicles and generators. They are designed with robust components that ensure reliability and longevity under strenuous conditions. Buyers in sectors such as transportation and construction should consider the weight and installation complexity of diesel alternators, as well as their capacity to support heavy electrical loads without failure.
What Are the Benefits of Smart Alternators?
Smart alternators incorporate electronic controls that optimize voltage regulation and power distribution, enhancing overall vehicle efficiency. These are commonly found in modern vehicles and electric systems, where precise power management is critical. While they offer significant advantages in terms of performance and fuel economy, buyers should be aware of the higher initial investment and the potential need for specialized knowledge during installation, making them more suitable for businesses with advanced technical capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of diagram alternator parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of diagram alternator parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Power generation for electric vehicles | Enhances vehicle reliability and energy efficiency | Quality of materials, compliance with international standards, and availability of technical support. |
| Agriculture | Alternators in irrigation systems | Ensures consistent operation of water pumps | Durability in harsh environments, voltage regulation capability, and adaptability to local power sources. |
| Construction | Power supply for heavy machinery and tools | Increases productivity by ensuring equipment reliability | Size, weight, and compatibility with existing machinery. |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in wind and solar energy systems | Facilitates energy conversion and storage | Efficiency ratings, compatibility with renewable systems, and availability of replacement parts. |
| Marine | Electrical systems in boats and ships | Provides reliable power for navigation and safety | Corrosion resistance, size constraints, and compliance with maritime regulations. |
How Are Diagram Alternator Parts Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, diagram alternator parts play a pivotal role in converting mechanical energy into electrical power, particularly for electric and hybrid vehicles. These components ensure that the vehicle’s battery remains charged and that electrical systems function efficiently. Problems such as battery failure and electrical system malfunctions can be mitigated by sourcing high-quality alternator parts, which are critical for maintaining vehicle reliability and performance. Buyers in this sector must consider the quality of materials and adherence to international automotive standards to ensure optimal functionality.
What Are the Applications of Diagram Alternator Parts in Agriculture?
In agriculture, diagram alternator parts are essential for powering irrigation systems, which are vital for crop production in regions with variable rainfall. Alternators provide the necessary electrical energy to run water pumps, ensuring that irrigation systems operate consistently and effectively. This reliability is crucial for maximizing crop yields and minimizing water waste. Buyers should focus on sourcing alternator parts that demonstrate durability against harsh environmental conditions and offer effective voltage regulation to adapt to fluctuating power sources.
How Do Diagram Alternator Parts Benefit the Construction Industry?
In the construction industry, diagram alternator parts are used to power heavy machinery and tools, ensuring that equipment operates smoothly on-site. The reliability of these components can significantly affect project timelines and productivity. When sourcing alternator parts, construction companies should prioritize components that are compact and lightweight, as well as compatible with their existing machinery to facilitate easy integration and minimal downtime.
How Are Diagram Alternator Parts Integrated into Renewable Energy Solutions?
Diagram alternator parts are increasingly being integrated into renewable energy systems, such as wind and solar installations, where they convert generated energy into usable electrical power. This application is crucial for energy storage systems, allowing excess energy to be stored efficiently. When sourcing alternator parts for renewable applications, businesses should consider efficiency ratings and compatibility with existing energy systems, as well as the availability of replacement parts to ensure long-term operational success.
What Role Do Diagram Alternator Parts Play in Marine Applications?
In the marine sector, diagram alternator parts are integral to the electrical systems of boats and ships, providing reliable power for navigation, communication, and safety equipment. The harsh marine environment necessitates sourcing alternator parts that are corrosion-resistant and compliant with maritime regulations. Buyers must also consider size constraints, as space is often limited on vessels, ensuring that the selected alternator fits seamlessly into the existing electrical infrastructure.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘diagram alternator parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Diagrams for Accurate Sourcing
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with interpreting complex diagrams of alternator parts. These diagrams are essential for ensuring they are sourcing the correct components, yet the intricate details can lead to misunderstandings. For example, a buyer in Nigeria may find it challenging to distinguish between the various terminals and their functions, leading to incorrect orders and potential downtime in operations. This confusion can result in costly mistakes, including purchasing parts that are incompatible with their existing systems.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest in training sessions or workshops focused on reading and interpreting alternator diagrams. Working with suppliers who provide detailed visual aids and annotations can also be beneficial. Additionally, buyers can request sample diagrams and parts during the sourcing process to ensure they understand the components clearly. Utilizing digital tools that allow for zooming in on diagrams or interactive platforms that explain each part in detail can enhance comprehension, ultimately leading to more accurate orders and reduced operational disruptions.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility Across Different Models
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is ensuring that the alternator parts they procure are compatible with various vehicle models or machinery types. For instance, a buyer in South America might be tasked with sourcing alternator components for a fleet that includes both older and newer models, each requiring specific parts. The risk of purchasing incompatible components is high, which can lead to delays in repairs and increased costs due to returns and restocking fees.
The Solution: To address compatibility issues, buyers should develop a comprehensive database of the vehicles or machines within their fleet, including model numbers and specific alternator requirements. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide cross-referencing tools or compatibility charts can streamline this process. Furthermore, establishing a relationship with manufacturers who offer customization options can help ensure that the right components are sourced for each model, minimizing the risk of errors and enhancing overall efficiency in maintenance operations.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Delays in Alternator Parts Procurement
The Problem: Supply chain delays can severely impact the procurement of alternator parts, especially for B2B buyers operating in regions with logistical challenges, such as the Middle East. Buyers may face long lead times, fluctuating prices, and inconsistent quality from suppliers, which complicates inventory management and planning. A buyer in Germany, for instance, might find that extended shipping times from overseas manufacturers hinder their ability to meet customer demands, leading to lost sales opportunities.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should diversify their supplier base by identifying local manufacturers or distributors who can provide faster turnaround times. Building strategic partnerships with multiple suppliers can also enhance resilience against supply chain disruptions. Implementing just-in-time inventory practices can help manage stock levels efficiently, ensuring that critical components are available when needed without overcommitting resources. Additionally, leveraging technology for real-time tracking of shipments and establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can help buyers anticipate delays and adjust their procurement strategies accordingly.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for diagram alternator parts
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Diagram Alternator Parts?
When selecting materials for diagram alternator parts, it’s essential to consider the unique demands of automotive applications, including performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. The following analysis explores four common materials used in alternator components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Alternator Components?
Aluminum is widely used for the outer housing of alternators due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It effectively dissipates heat generated during operation, which is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Aluminum also resists corrosion, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: The primary advantages of aluminum include its low weight, which contributes to overall vehicle efficiency, and its resistance to corrosion. Additionally, aluminum can be easily machined, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than other metals like steel, and it may not offer the same level of strength. In high-stress applications, aluminum components may require additional reinforcement.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with automotive fluids and its ability to withstand high temperatures make it ideal for alternator housings. However, buyers should ensure that the aluminum used meets international standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance.
Why is Copper a Preferred Choice for Electrical Components?
Copper is a critical material for the wiring and electrical components within alternators due to its excellent electrical conductivity. This property ensures efficient power transfer, which is essential for the alternator’s performance.
Pros: The key advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which minimizes energy loss during operation. Copper is also highly ductile, allowing for easy fabrication into wires and connectors.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of copper is its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in humid environments. This can lead to reduced performance over time if not properly insulated.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with electrical systems makes it a standard choice for alternator windings and connections. International buyers should consider the corrosion resistance of copper components, especially in regions with high humidity, and ensure compliance with relevant standards.
What Role Does Steel Play in Alternator Manufacturing?
Steel is often used in the construction of various internal components, such as the rotor and stator, due to its high strength and durability. The magnetic properties of certain steel alloys enhance the alternator’s efficiency in generating electrical power.
Pros: Steel’s strength provides structural integrity, allowing it to withstand the mechanical stresses encountered in automotive applications. Additionally, it is relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact overall vehicle weight and fuel efficiency. It is also prone to rust if not properly coated or treated.
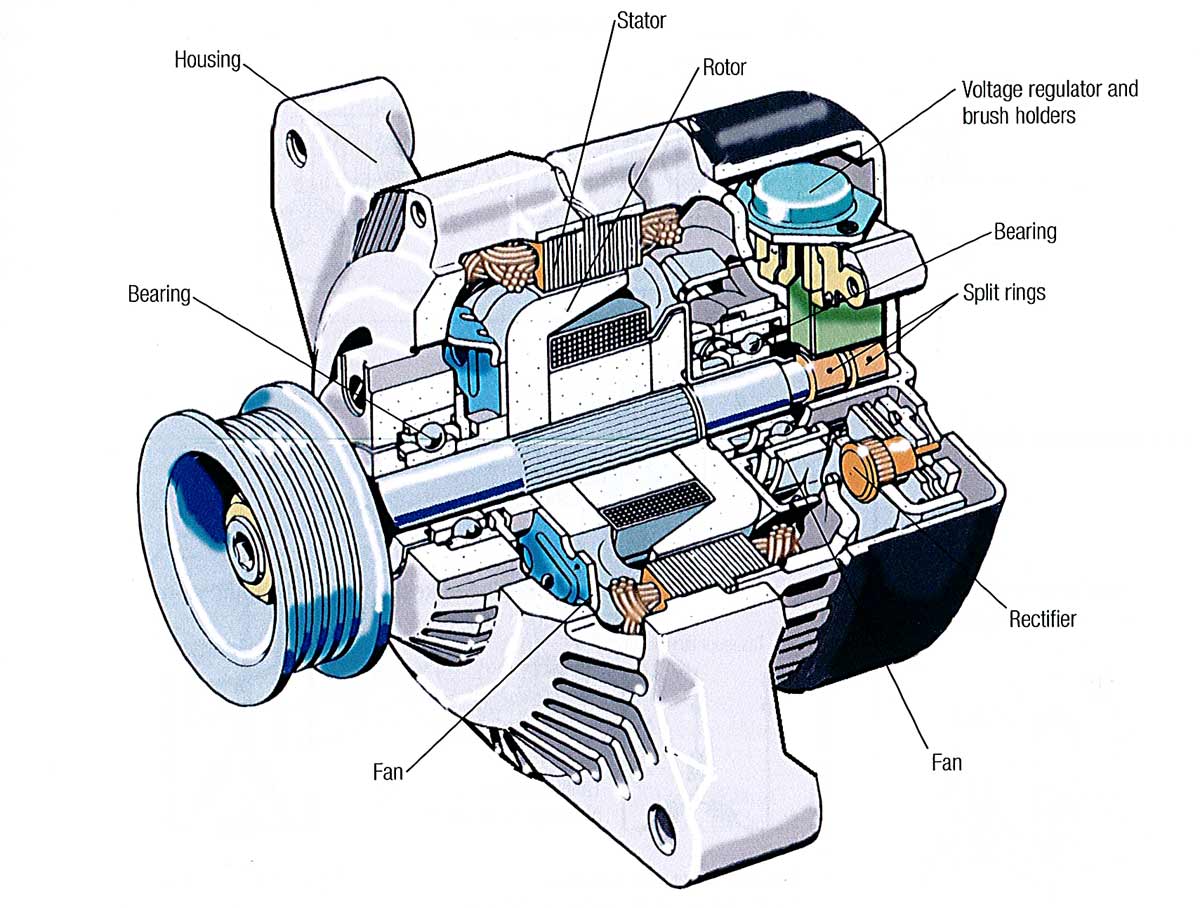
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
Impact on Application: Steel’s robustness makes it suitable for high-stress components within the alternator. Buyers should prioritize corrosion-resistant coatings to ensure longevity, particularly in regions with harsh environmental conditions.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Alternator Design?
Plastics are increasingly utilized in alternator designs for components such as housings and insulators due to their lightweight and insulating properties. They help reduce overall weight and improve energy efficiency.
Pros: The advantages of using plastic include its low weight, resistance to corrosion, and excellent electrical insulation properties. Plastics can also be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity.
Cons: The main limitation of plastic is its lower thermal resistance compared to metals, which may restrict its use in high-temperature environments. Additionally, plastics may not provide the same structural integrity as metals.
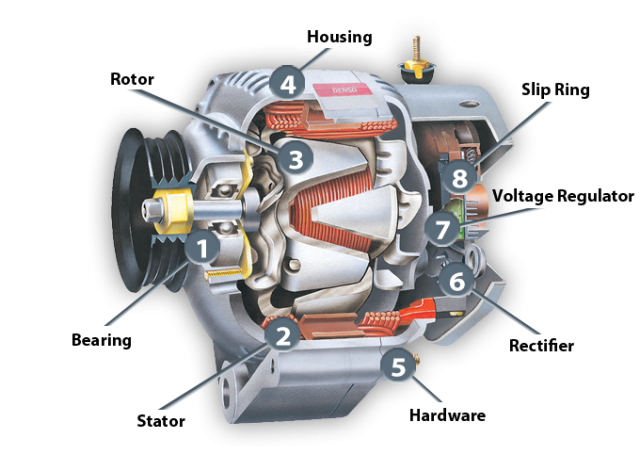
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
Impact on Application: Plastic components are particularly beneficial in reducing weight and improving energy efficiency. International buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with automotive industry standards for thermal and mechanical performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Diagram Alternator Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for diagram alternator parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Outer housing | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost compared to steel | Medium |
| Copper | Wiring and electrical connections | Excellent electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Steel | Rotor and stator | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | Low |
| Plastic | Housings and insulators | Lightweight and good insulation | Lower thermal resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in diagram alternator parts, enabling informed decisions that align with performance requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for diagram alternator parts
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Diagram Alternator Parts?
The manufacturing of alternator parts involves several key stages that ensure high performance and durability. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical in creating components that meet the rigorous demands of automotive applications.
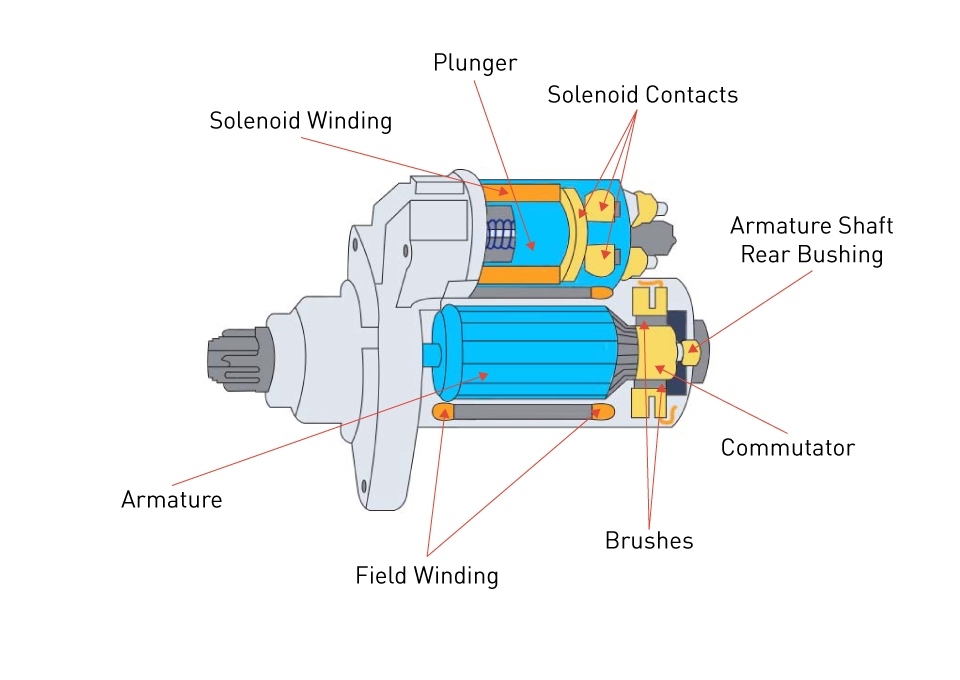
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
How Is Material Prepared for Alternator Components?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality aluminum is commonly used for the outer housing due to its lightweight and excellent heat dissipation properties. The material undergoes rigorous testing to verify its mechanical and thermal characteristics. Additionally, suppliers often conduct incoming quality control (IQC) checks to ensure that the raw materials meet specified standards before they proceed to the next phase.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Alternator Parts?
In the forming stage, various techniques are employed to shape the materials into usable components. Techniques such as die casting and machining are prevalent for creating intricate parts like the rotor and stator. The die-casting process allows for precise geometries and is particularly effective for producing complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. CNC machining is often utilized for critical components, ensuring tight tolerances that are essential for optimal performance.
How Are Alternator Parts Assembled and Finished?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to form the final alternator unit. Skilled technicians use automated assembly lines to ensure efficiency and consistency. During this phase, components such as the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator are assembled, often requiring the use of specialized tools to secure connections.
Finishing processes, such as anodizing or powder coating, may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetics. These finishing techniques not only contribute to the longevity of the components but also comply with industry-specific standards.
What Are the Quality Assurance Measures for Alternator Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that all alternator components meet international standards and customer expectations. The ISO 9001 certification is one of the most recognized standards that manufacturers pursue, as it demonstrates a commitment to quality management systems.
Which International and Industry-Specific Standards Are Relevant?
Apart from ISO 9001, other relevant certifications include CE marking for products sold in the European market and API standards for specific automotive applications. Compliance with these standards indicates that the alternator parts have undergone rigorous testing and meet safety and performance requirements.
How Are QC Checkpoints Established Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into the manufacturing process to monitor quality at various stages. The three main checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase focuses on verifying the quality of incoming materials before production begins. It typically involves visual inspections and material testing.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, IPQC ensures that each step adheres to quality standards. This can involve periodic checks of dimensional tolerances and functional testing of components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the manufacturing process, FQC is conducted to ensure that the final product meets all specifications. This may include performance testing and electrical testing of the assembled alternator.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and performance of alternator parts. Common methods include:
-
Electrical Testing: Assessing the output voltage and current to ensure compliance with specifications.
-
Thermal Testing: Evaluating the heat dissipation capabilities of components to prevent overheating during operation.
-
Vibration Testing: Simulating real-world conditions to check for structural integrity and performance under stress.
-
Life Cycle Testing: Running the alternator under simulated conditions to assess durability over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must perform due diligence when selecting suppliers for alternator parts. Here are effective strategies to verify supplier quality control practices:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into the manufacturer’s quality management systems and adherence to standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation on quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance, verifying that products meet specified requirements before shipment.
-
Evaluate Certifications: Ensure that the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) and that they are current.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is essential. Different regions may have varying regulations and standards, which can impact the compliance of alternator parts.

Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
-
Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with local standards that may differ from international norms. For example, EU regulations may impose stricter requirements than those in other regions.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers often involves understanding cultural nuances that can affect communication and quality expectations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality issues can also arise during transportation. Ensure your suppliers have robust logistics practices to maintain quality from the factory to the end-user.
In conclusion, a detailed understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for alternator parts is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the manufacturing stages, quality standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source high-quality components for their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘diagram alternator parts’
In today’s competitive automotive parts market, sourcing high-quality alternator parts is essential for ensuring reliability and performance. This step-by-step checklist aims to guide B2B buyers in procuring the right alternator components effectively, focusing on quality, compliance, and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical before starting the procurement process. This includes understanding the specific types of alternator parts needed, such as rotors, stators, rectifiers, and voltage regulators. Ensure that your specifications align with the vehicles or machinery for which the alternator parts will be used.
- Consider compatibility with existing systems to avoid operational issues.
- Specify performance requirements like voltage output and current capacity.
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Identifying reputable suppliers is paramount for ensuring the quality of alternator parts. Conduct thorough research to find companies with a proven track record in the automotive industry. Utilize online platforms, industry forums, and trade shows to gather information about potential suppliers.
- Look for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge supplier reliability.
- Evaluate their experience in supplying parts specific to your region, such as Africa, South America, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it is crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Do not solely rely on the information provided on their website; conduct independent research to verify their claims.
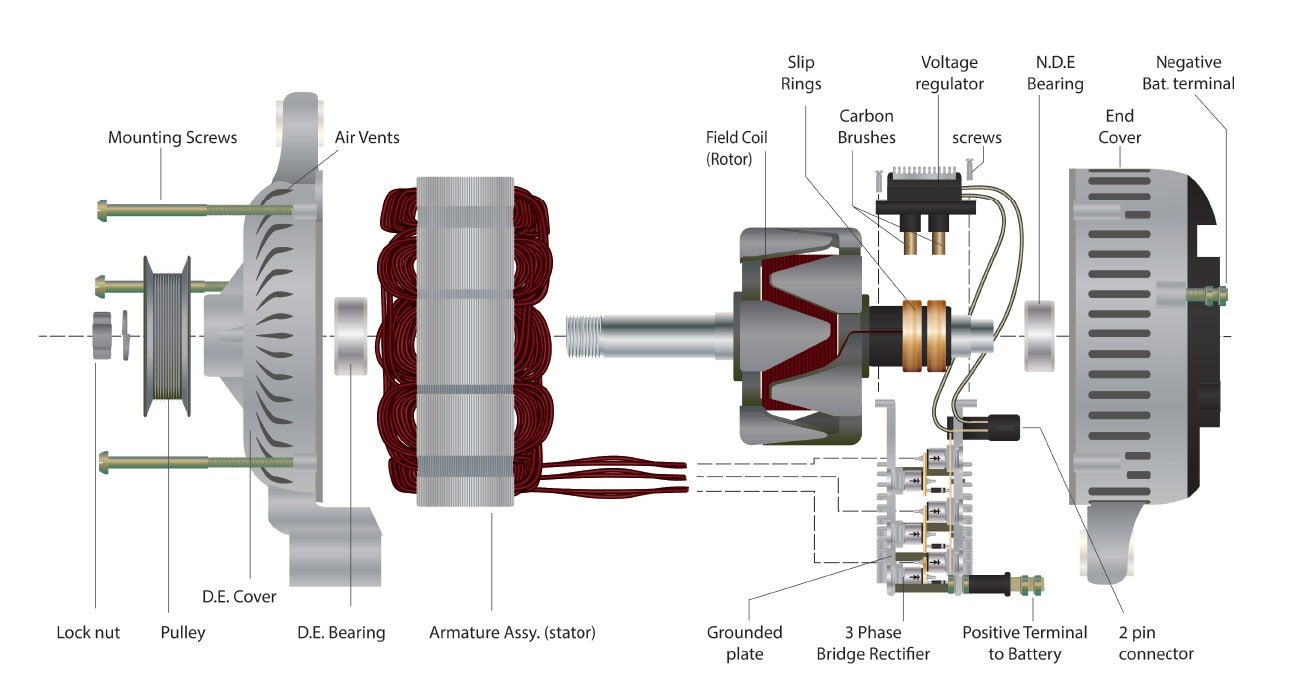
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
- Assess their certifications such as ISO or other relevant quality standards.
- Inquire about their manufacturing processes to ensure they meet international quality benchmarks.
Step 4: Verify Product Quality and Compliance
Quality assurance is essential for alternator parts, as subpar components can lead to system failures. Request samples or detailed product specifications to assess the quality of the alternator parts before placing a bulk order.
- Check for compliance with international standards to ensure the parts are safe and effective.
- Request documentation that proves adherence to quality regulations and safety standards.
Step 5: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Understanding the cost structure and payment terms is vital for maintaining budgetary control. Engage in discussions with potential suppliers regarding pricing, including any discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
- Clarify payment terms to avoid misunderstandings; consider options like letter of credit or escrow services for larger orders.
- Negotiate warranties and return policies to safeguard your investment.
Step 6: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication with your supplier can enhance the procurement process significantly. Establish clear lines of communication, including points of contact for technical support and order tracking.
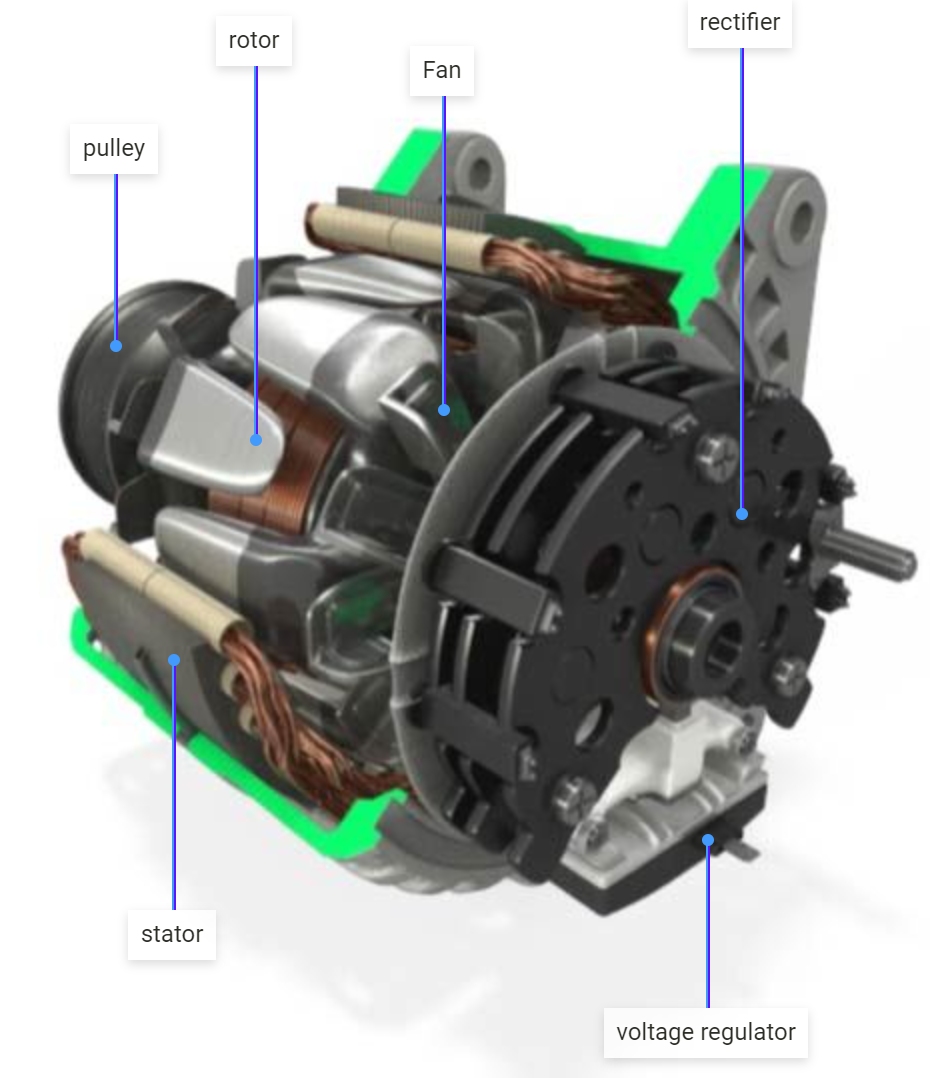
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
- Set regular updates to monitor the status of your order and address any issues promptly.
- Encourage feedback from your supplier regarding market trends and product enhancements.
Step 7: Evaluate Logistics and Delivery Options
Finally, consider the logistics involved in transporting alternator parts from the supplier to your location. Assess the delivery options available and the supplier’s ability to meet your timeline requirements.
- Review shipping methods and associated costs to find the most efficient solution.
- Ensure the supplier can handle customs clearance if shipping internationally, as this can significantly impact delivery times.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for alternator parts, ensuring they acquire high-quality components that meet their operational needs while fostering reliable supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for diagram alternator parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Diagram Alternator Parts?
When evaluating the cost structure of sourcing diagram alternator parts, several key components contribute to the overall price. Understanding these elements can help buyers make informed decisions and negotiate better deals.
-
Materials: The primary materials used in alternator production include aluminum for the housing, copper for the windings, and various polymers for insulation. The quality of these materials directly impacts performance and durability. Prices fluctuate based on global supply chain dynamics, making it essential for buyers to stay updated on market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the region. Countries with lower labor costs, such as those in Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing. However, it’s crucial to consider the skill level of the workforce, as more skilled labor may lead to higher initial costs but can improve product quality and reduce defects.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running a factory, such as utilities, rent, and salaries for non-production staff. Buyers should inquire about the overhead rates of potential suppliers, as these can influence pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial cost of tools and molds required for manufacturing alternator parts can be substantial. Buyers should assess whether the supplier has the necessary tooling capabilities, as custom tooling can significantly increase costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing effective QC processes ensures that the alternator parts meet specified standards. While additional QC measures may increase costs, they can lead to long-term savings by reducing the likelihood of defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are critical in international sourcing. Factors such as shipping methods, distance, and freight rates can substantially influence the total cost. Buyers should consider Incoterms to understand the responsibilities of each party in the shipping process.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary widely, depending on their market position and the competitiveness of their pricing strategy. It’s beneficial for buyers to understand the typical margins in their industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Diagram Alternator Parts Sourcing?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of diagram alternator parts, and understanding these can help buyers optimize their sourcing strategies.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) are often set by suppliers to ensure production efficiency. Higher order volumes typically result in better pricing, so buyers should consider consolidating orders to leverage bulk discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials or processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Quality Certifications: Parts that meet international quality standards often command higher prices. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East may prioritize certified parts, impacting the overall budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability, but they can also offer better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for clarifying the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and costs. This knowledge can help buyers avoid hidden fees and manage their logistics more effectively.
What Buyer Tips Should Be Considered for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
Navigating the complexities of sourcing diagram alternator parts requires strategic insights to maximize cost-efficiency.
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of the cost structure and market conditions. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms and pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, quality, and reliability. A lower initial price may result in higher TCO if the parts are prone to failure.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect the final cost. Engaging local experts can provide valuable insights into navigating these challenges.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly monitor market trends and emerging technologies in alternator manufacturing. This knowledge can empower buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions and anticipate price changes.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and buyer strategies, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing landscape for diagram alternator parts, ensuring they achieve the best possible outcomes. Always remember to review indicative prices carefully, as they can fluctuate based on numerous market factors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing diagram alternator parts With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Diagram Alternator Parts?
In the automotive and industrial sectors, understanding the components and functionality of an alternator is crucial for ensuring efficient energy conversion and reliability. While diagram alternator parts offer a detailed visualization of how these components work together to generate electrical energy from mechanical energy, alternative solutions or technologies also exist. These alternatives may provide different advantages in terms of performance, cost, and ease of use. This analysis will compare diagram alternator parts with two viable alternatives: battery management systems (BMS) and generator sets.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Diagram Alternator Parts | Battery Management Systems (BMS) | Generator Sets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in energy conversion; reliable for vehicle applications | Optimizes battery usage, prolonging life; less mechanical complexity | Provides high power output; suitable for off-grid applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; ongoing maintenance required | Varies based on features; can be cost-effective in the long run | Higher initial investment; operational costs depend on fuel type |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical knowledge for installation and maintenance | Can be integrated with existing systems; user-friendly interfaces available | Installation may require professional assistance; space considerations needed |
| Maintenance | Regular checks required; wear and tear on mechanical parts | Minimal maintenance; mostly software updates | Regular fuel and oil checks; can require significant maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Best for vehicles and equipment needing consistent power | Ideal for electric vehicles and renewable energy systems | Best for large scale power needs in remote locations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Battery management systems are sophisticated electronic systems that monitor and manage battery performance. They optimize charging cycles, balance battery cells, and extend the lifespan of batteries. The advantages of BMS include their ability to provide real-time data on battery health and performance, which is essential for electric vehicles and renewable energy applications. However, they do not generate power but rather manage the power stored in batteries. This makes them a complementary solution rather than a direct substitute for alternators.
Generator Sets
Generator sets serve as a robust alternative, providing electrical power through combustion engines or turbines. They can produce significant power output, making them ideal for industrial applications or remote areas without access to grid electricity. One of the primary benefits of generator sets is their ability to operate independently of other systems, offering versatility in various environments. However, they come with higher initial costs and ongoing fuel expenses, and they require more maintenance than alternators. Furthermore, their larger footprint may not be suitable for all applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between diagram alternator parts, battery management systems, or generator sets, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific requirements. Factors such as the nature of the application, the importance of energy efficiency, and budget constraints will guide the decision-making process. For automotive applications where reliability and efficiency are paramount, diagram alternator parts remain a strong choice. Conversely, for energy storage and management, a BMS may provide the optimal solution, while generator sets are best suited for high-demand scenarios in off-grid environments. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for diagram alternator parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Diagram Alternator Parts?
Understanding the technical properties of alternator parts is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact performance, reliability, and compatibility with existing systems. Here are several essential specifications that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the quality and type of materials used in the construction of alternator parts, such as aluminum for the housing and copper for windings.
– Importance: The choice of material affects the weight, durability, heat dissipation, and overall efficiency of the alternator. For instance, aluminum is preferred for its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for automotive applications. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in the dimensions of alternator parts, such as the rotor and stator.
– Importance: Maintaining tight tolerances ensures proper fit and function, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. In B2B settings, suppliers must provide parts that meet specified tolerances to ensure seamless integration into existing systems. -
Voltage Rating
– Definition: The maximum voltage that an alternator can safely produce, typically measured in volts (V).
– Importance: Voltage ratings are critical for compatibility with vehicle electrical systems. Buyers need to ensure that the alternator can provide sufficient power without exceeding the voltage limits of the battery and electronic components. -
Current Output
– Definition: The maximum amount of electrical current (measured in amperes, A) that an alternator can deliver to the battery and vehicle systems.
– Importance: Understanding current output is essential for buyers to ensure that the alternator can meet the power demands of the vehicle’s accessories and systems, especially in high-performance or commercial applications. -
Cooling Efficiency
– Definition: The ability of the alternator to dissipate heat generated during operation, often influenced by design features like internal or external cooling fans.
– Importance: Effective cooling is vital for maintaining performance and extending the lifespan of the alternator. Buyers should consider designs that enhance heat dissipation, especially in high-load scenarios.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Alternator Parts Industry?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Below are key terms that are frequently used in the industry:
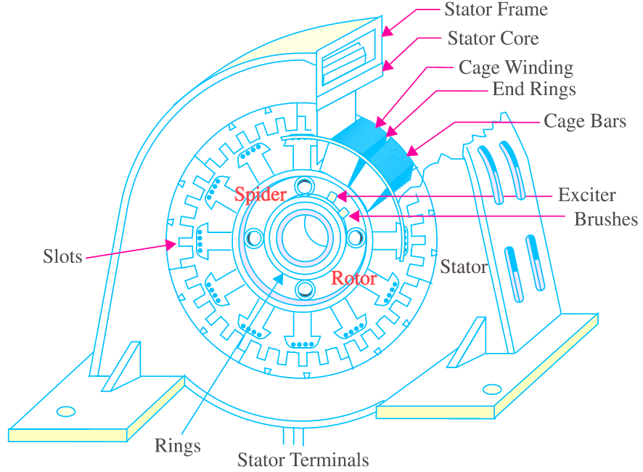
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often seek OEM parts for their reliability and compatibility with existing systems. Understanding OEM standards helps in sourcing high-quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. It helps buyers assess whether a supplier’s terms align with their purchasing capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent by a buyer to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ is a common practice to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of international standards that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and freight.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is critical for international transactions. -
Aftermarket
– Definition: Parts and accessories that are not sourced from the original manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers looking for cost-effective alternatives may consider aftermarket parts. Understanding the quality and warranty implications of these parts is vital for making informed decisions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing alternator parts, ensuring they select components that meet their operational needs and standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the diagram alternator parts Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Diagram Alternator Parts Sector?
The global market for diagram alternator parts is currently experiencing significant transformation, driven by advancements in automotive technology, increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), and a shift towards sustainability. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Germany and Nigeria) engage with this market, understanding these dynamics is crucial for informed sourcing decisions.
One of the most notable trends is the growing integration of smart technologies into alternators, including intelligent voltage regulators and data bus connections. These innovations enhance performance and efficiency, leading to lower fuel consumption and extended battery life. Buyers should also be aware of the increasing emphasis on lightweight materials, such as aluminum, which improve cooling efficiency and overall performance.
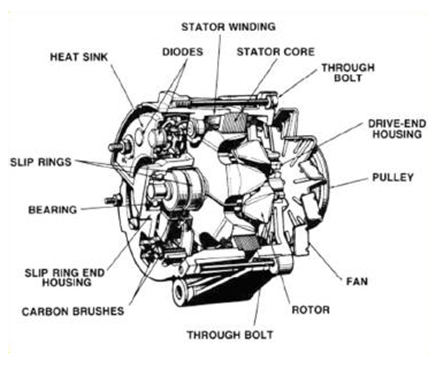
Illustrative image related to diagram alternator parts
Moreover, global supply chains are adapting to shifts in sourcing practices, with an emphasis on local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with international shipping and tariffs. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where local manufacturing capabilities are expanding. As these regions develop their automotive sectors, the demand for high-quality alternator parts is expected to rise, creating opportunities for both suppliers and buyers.
In conclusion, navigating the current market dynamics requires an understanding of technological advancements, local sourcing opportunities, and the evolving needs of consumers. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate adaptability and innovation in their offerings.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Diagram Alternator Parts Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly vital considerations in the diagram alternator parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste production, has prompted both consumers and businesses to seek out greener alternatives. For B2B buyers, understanding the implications of these factors can influence sourcing strategies and supplier relationships.
Adopting sustainable practices is not just beneficial for the planet; it can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize the use of eco-friendly materials and processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the shift towards electric vehicles has underscored the importance of sourcing components that minimize environmental impact. For instance, suppliers who utilize recycled materials or energy-efficient production methods in their alternator parts can offer a competitive edge. As regulations surrounding emissions and sustainability tighten globally, B2B buyers must align their sourcing strategies with these trends to remain compliant and relevant in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of the Diagram Alternator Parts Sector?
The evolution of the diagram alternator parts sector dates back to the early 20th century when the first alternators were introduced in automobiles. Initially, these components were rudimentary, primarily designed to meet basic electrical needs. However, as automotive technology advanced, so too did the complexity and functionality of alternators.
By the mid-20th century, the introduction of transistorized voltage regulators marked a significant turning point, allowing for more efficient power generation and distribution. This advancement paved the way for modern alternators, which now incorporate sophisticated technologies such as smart voltage regulation and cooling mechanisms.
Today, the focus has shifted to enhancing performance, efficiency, and sustainability. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles, the diagram alternator parts sector is poised for further innovation and growth. Understanding this historical context can provide B2B buyers with insights into the technological advancements that shape current and future sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of diagram alternator parts
-
How do I choose the right diagram alternator parts for my application?
To select the appropriate diagram alternator parts, consider the specific requirements of your automotive systems, such as voltage output, size constraints, and compatibility with existing components. Evaluate the specifications provided by manufacturers and ensure that the parts meet the necessary standards for your region. Additionally, consult with suppliers about customization options if your needs are unique. It’s also beneficial to request samples or detailed diagrams to confirm compatibility before placing bulk orders. -
What is the best way to verify the quality of alternator parts from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of alternator parts, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request product samples and detailed specifications to evaluate the materials and manufacturing processes used. Additionally, reading customer reviews and testimonials can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and product performance. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who offer warranties and guarantees can further safeguard your investment. -
What customization options are available for diagram alternator parts?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for diagram alternator parts to meet specific requirements. You can request variations in size, voltage output, and materials based on your application needs. Additionally, some suppliers may provide options for branding or modifications to align with your company’s specifications. When discussing customization, ensure clear communication about your requirements and timelines to avoid any delays in production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternator parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for alternator parts can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the specific part being ordered. Generally, MOQs can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their MOQ policies and explore options for lower MOQs if you are starting with a smaller business or testing new products. Some suppliers may offer flexibility, especially if you commit to future orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alternator parts internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely based on the supplier and the nature of the order. Common terms include payment in advance, net 30, or letter of credit arrangements. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings later. Consider using secure payment methods that provide buyer protection. Additionally, be aware of currency exchange rates and fees that may impact the total cost of your order. -
How can I efficiently manage logistics for importing alternator parts?
Efficient logistics management for importing alternator parts involves selecting reliable freight forwarders and understanding customs regulations in your destination country. Plan your shipments to optimize costs, considering factors like shipping methods (air vs. sea) and delivery times. Maintain clear communication with suppliers regarding shipping schedules and documentation requirements. Additionally, consider using logistics software to track shipments and manage inventory levels effectively. -
What should I know about quality assurance (QA) processes for alternator parts?
Quality assurance processes for alternator parts typically involve inspections at various stages of production, from raw materials to finished products. Request information from suppliers about their QA protocols, including testing methods and standards used. Many reputable manufacturers will perform tests on electrical performance, durability, and safety compliance. Establish a quality agreement that outlines expectations and inspection criteria to ensure that the parts you receive meet your quality standards. -
How do I handle discrepancies or defects in alternator parts after delivery?
In the event of discrepancies or defects in alternator parts, promptly contact the supplier to discuss the issues. Document the problems with photos and detailed descriptions to provide clear evidence. Most suppliers will have a return policy or warranty in place to address such situations. Be sure to understand the terms of these policies before placing your order. Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can facilitate smoother resolutions and minimize disruptions to your operations.
Top 6 Diagram Alternator Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electude – Automotive Alternators
Domain: electude.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: An alternator is a crucial automotive component that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, generating power for the vehicle’s electrical consumer units and battery. Key components include:
– Pulley: Transfers mechanical energy from the engine.
– Rotor: Creates the magnetic field for generating alternating current.
– Stator: The static part where voltage is generated.
– Rectifier: …
2. HowStuffWorks – Alternators
Domain: auto.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Alternators are small and lightweight, roughly the size of a coconut, constructed with an aluminum outer housing for heat dissipation and non-magnetization. Key components include:
– Drive pulley attached to the rotor shaft, converting mechanical energy to electrical power.
– Terminals: S terminal (senses battery voltage), IG terminal (ignition switch for voltage regulator), L terminal (closes c…
3. Facebook – Alternator Components Diagram
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Diagram of the main components of the alternator and their functions
4. Pinterest – Exploded View of an Alternator
5. AutoElectrics – Alternator Terminal Identification Chart
Domain: autoelectrics.net
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Alternator Terminal Identification Chart:
– Main Power Connections:
– B+, 30: Battery Positive
– B-, 31, D-, GRD: Battery Negative
– E: Earth – Battery Negative
– F, 67: Field/Rotor
– F: Field/Rotor
– FLD: Field/Rotor
– EXC: Excitation Field/Rotor
– DF: External control for Field current of Rotor
– C: Central Point of windings (check with manufacturer)
– N: Null – Ce…
6. Bosch – Alternator Parts
Domain: forums.tdiclub.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Main part number for Bosch alternator: 0123505011; Slip ring compatible with Bosch alternator: $9.50; Bearings: Pulley side bearing 6303 (17x47x14 mm), Voltage regulator side bearing 6203 (17x40x12 mm); Rebuild cost: $80-$90.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for diagram alternator parts
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of diagram alternator parts is pivotal for optimizing the efficiency and reliability of automotive systems across various international markets. By understanding the intricate components and operational mechanics of alternators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chains and reduce operational costs.
Investing in high-quality alternator parts not only guarantees improved performance but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who prioritize innovation and sustainability. As global demand for reliable automotive solutions continues to rise, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, companies must remain agile and responsive to market dynamics.
To capitalize on these opportunities, international buyers should actively seek partnerships with reputable manufacturers and distributors that align with their strategic goals. By leveraging data-driven insights and fostering collaboration, businesses can ensure they are well-positioned to meet the evolving needs of their customers. Embrace the future of automotive sourcing today—prioritize strategic partnerships to drive growth and innovation in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.