Einleitung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für die Anatomie des Autos
In einem zunehmend vernetzten globalen Markt ist es für B2B-Einkäufer, die fundierte Kaufentscheidungen treffen wollen, unerlässlich, die Anatomie des Autos zu verstehen. Die Beschaffung hochwertiger Automobilkomponenten kann eine große Herausforderung darstellen, vor allem, wenn man sich auf verschiedenen Märkten in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa bewegt. Dieser umfassende Leitfaden befasst sich mit den komplizierten Komponenten, die das Rückgrat moderner Fahrzeuge bilden, von Antriebssträngen und Aufhängungssystemen bis hin zu elektrischen Netzwerken und Sicherheitsfunktionen.
Durch die Erkundung der unzähligen Arten und Anwendungen von Autoteilen können Einkäufer wertvolle Einblicke in die Prozesse der Lieferantenprüfung, Kostenüberlegungen und die neuesten Innovationen in der Automobiltechnologie gewinnen. Dieser Leitfaden hebt nicht nur die wesentlichen Komponenten hervor, sondern bietet auch praktische Tipps zu Wartung und Betriebseffizienz, damit Unternehmen ihre Investitionen optimieren können.
Für internationale B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in aufstrebenden Märkten wie Nigeria und etablierten Volkswirtschaften wie Deutschland, ist diese Ressource ein wichtiges Hilfsmittel, um das operative Wissen zu erweitern und die Beschaffungsstrategien zu verbessern. Mit einem tiefgreifenden Verständnis der Anatomie des Automobils können Einkäufer die Komplexität der Beschaffung sicher steuern und sicherstellen, dass sie die besten Produkte für ihre spezifischen Bedürfnisse erhalten, was letztlich zu Wachstum und Erfolg in ihren Automobilgeschäften führt.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 4 Anatomie der Autohersteller & Lieferanten Liste
- Einleitung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für die Anatomie des Autos
- Verständnis der Anatomie des Autos Typen und Variationen
- Wichtige industrielle Anwendungen der Anatomie des Autos
- 3 häufige Schmerzpunkte der Benutzer für die ‘Anatomie des Autos’ und ihre Lösungen
- Leitfaden zur strategischen Materialauswahl für die Anatomie des Autos
- Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für die Anatomie des Autos
- Praktischer Leitfaden für die Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für die ‘Anatomie des Autos’
- Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Anatomie des Autos Sourcing
- Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich der Anatomie des Autos mit anderen Lösungen
- Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für die Anatomie des Autos
- Navigieren durch Marktdynamik und Beschaffungstrends in der Anatomie des Automobilsektors
- Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer zur Anatomie des Autos
- Strategische Beschaffung - Fazit und Ausblick für die Anatomie des Autos
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Verständnis der Anatomie des Autos Typen und Variationen
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limousine | Viertüriges Design, geräumiger Innenraum, komfortabel für Familien | Flottenfahrzeuge, Unternehmenstransport | Vorteile: Komfortabel, gute Kraftstoffeffizienz. Nachteile: Begrenzter Laderaum im Vergleich zu SUVs. |
| SUV (Sport Utility Vehicle) | Höhere Bodenfreiheit, vielseitiger Laderaum, oft AWD | Gütertransport, Geländetauglichkeit | Vorteile: Großer Laderaum, Geländetauglichkeit. Nachteile: Generell geringere Kraftstoffeffizienz. |
| Schrägheck | Kompaktes Design, Heckklappe, flexibler Innenraum | Städtische Lieferfahrzeuge, Transport von Kleinunternehmen | Vorteile: Einfaches Parken, vielseitiger Raum. Nachteile: Weniger leistungsstarke Motoren, die auf langen Fahrten weniger komfortabel sein können. |
| Kleintransporter | Offener Laderaum, robuste Anhängelast | Bauwesen, Landwirtschaft, Logistik | Vorteile: Hohe Nutzlastkapazität, robust. Nachteile: Begrenzter Fahrgastraum, kann kraftstoffsparend sein. |
| Elektrofahrzeug (EV) | Batteriebetrieben, emissionsarm, oft mit fortschrittlichen technischen Funktionen | Umweltfreundliche Flottenoptionen, städtische Lieferungen | Vorteile: Geringere Betriebskosten, umweltfreundlich. Nachteile: Die Ladeinfrastruktur kann unzureichend sein. |
Was sind die wichtigsten Merkmale von Limousinen für B2B-Käufer?
Limousinen zeichnen sich durch ihre viertürige Konfiguration und ihren geräumigen Innenraum aus, was sie ideal für den Transport von Unternehmen und Familien macht. Sie bieten ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis von Komfort und Kraftstoffeffizienz, was für Unternehmen, die einen Fuhrpark verwalten, von entscheidender Bedeutung ist. B2B-Käufer sollten die Gesamtbetriebskosten, einschließlich Kraftstoff- und Wartungskosten, berücksichtigen, da Limousinen auf lange Sicht wirtschaftlich sein können.
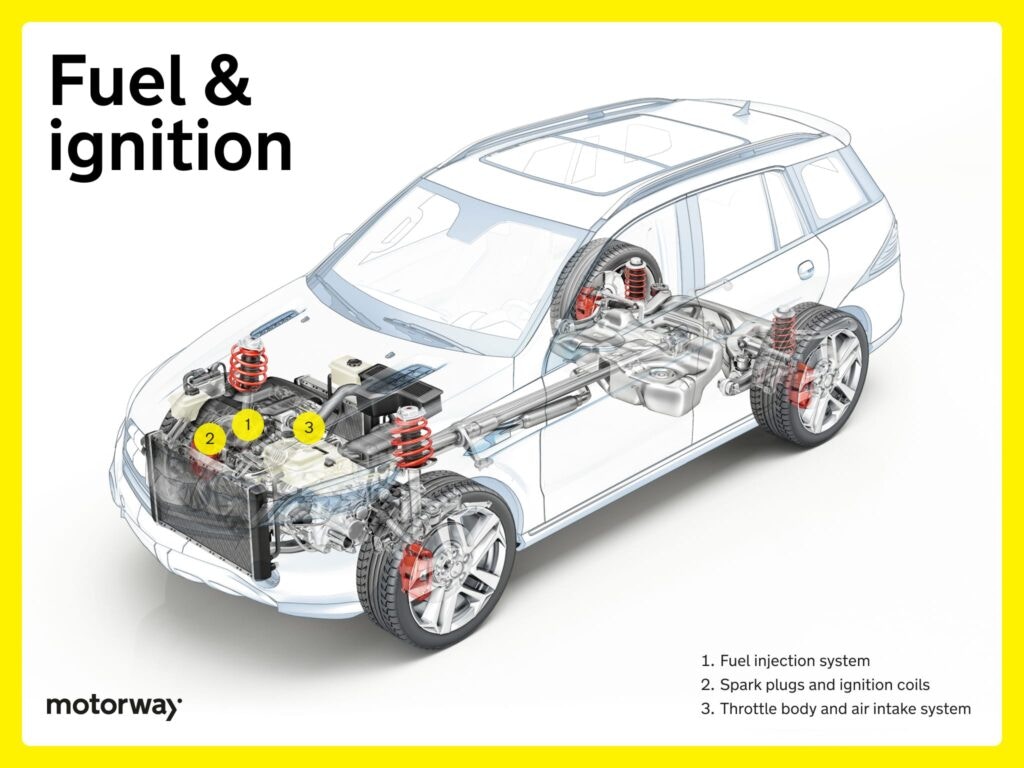
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Wie erfüllen SUVs die verschiedenen geschäftlichen Anforderungen?
Sport Utility Vehicles (SUVs) zeichnen sich durch eine größere Bodenfreiheit und einen vielseitigen Laderaum aus, wodurch sie sich für verschiedene Anwendungen eignen, vom Transport von Gütern bis hin zu Outdoor-Abenteuern. Ihr Allradantrieb (AWD) macht sie für Unternehmen in Regionen mit schwierigem Terrain attraktiv. Käufer sollten jedoch den höheren Kraftstoffverbrauch gegen die Vorteile des größeren Platzangebots und der höheren Leistungsfähigkeit abwägen.
Welche Vorteile bieten Schräghecklimousinen für städtische Unternehmen?
Fließhecklimousinen sind kompakte Fahrzeuge, die über eine Heckklappe verfügen, die einen flexiblen Transport ermöglicht. Ihre geringe Größe macht sie ideal für städtische Umgebungen, in denen das Parken eine Herausforderung sein kann. Für Unternehmen, die häufig kurze Fahrten oder Lieferungen in der Stadt durchführen müssen, können Schrägheckfahrzeuge von Vorteil sein. Käufer sollten sich jedoch über mögliche Einschränkungen bei der Motorleistung und dem Komfort bei längeren Fahrten im Klaren sein.
Warum sind Pickup Trucks in bestimmten Branchen unverzichtbar?
Pickup-Trucks sind bekannt für ihre offene Ladefläche und ihre beeindruckende Anhängelast, was sie in Branchen wie dem Baugewerbe und der Landwirtschaft unverzichtbar macht. Ihre robuste Bauweise ermöglicht schwere Aufgaben, was für Unternehmen, die einen zuverlässigen Materialtransport benötigen, ein großer Vorteil sein kann. B2B-Käufer sollten auf ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Nutzlast und Fahrgastkomfort achten, da Pickups unter Umständen den Innenraum zugunsten des Nutzens opfern.
Wie passen Elektrofahrzeuge (EVs) in moderne Unternehmensstrategien?
Elektrofahrzeuge (EVs) erfreuen sich aufgrund ihrer geringen Emissionen und ihrer fortschrittlichen technischen Eigenschaften zunehmender Beliebtheit. Sie eignen sich besonders für Unternehmen, die ihre Bemühungen um Nachhaltigkeit verstärken und gleichzeitig ihre Betriebskosten senken wollen. B2B-Einkäufer sollten die Verfügbarkeit von Ladeinfrastruktur in ihrem Einsatzgebiet berücksichtigen, da dies die Praktikabilität der Integration von E-Fahrzeugen in ihre Flotte erheblich beeinflussen kann.
Wichtige industrielle Anwendungen der Anatomie des Autos
| Branche/Sektor | Spezifische Anwendung der Anatomie des Fahrzeugs | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilbau | Konstruktion und Herstellung von Motorkomponenten | Verbessert die Leistung und Effizienz von Fahrzeugen, was zu höheren Verkaufszahlen führt | Qualität der Materialien, Feinmechanik, Einhaltung der internationalen Normen |
| Flottenmanagement | Wartungsplanung auf der Grundlage von Komponentenwissen | Reduziert Ausfallzeiten und Reparaturkosten und optimiert die betriebliche Effizienz | Verfügbarkeit von Ersatzteilen, Serviceverträgen und technischer Unterstützung |
| Automotive Aftermarket | Anpassungen und Ersatzteile | Bietet Wettbewerbsvorteile durch einzigartige Angebote | Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Fahrzeugmodellen, Qualitätssicherung und Preisstrategien |
| Bildung und Ausbildung im Automobilbereich | Lehrplanentwicklung zu Fahrzeugsystemen | Bereitet qualifizierte Arbeitskräfte vor und erhöht die Beschäftigungsfähigkeit im Sektor | Akkreditierung von Ausbildungsprogrammen, Industriepartnerschaften und Verfügbarkeit von Ressourcen |
| Umweltdienste | Technologien zur Emissionskontrolle | Erfüllt behördliche Anforderungen und stärkt den Ruf der Marke | Innovation bei Abgas- und Kraftstoffsystemen, Nachhaltigkeitspraktiken und Kosteneffizienz |
Wie wird die Anatomie des Autos im Automobilbau angewandt?
Im Automobilbau ist das Verständnis der Anatomie des Fahrzeugs entscheidend für die Konstruktion und Produktion von Motorkomponenten. Indem sie sich auf die Feinheiten des Antriebsstrangs und anderer kritischer Systeme konzentrieren, können die Hersteller die Fahrzeugleistung und die Kraftstoffeffizienz verbessern. Dieses Wissen führt zur Entwicklung innovativer Lösungen, mit denen sich Produkte auf einem wettbewerbsintensiven Markt differenzieren können. Internationale Einkäufer sollten bei der Beschaffung auf Lieferanten setzen, die für hochwertige Materialien und Präzisionstechnik bekannt sind und die Einhaltung globaler Automobilstandards gewährleisten.
Welche Rolle spielt die Fahrzeuganatomie im Fuhrparkmanagement?
Fuhrparkmanagementunternehmen nutzen ihr Wissen über die Anatomie des Fahrzeugs, um die Wartung effizient zu planen. Indem sie die spezifischen Funktionen und Verschleißmuster der Komponenten kennen, können Flottenmanager Reparaturen vorhersehen und die Ausfallzeiten der Fahrzeuge reduzieren. Dieser proaktive Ansatz spart nicht nur Kosten, sondern verbessert auch die Gesamteffizienz des Betriebs. Für internationale Käufer ist es wichtig, bei der Auswahl von Partnern die Verfügbarkeit von Ersatzteilen und die Zuverlässigkeit von Serviceverträgen zu berücksichtigen, um einen reibungslosen Flottenbetrieb zu gewährleisten.
Wie wird die Anatomie des Autos auf dem Kfz-Ersatzteilmarkt genutzt?
Auf dem Kfz-Ersatzteilmarkt sind Unternehmen, die sich auf Anpassungen und Ersatzteile spezialisiert haben, stark auf die Kenntnis der Anatomie eines Fahrzeugs angewiesen. Dank dieser Kenntnisse können sie maßgeschneiderte Lösungen für spezifische Kundenbedürfnisse anbieten und sich so einen Wettbewerbsvorteil verschaffen. Internationale Einkäufer müssen sich auf die Beschaffung von Teilen konzentrieren, die mit einer breiten Palette von Fahrzeugmodellen kompatibel sind, und eine Qualitätssicherung gewährleisten, um das Vertrauen der Kunden zu gewinnen. Auch die Preisstrategien sollten den einzigartigen Mehrwert der maßgeschneiderten Lösungen widerspiegeln.
Warum sind Kenntnisse der Autoanatomie wichtig für die Kfz-Ausbildung?
Die Anatomie des Autos ist ein grundlegendes Element in der Kfz-Aus- und Weiterbildung. Durch die Entwicklung von Lehrplänen, die das Innenleben von Fahrzeugen betonen, können Bildungseinrichtungen Studenten auf Karrieren im Automobilsektor vorbereiten. Dieses Wissen verbessert die Beschäftigungsfähigkeit und stattet die Arbeitskräfte mit wichtigen Fähigkeiten aus. Für internationale Einkäufer in diesem Sektor ist die Zusammenarbeit mit akkreditierten Ausbildungsprogrammen und die Gewährleistung des Zugangs zu relevanten Ressourcen von entscheidender Bedeutung für die Förderung eines qualifizierten Arbeitskräftepools.
Wie kann das Verständnis der Autoanatomie den Umweltdiensten nützen?
Umweltdienste nutzen ihr Wissen über die Anatomie des Autos, um Technologien zur Emissionskontrolle zu entwickeln, die den gesetzlichen Normen entsprechen. Indem sie sich auf effiziente Abgas- und Kraftstoffsysteme konzentrieren, können diese Unternehmen die Nachhaltigkeit von Fahrzeugen verbessern und den Ruf der Marke ihrer Kunden stärken. Internationale Einkäufer sollten nach innovativen Lösungen Ausschau halten, bei denen die Nachhaltigkeit im Vordergrund steht und die gleichzeitig kosteneffizient sind, da dies zu langfristigen Vorteilen bei der Einhaltung von Umweltvorschriften und einer besseren Marktpositionierung führen kann.
3 häufige Schmerzpunkte der Benutzer für die ‘Anatomie des Autos’ und ihre Lösungen
Szenario 1: Verstehen der Komponentenfunktionalität für Wartungsentscheidungen
Das Problem: B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in der Automobilindustrie, haben oft Schwierigkeiten, die komplizierten Funktionen verschiedener Fahrzeugkomponenten zu verstehen. Diese Unkenntnis kann zu schlechten Wartungsentscheidungen führen, die höhere Betriebskosten und potenzielle Ausfallzeiten des Fahrzeugs zur Folge haben. So erkennt ein Käufer vielleicht nicht die entscheidende Rolle des Federungssystems für die Stabilität und den Komfort des Fahrzeugs und vernachlässigt daher dessen Wartung. Dieses Versäumnis kann nicht nur die Kundenzufriedenheit beeinträchtigen, sondern auch das Unfallrisiko erhöhen, was rechtliche und finanzielle Folgen haben kann.

Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Die Lösung: Um dieser Herausforderung zu begegnen, sollten B2B-Einkäufer in umfassende Schulungsprogramme für ihre Wartungsteams investieren. Diese Programme sollten die Anatomie von Autos abdecken und sich auf die Funktionalität und Bedeutung von Schlüsselkomponenten wie Antriebsstrang, Aufhängung und Bremssystem konzentrieren. Darüber hinaus können Käufer detaillierte technische Handbücher und digitale Ressourcen nutzen, die visuelle Hilfen und Erklärungen zu den einzelnen Komponenten bieten. Die Zusammenarbeit mit Automobilexperten bei der Durchführung von Workshops kann das Verständnis weiter verbessern und sicherstellen, dass alle Teammitglieder in der Lage sind, fundierte Wartungsentscheidungen zu treffen, was letztlich zu einer höheren Zuverlässigkeit des Fahrzeugs und zu mehr Vertrauen bei den Kunden führt.
Szenario 2: Beschaffung von Qualitäts-Ersatzteilen
Das Problem: Ein häufiges Problem für B2B-Einkäufer ist die Beschaffung hochwertiger Ersatzteile, die der Anatomie des Fahrzeugs entsprechen. Viele Einkäufer stehen vor dem Dilemma, zwischen kostengünstigen Optionen und der Gewährleistung der Zuverlässigkeit und Sicherheit der Teile wählen zu müssen. Die Entscheidung für minderwertige Komponenten kann zu einer schlechten Fahrzeugleistung und höheren Reparaturkosten führen, während hochwertige Teile das Budget belasten können, insbesondere für Unternehmen, die in preissensiblen Märkten wie Afrika und Südamerika tätig sind.
Die Lösung: Um diese Beschaffungsherausforderung effektiv zu meistern, sollten Einkäufer enge Beziehungen zu seriösen Lieferanten aufbauen, die sich auf Automobilkomponenten spezialisiert haben. Eine gründliche Marktforschung zur Ermittlung von Herstellern, die für ihre Qualitätssicherung bekannt sind, ist von entscheidender Bedeutung. Darüber hinaus können Einkäufer die Technologie nutzen, indem sie Plattformen einsetzen, die Bewertungen und Beurteilungen für verschiedene Lieferanten anbieten. Die Einführung eines standardisierten Bewertungsprozesses für Teile, der Kriterien wie Haltbarkeit, Garantie und Einhaltung von Sicherheitsstandards umfasst, kann helfen, Beschaffungsentscheidungen zu rationalisieren. Wenn Unternehmen langfristig der Qualität den Vorrang vor den Kosten geben, können sie Wartungsprobleme reduzieren und die Gesamtleistung des Fahrzeugs verbessern.
Szenario 3: Anpassung an den technologischen Fortschritt
Das Problem: Angesichts der rasanten Entwicklung der Automobiltechnologie ist es für B2B-Einkäufer oft schwierig, mit den neuen Funktionen und Systemen, die in moderne Fahrzeuge integriert sind, Schritt zu halten. Dadurch kann eine Wissenslücke entstehen, die ihre Fähigkeit, Fahrzeuge effektiv zu verkaufen oder zu warten, beeinträchtigt. So erfordert beispielsweise die Einführung fortschrittlicher Fahrerassistenzsysteme (ADAS) und hybrider Antriebsstränge spezielle Kenntnisse und Fähigkeiten, die bei den vorhandenen Mitarbeitern möglicherweise nicht vorhanden sind.
Die Lösung: Um diese Lücke zu schließen, müssen B2B-Einkäufer der kontinuierlichen Weiterbildung und der beruflichen Entwicklung ihrer Teams Priorität einräumen. Partnerschaften mit Schulungseinrichtungen, die Kurse über die neuesten Automobiltechnologien anbieten, können von Vorteil sein. Außerdem sollten Einkäufer in Erwägung ziehen, praktische Schulungen mit echten Fahrzeugen durchzuführen, um praktische Erfahrungen zu sammeln. Investitionen in Diagnosewerkzeuge und Software, die den Technikern helfen, neue Systeme besser zu verstehen und Fehler zu beheben, erhöhen ebenfalls die betriebliche Effizienz. Die Betonung einer Kultur des Lernens und der Anpassung innerhalb des Unternehmens wird nicht nur das Serviceangebot verbessern, sondern auch die Kundentreue fördern, da die Unternehmen für ihr Fachwissen über die neuesten Entwicklungen in der Automobilindustrie bekannt sind.
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Leitfaden zur strategischen Materialauswahl für die Anatomie des Autos
Was sind die wichtigsten Materialien, die in der Anatomie eines Autos verwendet werden?
Bei der Auswahl von Werkstoffen für die verschiedenen Komponenten eines Fahrzeugs müssen mehrere Faktoren berücksichtigt werden, darunter Leistungseigenschaften, Kosten und Fertigungsaufwand. Im Folgenden analysieren wir vier gängige Materialien, die in der Automobilindustrie verwendet werden, und konzentrieren uns dabei auf ihre Eigenschaften, Vorteile, Nachteile und Auswirkungen auf internationale B2B-Käufer.
Wie verhält sich Stahl in Automobilanwendungen?
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Stahl ist bekannt für seine hohe Zugfestigkeit, Haltbarkeit und Fähigkeit, hohen Temperaturen und Drücken standzuhalten. Außerdem bietet er eine gute Korrosionsbeständigkeit, wenn er mit Beschichtungen behandelt wird.
Vor- und Nachteile: Stahl ist relativ kostengünstig und weithin verfügbar, was ihn zu einer kosteneffizienten Wahl für viele Automobilkomponenten macht, z. B. für das Fahrgestell und die Karosserieteile. Allerdings ist er schwerer als alternative Materialien, was sich negativ auf die Kraftstoffeffizienz auswirken kann. Außerdem kann der Herstellungsprozess komplex sein und erfordert einen erheblichen Energieaufwand.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Stahl ist mit verschiedenen Medien, einschließlich Kraft- und Schmierstoffen, verträglich und eignet sich daher gut für Strukturbauteile. Sein Gewicht kann jedoch eine sorgfältige Überlegung bei der Konstruktion erfordern, um die Kraftstoffeffizienz zu optimieren.
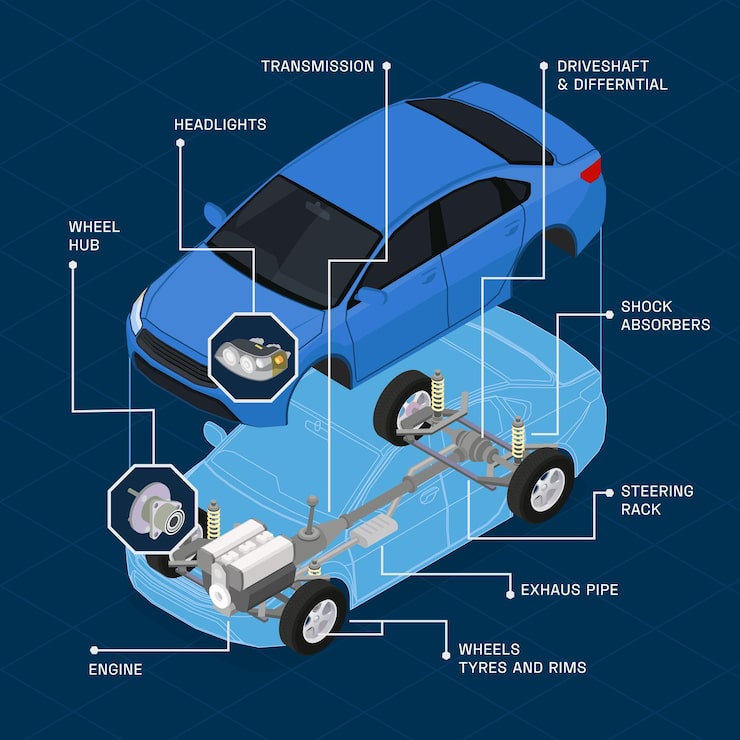
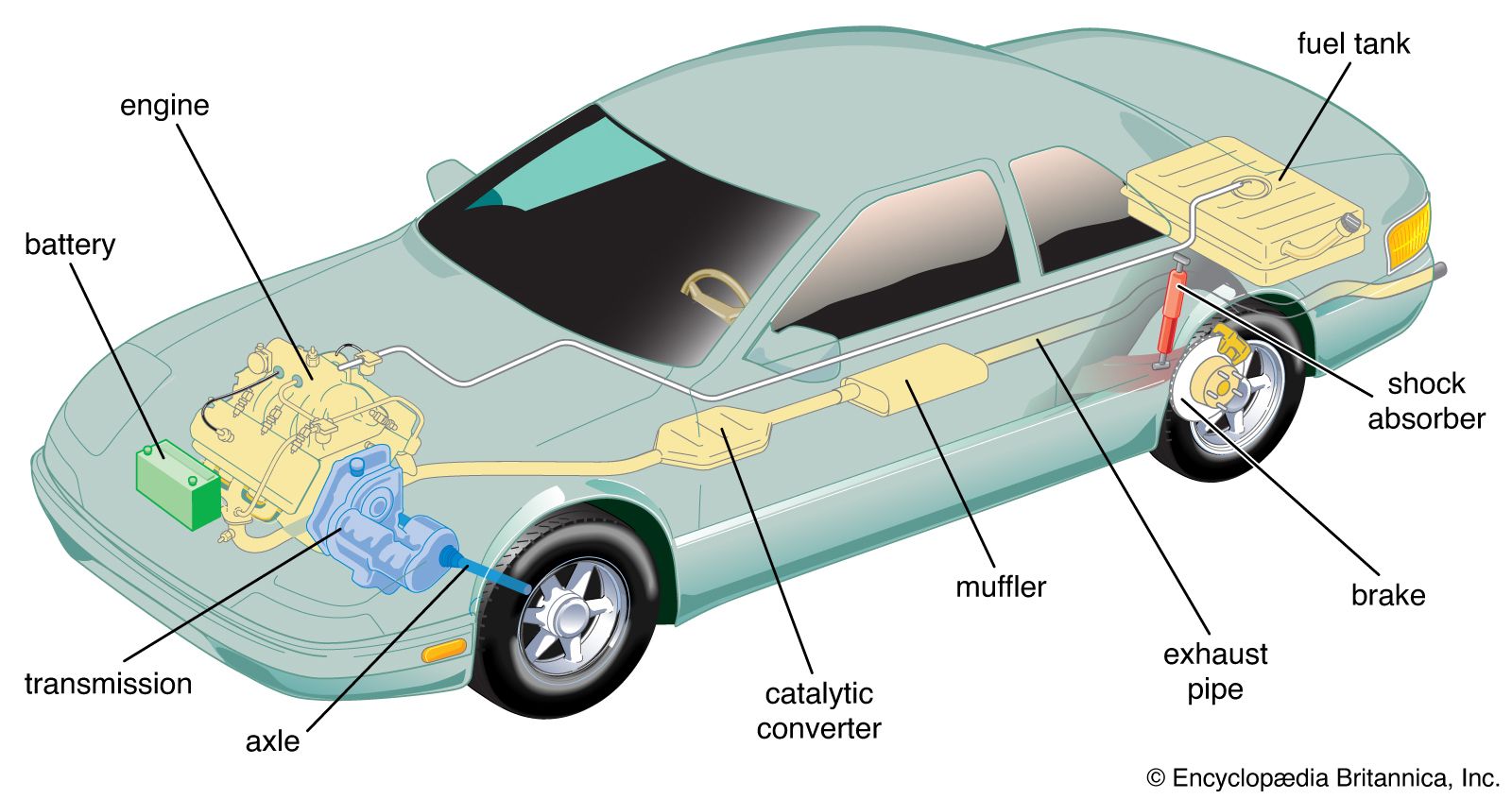
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Einhaltung internationaler Normen wie ASTM und DIN ist entscheidend. Käufer aus Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika könnten die Verfügbarkeit vor Ort als vorteilhaft empfinden, während europäische Käufer fortschrittlichen Stahlsorten, die eine bessere Leistung bieten, den Vorzug geben könnten.
Welche Rolle spielt Aluminium im Automobilbau?
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Aluminium ist leicht, korrosionsbeständig und hat eine hervorragende Wärmeleitfähigkeit. Außerdem lässt es sich leicht formen und verformen und eignet sich daher für komplexe Konstruktionen.
Vor- und Nachteile: Der Hauptvorteil von Aluminium ist seine Gewichtsersparnis, die die Kraftstoffeffizienz und die Leistung verbessert. Es ist jedoch teurer als Stahl und kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen weniger haltbar sein, insbesondere bei hoher Beanspruchung.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminium wird häufig für Motorkomponenten, Räder und Karosserieteile verwendet. Aufgrund seiner Korrosionsbeständigkeit ist es ideal für Fahrzeuge, die in feuchten oder küstennahen Umgebungen eingesetzt werden, wo Rost ein Problem darstellt.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer sollten sich über die verschiedenen Aluminiumsorten und ihre spezifischen Anwendungen im Klaren sein. Auch die Einhaltung von Umweltvorschriften ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere in Europa, wo der Nachhaltigkeit zunehmend Priorität eingeräumt wird.
Wie trägt Kunststoff zum Automobildesign bei?
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Kunststoffe, einschließlich Polycarbonat und Polypropylen, sind leicht, korrosionsbeständig und können in komplizierte Formen gebracht werden. Außerdem bieten sie gute thermische und elektrische Isolationseigenschaften.
Vor- und Nachteile: Das geringe Gewicht von Kunststoffen kann das Gesamtgewicht eines Fahrzeugs erheblich reduzieren und damit die Kraftstoffeffizienz verbessern. Allerdings sind sie unter Umständen nicht so stabil wie Metalle und können im Laufe der Zeit durch UV-Strahlung beschädigt werden.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Kunststoffe werden häufig für Innenraumteile wie Armaturenbretter und Verkleidungen sowie für Außenteile wie Stoßstangen verwendet. Aufgrund ihrer Verträglichkeit mit verschiedenen Chemikalien eignen sie sich für viele Anwendungen im Automobilbereich.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer sollten auf die Recyclingfähigkeit von Kunststoffen und die Einhaltung von Vorschriften über gefährliche Stoffe achten. In Europa kann sich beispielsweise die REACH-Verordnung auf die Auswahl bestimmter Kunststoffmaterialien auswirken.
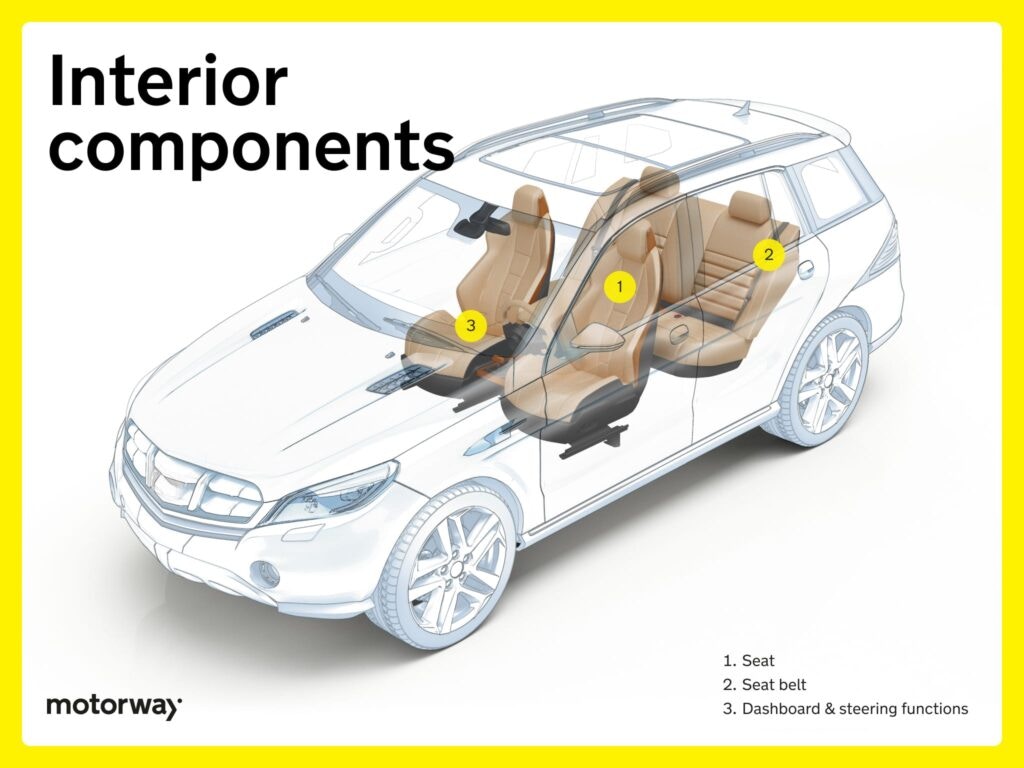
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Welche Vorteile bieten Verbundwerkstoffe im Automobilbereich?
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Verbundwerkstoffe wie Kohlefaser und Glasfaser sind bekannt für ihr gutes Verhältnis von Festigkeit zu Gewicht und ihre Korrosions- und Ermüdungsbeständigkeit.
Vor- und Nachteile: Verbundwerkstoffe können das Fahrzeuggewicht bei gleichbleibender Festigkeit erheblich reduzieren, was sich positiv auf Leistung und Kraftstoffverbrauch auswirkt. Sie sind jedoch in der Regel teurer und können spezielle Herstellungsverfahren erfordern, wodurch sie für preisbewusste Käufer weniger zugänglich sind.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Verbundwerkstoffe werden häufig in Hochleistungsfahrzeugen und in Anwendungen eingesetzt, bei denen Gewichtseinsparungen von entscheidender Bedeutung sind, z. B. bei der Konstruktion von Karosserieteilen und Strukturkomponenten.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die hohen Kosten von Verbundwerkstoffen können ihre Verwendung auf Märkten mit niedrigeren Kosten einschränken. Käufer sollten sich auch darüber im Klaren sein, dass für die Arbeit mit diesen Materialien spezielle Kenntnisse und Ausrüstungen erforderlich sind, was sich auf die Logistik in der Lieferkette auswirken kann.
Übersichtstabelle zur Materialauswahl für Automobilkomponenten
| Material | Typischer Anwendungsfall für die Anatomie des Fahrzeugs | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stahl | Fahrgestell, Karosserieteile | Hohe Festigkeit, kostengünstig | Schwere, komplexe Fertigung | Med |
| Aluminium | Motorkomponenten, Räder | Leichtes Gewicht, korrosionsbeständig | Teurer, weniger haltbar | Hoch |
| Kunststoff | Innenausstattung, Stoßstangen | Leicht, formbar | Weniger stark, UV-Zersetzung | Niedrig |
| Komposit | Hochleistungs-Karosserieteile, Strukturen | Hohes Verhältnis von Festigkeit zu Gewicht | Teuer, erfordert spezielle Verfahren | Hoch |
Dieser strategische Leitfaden für die Materialauswahl bietet B2B-Einkäufern im Automobilsektor wichtige Einblicke und ermöglicht fundierte Entscheidungen, die mit Leistungsanforderungen, Kostenbeschränkungen und regionalen Vorschriften in Einklang stehen.
Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für die Anatomie des Autos
Was sind die wichtigsten Phasen des Automobilherstellungsprozesses?
Die Herstellung von Automobilen ist ein komplexer und vielschichtiger Prozess, der Präzision, Koordination und die Einhaltung strenger Qualitätsstandards erfordert. Zu den wichtigsten Schritten bei der Herstellung von Fahrzeugteilen gehören die Materialvorbereitung, die Formgebung, die Montage und die Endbearbeitung.
Wie wird das Material im Automobilbau vorbereitet?
Die Materialvorbereitung ist der erste entscheidende Schritt im Herstellungsprozess. Je nach den Spezifikationen der verschiedenen Fahrzeugkomponenten werden unterschiedliche Materialien wie Stahl, Aluminium, Kunststoffe und Verbundwerkstoffe beschafft. Die Zulieferer müssen sicherstellen, dass die Materialien bestimmte Normen wie ASTM- oder ISO-Zertifizierungen erfüllen.
In dieser Phase werden die Materialien verschiedenen Behandlungen wie Schneiden, Formen und Oberflächenbehandlung unterzogen, um ihre Eigenschaften zu verbessern. Stahl kann zum Beispiel verzinkt werden, um Korrosion zu verhindern, während Aluminiumteile für zusätzliche Haltbarkeit eloxiert werden können. In dieser Phase werden auch Qualitätskontrollen durchgeführt, um sicherzustellen, dass die Materialien den erforderlichen Spezifikationen entsprechen.
Welche Techniken werden in der Formgebungsphase verwendet?
In der Umformungsphase werden die Rohmaterialien in die spezifischen Formen gebracht, die für die verschiedenen Autoteile benötigt werden. Zu den in dieser Phase verwendeten Techniken gehören Stanzen, Gießen, Schmieden und maschinelle Bearbeitung.
-
Stanzen: Diese Technik wird häufig für die Herstellung von Blechteilen, wie z. B. Karosserieteilen, verwendet. Große Pressen stanzen die Bleche in die gewünschte Form.
-
Gießen: Für komplexe Formen wird häufig das Gießverfahren verwendet. Geschmolzenes Metall wird in Formen gegossen, die komplizierte Designs ermöglichen, die mit anderen Methoden nur schwer zu erreichen wären.
-
Schmieden: Dieses Verfahren wird für hochfeste Bauteile wie Achsen und Kurbelwellen verwendet. Das Metall wird erhitzt und unter Druck geformt, wodurch seine strukturelle Integrität verbessert wird.
-
Bearbeitung: Präzisionsbearbeitungsverfahren wie CNC (Computer Numerical Control) werden eingesetzt, um exakte Abmessungen und Toleranzen zu erreichen, insbesondere bei Motorkomponenten.
Jede dieser Techniken muss strenge Qualitätskontrollen durchlaufen, um sicherzustellen, dass die Abmessungen, Toleranzen und Materialeigenschaften den in den technischen Spezifikationen festgelegten Standards entsprechen.
Wie werden die Komponenten im Automobilbau zusammengesetzt?
Sobald die Einzelteile geformt sind, beginnt die Montagephase. In dieser Phase werden verschiedene Komponenten zu Unterbaugruppen und schließlich zum kompletten Fahrzeug zusammengefügt.
Automobilhersteller setzen häufig Fließbandtechniken ein, um die Effizienz zu steigern. Jedem Arbeiter oder Roboterarm wird eine bestimmte Aufgabe zugewiesen, um einen rationellen Prozess zu gewährleisten. Überall am Fließband sind Kontrollpunkte für die Qualitätskontrolle eingerichtet, an denen die Inspektoren überprüfen, ob jedes Bauteil korrekt eingebaut ist und die Baugruppe den Konstruktionsspezifikationen entspricht.
Was geschieht in der Endphase der Automobilherstellung?
In der Endbearbeitungsphase wird das Fahrzeug für die Auslieferung an den Kunden vorbereitet. Diese Phase umfasst die Lackierung, Detaillierung und den Einbau von Innenraumkomponenten. Fortgeschrittene Techniken wie Roboterlackiersysteme sorgen für ein einheitliches und hochwertiges Finish.
Die Qualitätssicherung während der Endfertigung umfasst die Überprüfung der Lackkonsistenz, der Oberflächenfehler und des ordnungsgemäßen Einbaus aller Innen- und Außenmerkmale. Abschließende Inspektionen werden durchgeführt, um sicherzustellen, dass das Fahrzeug alle gesetzlichen und sicherheitstechnischen Standards erfüllt, bevor es das Werk verlässt.
Welche Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen sind in der Automobilherstellung unerlässlich?
Die Qualitätssicherung (QS) in der Automobilproduktion ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, um sicherzustellen, dass die Fahrzeuge sicher und zuverlässig sind und die Erwartungen der Kunden erfüllen. Die Umsetzung wirksamer QS-Maßnahmen hilft, Fehler zu vermeiden und die Einhaltung internationaler Normen zu gewährleisten.
Welche internationalen Normen gelten für die Qualitätssicherung in der Automobilindustrie?
Internationale Normen wie die ISO 9001 für Qualitätsmanagementsysteme sind in der Automobilindustrie weit verbreitet. Diese Normen bieten einen Rahmen für die Gewährleistung einer gleichbleibenden Qualität in den Produktionsprozessen.
Neben der ISO gibt es auch branchenspezifische Normen wie die IATF 16949, die sich auf das Qualitätsmanagement in der Automobilproduktion konzentriert. Die Einhaltung dieser Normen ist von entscheidender Bedeutung für Hersteller, die sich auf internationalen Märkten, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, einen Namen machen wollen.
Was sind die wichtigsten Punkte der Qualitätskontrolle in der Automobilherstellung?
Qualitätskontrollpunkte sind während des gesamten Herstellungsprozesses wichtig, um Fehler frühzeitig zu erkennen und sicherzustellen, dass das Endprodukt den Spezifikationen entspricht. Zu den wichtigsten Kontrollpunkten gehören:
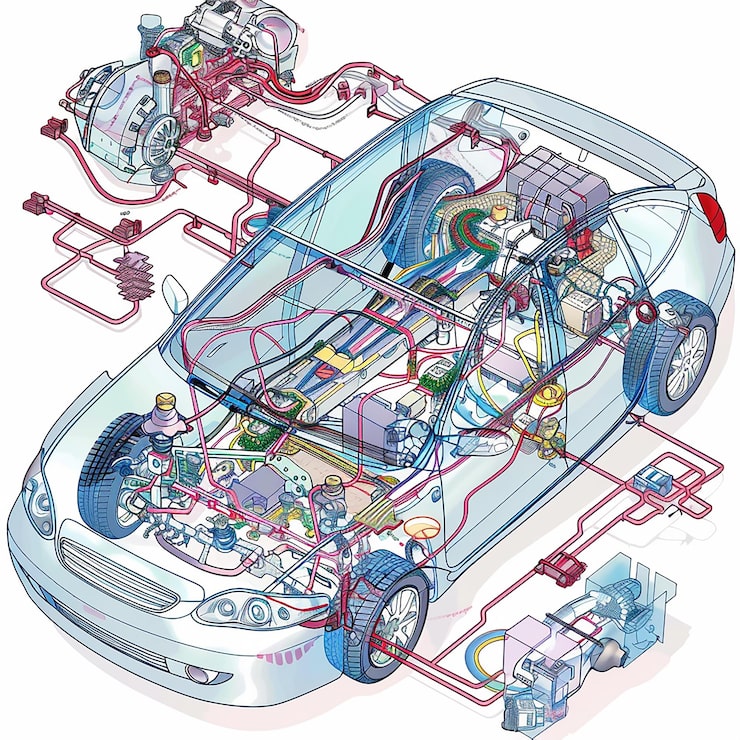
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): Dabei werden Rohstoffe und Bauteile bei ihrer Ankunft auf die Einhaltung vorgegebener Normen überprüft.
-
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): Während des Herstellungsprozesses durchgeführte Inspektionen helfen, Probleme frühzeitig zu erkennen. Techniken wie die statistische Prozesskontrolle (SPC) können zur Überwachung der Produktionsmetriken eingesetzt werden.
-
Endkontrolle (FQC): Vor der Auslieferung des Fahrzeugs wird in einer Endkontrolle überprüft, ob alle Komponenten korrekt eingebaut wurden und das Fahrzeug alle Sicherheits- und Qualitätsstandards erfüllt.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrolle ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
Für B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere auf internationalen Märkten, ist die Überprüfung der Qualitätskontrollverfahren eines Lieferanten von entscheidender Bedeutung. Hier sind einige Strategien, um die Einhaltung der Vorschriften durch den Lieferanten sicherzustellen:
-
Prüfungen: Die Durchführung regelmäßiger Audits in den Produktionsstätten der Lieferanten kann Aufschluss über deren Qualitätskontrollverfahren geben. Die Audits sollten die Einhaltung der Qualitätsstandards und die Wirksamkeit der Qualitätssicherungsprozesse bewerten.
-
Qualitätsberichte: Die Anforderung detaillierter Qualitätsberichte kann Einkäufern helfen, die Leistung eines Lieferanten zu verstehen. Diese Berichte sollten Kennzahlen zu Fehlerquoten, ergriffenen Abhilfemaßnahmen und zur Einhaltung internationaler Normen enthalten.
-
Inspektionen durch Dritte: Die Beauftragung von Inspektionsstellen durch Dritte kann eine unvoreingenommene Bewertung der Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen eines Lieferanten bieten. Diese Inspektionen können besonders für Einkäufer wertvoll sein, die mit lokalen Lieferanten nicht vertraut sind.
Welche Nuancen der Qualitätskontrolle und Zertifizierung sollten internationale B2B-Einkäufer beachten?
Internationale B2B-Einkäufer sollten sich der Nuancen bei der Qualitätskontrolle und Zertifizierung bewusst sein, die von Region zu Region sehr unterschiedlich sein können. So können sich beispielsweise die europäischen Normen von denen in Afrika oder Südamerika unterscheiden. Die Einkäufer müssen sicherstellen, dass die Lieferanten die für ihren Zielmarkt geltenden spezifischen Vorschriften und Normen einhalten.
Außerdem ist es wichtig, die lokalen Zertifizierungsanforderungen zu kennen. So ist beispielsweise die CE-Kennzeichnung für Produkte, die im Europäischen Wirtschaftsraum verkauft werden, unerlässlich, während in anderen Regionen möglicherweise andere Standards gelten. Einkäufer sollten gründliche Nachforschungen anstellen, um sicherzustellen, dass ihre Lieferanten alle erforderlichen Zertifizierungen und Qualitätsstandards für ihre spezifischen Märkte erfüllen.
Schlussfolgerung
Die Herstellungsverfahren und Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen in der Automobilindustrie sind für die Lieferung zuverlässiger und sicherer Fahrzeuge unerlässlich. Wenn internationale B2B-Einkäufer diese Prozesse verstehen, können sie bei der Auswahl von Lieferanten fundierte Entscheidungen treffen und sicherstellen, dass sie hochwertige Produkte erhalten, die ihren Spezifikationen entsprechen. Eine sorgfältige Überprüfung der Qualitätskontrollverfahren der Lieferanten ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, vor allem wenn man sich auf den komplexen internationalen Märkten bewegt.
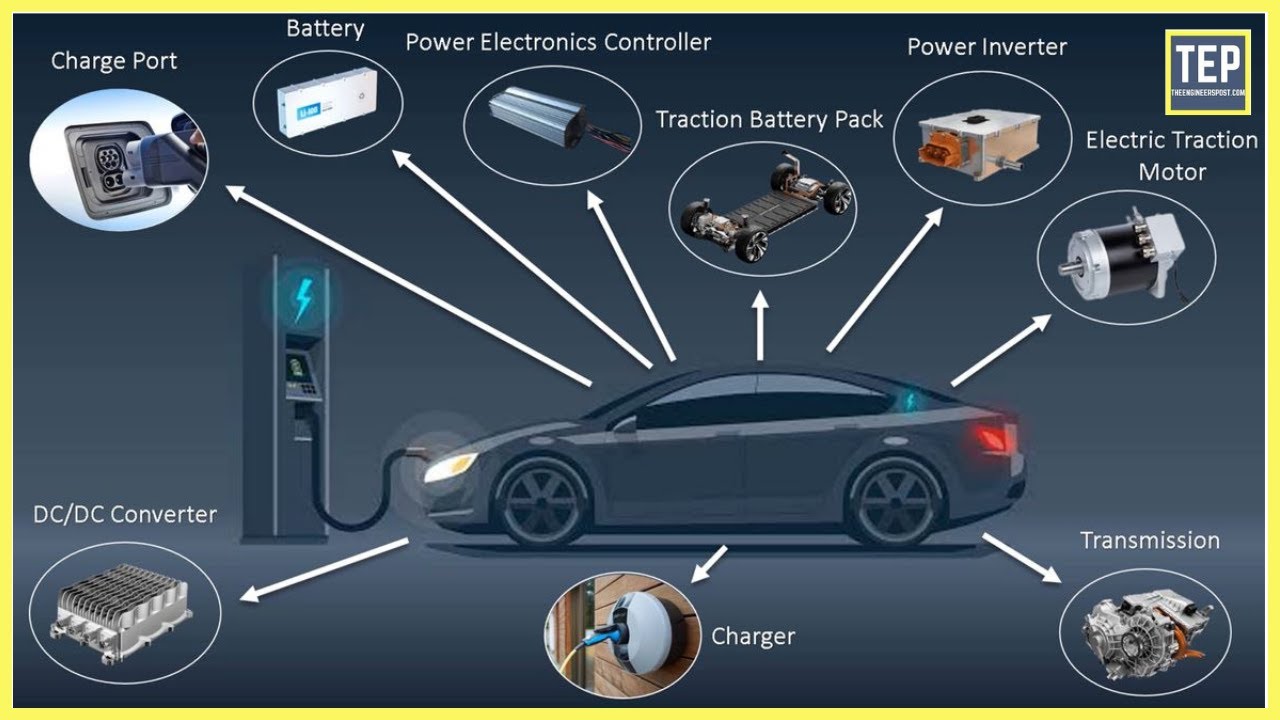
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Praktischer Leitfaden für die Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für die ‘Anatomie des Autos’
Um bei der Beschaffung von Autoanatomiekomponenten erfolgreich zu sein, müssen B2B-Einkäufer einen strukturierten Ansatz verfolgen. Diese Checkliste soll Sie durch die einzelnen Schritte führen und sicherstellen, dass Sie fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die mit Ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen übereinstimmen.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Bevor Sie sich mit Lieferanten in Verbindung setzen, sollten Sie die technischen Spezifikationen der von Ihnen benötigten Fahrzeugteile klar umreißen. Dazu gehören Angaben zu den Materialien, Abmessungen und Leistungsstandards, die für jedes Teil erforderlich sind. Eine genaue Spezifikation erleichtert den Vergleich von Lieferanten und stellt sicher, dass sich die Komponenten nahtlos in Ihren Betrieb integrieren lassen.
- Berücksichtigen Sie regionale Standards: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die Komponenten den örtlichen Vorschriften und den für Ihren Markt geltenden Industrienormen entsprechen.
- Bewertung der Kompatibilität: Überprüfen Sie, ob die Spezifikationen mit den vorhandenen Systemen oder Fahrzeugen übereinstimmen, um kostspielige Änderungen zu vermeiden.
Schritt 2: Potenzielle Lieferanten recherchieren
Führen Sie gründliche Recherchen durch, um potenzielle Lieferanten zu finden, die sich auf Anatomiekomponenten für Autos spezialisiert haben. Suchen Sie nach Unternehmen mit einem guten Ruf in Ihren Zielmärkten - Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa.
- Nutzen Sie die Online-Plattformen: Nutzen Sie B2B-Marktplätze und Branchenverzeichnisse, um Lieferanten mit geprüften Qualifikationen zu finden.
- Prüfen Sie Bewertungen und Rezensionen: Achten Sie auf das Feedback anderer Käufer, um Zuverlässigkeit und Qualität zu beurteilen.
Schritt 3: Lieferantenzertifizierungen bewerten
Bevor Sie sich für einen Lieferanten entscheiden, sollten Sie dessen Zertifizierungen und Qualitätsmanagementsysteme überprüfen. Dieser Schritt ist entscheidend, um sicherzustellen, dass die Komponenten den Sicherheits- und Qualitätsstandards entsprechen.
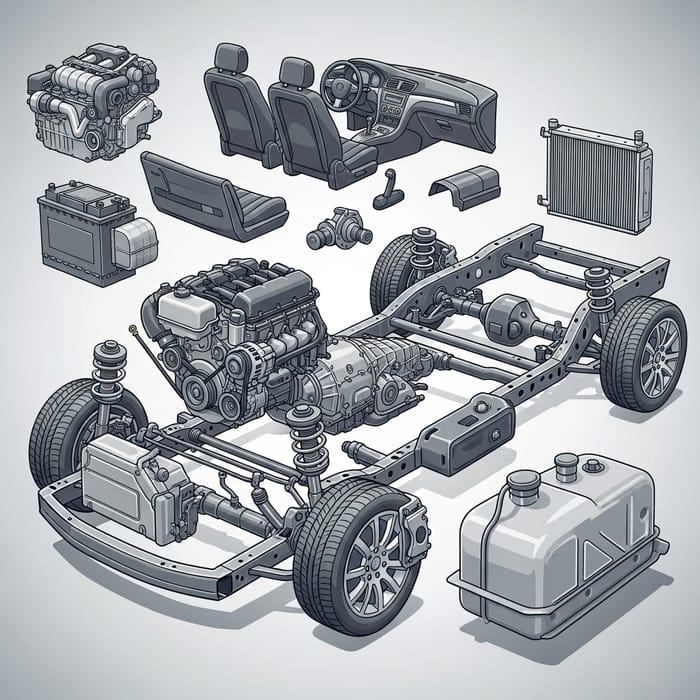
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
- ISO-Zertifizierungen: Achten Sie auf Lieferanten mit ISO 9001 oder anderen einschlägigen Zertifizierungen, die ihr Engagement für Qualität belegen.
- Einhaltung der örtlichen Vorschriften: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Lieferant die in Ihrer Region geltenden Normen und Vorschriften für die Automobilindustrie einhält.
Schritt 4: Muster zum Testen anfordern
Sobald Sie eine Vorauswahl an potenziellen Lieferanten getroffen haben, sollten Sie Muster der Komponenten anfordern, die Sie kaufen möchten. Das Testen von Mustern ist wichtig, um deren Qualität und Leistung zu beurteilen, bevor Sie eine Großbestellung aufgeben.
- Führen Sie gründliche Bewertungen durch: Testen Sie die Haltbarkeit, Kompatibilität und Leistung unter realen Bedingungen.
- Technische Teams einbeziehen: Lassen Sie Ihre Technik- oder Wartungsteams die Muster beurteilen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie Ihren Spezifikationen entsprechen.
Schritt 5: Verhandeln Sie Bedingungen und Preise
Nehmen Sie Gespräche mit Lieferanten auf, um Bedingungen, Preise und Liefertermine auszuhandeln. Dies ist eine Gelegenheit, eine langfristige Beziehung aufzubauen, von der beide Parteien profitieren.
- Ziehen Sie Rabatte bei Großeinkäufen in Betracht: Wenn Sie große Mengen bestellen möchten, erkundigen Sie sich nach Mengenrabatten oder flexiblen Zahlungsbedingungen.
- Klären Sie die Garantie- und Rückgabebedingungen: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass Sie die Garantiebedingungen und das Verfahren für die Rückgabe oder den Umtausch im Falle von Mängeln kennen.
Schritt 6: Abschluss der Bestellung und Logistik
Nachdem Sie die Bedingungen ausgehandelt haben, schließen Sie Ihre Bestellung ab und kümmern sich um die Logistik. Stellen Sie sicher, dass sich beide Parteien über Lieferfristen und Versandmethoden im Klaren sind.
- Bestätigen Sie die Dokumentation: Überprüfen Sie, ob alle erforderlichen Unterlagen, einschließlich Rechnungen und Versanddetails, in Ordnung sind.
- Planen Sie die Zollabfertigung: Bereiten Sie sich bei der Einfuhr auf die Zollbestimmungen und Gebühren vor, die für Ihre Sendung anfallen können.
Schritt 7: Kontinuierliche Kommunikation etablieren
Pflegen Sie während des gesamten Beschaffungsprozesses eine offene Kommunikation mit Ihrem Lieferanten. So können Sie eventuell auftretende Probleme ansprechen und eine partnerschaftliche Beziehung fördern.
- Regelmäßige Aktualisierungen: Bitten Sie um Aktualisierungen der Produktions- und Lieferfristen, um sicherzustellen, dass diese mit Ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen übereinstimmen.
- Rückkopplungsschleife: Geben Sie Feedback zu den erhaltenen Komponenten, um zukünftige Transaktionen zu verbessern.
Anhand dieser strukturierten Checkliste können B2B-Einkäufer die Komplexität der Beschaffung von Autoanatomiekomponenten effektiv bewältigen und dabei Qualität, Compliance und betriebliche Effizienz sicherstellen.
Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Anatomie des Autos Sourcing
Was sind die wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten bei der Beschaffung von Autoanatomieteilen?
Das Verständnis der Kostenstruktur bei der Beschaffung von Komponenten für die Anatomie eines Autos ist für B2B-Einkäufer von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere für diejenigen, die auf verschiedenen internationalen Märkten tätig sind. Zu den wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten gehören Material, Arbeit, Fertigungsgemeinkosten, Werkzeuge, Qualitätskontrolle, Logistik und Gewinnspanne.
-
Materialien: Die Wahl der Materialien hat einen erheblichen Einfluss auf die Gesamtkosten. Hochleistungswerkstoffe wie fortschrittliche Verbundwerkstoffe oder Spezialmetalle können den Preis erhöhen, bieten aber eine bessere Haltbarkeit und Leistung. Umgekehrt kann die Wahl von Standardmaterialien die Kosten senken, aber möglicherweise die Qualität beeinträchtigen.
-
Arbeit: Die Arbeitskosten variieren je nach Region und werden durch das für die Produktion erforderliche Qualifikationsniveau beeinflusst. In Ländern mit höheren Arbeitskosten, wie z. B. Deutschland, investieren die Hersteller häufig in die Automatisierung, um die Kosten zu senken. Im Gegensatz dazu bieten Länder wie Nigeria zwar niedrigere Arbeitskosten, könnten aber Probleme mit der Verfügbarkeit von Fachkräften haben.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: Hierunter fallen die Ausgaben für die Produktionsanlage, einschließlich Versorgungsleistungen, Wartung der Anlagen und Verwaltungskosten. Effiziente Herstellungsverfahren und Größenvorteile können dazu beitragen, die Gemeinkosten zu senken.
-
Werkzeuge: Werkzeugkosten sind mit der Herstellung von Formen und Gesenken verbunden, die für die Fertigung bestimmter Teile erforderlich sind. Kundenspezifische Werkzeuge können teuer sein, vor allem bei geringen Stückzahlen. Daher ist es wichtig, das Kosten-Nutzen-Verhältnis von Investitionen in maßgeschneiderte Lösungen gegenüber der Verwendung von Standardwerkzeugen abzuwägen.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Strenge Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen sind unerlässlich, um die Zuverlässigkeit und Sicherheit von Automobilkomponenten zu gewährleisten. Dies erhöht zwar die Anschaffungskosten, kann aber langfristig Geld sparen, da das Risiko von Mängeln und Rückrufaktionen verringert wird.
-
Logistik: Die Kosten für den Transport von Teilen vom Hersteller zum Käufer können je nach Entfernung, Transportart und Versandbedingungen erheblich variieren. Internationale Käufer sollten die Incoterms berücksichtigen, in denen die Zuständigkeiten für Versand, Versicherung und Zölle festgelegt sind und die sich auf die gesamten Logistikkosten auswirken.
-
Marge: Die Lieferanten bauen in der Regel eine Gewinnspanne in ihre Preisstruktur ein, die je nach Wettbewerb und Nachfrage auf dem Markt variieren kann. Das Verständnis der Wettbewerbslandschaft kann den Einkäufern helfen, bessere Preise auszuhandeln.
Welche Faktoren beeinflussen die Preisgestaltung für Autoteile?
Mehrere Faktoren können sich auf die Preisgestaltung von Anatomiekomponenten für Autos auswirken, insbesondere für internationale Käufer:
-
Volumen und Mindestbestellmenge (MOQ): Der Einkauf in großen Mengen kann zu erheblichen Rabatten führen. Die Lieferanten legen oft Mindestmengen fest, die sich auf die Preisgestaltung auswirken können, so dass es für Einkäufer wichtig ist, ihren Bedarf mit den Anforderungen der Lieferanten abzugleichen.
-
Spezifikationen und Anpassung: Die Anpassung von Komponenten an spezifische Anforderungen kann die Kosten in die Höhe treiben. Käufer sollten die Vorteile einer individuellen Anpassung gegen Standardangebote abwägen, die ihre Anforderungen ohne zusätzliche Kosten erfüllen.
-
Qualität und Zertifizierungen: Komponenten, die strenge Qualitätsnormen erfüllen oder über Zertifizierungen (z. B. ISO, TS) verfügen, können einen hohen Preis haben. Die Investition in zertifizierte Teile kann jedoch die Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit des Fahrzeugs erhöhen.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Der Ruf und die Zuverlässigkeit der Anbieter können die Preisgestaltung beeinflussen. Etablierte Anbieter können aufgrund ihrer nachweislichen Erfolgsbilanz höhere Preise verlangen, während neuere Marktteilnehmer niedrigere Preise anbieten könnten, um Marktanteile zu gewinnen.
Wie können Einkäufer effektiv verhandeln und die Kosteneffizienz sicherstellen?
Für internationale B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, ist effektives Verhandeln der Schlüssel zur Kosteneffizienz. Hier sind einige Tipps:
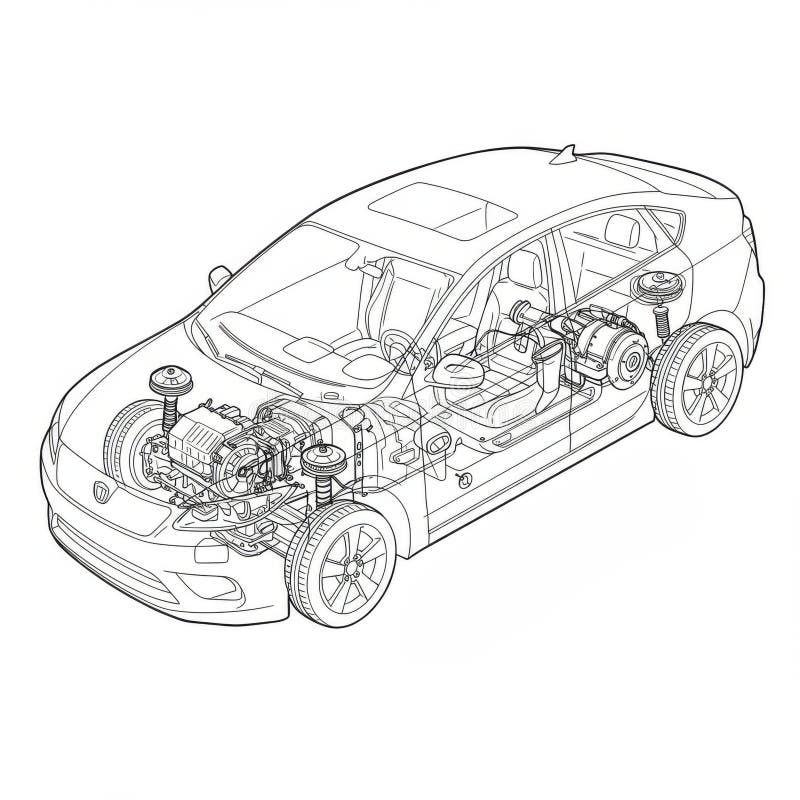
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
-
Beziehungen nutzen: Der Aufbau enger Beziehungen zu Lieferanten kann zu besseren Konditionen und Preisen führen. Langfristige Partnerschaften führen oft zu Treuerabatten.
-
Berücksichtigen Sie die Gesamtbetriebskosten (Total Cost of Ownership, TCO): Berücksichtigen Sie nicht nur den Anschaffungspreis, sondern auch die langfristigen Kosten für Wartung, Haltbarkeit und Leistung. Ein preisgünstiges Bauteil ist nicht immer der beste Wert.
-
Achten Sie auf preisliche Nuancen: Die Kenntnis der lokalen Marktbedingungen und Währungsschwankungen kann bei Verhandlungen von Vorteil sein. Einkäufer sollten sich auch über Handelszölle und Vorschriften informieren, die sich auf die Kosten auswirken könnten.
Was sollten Einkäufer bei der Preisgestaltung beachten?
Es ist wichtig zu wissen, dass die Preise für Anatomiekomponenten für Autos je nach den oben genannten Faktoren stark variieren können. Auch wenn die Richtpreise als Orientierungshilfe dienen können, sollten Käufer eine gründliche Marktforschung durchführen und sich mit mehreren Anbietern in Verbindung setzen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie das bestmögliche Angebot erhalten, das auf ihre spezifischen Bedürfnisse zugeschnitten ist.
Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich der Anatomie des Autos mit anderen Lösungen
Einführung in alternative Lösungen in der Automobilanatomie
In der Automobilindustrie ist das Verständnis der Anatomie eines Autos entscheidend für eine effektive Wartung, Sicherheit und Leistung. Es gibt jedoch alternative Lösungen und Technologien, mit denen ähnliche Ziele erreicht werden können, entweder durch die Verbesserung herkömmlicher Fahrzeuge oder durch völlig andere Ansätze für den Transport. In dieser Analyse wird die Anatomie des Autos im Vergleich zu zwei praktikablen Alternativen untersucht: Elektrofahrzeuge (EVs) und Hybridfahrzeuge. Jede Option bietet einzigartige Vorteile und Herausforderungen, die B2B-Käufer berücksichtigen müssen, wenn sie eine fundierte Kaufentscheidung treffen wollen.
Vergleichstabelle
| Vergleichsaspekt | Anatomie des Autos | Elektrofahrzeuge (EVs) | Hybrid-Fahrzeuge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Hohe Leistungsabgabe, traditioneller Brennstoff | Sofortiges Drehmoment, typischerweise im unteren Bereich | Ausgewogene Leistung mit beiden Motoren |
| Kosten | Moderate Anschaffungskosten, laufende Kraftstoffkosten | Höhere Anfangskosten, niedrigere Betriebskosten | Moderate Anschaffungskosten, unterschiedliche Kraftstoffkosten |
| Einfache Implementierung | Standard-Herstellungsverfahren | Erfordert Ladeinfrastruktur | Einfache Integration in bestehende Systeme |
| Wartung | Regelmäßige Wartung erforderlich | Weniger bewegliche Teile, geringerer Wartungsaufwand | Komplexer aufgrund der dualen Systeme |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Ideal für Langstreckenreisen | Am besten geeignet für Stadtpendler und umweltbewusste Käufer | Vielseitig, geeignet für unterschiedliche Fahrbedingungen |
Detaillierte Aufschlüsselung der Alternativen
Elektrofahrzeuge (EVs)
Elektrofahrzeuge stellen einen bedeutenden Wandel in der Automobiltechnologie dar, da sie ausschließlich mit elektrischer Energie betrieben werden. Dies führt zu einem sofortigen Drehmoment und einem sanften Fahrgefühl. Die höheren Anschaffungskosten von Elektrofahrzeugen können jedoch für viele Käufer ein Hindernis darstellen. Außerdem kann die Notwendigkeit einer Ladeinfrastruktur ihre Praxistauglichkeit in Regionen mit weniger entwickelten Stromnetzen einschränken. Trotz dieser Herausforderungen bieten E-Fahrzeuge niedrigere Betriebskosten und geringere Emissionen, was sie für Unternehmen, die auf Nachhaltigkeit achten, interessant macht.
Hybrid-Fahrzeuge
Hybridfahrzeuge kombinieren herkömmliche Verbrennungsmotoren mit elektrischem Antrieb und ermöglichen so eine verbesserte Kraftstoffeffizienz und geringere Emissionen. Sie bieten eine ausgewogene Leistung und eignen sich daher für eine Reihe von Fahrbedingungen. Einer der Hauptvorteile von Hybridfahrzeugen besteht darin, dass sie ohne umfangreiche Ladeinfrastruktur betrieben werden können, da sie bei Bedarf mit Benzin betrieben werden können. Die Komplexität eines Elektro- und eines Benzinsystems kann jedoch im Vergleich zu reinen Elektrofahrzeugen oder herkömmlichen Fahrzeugen zu einem höheren Wartungsbedarf und höheren Kosten führen.
Fazit: Die richtige Lösung für Ihre Anforderungen auswählen
Bei der Bewertung der Anatomie des Autos im Vergleich zu alternativen Lösungen wie Elektro- und Hybridfahrzeugen müssen B2B-Käufer ihre spezifischen betrieblichen Anforderungen, Budgetbeschränkungen und die in ihrer Region vorhandene Infrastruktur berücksichtigen. Jede Option hat ihre Stärken und Schwächen, und die richtige Wahl hängt von Faktoren wie dem Verwendungszweck der Fahrzeuge, der Bedeutung der Nachhaltigkeit und den Gesamtbetriebskosten im Laufe der Zeit ab. Indem sie ihre Wahl mit den strategischen Unternehmenszielen in Einklang bringen, können Käufer fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die die Leistung und Effizienz ihrer Flotte verbessern.
Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für die Anatomie des Autos
Was sind die wichtigsten technischen Eigenschaften, die für die Anatomie eines Autos relevant sind?
Für B2B-Einkäufer ist es von entscheidender Bedeutung, die technischen Eigenschaften von Fahrzeugkomponenten zu kennen, insbesondere wenn sie Teile für die Beschaffung oder Wartung bewerten. Hier sind einige wesentliche Spezifikationen, die Sie beachten sollten:
-
Werkstoffgüte
– Definition: Werkstoffsorte bezeichnet die Klassifizierung von Werkstoffen auf der Grundlage ihrer mechanischen Eigenschaften, wie Zugfestigkeit, Härte und Korrosionsbeständigkeit.
– Bedeutung: Die Wahl der richtigen Materialqualität gewährleistet Haltbarkeit und Sicherheit. Hochfester Stahl wird zum Beispiel häufig für kritische Komponenten wie das Fahrgestell verwendet, um die Sicherheit und Leistung zu erhöhen. -
Toleranz
– Definition: Die Toleranz gibt die zulässige Abweichung von einem Standardmaß an. Sie ist in der Feinmechanik von entscheidender Bedeutung, da bereits geringe Abweichungen zum Ausfall von Bauteilen führen können.
– Bedeutung: Bei der Beschaffung von Teilen ist es wichtig, die Toleranzgrenzen zu kennen. Enge Toleranzen sind für Komponenten wie Motorenteile erforderlich, bei denen sich die Präzision auf Leistung und Langlebigkeit auswirkt. -
Tragfähigkeit
– Definition: Die Tragfähigkeit ist das maximale Gewicht, das ein Bauteil tragen kann, ohne zu versagen.
– Bedeutung: Bei Bauteilen wie der Aufhängung und den Reifen hilft die Kenntnis der Tragfähigkeit bei der Auswahl von Teilen, die für ein bestimmtes Fahrzeuggewicht geeignet sind, um Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit zu gewährleisten. -
Wärmewiderstand
– Definition: Die thermische Beständigkeit misst die Fähigkeit eines Materials, hohen Temperaturen standzuhalten, ohne sich zu verschlechtern.
– Bedeutung: Bei Automotoren und Auspuffanlagen verhindern Materialien mit hoher Wärmebeständigkeit eine Überhitzung, die zu katastrophalen Ausfällen führen kann. Dies ist besonders wichtig für Käufer in heißen Klimazonen. -
Korrosionsbeständigkeit
– Definition: Die Korrosionsbeständigkeit gibt an, wie gut ein Material dem durch Umwelteinflüsse wie Feuchtigkeit und Chemikalien verursachten Abbau widerstehen kann.
– Bedeutung: Bauteile wie Brems- und Auspuffanlagen sind korrosionsanfällig. Die Auswahl von Teilen mit hoher Korrosionsbeständigkeit verlängert ihre Lebensdauer und senkt die Wartungskosten.
Was sind gängige Fachterminologien in der Automobilindustrie?
Die Vertrautheit mit dem Branchenjargon verbessert die Kommunikation und die Entscheidungsfindung im B2B-Automobilbereich. Hier sind einige wichtige Begriffe, die Sie kennen sollten:

Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
-
OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
– Definition: Ein OEM ist ein Unternehmen, das Teile und Geräte herstellt, die von einem anderen Hersteller vermarktet werden können.
– Bedeutung: B2B-Käufer bevorzugen oft OEM-Teile wegen ihrer garantierten Qualität und Kompatibilität mit bestehenden Systemen, insbesondere in Regionen mit strengen Automobilvorschriften. -
MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
– Definition: MOQ ist die kleinste Menge eines Produkts, die ein Lieferant zu verkaufen bereit ist.
– Bedeutung: Das Verständnis der MOQ ist für die Budgetverwaltung und die Bestandsplanung von entscheidender Bedeutung. Einkäufer in Schwellenländern müssen unter Umständen MOQs aushandeln, um sie mit ihren Einkaufsmöglichkeiten in Einklang zu bringen. -
RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
– Definition: Eine RFQ ist ein Dokument, das von einem Einkäufer ausgestellt wird, um Preisangebote von Lieferanten für bestimmte Produkte oder Dienstleistungen anzufordern.
– Bedeutung: Der effektive Einsatz von RFQs hilft Einkäufern, Preise und Dienstleistungen zu vergleichen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie wettbewerbsfähige Preise erhalten und gleichzeitig Qualitätsstandards einhalten. -
Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
– Definition: Die Incoterms sind eine Reihe von vordefinierten internationalen Handelsklauseln, die von der Internationalen Handelskammer veröffentlicht werden und die Verantwortlichkeiten von Käufern und Verkäufern klären.
– Bedeutung: Das Verständnis der Incoterms ist für internationale Transaktionen entscheidend. Sie legen fest, wer für den Versand, die Versicherung und die Zölle verantwortlich ist, und wirken sich auf die gesamten Anlandekosten der Teile aus. -
Ersatzteilmarkt
– Definition: Der Aftermarket ist der Markt für Teile und Zubehör, die nicht von der Erstausrüstung stammen.
– Bedeutung: Die Käufer sollten sich über die Optionen auf dem Ersatzteilmarkt informieren, da sie oft kostengünstige Alternativen zu den OEM-Teilen bieten, was besonders auf kostensensiblen Märkten von Bedeutung sein kann. -
Vorlaufzeit
– Definition: Die Durchlaufzeit ist der Zeitraum zwischen der Einleitung eines Prozesses und seinem Abschluss, insbesondere im Rahmen der Auftragsabwicklung.
– Bedeutung: Die Kenntnis der Vorlaufzeiten ist für die Bestandsverwaltung von entscheidender Bedeutung. Kürzere Vorlaufzeiten können sich erheblich auf die Effizienz der Lieferkette auswirken, insbesondere für Unternehmen, die auf schnelllebigen Märkten tätig sind.
Wenn B2B-Einkäufer diese technischen Eigenschaften und Fachterminologien verstehen, können sie fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die ihre Beschaffungsprozesse optimieren und die Leistung und Sicherheit von Automobilkomponenten verbessern.
Navigieren durch Marktdynamik und Beschaffungstrends in der Anatomie des Automobilsektors
Was sind die aktuelle Marktdynamik und die wichtigsten Trends in der Anatomie des Automobilsektors?
Die Automobilindustrie befindet sich in einer Umbruchphase, die von technologischen Fortschritten, sich verändernden Verbraucherpräferenzen und gesetzlichem Druck bestimmt wird. Internationale B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, beobachten signifikante Verschiebungen bei den Beschaffungstrends. Zu den wichtigsten Treibern gehört die Zunahme von Elektrofahrzeugen (EVs), die eine Neubewertung von Komponenten wie Batterien, Motoren und Ladesystemen erforderlich machen. In Märkten wie Nigeria und Deutschland verändert der Vorstoß zur Einführung von Elektrofahrzeugen die Beziehungen zu den Zulieferern, da die Unternehmen nach Komponenten suchen, die neue Leistungs- und Nachhaltigkeitsstandards erfüllen.
Aufkommende Technologien wie künstliche Intelligenz (KI) und das Internet der Dinge (IoT) beeinflussen auch die Anatomie von Autos. Diese Technologien verbessern die betriebliche Effizienz, von Fertigungsprozessen bis hin zum Lieferkettenmanagement, und schaffen so Möglichkeiten für B2B-Partnerschaften. So kann beispielsweise eine durch das IoT unterstützte vorausschauende Wartung Ausfallzeiten reduzieren, was einen Wettbewerbsvorteil für Unternehmen in der Lieferkette darstellt. Darüber hinaus wird die Integration fortschrittlicher Werkstoffe, wie leichter Verbundwerkstoffe, für die Einhaltung von Kraftstoffeffizienzstandards und die Verbesserung der Fahrzeugleistung immer wichtiger.
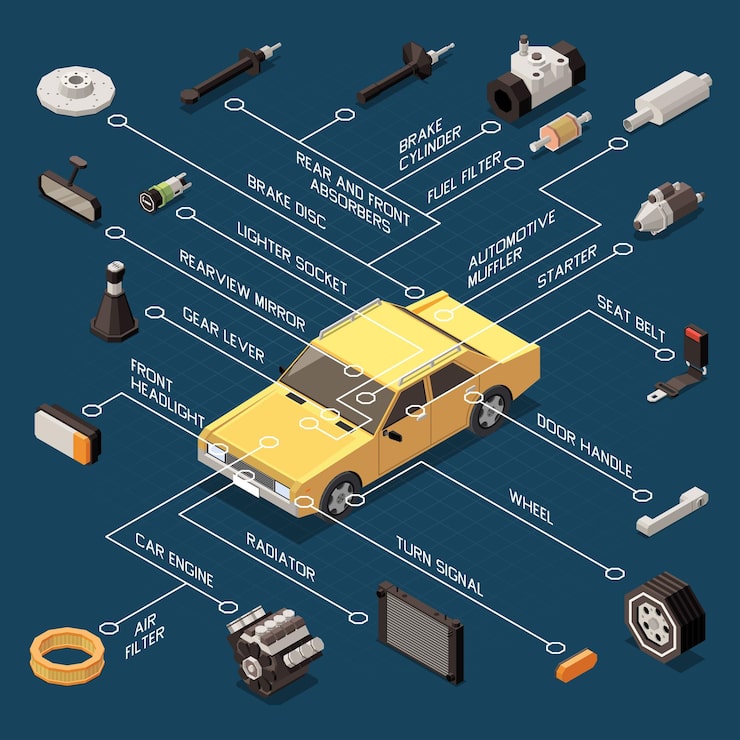
Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Ein weiterer wichtiger Trend ist die Globalisierung der Lieferketten. Auf der Suche nach zuverlässigen Partnern legen internationale Einkäufer den Schwerpunkt auf Qualität und die Einhaltung internationaler Standards. Die Marktdynamik wird zunehmend von geopolitischen Faktoren beeinflusst, was sich auf die Beschaffungsstrategien auswirkt. Unternehmen müssen flexibel bleiben und sich an die sich ändernde Handelspolitik und Zölle anpassen, die sich auf die Kosten und Verfügbarkeit von Komponenten auswirken.
Wie prägen Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung die Anatomie des Automobilsektors?
Nachhaltigkeit ist in der Automobilindustrie zu einem wichtigen Thema geworden, insbesondere für B2B-Käufer, die sich auf die Anatomie des Autos konzentrieren. Die Umweltauswirkungen von Autoproduktion und -betrieb führen zu einer Umstellung auf umweltfreundlichere Praktiken. Einkäufer geben zunehmend Lieferanten den Vorzug, die sich für eine nachhaltige Beschaffung einsetzen, wozu auch die Verwendung von recycelten Materialien und die Minimierung von Abfällen bei der Produktion gehören.
Ethische Lieferketten sind ebenfalls auf dem Vormarsch. Einkäufer suchen nach Partnern, die sich an faire Arbeitsbedingungen und Umweltstandards halten und sicherstellen, dass jedes Bauteil - vom Motor bis zur Innenausstattung - ethischen Richtlinien entspricht. Zertifizierungen wie ISO 14001 für das Umweltmanagement und SA8000 für die soziale Verantwortung werden für Zulieferer, die internationale Kunden anziehen wollen, immer wichtiger.
Außerdem steigt die Nachfrage nach ‘grünen’ Materialien. Komponenten wie biobasierte Kunststoffe, nachhaltiges Gummi für Reifen und umweltfreundliche Beschichtungen sind zunehmend gefragt. Durch die Ausrichtung auf nachhaltige Praktiken verbessern Unternehmen nicht nur ihr Markenimage, sondern erschließen auch ein wachsendes Marktsegment, in dem Umweltverantwortung eine große Rolle spielt.
Was ist die kurze Entwicklung der Autoanatomie, die für B2B-Käufer relevant ist?
Die Entwicklung der Anatomie des Automobils ist von bedeutenden technologischen Fortschritten und veränderten Verbrauchererwartungen geprägt. Ursprünglich waren Autos einfache mechanische Geräte, die auf grundlegende Funktionen ausgerichtet waren. Mit Beginn des 20. Jahrhunderts jedoch veränderten Innovationen wie Elektrostarter und Automatikgetriebe das Fahrerlebnis und machten die Fahrzeuge zugänglicher und benutzerfreundlicher.
Als Ende des 20. Jahrhunderts die Sorge um die Umwelt zunahm, begann die Industrie, der Kraftstoffeinsparung und der Emissionsreduzierung Priorität einzuräumen, was zur Entwicklung von Katalysatoren und effizienteren Motoren führte. Heute definiert der Wandel hin zu Elektro- und Hybridfahrzeugen die Anatomie von Autos neu, wobei der Schwerpunkt auf der Batterietechnologie und dem elektrischen Antriebsstrang liegt.
Für B2B-Einkäufer ist es entscheidend, diese Entwicklung zu verstehen. Es liefert nicht nur Informationen für Beschaffungsentscheidungen, sondern zeigt auch, wie wichtig es ist, mit Lieferanten zusammenzuarbeiten, die an der Spitze der Innovation stehen. Da sich die Anatomie von Autos ständig weiterentwickelt, können Unternehmen, die über diese Veränderungen informiert sind, sich anpassen und in einem zunehmend wettbewerbsintensiven Umfeld erfolgreich sein.
Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer zur Anatomie des Autos
-
Wie stelle ich die Qualität von Autoteilen sicher, wenn ich sie international beschaffe?
Um die Qualität von Fahrzeugteilen bei der internationalen Beschaffung zu gewährleisten, ist eine gründliche Überprüfung der Lieferanten unerlässlich. Dazu gehört die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, früheren Kundenrezensionen und der Einhaltung internationaler Normen wie ISO oder IATF 16949. Auch das Anfordern von Mustern für Tests kann Aufschluss über die Produktqualität geben. Die Erstellung klarer Qualitätssicherungsprotokolle und die regelmäßige Kommunikation mit den Lieferanten können dazu beitragen, die Standards während des gesamten Produktionsprozesses aufrechtzuerhalten und sicherzustellen, dass die Komponenten Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen erfüllen. -
Wie kann ich Autoteile am besten für meinen Markt anpassen?
Der beste Ansatz für die Anpassung von Fahrzeugkomponenten besteht darin, die spezifischen Bedürfnisse und Vorlieben Ihres Zielmarktes zu verstehen. Führen Sie Marktforschung durch, um lokale Trends, Vorschriften und Verbrauchervorlieben zu ermitteln. Arbeiten Sie eng mit Ihren Zulieferern zusammen, um machbare Änderungen zu besprechen, sei es beim Design, bei den Materialien oder bei den Funktionen. Die Einrichtung eines klaren Kommunikationskanals erleichtert effiziente Iterationen von Prototypen und stellt sicher, dass das Endprodukt den Anforderungen Ihres Marktes entspricht und gleichzeitig herstellbar ist. -
Was sind die typischen Mindestbestellmengen (MOQ) für Autoteile?
Die Mindestbestellmengen (MOQ) für Autoteile können je nach Lieferant und spezifischem Bauteil erheblich variieren. In der Regel liegen die MOQs zwischen 100 und 1.000 Stück für Standardkomponenten, während für kundenspezifische Teile höhere Mindestmengen erforderlich sein können. Es ist wichtig, MOQs im Vorfeld mit potenziellen Lieferanten zu besprechen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie mit Ihrer Einkaufsstrategie übereinstimmen. Darüber hinaus kann es sich als vorteilhaft erweisen, MOQs auszuhandeln, insbesondere wenn Sie eine langfristige Partnerschaft oder ein erhöhtes Auftragsvolumen nachweisen können. -
Mit welchen Zahlungsbedingungen muss ich rechnen, wenn ich Autoteile international beschaffe?
Die Zahlungsbedingungen bei der Beschaffung von Autoteilen können von Lieferant zu Lieferant sehr unterschiedlich sein. Üblich sind Netto 30 oder Netto 60, wobei die Zahlung innerhalb von 30 oder 60 Tagen nach Lieferung fällig ist. Einige Lieferanten verlangen eine Vorauszahlung, in der Regel 30% des gesamten Auftragswerts, wobei der Restbetrag bei Lieferung zu zahlen ist. Es ist ratsam, die Zahlungsbedingungen während der Verhandlungen zu klären und sichere Zahlungsmethoden wie Akkreditive in Betracht zu ziehen, um Ihre Interessen bei internationalen Transaktionen zu schützen. -
Wie kann ich die Logistik beim Import von Autoteilen effizient gestalten?
Ein effizientes Logistikmanagement für den Import von Fahrzeugteilen erfordert die Auswahl zuverlässiger Spediteure und die Kenntnis der Versandvorschriften sowohl des Export- als auch des Importlandes. Die Festlegung eines klaren Zeitplans für die Produktion und den Versand hilft bei der Koordinierung der Liefertermine. Der Einsatz von Technologien, wie z. B. Sendungsverfolgungssystemen, kann Echtzeit-Updates zu den Sendungen liefern. Machen Sie sich außerdem mit den Zollabfertigungsverfahren vertraut, um Verzögerungen zu vermeiden und die Einhaltung der örtlichen Vorschriften zu gewährleisten. -
Was sind die wichtigsten Sicherheitsmerkmale, auf die man bei Autoteilen achten sollte?
Bei der Beschaffung von Autoteilen, insbesondere für Märkte mit strengen Sicherheitsvorschriften, ist es wichtig, den Sicherheitsmerkmalen Vorrang zu geben. Achten Sie auf Komponenten, die internationale Sicherheitsstandards und Zertifizierungen erfüllen. Zu den wichtigsten Merkmalen gehören wirksame Bremssysteme, robuste Aufhängungskomponenten und zuverlässige elektrische Systeme mit integrierten Sicherheitsmaßnahmen. Erkundigen Sie sich außerdem nach Tests oder Crash-Sicherheitsbewertungen, die an den Komponenten durchgeführt wurden, um sicherzustellen, dass sie einen optimalen Schutz für Fahrer und Passagiere bieten. -
Wie kann ich die Zuverlässigkeit eines Autoteilelieferanten beurteilen?
Die Beurteilung der Zuverlässigkeit eines Autozulieferers umfasst mehrere Schritte. Beginnen Sie mit der Überprüfung der Unternehmensgeschichte, einschließlich der Jahre der Geschäftstätigkeit und der Kundenreferenzen. Fordern Sie Referenzen von früheren Kunden an, insbesondere von solchen aus Ihrer Branche. Prüfen Sie außerdem die Produktionskapazitäten und die Qualitätskontrollverfahren des Unternehmens. Ein zuverlässiger Lieferant sollte auch über transparente Kommunikationspraktiken verfügen und auf Anfragen reagieren. Wenn möglich, können Besuche vor Ort weitere Sicherheit über die Betriebsstandards geben. -
Welche Vorschriften muss ich bei der Einfuhr von Autoteilen in mein Land beachten?
Wenn Sie Autoteile importieren, ist es wichtig, dass Sie die spezifischen Vorschriften für Kfz-Teile in Ihrem Land kennen. Dazu gehören die Einhaltung von Sicherheits- und Emissionsnormen, Einfuhrzölle und Anforderungen an die Zolldokumentation. Informieren Sie sich über alle Zertifizierungen oder Prüfungen, die für Fahrzeugteile erforderlich sein können. Die Beratung durch Rechtsexperten oder Zollmakler kann Ihnen dabei helfen, sich in diesen Vorschriften zurechtzufinden und sicherzustellen, dass Ihre Importe den lokalen Gesetzen entsprechen und mögliche Strafen oder Verzögerungen vermieden werden.
Top 4 Anatomie der Autohersteller & Lieferanten Liste
1. Auffenberg Carbondale - Wesentliche Autokomponenten
Domäne: auffenbergcarbondale.com
Registriert: 2002 (23 Jahre)
Einleitung: Der Text behandelt die grundlegenden Komponenten eines Autos, einschließlich des Antriebsstrangs (Motor, Getriebe, Antriebswelle, Differential), des Aufhängungssystems (Federn, Stoßdämpfer, Gestänge), des Bremssystems (Bremspedal, Hauptzylinder, Bremsleitungen, Trommel- oder Scheibenbremsen), des elektrischen Systems (Drähte, Sicherungen, Stromkreise, Batterie, Lichtmaschine), der Innenausstattung (verstellbare Sitze, Klimaanlage, Infotainmentsystem)...
2. Moog - Teile für Lenkung und Aufhängung
Domäne: moogparts.com
Registriert: 2005 (20 Jahre)
Einleitung: Teile eines Autos: Lenkung (Lenkzwischenhebel, Umlenkhebel, Lenkstabilisatoren, komplettes, vormontiertes Lenkgestänge, Spurstangen), Aufhängung (Stabilisatorensätze, Ausrichtteile, Buchsen, Schraubenfedern, Querlenker, Querlenker, Kugelgelenke), Antriebsstrang (Zapfwelle, Kardangelenke, Kupplungen, Gleichlaufachsen), Radsatz (komplette Achsschenkel, Nabenbaugruppen).
3. Facebook - Schlüsselkomponenten der Automobilindustrie
Domäne: facebook.com
Registriert: 1997 (28 Jahre)
Einleitung: 1. Wischer: Mechanische Arme mit Gummiblättern für freie Sicht. 2. Windschutzscheibe: Frontscheibe aus Verbundsicherheitsglas für Schutz und Sicht. 3. Dach: Oberer Teil für strukturelle Integrität und Schutz vor den Elementen. 4. Äußere Fenster: Äußere Oberfläche der Seitenfenster für Sicht und Belüftung. 5. Seitenfenster: Fenster an den Fahrzeugtüren für die Sicht der Fahrgäste und für Frischluft. 6. Viertelfenster...
4. Fahrzeuge - Haupttypen und Komponenten des Antriebsstrangs
Domäne: medium.com
Registriert: 1998 (27 Jahre)
Einleitung: 1. Arten von Fahrzeugen: Zweiradantrieb (2WD), Hinterradantrieb mit Frontmotor, Vorderradantrieb mit Frontmotor, quer eingebauter Motor, Motor hinter dem Getriebe, Motor vor dem Getriebe, Hinterradantrieb mit Heckmotor, Vierradantrieb (4WD). 2. Komponenten des Antriebsstrangs: Triebwerk, Motor, Antriebsstrang, Kupplung, Getriebe, Welle, Differential, elektrische Anlage, Zündanlage, Stern...
Strategische Beschaffung - Fazit und Ausblick für die Anatomie des Autos
Was sind die wichtigsten Erkenntnisse für B2B-Einkäufer in der Automobilbranche?
Die Anatomie eines Autos zu verstehen, ist für internationale B2B-Einkäufer von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere für diejenigen, die an der Beschaffung von Automobilkomponenten oder Fahrzeugen beteiligt sind. Schlüsselkomponenten wie der Antriebsstrang, das Bremssystem und die elektrischen Systeme sind nicht nur grundlegend für die Leistung des Fahrzeugs, sondern auch entscheidend für die Bewertung von Lieferanten und Herstellern. Ein umfassendes Verständnis dieser Elemente ermöglicht es Einkäufern, fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen, die die Effizienz der Lieferkette optimieren und die Produktqualität verbessern.
Wie kann Strategic Sourcing die Beschaffung in der Automobilindustrie verbessern?
Die strategische Beschaffung in der Automobilindustrie ermöglicht es Unternehmen, Marktkenntnisse und Zuliefererkapazitäten effektiv zu nutzen. Durch die Konzentration auf qualitativ hochwertige Teile und innovative Technologien können Einkäufer Kosten senken, die Zuverlässigkeit von Fahrzeugen verbessern und die Einhaltung regionaler Sicherheitsstandards gewährleisten. Dieser proaktive Ansatz ist für Unternehmen, die auf wettbewerbsintensiven Märkten in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa erfolgreich sein wollen, unerlässlich.
Was kommt als Nächstes auf B2B-Einkäufer in der Automobilbranche zu?
Da sich die Automobillandschaft ständig weiterentwickelt, insbesondere mit Fortschritten bei elektrischen und autonomen Fahrzeugen, ist es wichtig, den Branchentrends voraus zu sein. Internationale B2B-Einkäufer werden ermutigt, mit Lieferanten zusammenzuarbeiten, die Innovation und Nachhaltigkeit in den Vordergrund stellen. Durch die Förderung starker Partnerschaften und ein wachsames Auge auf technologische Entwicklungen können sich Unternehmen für den zukünftigen Erfolg auf dem dynamischen Automobilmarkt positionieren. Nutzen Sie diese Gelegenheit, um Ihre Beschaffungsstrategie zu verbessern und Ihr Unternehmen voranzubringen.
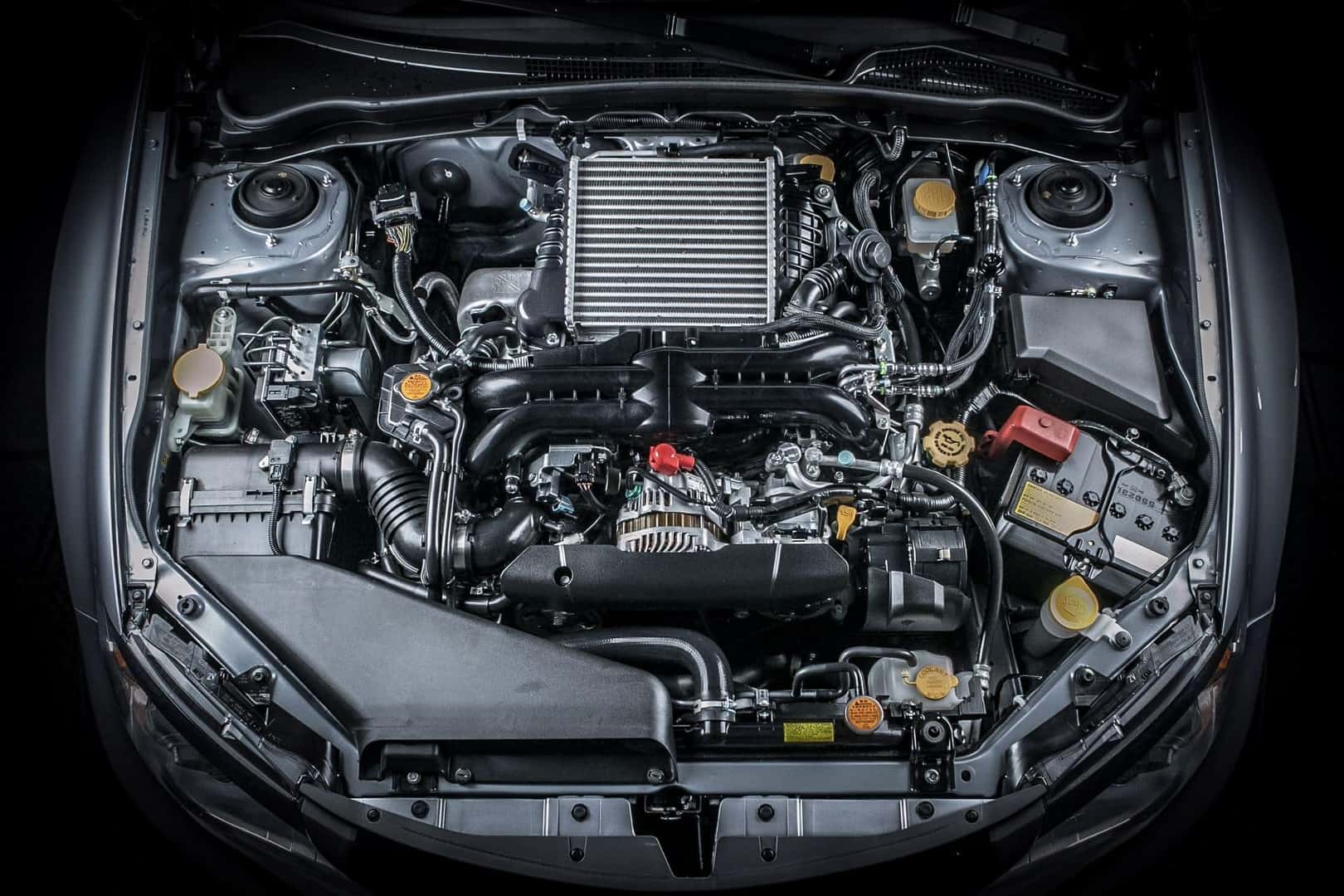

Anschauliches Bild zur Anatomie des Fahrzeugs
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.