Einführung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für Anlasser-Magnetspulen und Relais
Wenn es um die Beschaffung zuverlässiger Komponenten wie Anlassermagnete und Relais geht, stehen internationale B2B-Einkäufer vor einer großen Herausforderung: Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass das richtige Produkt für verschiedene Anwendungen auf unterschiedlichen Märkten geeignet ist. Um fundierte Beschaffungsentscheidungen treffen zu können, ist es wichtig, die Unterschiede zwischen Anlassermagneten und Relais zu verstehen. Dieser Leitfaden befasst sich mit den Feinheiten dieser beiden unverzichtbaren Komponenten, untersucht ihre Arten, Anwendungen und die entscheidenden Faktoren, die bei der Bewertung von Lieferanten zu berücksichtigen sind.
Von der Automobilindustrie bis hin zu Industriemaschinen kann die Leistung von Anlassermagneten und -relais die betriebliche Effizienz und Sicherheit erheblich beeinflussen. Einkäufer profitieren von einem umfassenden Überblick, der nicht nur die wichtigsten Unterschiede zwischen diesen Geräten aufzeigt, sondern auch Einblicke in bewährte Verfahren zur Lieferantenprüfung, Kostenanalyse und Qualitätssicherung bietet. Dieser Leitfaden geht auf häufige Fallstricke ein und hebt die wesentlichen Merkmale hervor. So können B2B-Einkäufer aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa - einschließlich Märkten wie Vietnam und Brasilien - fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen und Budgetvorgaben in Einklang stehen.
Mit diesem Wissen können sich Einkäufer sicher auf dem globalen Markt bewegen und sicherstellen, dass sie die richtigen Komponenten beschaffen, um ihre Geschäftsabläufe zu verbessern und gleichzeitig die Risiken im Zusammenhang mit minderwertigen Produkten zu minimieren. Diese Ressource ist ein unverzichtbares Instrument für alle, die ihre Lieferkette optimieren und in einem wettbewerbsintensiven Umfeld langfristig erfolgreich sein wollen.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 2 Anlasser-Magnetventil vs. Relais Liste der Hersteller & Lieferanten
- Einführung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für Anlasser-Magnetspulen und Relais
- Verstehen von Anlassermagneten und Relais Typen und Variationen
- Wichtigste industrielle Anwendungen von Startermagneten und Relais
- 3 häufige Benutzer Schmerzpunkte für ‘Anlasser Magnetspule vs Relais’ & ihre Lösungen
- Strategischer Leitfaden für die Materialauswahl für Anlassermagneten und Relais
- Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für Startermagnete und Relais
- Praktische Anleitung zur Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais’.’
- Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Beschaffung von Anlasser-Magneten und Relais
- Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich zwischen Startermagnet und Relais mit anderen Lösungen
- Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für Anlasser und Relais
- Navigation der Marktdynamik und der Beschaffungstrends im Sektor Anlassermagnete und Relais
- Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Einkäufer von Startermagneten vs. Relais
- Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Verstehen von Anlassermagneten und Relais Typen und Variationen
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elektromagnetisches Relais | Signalsteuerung mit geringem Stromverbrauch, kompaktes Design | Automobilindustrie, Industriemaschinen | Vorteile: Kostengünstig, vielseitig. Nachteile: Begrenzte Strombelastbarkeit im Vergleich zu Magnetspulen. |
| Anlasser-Magnetspule | Direkt an den Anlasser angeschlossen, hohe Strombelastbarkeit | Automobilindustrie, Schwermaschinen | Vorteile: Höhere Stromkapazität, direktes Engagement. Nachteile: Potenziell komplexer zu ersetzen. |
| Verriegelungsrelais | Behält den Zustand ohne kontinuierliche Stromversorgung bei | Automatisierungssysteme, HVAC | Vorteile: Energieeffizient und zuverlässig. Nachteile: Teurer als Standardrelais. |
| Halbleiterrelais | Keine beweglichen Teile, schnellere Schaltmöglichkeiten | Industrielle Automatisierung, HVAC-Systeme | Vorteile: Lange Lebensdauer, minimale Wärmeentwicklung. Nachteile: Höhere Anschaffungskosten. |
| Miniatur-Relais | Kompakte Größe, entwickelt für Anwendungen mit geringem Stromverbrauch | Unterhaltungselektronik, Automobilindustrie | Vorteile: Platzsparend, effizient. Nachteile: Begrenzte Stromkapazität. |
Was sind die wichtigsten Merkmale von elektromagnetischen Relais für B2B-Käufer?
Elektromagnetische Relais sind integrale Bestandteile in verschiedenen Anwendungen, insbesondere in Kraftfahrzeugen und Industriemaschinen. Sie arbeiten, indem sie ein Signal mit geringem Stromverbrauch zur Steuerung eines größeren Schaltkreises verwenden. Ihr kompaktes Design ermöglicht eine einfache Integration in bestehende Systeme, was sie zu einer beliebten Wahl für Hersteller macht, die ihren Betrieb rationalisieren wollen. Sie sind zwar kostengünstig, aber ihre begrenzte Strombelastbarkeit kann bei Anwendungen, die eine höhere Leistung erfordern, ein Nachteil sein.
Wie heben sich Anlasser-Magnetventile auf dem Markt ab?
Anlassermagnete sind speziell dafür ausgelegt, den Anlasser direkt zu betätigen, was sie zu einem unverzichtbaren Bestandteil von Kfz-Anwendungen macht. Sie sind für ihre Fähigkeit bekannt, hohe Stromlasten zu bewältigen, was für das Anlassen von Motoren entscheidend ist. B2B-Käufer sollten die Komplexität der Installation berücksichtigen, da Magnetspulen oft schwieriger zu ersetzen sind als Relais. Aufgrund ihrer Zuverlässigkeit in Situationen, in denen hohe Anforderungen gestellt werden, werden sie bevorzugt im Schwermaschinen- und Automobilsektor eingesetzt.
Warum werden Verriegelungsrelais in der Automatisierung immer beliebter?
Selbsthaltende Relais sind insofern einzigartig, als sie ihren Zustand beibehalten, ohne ständig Strom zu benötigen, was sie ideal für Automatisierungssysteme und HLK-Anwendungen macht. Dieses energieeffiziente Design reduziert nicht nur den Stromverbrauch, sondern erhöht auch die Zuverlässigkeit des Systems. Sie sind zwar in der Regel teurer als Standardrelais, aber die langfristigen Einsparungen bei den Energiekosten können die Investition für Unternehmen rechtfertigen, die ihren Betrieb optimieren wollen.
Welche Vorteile bieten Halbleiterrelais für industrielle Anwendungen?
Halbleiterrelais (SSRs) revolutionieren die industrielle Automatisierung, da sie schnellere Schaltfunktionen und eine längere Lebensdauer bieten, da sie keine beweglichen Teile haben. Sie sind besonders nützlich in Umgebungen, in denen die Wärmeentwicklung minimiert werden muss. B2B-Käufer sollten sich jedoch der höheren Anschaffungskosten bewusst sein, die mit SSRs im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Relais verbunden sind. Die Investition kann im Laufe der Zeit zu geringeren Wartungskosten und höherer Betriebseffizienz führen.
Wie passen Miniaturrelais in die Unterhaltungselektronik?
Miniaturrelais sind speziell für Anwendungen mit geringem Stromverbrauch konzipiert und werden häufig in der Unterhaltungselektronik und in Automobilsystemen eingesetzt. Ihre kompakte Größe ermöglicht eine effiziente Nutzung des Platzes, was in modernen elektronischen Designs entscheidend ist. Während sie eine effiziente Lösung für kleinere Geräte bieten, kann ihre begrenzte Stromkapazität ihre Verwendung in anspruchsvolleren Anwendungen einschränken. B2B-Käufer sollten vor der Auswahl von Miniaturrelais den Leistungsbedarf ihrer Geräte prüfen.
Wichtigste industrielle Anwendungen von Startermagneten und Relais
| Branche/Sektor | Spezifische Anwendung von Anlasser-Magneten und Relais | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Motorzündsysteme in Fahrzeugen | Sorgt für ein zuverlässiges Anlassen des Motors und erhöht die Leistung und Sicherheit des Fahrzeugs. | Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Fahrzeugmodellen und Einhaltung der örtlichen Vorschriften. |
| Landwirtschaftliche Maschinen | Startsysteme in Traktoren und Erntemaschinen | Erhöht die betriebliche Effizienz und minimiert die Ausfallzeiten während kritischer landwirtschaftlicher Jahreszeiten. | Langlebigkeit und Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen raue Umweltbedingungen. |
| Baumaschinen | Energiemanagement in schweren Maschinen wie Baggern | Erleichtert einen effizienten Betrieb und verringert das Risiko eines Geräteausfalls vor Ort. | Beschaffung von Teilen, die spezifische Leistungsanforderungen und Industrienormen erfüllen. |
| Marine und Schifffahrt | Motorstart- und Kontrollsysteme in Schiffen | Erhöht die Zuverlässigkeit und Sicherheit im Schiffsbetrieb und verhindert kostspielige Verzögerungen. | Bedarf an korrosionsbeständigen Materialien und Einhaltung der Vorschriften für den Seeverkehr. |
| Industrielle Automatisierung | Steuerungssysteme in Produktionsanlagen | Verbessert die Automatisierungseffizienz und reduziert manuelle Eingriffe, was zu Kosteneinsparungen führt. | Bedarf an hochwertigen Komponenten, die hohen Zyklen und Belastungen standhalten. |
Wie werden Anlassermagnete und -relais in der Automobilindustrie eingesetzt?
In der Automobilbranche sind Anlassermagnete und -relais wichtige Bestandteile von Motorzündsystemen. Sie ermöglichen es einem Zündschalter mit geringer Leistung, einen Hochleistungsanlasser zu aktivieren und so einen zuverlässigen Motorstart zu gewährleisten. Defekte Magnetspulen oder Relais können zu Problemen führen, z. B. wenn der Motor nicht anspringt oder intermittierend arbeitet. B2B-Einkäufer in diesem Sektor sollten auf die Kompatibilität mit einer Vielzahl von Fahrzeugmodellen achten und sicherstellen, dass die lokalen Vorschriften eingehalten werden, insbesondere auf unterschiedlichen Märkten wie Afrika und Südamerika.
Welche Rolle spielen Anlassermagnete und Relais in Landmaschinen?
In der Landtechnik sind Anlassermagnete und -relais für die Startsysteme von Traktoren und Erntemaschinen unerlässlich. Diese Komponenten ermöglichen ein effizientes Anlassen des Motors, was während der landwirtschaftlichen Hochsaison von entscheidender Bedeutung ist. Ausfallzeiten aufgrund von Anlasserausfällen können zu erheblichen finanziellen Verlusten führen. Die Käufer müssen bei der Beschaffung von langlebigen Magnetventilen und Relais darauf achten, dass sie den rauen Außenbedingungen standhalten und in unterschiedlichen Klimazonen wie im Nahen Osten und Brasilien zuverlässig arbeiten.
Wie werden Anlassermagnete und -relais in Baumaschinen eingesetzt?
Baumaschinen sind in hohem Maße auf Anlassermagnete und Relais für das Energiemanagement von Maschinen wie Baggern und Planierraupen angewiesen. Diese Komponenten sorgen dafür, dass schwere Maschinen effizient arbeiten und das Risiko von Ausfällen auf Baustellen verringert wird. Für B2B-Einkäufer ist es von entscheidender Bedeutung, Teile zu beschaffen, die den spezifischen Leistungsanforderungen und Industriestandards entsprechen und den strengen Anforderungen der Baustellenumgebung standhalten.
Welche Anwendungen gibt es für Anlassermagnete und Relais in der Schifffahrtsindustrie?
In der Schifffahrtsindustrie sind Anlassermagnete und -relais von entscheidender Bedeutung für das Anlassen von Motoren und die Steuerung von Schiffen. Ihre Zuverlässigkeit wirkt sich direkt auf den Schiffsbetrieb aus, da ein Motorausfall zu kostspieligen Verzögerungen und Sicherheitsrisiken führen kann. Einkäufer in diesem Sektor müssen sich auf die Beschaffung von korrosionsbeständigen Materialien und Komponenten konzentrieren, die den maritimen Vorschriften entsprechen, um Langlebigkeit und Leistung in anspruchsvollen maritimen Umgebungen zu gewährleisten.
Wie verbessern Anlassermagnete und Relais die industrielle Automatisierung?
In der Industrieautomation sind Startermagnete und Relais von entscheidender Bedeutung für die Steuerungen von Produktionsanlagen. Sie erleichtern die Automatisierung von Prozessen, verringern den Bedarf an manuellen Eingriffen und erhöhen die Gesamteffizienz. B2B-Einkäufer sollten hochwertigen Komponenten den Vorzug geben, die hohen Zyklen und Belastungen standhalten, eine gleichbleibende Leistung gewährleisten und Betriebsunterbrechungen in Produktionsstätten in Europa und darüber hinaus minimieren.
3 häufige Benutzer Schmerzpunkte für ‘Anlasser Magnetspule vs Relais’ & ihre Lösungen
Szenario 1: Verwirrung bei der Komponentenauswahl für Starter-Systeme
Das Problem: B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in der Kfz-Reparatur- und -Zulieferindustrie, stehen oft vor der Frage, ob sie Anlassermagnete oder Relais für ihren Fahrzeugbestand beschaffen sollen. Diese Verwirrung kann von der austauschbaren Verwendung dieser Begriffe auf dem Markt herrühren, was zu Missverständnissen und der Beschaffung falscher Teile führt. Solche Probleme können zu längeren Ausfallzeiten für Reparaturen, zu Umsatzeinbußen und zu unzufriedenen Kunden führen, die auf ihre Fahrzeuge für den Transport oder für gewerbliche Aktivitäten angewiesen sind.
Die Lösung: Um dieses Problem zu lösen, sollten Einkäufer einen systematischen Ansatz für die Beschaffung von Komponenten verfolgen. Investieren Sie zunächst in umfassende Schulungen für Ihre Mitarbeiter, damit diese die technischen Unterschiede zwischen Anlasser-Magneten und Relais verstehen. Erstellen Sie einen detaillierten Teilekatalog, der Spezifikationen, Kompatibilitätstabellen und Diagramme enthält, um zu verdeutlichen, in welchen Fahrzeugen Magnetspulen und Relais verwendet werden. Nutzen Sie außerdem Partnerschaften mit namhaften Herstellern, die Expertenwissen und Unterstützung bieten können. Stellen Sie bei Ihren Kaufentscheidungen sicher, dass Sie Querverweise zu den Fahrzeugmodellen und den spezifischen Komponenten, die sie benötigen, herstellen, um das Fehlerrisiko zu minimieren und sicherzustellen, dass die richtigen Teile auf Lager sind.
Szenario 2: Umgang mit hohen Ausfallraten bei elektrischen Komponenten
Das Problem: Unternehmen im Automobilsektor haben häufig mit hohen Ausfallquoten bei Anlassermagneten und Relais zu kämpfen, was sich in Form von Ersatzbeschaffungen und Garantieansprüchen als kostspielig erweisen kann. Solche Ausfälle führen nicht nur zu finanziellen Verlusten, sondern schädigen auch den Ruf von Unternehmen, die als Anbieter minderwertiger Produkte wahrgenommen werden. Dieses Szenario ist besonders häufig in Regionen anzutreffen, in denen Umweltbedingungen wie Feuchtigkeit oder extreme Temperaturen elektrische Ausfälle verschlimmern können.
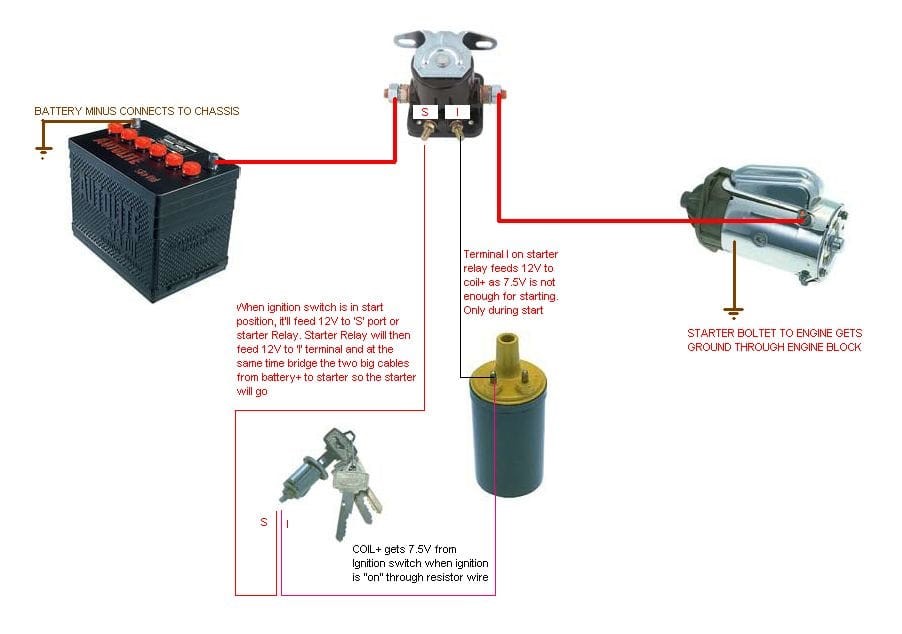
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
Die Lösung: Um dieses Problem zu bekämpfen, sollten B2B-Einkäufer vorrangig hochwertige, langlebige Komponenten beschaffen, die speziell für die örtlichen Bedingungen entwickelt wurden. Führen Sie eine gründliche Marktrecherche durch, um Lieferanten zu finden, die Produkte anbieten, die auf ihre Zuverlässigkeit in schwierigen Umgebungen getestet wurden. Achten Sie bei der Bewertung von Komponenten auf Zertifizierungen, die deren Qualität und Leistung bestätigen. Führen Sie ein solides Qualitätssicherungsprogramm ein, um die Leistung der Komponenten nach der Installation zu überwachen, damit Sie rechtzeitig Rückmeldungen erhalten und Ihren Bestand anpassen können. Ziehen Sie außerdem in Erwägung, eine Beziehung zu Herstellern aufzubauen, um maßgeschneiderte Lösungen oder kundenspezifische Komponenten zu erhalten, die besonderen Umweltanforderungen standhalten.
Szenario 3: Unzulänglichkeiten bei der Diagnose von elektrischen Problemen
Das Problem: Eine häufige Herausforderung für Kfz-Servicestellen ist die Ineffizienz bei der Diagnose, ob ein Startproblem auf ein defektes Magnetventil oder Relais zurückzuführen ist. Die Techniker verbringen oft zu viel Zeit mit der Fehlersuche, was zu Frustration und erhöhten Arbeitskosten führen kann. Verschärft wird dieses Problem durch die Komplexität moderner Fahrzeuge, bei denen die Integration elektronischer Systeme die Ursache von Startproblemen verschleiern kann.
Die Lösung: Um die Effizienz der Diagnose zu steigern, sollten B2B-Kunden in fortschrittliche Diagnosewerkzeuge und in die Ausbildung ihrer Techniker investieren. Rüsten Sie Ihr Servicezentrum mit multifunktionalen Diagnosegeräten aus, mit denen sowohl Anlassermagnete als auch Relais effektiv getestet werden können. Darüber hinaus sollten Sie ein standardisiertes Diagnoseprotokoll erstellen, das die Techniker durch einen systematischen Fehlerbehebungsprozess führt. Dabei sollten auch verwandte Komponenten wie die Batterie und die Verkabelung überprüft werden, bevor auf ein Magnetventil- oder Relaisproblem geschlossen wird. Fortlaufende Schulungen zu den neuesten Technologien und Diagnosetechniken werden Ihre Techniker befähigen, ihre Problemlösungsfähigkeiten zu verbessern und letztendlich die Reparaturzeiten zu verkürzen.
Strategischer Leitfaden für die Materialauswahl für Anlassermagneten und Relais
Welche Materialien werden üblicherweise in Anlassermagneten und -relais verwendet?
Bei der Auswahl von Werkstoffen für Anlassermagnete und Relais ist es wichtig, die spezifischen Anforderungen der Anwendung zu berücksichtigen, einschließlich der elektrischen Leistung, der Umweltbedingungen und der Fertigungsmöglichkeiten. Im Folgenden werden vier gängige Materialien für diese Komponenten analysiert: Kupfer, Aluminium, Kunststoff und Stahl.
Wie trägt Kupfer zur Leistung von Anlassermagneten und Relais bei?
Kupfer ist weithin für seine hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit bekannt und wird daher bevorzugt für die Verdrahtung und die Kontakte in Anlassermagneten und Relais verwendet. Seine hohe thermische und elektrische Leitfähigkeit gewährleistet eine effiziente Energieübertragung, die für einen zuverlässigen Betrieb entscheidend ist.
Vorteile: Die hervorragende Leitfähigkeit von Kupfer führt zu einem geringeren Widerstand, was die Leistung erhöht und die Wärmeentwicklung verringert. Außerdem ist es relativ leicht zu verarbeiten und ermöglicht komplexe Konstruktionen.
Nachteile: Kupfer ist jedoch anfällig für Korrosion, insbesondere in feuchten oder salzhaltigen Umgebungen, was im Laufe der Zeit zu Ausfällen führen kann. Außerdem ist es teurer als Alternativen wie Aluminium.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Kupfer ist für Hochstromanwendungen geeignet, aber seine Korrosionsanfälligkeit muss berücksichtigt werden, insbesondere in Regionen mit rauem Klima.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Einhaltung internationaler Normen wie ASTM B170 für Kupferdraht ist unerlässlich. Einkäufer in Afrika, Südamerika und dem Nahen Osten sollten auch lokale Beschaffungsmöglichkeiten in Betracht ziehen, um die Kosten zu senken.
Warum ist Aluminium eine brauchbare Alternative für Anlassermagnete und -relais?
Aluminium wird aufgrund seines geringen Gewichts und seiner guten Leitfähigkeit zunehmend in Anlassermagneten und Relais eingesetzt. Aluminium ist zwar nicht so leitfähig wie Kupfer, bietet aber ein günstiges Verhältnis zwischen Festigkeit und Gewicht.
Vorteile: Aluminium ist korrosionsbeständig und daher für Außenanwendungen geeignet. Außerdem ist es preiswerter als Kupfer, was die Gesamtproduktionskosten senken kann.
Nachteile: Die geringere Leitfähigkeit bedeutet, dass Aluminiumkomponenten größere Querschnitte benötigen, um die gleiche Leistung wie Kupfer zu erzielen, was die Herstellung möglicherweise komplizierter macht.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminium ist ideal für Anwendungen, bei denen eine Gewichtsreduzierung von entscheidender Bedeutung ist, wie z. B. in der Automobil- und Luftfahrtbranche.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer sollten sich vergewissern, dass Normen wie ASTM B221 für Aluminium-Strangpressprofile eingehalten werden, und die Verfügbarkeit von Aluminiumlegierungen in ihren Regionen berücksichtigen.
Welche Rolle spielt Kunststoff bei Anlassermagneten und -relais?
Kunststoffe, insbesondere Thermoplaste, werden häufig für die Isolierung und das Gehäuse von Anlassermagneten und -relais verwendet. Ihre elektrischen Isoliereigenschaften sind entscheidend für die Vermeidung von Kurzschlüssen.
Vorteile: Kunststoffe sind leicht, kostengünstig und können in komplexe Formen gegossen werden, was vielseitige Designs ermöglicht. Außerdem weisen sie eine gute chemische Beständigkeit auf.
Nachteile: Allerdings halten Kunststoffe hohen Temperaturen und mechanischen Belastungen nicht so gut stand wie Metalle, was im Laufe der Zeit zu einer Verschlechterung führen kann.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Kunststoffbauteile eignen sich für Anwendungen mit geringem bis mittlerem Stromverbrauch, erfordern aber möglicherweise zusätzlichen Schutz in Umgebungen mit hohen Temperaturen.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Einhaltung von Normen wie UL 94 für Entflammbarkeit und ISO 9001 für Qualitätsmanagement kann für die Gewährleistung der Produktzuverlässigkeit entscheidend sein.
Wie erhöht Stahl die Haltbarkeit von Anlassermagneten und -relais?
Stahl wird aufgrund seiner Festigkeit und Langlebigkeit häufig für die strukturellen Komponenten von Anlassermagneten und -relais verwendet. Er ist besonders nützlich bei Anwendungen, die eine robuste mechanische Unterstützung erfordern.
Vorteile: Stahl bietet eine hohe Zugfestigkeit und ist resistent gegen Verformung, so dass er sich für schwere Anwendungen eignet.
Nachteile: Nachteilig ist, dass Stahl schwerer ist als andere Materialien und bei unsachgemäßer Beschichtung oder Behandlung rostanfällig sein kann.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Stahl ist ideal für Umgebungen, in denen mechanische Beanspruchung ein Problem darstellt, aber sein Gewicht kann ein Nachteil bei Anwendungen sein, bei denen ein möglichst geringes Gewicht wichtig ist.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer sollten korrosionsbeständige Beschichtungen in Betracht ziehen und sicherstellen, dass Normen wie die ASTM A36 für Baustahl eingehalten werden.
Übersichtstabelle zur Materialauswahl für Anlassermagnete und -relais
| Material | Typischer Anwendungsfall für Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kupfer | Hochstromverkabelung und Kontakte | Hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Korrosionsanfällig | Hoch |
| Aluminium | Leichtbaukomponenten für die Automobilindustrie | Korrosionsbeständig und leicht | Geringere Leitfähigkeit als Kupfer | Mittel |
| Kunststoff | Isolierung und Gehäuse | Kostengünstig und vielseitig | Begrenzte Hochtemperaturbeständigkeit | Niedrig |
| Stahl | Strukturelle Komponenten für Langlebigkeit | Hohe Festigkeit und Haltbarkeit | Schwerer und anfällig für Rost | Mittel |
Dieser Leitfaden für die Materialauswahl bietet B2B-Einkäufern in verschiedenen Regionen verwertbare Erkenntnisse und gewährleistet fundierte Entscheidungen, die mit den Leistungsanforderungen und Umweltbedingungen in Einklang stehen.
Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für Startermagnete und Relais
Was sind die wichtigsten Schritte im Herstellungsprozess von Anlassermagneten und -relais?
Der Herstellungsprozess von Anlassermagneten und -relais umfasst mehrere kritische Phasen, die alle für die Herstellung qualitativ hochwertiger Komponenten, die den Industriestandards entsprechen, unerlässlich sind.
Materialvorbereitung
Der erste Schritt bei der Herstellung ist die Materialvorbereitung, bei der Rohstoffe wie Kupfer, Stahl und verschiedene Kunststoffe beschafft werden. Bei Magneten wird üblicherweise Kupferdraht für die Wicklung der Spulen verwendet, während für das Gehäuse häufig Stahl eingesetzt wird. Die Lieferanten sollten auf die Qualität der Materialien geprüft werden, da die Haltbarkeit und Funktionalität des Endprodukts stark von diesem Schritt abhängen.
Formgebung und Verformung
In der zweiten Phase werden die Bauteile geformt und gestaltet. Bei Magneten umfasst dies das Wickeln von Kupferdraht zu Spulen und die Formgebung von Metallteilen durch Verfahren wie Stanzen oder Schmieden. Für Relais sind oft komplexere Verfahren erforderlich, einschließlich des präzisen Formens von Kunststoffgehäusen, in denen die elektronischen Komponenten untergebracht sind. Techniken wie CNC-Bearbeitung und Laserschneiden können ebenfalls eingesetzt werden, um die erforderliche Präzision zu erreichen.
Montage
Der dritte Schritt ist die Montage, bei der alle Komponenten zusammengeführt werden. In der Magnetproduktion bedeutet dies, die Spule am Gehäuse zu befestigen, einen Stößelmechanismus zu integrieren und sicherzustellen, dass alle Teile richtig zusammenpassen. Bei Relais umfasst die Montage die Integration von Spule, Anker und Kontaktpunkten. Automatisierte Montagelinien sind üblich, aber auch die manuelle Montage wird für hochpräzise Aufgaben eingesetzt. Qualitätskontrollen in dieser Phase sind entscheidend, um sicherzustellen, dass die Komponenten korrekt zusammengebaut und funktionsfähig sind.
Endbearbeitung
Die letzte Phase der Herstellung ist die Endbearbeitung, die Behandlungen wie Beschichten, Lackieren oder Polieren umfassen kann. Dies verbessert nicht nur die Ästhetik, sondern schützt die Bauteile auch vor Umwelteinflüssen. Bei Magneten und Relais kann eine galvanische Beschichtung oder ein Schutzanstrich die Korrosionsbeständigkeit verbessern, was für Produkte, die in der Automobilindustrie und in industriellen Anwendungen eingesetzt werden, besonders wichtig ist.
Wie wird die Qualitätssicherung bei der Herstellung von Magneten und Relais umgesetzt?
Die Qualitätssicherung (QS) ist ein wichtiger Aspekt des Herstellungsprozesses, der sicherstellt, dass die Produkte sowohl internationalen als auch branchenspezifischen Normen entsprechen.
Welche internationalen Normen gelten für Anlasser-Magnetventile und -Relais?
Internationale Normen wie die ISO 9001 sind für die Aufrechterhaltung eines einheitlichen Qualitätsmanagementsystems von entscheidender Bedeutung. Diese Zertifizierung zeigt, dass die Hersteller in ihren Produktionsprozessen strenge Qualitätsstandards einhalten. Darüber hinaus bedeutet die Einhaltung der CE-Kennzeichnung, dass die Produkte die EU-Sicherheits- und Umweltanforderungen erfüllen, während die API-Normen für bestimmte industrielle Anwendungen gelten können.
Was sind die wichtigsten Punkte der Qualitätskontrolle?
Die Kontrollpunkte für die Qualitätskontrolle (QC) sind strategisch über den gesamten Herstellungsprozess verteilt:
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): An diesem ersten Kontrollpunkt werden die Rohstoffe auf ihre Übereinstimmung mit den Spezifikationen geprüft, bevor die Produktion beginnt.
-
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): IPQC wird während des Fertigungsprozesses durchgeführt und stellt sicher, dass in jeder Phase die Qualitätsstandards eingehalten werden. Dazu kann die Überwachung von Parametern wie Temperatur und Druck während der Formgebung von Bauteilen gehören.
-
Endkontrolle (FQC): Die Endkontrolle erfolgt nach der Montage und Fertigstellung. In dieser Phase werden die Magnetspulen und Relais einer Funktionsprüfung unterzogen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie unter den erwarteten Bedingungen korrekt funktionieren.
Welche Prüfverfahren werden in der Qualitätssicherung üblicherweise eingesetzt?
Die Hersteller wenden verschiedene Prüfverfahren an, um die Funktionalität und Zuverlässigkeit von Magneten und Relais zu überprüfen.
-
Elektrische Prüfung: Dazu gehört die Überprüfung des Spulenwiderstands, der Stromaufnahme und der Reaktionszeit, um sicherzustellen, dass die Komponenten den elektrischen Belastungen in realen Anwendungen gewachsen sind.
-
Mechanische Prüfung: Tests wie Vibrations- und Schocktests bewerten die Haltbarkeit der Komponenten unter extremen Bedingungen und simulieren die Belastungen, denen sie in der Automobilbranche oder in industriellen Umgebungen ausgesetzt sein können.
-
Umweltprüfungen: Komponenten können Temperaturwechsel- und Feuchtigkeitstests unterzogen werden, um sicherzustellen, dass sie rauen Umgebungsbedingungen standhalten, was besonders für Anwendungen in Regionen mit extremen Klimabedingungen wichtig ist.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrollprozesse ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
Für B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, ist die Überprüfung der Qualitätskontrollprozesse eines Lieferanten von größter Bedeutung.
Welche Methoden gibt es für Lieferantenaudits?
Einkäufer können Lieferantenaudits durchführen, um die Herstellungsverfahren und Qualitätssicherungspraktiken direkt zu bewerten. Diese Audits können eine Überprüfung der Zertifizierungen des Lieferanten, der Inspektionsberichte und der Einhaltung der internationalen Normen beinhalten.

Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
Welche Rolle spielen die Inspektionen durch Dritte?
Die Beauftragung von Inspektionsdiensten durch Dritte kann eine unvoreingenommene Bewertung der Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen eines Lieferanten liefern. Diese Inspektoren können stichprobenartige Kontrollen während der Produktion und in der Endphase durchführen und so sicherstellen, dass die Produkte vor dem Versand den vereinbarten Spezifikationen entsprechen.
Was sind die QC/CERT-Nuancen für internationale Einkäufer?
Internationale Einkäufer müssen sich der spezifischen Zertifizierungsnuancen bewusst sein, die ihre Beschaffungsentscheidungen beeinflussen können. Bestimmte Länder können zum Beispiel besondere Vorschriften für Automobilkomponenten haben. Die Kenntnis dieser Vorschriften kann Einkäufern helfen, Probleme mit der Einhaltung von Vorschriften zu vermeiden und die Produktakzeptanz in ihren jeweiligen Märkten sicherzustellen.
Schlussfolgerung
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass die Herstellungsverfahren und Qualitätssicherungspraktiken für Anlassermagnete und Relais komplex und entscheidend für die Gewährleistung der Zuverlässigkeit und Leistung der Produkte sind. Wenn internationale B2B-Einkäufer diese Prozesse verstehen, können sie bei der Auswahl von Lieferanten fundierte Entscheidungen treffen und sicherstellen, dass sie qualitativ hochwertige Komponenten erwerben, die ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen entsprechen.

Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
Praktische Anleitung zur Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais’.’
Einführung
Dieser Leitfaden dient als praktische Checkliste für B2B-Einkäufer, die Anlassermagnete und -relais beschaffen wollen. Das Verständnis der Unterschiede und spezifischen Anforderungen dieser Komponenten ist entscheidend für die Gewährleistung einer zuverlässigen Motorleistung in verschiedenen Fahrzeugen. Wenn Sie diese Schritte befolgen, können Einkäufer fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die ihre Beschaffungsstrategie verbessern.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Legen Sie die technischen Spezifikationen für die Anlasser-Magnetspule oder das Relais klar dar. Dazu gehören die Spannungswerte, die Stromkapazität und die physischen Abmessungen. Eine genaue Definition trägt dazu bei, die Kompatibilität mit bestehenden Systemen zu gewährleisten und kostspielige Rücksendungen oder Ersatzlieferungen zu vermeiden.
- Spannungswerte: Bestimmen Sie die Spannung, mit der Ihr Fahrzeug betrieben wird (z. B. 12 oder 24 V).
- Derzeitige Kapazität: Beurteilen Sie den Leistungsbedarf des Anlassers, um einen Magneten oder ein Relais auszuwählen, das die Last bewältigen kann.
Schritt 2: Forschung Markttrends und Anwendungen
Untersuchen Sie die aktuellen Markttrends und Anwendungen für Anlassermagnete und -relais. Die Kenntnis der neuesten Technologien und gängiger Anwendungen kann Ihnen bei der Auswahl helfen und die für Ihre Bedürfnisse am besten geeigneten Produkte ermitteln.
- Aufstrebende Technologien: Bleiben Sie auf dem Laufenden über die Fortschritte in der Magnet- und Relaistechnik.
- Industrieanwendungen: Analysieren Sie, wie verschiedene Branchen diese Komponenten nutzen, um Ihre Beschaffungsstrategie zu verbessern.
Schritt 3: Potenzielle Lieferanten bewerten
Bevor Sie eine Verpflichtung eingehen, sollten Sie potenzielle Lieferanten gründlich prüfen. Dazu gehört die Beurteilung ihres Rufs, ihrer Produktqualität und ihres Kundendienstes. Zuverlässige Lieferanten können Ihre Gesamtzufriedenheit mit dem Beschaffungsprozess erheblich beeinflussen.
- Unternehmensprofile: Fordern Sie detaillierte Unternehmensprofile und Produktkataloge an.
- Referenzen: Erkundigen Sie sich nach Referenzen von anderen Unternehmen, die ähnliche Bedürfnisse haben und mit dem Anbieter zusammengearbeitet haben.
Schritt 4: Überprüfen von Zertifizierungen und Konformität
Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Produkte den einschlägigen Industrienormen und Zertifizierungen entsprechen. Dies ist entscheidend für die Aufrechterhaltung der Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit, insbesondere in Regionen mit strengen Vorschriften.
- ISO-Zertifizierungen: Prüfen Sie, ob der Lieferant ISO- oder andere relevante Zertifizierungen besitzt.
- Produktkonformität: Überprüfen Sie, ob die Produkte den lokalen und internationalen Sicherheitsstandards entsprechen.
Schritt 5: Muster anfordern und Tests durchführen
Bevor Sie Ihre Bestellung abschließen, sollten Sie Muster der Anlassermagnete und -relais anfordern. Das Testen dieser Muster kann helfen, ihre Kompatibilität und Leistung in Ihrer spezifischen Anwendung zu bestätigen.
- Leistungstests: Prüfen Sie die Muster unter realen Bedingungen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie Ihren Spezifikationen entsprechen.
- Qualitätssicherung: Nutzen Sie diese Gelegenheit, um die allgemeine Qualität und Haltbarkeit der Produkte zu beurteilen.
Schritt 6: Verhandeln Sie die Allgemeinen Geschäftsbedingungen
Führen Sie Gespräche, um vorteilhafte Bedingungen auszuhandeln, einschließlich Preisgestaltung, Lieferfristen und Garantievereinbarungen. Dieser Schritt ist wichtig, um eine für beide Seiten vorteilhafte Beziehung zu gewährleisten.
- Flexibilität in der Preisgestaltung: Achten Sie auf Mengenrabatte oder Sonderangebote, die sich nach dem Umfang Ihrer Bestellung richten.
- Lieferfristen: Legen Sie klare Zeitpläne für die Lieferung fest, um Unterbrechungen Ihres Betriebs zu vermeiden.
Schritt 7: Überprüfen und Abschließen des Kaufvertrags
Sobald alle Bedingungen vereinbart sind, überprüfen Sie den Kaufvertrag sorgfältig, bevor Sie die Bestellung abschließen. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass alle Spezifikationen, Bedingungen und Konditionen in dem Dokument korrekt wiedergegeben sind.
- Juristische Überprüfung: Ziehen Sie in Erwägung, die Vereinbarung von einem Rechtsexperten überprüfen zu lassen, um Ihre Interessen zu schützen.
- Dokumentation: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass alle erforderlichen Unterlagen, einschließlich Garantien und Servicevereinbarungen, beigefügt sind.
Anhand dieser Checkliste können B2B-Einkäufer ihren Beschaffungsprozess für Anlassermagnete und -relais rationalisieren, was zu einer besseren betrieblichen Effizienz und Produktzuverlässigkeit führt.

Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Beschaffung von Anlasser-Magneten und Relais
Bei der Bewertung der Kosten und Preise für die Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten im Vergleich zu Relais ist es entscheidend, die verschiedenen Komponenten zu verstehen, die zur Gesamtkostenstruktur beitragen. In dieser Analyse werden die Kostenkomponenten aufgeschlüsselt, preisbeeinflussende Faktoren ermittelt und umsetzbare Tipps für Einkäufer gegeben, insbesondere auf internationalen Märkten wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa.
Was sind die wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten für Anlassermagnete und -relais?
-
Materialien: Die Rohstoffkosten haben einen erheblichen Einfluss auf die Preisgestaltung sowohl von Anlassermagneten als auch von Relais. Magnetspulen erfordern aufgrund ihrer höheren Stromschaltkapazität im Allgemeinen hochwertigere Metalle und Isoliermaterialien, was zu höheren Kosten führen kann. Im Gegensatz dazu können für Relais weniger teure Materialien verwendet werden, was zu einem niedrigeren Preis beiträgt.
-
Arbeit: Die Arbeitskosten können je nach geografischem Standort und der Komplexität des Herstellungsprozesses variieren. So können Regionen mit niedrigeren Arbeitskosten wettbewerbsfähigere Preise bieten. Allerdings kann der Bedarf an qualifizierten Arbeitskräften für die Montage von Magneten, die oft eine präzise Technik erfordert, die Kosten in die Höhe treiben.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: Dazu gehören Versorgungsleistungen, Wartung und andere indirekte Kosten im Zusammenhang mit der Produktion. Die Gemeinkosten können je nach Produktionsvolumen schwanken; höhere Volumina verringern in der Regel die Gemeinkosten pro Einheit.
-
Werkzeuge: Die Erstinvestition in Werkzeuge kann beträchtlich sein, insbesondere bei kundenspezifischen Komponenten. Magnete erfordern aufgrund ihrer Komplexität oft anspruchsvollere Werkzeuge, was sich auf den Preis auswirken kann. Käufer sollten dies bei der Bewertung der Gesamtbetriebskosten berücksichtigen.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Die Sicherstellung, dass die Produkte den Qualitätsstandards entsprechen, verursacht zusätzliche Kosten. Hubmagnete, die für das Anlassen von Motoren entscheidend sind, erfordern oft strengere Qualitätskontrollverfahren, was den Preis im Vergleich zu Relais erhöhen kann.
-
Logistik: Die Kosten für den Transport von Komponenten können je nach Versandart und Entfernung erheblich variieren. Käufer sollten die Logistikkosten einkalkulieren, insbesondere bei internationalen Sendungen, die durch Incoterms und Zölle beeinflusst werden können.
-
Marge: Die Gewinnspannen der Lieferanten können je nach Wettbewerb auf dem Markt und dem wahrgenommenen Wert der Komponenten variieren. Höhere Margen können bei Magnetventilen aufgrund ihrer Komplexität und kritischen Funktion gerechtfertigt sein.
Was beeinflusst die Preisgestaltung von Magneten und Relais?
-
Menge/Mindestbestellmenge: Mindestbestellmengen (MOQ) können die Preisgestaltung erheblich beeinflussen. Lieferanten gewähren oft Rabatte für Großeinkäufe, was für Unternehmen, die ihre Kosten senken wollen, von Vorteil sein kann.
-
Spezifikationen und Anpassung: Kundenspezifische Spezifikationen führen oft zu höheren Kosten, da spezielle Materialien oder Herstellungsverfahren erforderlich sind. Die Käufer müssen die Vorteile der kundenspezifischen Anpassung gegen die höheren Kosten abwägen.
-
Qualität und Zertifizierungen: Komponenten, die internationalen Qualitätsstandards oder spezifischen Zertifizierungen (z. B. ISO, CE) entsprechen, können höhere Preise erzielen. Käufer auf regulierten Märkten sollten der Qualität den Vorzug geben, auch wenn dies zu höheren Vorabkosten führt.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Die Zuverlässigkeit und der Ruf des Lieferanten können die Preisgestaltung beeinflussen. Etablierte Anbieter mit nachgewiesener Erfolgsbilanz können einen Aufschlag verlangen, während neue Marktteilnehmer möglicherweise niedrigere Preise anbieten, um Marktanteile zu gewinnen.
-
Incoterms: Die Lieferbedingungen können die Gesamtkosten beeinflussen. Käufer sollten sich über die Auswirkungen der verschiedenen Incoterms im Klaren sein, da sie bestimmen, wer das Risiko und die Kosten für Transport und Zollabfertigung trägt.
Wie können internationale B2B-Einkäufer ihre Kosten optimieren?
-
Verhandlung: Die Aufnahme von Verhandlungen mit Lieferanten kann zu besseren Preisen führen, insbesondere bei größeren Aufträgen. Einkäufer sollten bereit sein, über Volumen, Zahlungsbedingungen und Lieferpläne zu sprechen, um sich günstige Konditionen zu sichern.
-
Fokus auf Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO): Berücksichtigen Sie nicht nur den Kaufpreis, sondern auch die Gesamtbetriebskosten, zu denen auch die Kosten für Installation, Wartung und mögliche Ausfallzeiten gehören. Die Wahl einer höherwertigen Komponente kann langfristig zu niedrigeren Kosten führen.
-
Preisdifferenzen verstehen: In verschiedenen Regionen können unterschiedliche Marktbedingungen herrschen, die sich auf die Preisgestaltung auswirken. Käufer sollten sich über lokale Markttrends, Währungsschwankungen und wirtschaftliche Faktoren informieren, die sich auf die Kosten auswirken könnten.
-
Diversifizierung der Lieferanten: Der Aufbau von Beziehungen zu mehreren Lieferanten kann eine Hebelwirkung bei Verhandlungen entfalten und die Abhängigkeit von einer einzigen Quelle verringern, was zu einer besseren Preisgestaltung führen kann.
Schlussfolgerung
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass die Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten und -relais ein komplexes Zusammenspiel von Kostenkomponenten und Preiseinflussfaktoren beinhaltet. Wenn internationale B2B-Einkäufer diese Faktoren verstehen, können sie fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen und Budgetvorgaben in Einklang stehen. Denken Sie daran, dass die Preise je nach Auftragslage stark variieren können, und es ist ratsam, die Beschaffung mit einer umfassenden Kostenanalyse im Hinterkopf anzugehen.
Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich zwischen Startermagnet und Relais mit anderen Lösungen
Einführung in alternative Lösungen bei Startsystemen
Bei der Bewertung von Anlassersystemen ziehen Unternehmen häufig sowohl Anlassermagnete als auch Relais in Betracht. Es gibt jedoch alternative Lösungen, mit denen ähnliche Ziele erreicht werden können und die gleichzeitig spezifische betriebliche Anforderungen erfüllen. Ein Verständnis dieser Alternativen kann B2B-Käufern Optionen bieten, die für ihre Anwendungen besser geeignet sind, sei es in der Automobilindustrie, in der Industrie oder in anderen Bereichen des Maschinenbaus.
Vergleichstabelle Startermagnet vs. Relais und alternative Lösungen
| Vergleichsaspekt | Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais | Halbleiterrelais | Direkter Batterieanschluss |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Hochstromschaltung; in der Regel zuverlässiger beim Anlassen von Motoren. | Schnelles Schalten, minimaler Leistungsverlust und längere Lebensdauer. | Direkte Kraftübertragung; hohes Ausgangsdrehmoment. |
| Kosten | Moderate Kosten; variiert je nach Marke und Anwendung. | Höhere Anfangskosten; aufgrund der Langlebigkeit auf lange Sicht kosteneffektiv. | Niedrige Anfangskosten; potenziell höhere Betriebskosten aufgrund von Verschleiß. |
| Einfache Implementierung | Im Allgemeinen einfach zu installieren; integriert mit dem Anlasser. | Erfordert komplexere Schaltkreise; möglicherweise werden zusätzliche Komponenten benötigt. | Einfache Installation; direkte Verkabelung mit der Batterie. |
| Wartung | Mäßig; erfordert möglicherweise regelmäßige Kontrollen auf Verschleiß und Korrosion. | Minimal; in der Regel wartungsfrei. | Hoch; verschleißanfällig und muss möglicherweise häufig ausgetauscht werden. |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Ideal für Kraftfahrzeuge und schwere Maschinen, bei denen eine hohe Leistung erforderlich ist. | Am besten geeignet für Anwendungen, die hohe Schaltgeschwindigkeiten und geringe Verlustleistung erfordern, wie z. B. HLK-Systeme. | Geeignet für einfache Systeme, bei denen die Kosten im Vordergrund stehen und eine hohe Effizienz weniger wichtig ist. |
Detaillierte Aufschlüsselung der alternativen Lösungen
1. Halbleiterrelais (SSR)
Halbleiterrelais sind elektronische Schaltgeräte, die Halbleitereigenschaften nutzen, um ohne bewegliche Teile ein- oder auszuschalten. Sie bieten schnellere Schaltzeiten als herkömmliche mechanische Relais oder Magnetspulen und eignen sich daher ideal für Anwendungen, die Hochgeschwindigkeitsvorgänge erfordern. Während die Anschaffungskosten für SSRs im Allgemeinen höher sind, können ihre Langlebigkeit und ihr minimaler Wartungsbedarf im Laufe der Zeit zu niedrigeren Gesamtbetriebskosten führen. Sie können jedoch nicht so hohe Stromlasten wie Magnetspulen bewältigen, was ihren Einsatz in Hochleistungsanwendungen einschränkt.
2. Direkter Batterieanschluss
Bei dieser Methode wird der Anlasser direkt an die Batterie angeschlossen, wobei das Relais oder die Magnetspule vollständig umgangen werden. Sie ermöglicht eine maximale Drehmomentabgabe und kann in Situationen, in denen sofortige Leistung erforderlich ist, sehr effektiv sein. Allerdings kann dieser Ansatz zu einem erheblichen Verschleiß des Anlassers führen und aufgrund des häufigen Austauschs höhere Betriebskosten verursachen. Darüber hinaus ergeben sich Sicherheitsbedenken, da direkte Verbindungen bei unsachgemäßer Handhabung die Gefahr von Kurzschlüssen oder Bränden bergen können.
Schlussfolgerung: Wie Sie die richtige Lösung für Ihre Bedürfnisse wählen
Die Auswahl der richtigen Startsystemlösung erfordert eine sorgfältige Abwägung der spezifischen betrieblichen Anforderungen und Zwänge. B2B-Käufer sollten Faktoren wie Leistungsanforderungen, Budgetbeschränkungen, Installationsmöglichkeiten und Wartungsvorlieben bewerten. Für Anwendungen, die eine hohe Zuverlässigkeit und Leistung erfordern, können Anlasser mit Magnetspulen die bessere Wahl sein. In Umgebungen, in denen Effizienz und Geschwindigkeit im Vordergrund stehen, könnten dagegen Halbleiterrelais die bessere Wahl sein. Direkte Batterieanschlüsse können für preisbewusste Käufer geeignet sein, sollten aber wegen möglicher langfristiger Kosten und Sicherheitsprobleme mit Vorsicht genossen werden. Durch eine sorgfältige Bewertung dieser Alternativen können Unternehmen sicherstellen, dass sie in Lösungen investieren, die mit ihren betrieblichen Zielen übereinstimmen.
Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für Anlasser und Relais
Was sind die wichtigsten technischen Eigenschaften von Anlassermagneten und -relais?
Bei der Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten und -relais ist die Kenntnis ihrer kritischen Spezifikationen von entscheidender Bedeutung, um die Kompatibilität und Leistung in Kfz-Anwendungen zu gewährleisten. Hier sind einige wichtige technische Eigenschaften, die Sie beachten sollten:
-
Werkstoffgüte
Die in Anlassermagneten und -relais verwendeten Materialien haben einen erheblichen Einfluss auf deren Haltbarkeit und Funktionalität. Zu den gängigen Materialien gehören Kupfer für die elektrischen Kontakte aufgrund seiner hervorragenden Leitfähigkeit und Stahl oder Aluminium für das Gehäuse, das für strukturelle Integrität sorgt. Die Wahl hochwertiger Materialien kann die Korrosions- und Hitzebeständigkeit erhöhen und eine lange Lebensdauer in unterschiedlichen Umgebungen gewährleisten. -
Aktuelle Bewertung
Diese Angabe gibt den maximalen Strom an, den die Magnetspule oder das Relais ohne Ausfall verarbeiten kann. Für B2B-Käufer ist es entscheidend, die Stromstärke mit den Anforderungen des jeweiligen Fahrzeugs oder der Anwendung abzugleichen. Eine Unterschätzung dieser Stromstärke kann zu Überhitzung und vorzeitigem Ausfall führen, während eine Überschätzung unnötige Kosten verursachen kann. -
Spulenspannung
Die Spulenspannung ist die Spannung, die erforderlich ist, um die Magnetspule oder das Relais zu aktivieren. In der Regel liegt sie bei Kraftfahrzeuganwendungen zwischen 12 und 24 V. Die Kenntnis der Spulenspannung ist wichtig, um sicherzustellen, dass die Komponente im elektrischen System des Fahrzeugs effizient arbeitet. Unangepasste Spannungswerte können zu Fehlfunktionen oder Schäden führen. -
Reaktionszeit
Diese Eigenschaft definiert, wie schnell der Magnet oder das Relais bei Auslösung von einem offenen in einen geschlossenen Zustand wechseln kann. Schnelle Reaktionszeiten sind bei Anwendungen im Automobilbereich entscheidend, wo die Zeitsteuerung die Motorleistung beeinflussen kann. Käufer sollten diesen Faktor berücksichtigen, vor allem in Hochleistungs- oder Rennsportumgebungen, wo eine schnelle Aktivierung unerlässlich ist. -
Betriebstemperaturbereich
Diese Spezifikation beschreibt die Umgebungsbedingungen, denen die Magnetspule oder das Relais standhalten kann. Komponenten müssen bei unterschiedlichen Temperaturen effektiv funktionieren, insbesondere in Regionen mit extremen Wetterbedingungen. Ein breiterer Betriebstemperaturbereich kann ein bedeutender Vorteil sein und bietet Vielseitigkeit auf verschiedenen Märkten. -
Montage Typ
Die Montagekonfiguration eines Anlassermagneten oder -relais kann sich auf die Installationsfreundlichkeit und Kompatibilität mit bestimmten Fahrzeugen auswirken. Zu den Optionen gehören Anschraub-, Einrast- oder Direktverdrahtungstypen. Die Kenntnis der Montageanforderungen trägt dazu bei, dass sich die Komponente nahtlos in die vorgesehene Anwendung einfügt und Installationsprobleme minimiert werden.
Was sind die gängigen Fachausdrücke auf dem Markt für Anlasser-Magnetventile und -Relais?
Die Vertrautheit mit dem Branchenjargon ist für eine effektive Kommunikation und Verhandlung bei B2B-Transaktionen entscheidend. Im Folgenden finden Sie einige gängige Begriffe im Zusammenhang mit Anlassermagneten und -relais:
-
OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
Dieser Begriff bezieht sich auf Unternehmen, die Teile herstellen, die bei der Originalherstellung von Fahrzeugen verwendet werden. Bei der Beschaffung von Bauteilen bevorzugen die Käufer häufig OEM-Teile, um Kompatibilität und Qualität zu gewährleisten. -
MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
Die MOQ gibt die kleinste Menge eines Produkts an, die ein Lieferant zu verkaufen bereit ist. Die Kenntnis der MOQ ist für Einkäufer von entscheidender Bedeutung, um ihre Bestände effektiv zu verwalten und Über- oder Unterbestände zu vermeiden. -
RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
Eine Anfrage ist ein formelles Dokument, das zur Einholung von Preisangeboten von Lieferanten verwendet wird. Darin werden die spezifischen Anforderungen und Spezifikationen für die Komponenten dargelegt, so dass die Einkäufer die Angebote effizient vergleichen können. -
Incoterms
Internationale Handelsklauseln (Incoterms) sind standardisierte Handelsbedingungen, die die Verantwortlichkeiten von Käufern und Verkäufern bei internationalen Transaktionen festlegen. Die Vertrautheit mit diesen Bedingungen hilft bei der Klärung von Versandkosten, Risikoübergang und Lieferverantwortung, was für die grenzüberschreitende Beschaffung von entscheidender Bedeutung ist. -
Vorlaufzeit
Damit ist die Zeit gemeint, die von der Bestellung bis zur Lieferung vergeht. Die Kenntnis der Vorlaufzeiten ist für das Lieferkettenmanagement von entscheidender Bedeutung und hilft den Unternehmen bei der Planung ihrer Tätigkeiten, um Verzögerungen zu vermeiden. -
Ersatzteilmarkt
Dieser Begriff bezieht sich auf Teile und Zubehör, die nicht vom Originalhersteller stammen. Aftermarket-Komponenten können kostengünstige Alternativen für Käufer bieten, die nach Ersatz- oder Aufrüstungsoptionen für Magnetventile und Relais suchen.
Wenn B2B-Einkäufer diese technischen Eigenschaften und Handelsbedingungen kennen, können sie fundierte Entscheidungen treffen und sicherstellen, dass sie die richtigen Startermagnete und Relais für ihre Anwendungen auswählen.
Navigation der Marktdynamik und der Beschaffungstrends im Sektor Anlassermagnete und Relais
Was sind die aktuelle Marktdynamik und die wichtigsten Trends im Sektor Anlasser-Magneten und Relais?
Der weltweite Markt für Anlasser und Relais erlebt ein bedeutendes Wachstum, das durch verschiedene Faktoren angetrieben wird, darunter die steigende Nachfrage nach Fahrzeugen, Fortschritte in der Automobiltechnologie und die zunehmende Verbreitung von Elektro- und Hybridfahrzeugen. Da die Märkte in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa expandieren, wird der Bedarf an zuverlässigen Anlassersystemen immer größer. Internationale B2B-Einkäufer sind besonders darauf bedacht, qualitativ hochwertige Komponenten zu beschaffen, die den unterschiedlichsten Umweltbedingungen standhalten, da in diesen Regionen oft unterschiedliche Klimabedingungen herrschen, die sich auf die Fahrzeugleistung auswirken.
Neue Technologien wie intelligente Sensoren und IoT-fähige Geräte verändern die Art und Weise, wie Startersysteme entwickelt und hergestellt werden. Diese Innovationen verbessern nicht nur die Leistung, sondern ermöglichen auch eine Echtzeit-Diagnose und senken so die Wartungskosten. Darüber hinaus veranlasst die zunehmende Elektrifizierung von Fahrzeugen die Hersteller dazu, in Forschung und Entwicklung zu investieren, um die Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit von Magnetventilen und Relais zu verbessern und sie zu integralen Komponenten in modernen Fahrzeugen zu machen.
Darüber hinaus entwickelt sich die Wettbewerbslandschaft weiter: Anbieter aus Schwellenländern wie Vietnam und Brasilien bieten kostengünstige Lösungen an, ohne Kompromisse bei der Qualität einzugehen. B2B-Einkäufer sollten auf die Fähigkeiten der Lieferanten achten und sicherstellen, dass sie internationale Standards und Zertifizierungen erfüllen können. Die Nutzung digitaler Plattformen für Beschaffung und Einkauf kann die Abläufe rationalisieren und Zugang zu einer breiteren Palette von Produkten und Lieferanten bieten, wodurch die Effizienz der Lieferkette insgesamt verbessert wird.
Wie wirken sich Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung auf den Markt für Startermagnete und Relais aus?
Da die Automobilindustrie mit ökologischen Herausforderungen zu kämpfen hat, sind Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung für B2B-Einkäufer im Bereich Anlassermagnete und Relais zu entscheidenden Faktoren geworden. Die Produktionsprozesse für diese Komponenten können erhebliche Auswirkungen auf die Umwelt haben, einschließlich der Erschöpfung von Ressourcen und der Verschmutzung. Folglich bevorzugen internationale Einkäufer zunehmend Lieferanten, die nachhaltige Praktiken anwenden, wie z. B. die Verwendung von recycelbaren Materialien und die Reduzierung von Abfällen in ihren Herstellungsprozessen.

Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
Die Nachfrage nach ‘grünen’ Zertifizierungen steigt, da die Käufer Lieferanten suchen, die internationale Umweltstandards einhalten. Zertifizierungen wie ISO 14001, die sich auf wirksame Umweltmanagementsysteme konzentrieren, werden für Unternehmen, die sich auf dem Markt Glaubwürdigkeit und Vertrauen verschaffen wollen, immer wichtiger. Darüber hinaus werden Materialien wie recycelte Metalle und umweltfreundliche Kunststoffe bevorzugt, um den globalen Nachhaltigkeitszielen und den Erwartungen der Verbraucher gerecht zu werden.
Ethische Lieferketten sind ebenso wichtig; B2B-Einkäufer prüfen ihre Lieferanten, um faire Arbeitspraktiken und Transparenz während des gesamten Beschaffungsprozesses sicherzustellen. Dies stärkt nicht nur den Ruf der Marke, sondern mindert auch die Risiken, die mit Unterbrechungen der Lieferkette verbunden sind. Indem sie Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung in ihre Beschaffungsstrategien einbeziehen, können Unternehmen zu einer verantwortungsvolleren Automobilindustrie beitragen und gleichzeitig eine zunehmend umweltbewusste Kundschaft ansprechen.
Was ist die kurze Entwicklung und Geschichte von Anlassermagneten und Relais?
Die Entwicklung von Anlassermagneten und -relais geht auf das frühe 20. Jahrhundert zurück, als die ersten elektrischen Anlasser in Automobilen eingeführt wurden. Ursprünglich waren diese Geräte rudimentär und basierten auf mechanischen Systemen, um den Motor in Gang zu setzen. Mit dem Fortschritt der Automobiltechnik wurde der Bedarf an zuverlässigeren und effizienteren Systemen deutlich.
In den 1950er und 1960er Jahren begannen Magnetspulen und Relais, elektromagnetische Prinzipien zu nutzen, die eine bessere Steuerung von Schaltkreisen mit hoher Leistung durch Signale mit geringer Leistung ermöglichten. Dies markierte einen bedeutenden Wandel, da es den Herstellern ermöglichte, kompaktere und effizientere Komponenten zu produzieren. Im Laufe der Jahrzehnte haben Fortschritte bei den Materialien und Fertigungstechniken die Leistung und Haltbarkeit dieser Geräte weiter verbessert.
Heute hat die Integration von Elektronik in Anlassersysteme zur Entwicklung von intelligenten Magneten und Relais geführt, die mit Fahrzeugsystemen kommunizieren können und Echtzeitdaten und -diagnosen liefern. Diese Entwicklung spiegelt die allgemeinen Trends in der Automobilindustrie in Richtung Automatisierung, Effizienz und Nachhaltigkeit wider und macht Anlassermagnete und -relais zu wichtigen Komponenten in modernen Fahrzeugen.
Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Einkäufer von Startermagneten vs. Relais
-
Wie erkenne ich, ob ich einen Anlassermagneten oder ein Relais benötige?
Um festzustellen, ob Sie eine Anlassermagnetspule oder ein Relais benötigen, prüfen Sie zunächst die Symptome der Fehlfunktion. Wenn Ihr Fahrzeug beim Startversuch Anzeichen wie ein einzelnes Klicken zeigt, könnte dies auf ein defektes Solenoid hinweisen. Wenn der Anlasser dagegen nur sporadisch oder gar nicht anspringt, könnte ein Relaisproblem vorliegen. Konsultieren Sie das Handbuch Ihres Fahrzeugs oder einen vertrauenswürdigen Techniker, um festzustellen, welche Komponente für Ihr spezielles Modell geeignet ist, zumal einige Fahrzeuge beide verwenden. -
Welches ist das beste Anlasser-Magnetventil für Schwerlastanwendungen?
Für Hochleistungsanwendungen sollten Sie nach Magneten suchen, die für höhere Stromstärken und eine robuste Konstruktion ausgelegt sind. Marken, die für ihre Langlebigkeit in industriellen Umgebungen bekannt sind, wie Bosch oder Denso, werden häufig empfohlen. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Magnet die spezifischen Spannungs- und Stromstärkenanforderungen Ihrer Anwendung erfüllt. Ziehen Sie außerdem Magnete mit wetterfesten Eigenschaften in Betracht, wenn sie rauen Umgebungen ausgesetzt sind, da dies die Langlebigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit erhöhen kann. -
Welche Faktoren sollte ich bei der internationalen Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten und Relais berücksichtigen?
Bei der internationalen Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten und Relais sollten Sie den Ruf des Lieferanten, die Einhaltung internationaler Qualitätsstandards und die Verfügbarkeit von Zertifizierungen wie ISO oder CE prüfen. Berücksichtigen Sie die Produktionskapazitäten, die Vorlaufzeiten und die Fähigkeit des Lieferanten, Produkte an Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen anzupassen. Beurteilen Sie außerdem die logistischen Möglichkeiten, einschließlich der Versandoptionen und -kosten, um eine rechtzeitige Lieferung an Ihren Standort zu gewährleisten. -
Wie hoch sind die Mindestbestellmengen (MOQs) für Anlassermagnete und Relais?
Die Mindestbestellmengen (MOQs) können je nach Anbieter und Produkt stark variieren. Bei Standardartikeln können die Mindestbestellmengen zwischen 50 und 500 Stück liegen, während für Sonderanfertigungen größere Mengen erforderlich sein können. Lassen Sie sich die MOQs immer von potenziellen Lieferanten bestätigen, um Ihre Einkaufsstrategie mit deren Anforderungen abzustimmen. Wenn Sie klein anfangen, suchen Sie nach Lieferanten, die flexible Mindestbestellmengen anbieten, oder erwägen Sie den gemeinsamen Einkauf mit anderen Unternehmen, um die Mindestmenge zu erreichen. -
Wie kann ich die Qualität von Anlassermagneten und Relais sicherstellen, wenn ich sie in großen Mengen kaufe?
Um die Qualität beim Kauf von Anlassermagneten und Relais in großen Mengen zu gewährleisten, sollten Sie Muster anfordern, bevor Sie eine große Bestellung aufgeben. Führen Sie gründliche Lieferantenaudits durch, einschließlich der Überprüfung der Herstellungsverfahren und Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen. Achten Sie außerdem auf Prüfzertifikate Dritter und Kundenrezensionen. Legen Sie in Ihrer Kaufvereinbarung klare Qualitätsstandards fest und erwägen Sie die Einführung eines Qualitätssicherungsprozesses nach Erhalt der Produkte, um die Einhaltung der Spezifikationen zu überprüfen. -
Welche Zahlungsbedingungen werden normalerweise für internationale Käufe von Anlassermagneten und -relais angeboten?
Die Zahlungsbedingungen für internationale Einkäufe können variieren, zu den üblichen Optionen gehören jedoch Vorauszahlung, Akkreditiv und Nettobedingungen (z. B. netto 30 oder netto 60 Tage). Es ist wichtig, die Zahlungsbedingungen zu besprechen und auszuhandeln, die für beide Parteien akzeptabel sind, und dabei Faktoren wie den Auftragsumfang und die Vertrauenswürdigkeit des Lieferanten zu berücksichtigen. Die Verwendung sicherer Zahlungsmethoden wie PayPal oder Treuhanddienste kann das Risiko bei internationalen Transaktionen ebenfalls verringern. -
Was sind die üblichen Versandoptionen für internationale Bestellungen von Anlassermagneten und Relais?
Zu den üblichen Versandoptionen für internationale Bestellungen gehören Luftfracht, Seefracht und Kurierdienste. Luftfracht ist schneller, aber teurer, während Seefracht für größere Sendungen kostengünstig ist, aber länger dauert. Wählen Sie eine Versandart je nach Dringlichkeit, Budget und Umfang der Bestellung. Ziehen Sie außerdem Lieferanten in Betracht, die einen Haus-zu-Haus-Service anbieten, um die Logistik zu vereinfachen und die Komplexität der Zollabfertigung zu verringern. -
Wie gehe ich bei der Zollabfertigung von Anlasser-Magneten und -Relais vor?
Um die Zollabfertigung von Anlassermagneten und Relais effizient abzuwickeln, stellen Sie sicher, dass alle Unterlagen korrekt und vollständig sind, einschließlich Handelsrechnungen, Packlisten und Versandetiketten. Arbeiten Sie mit Ihrem Lieferanten zusammen, um alle erforderlichen Zertifizierungen zu erhalten und die Einfuhrbestimmungen Ihres Landes einzuhalten. Die Einschaltung eines Zollmaklers kann den Prozess ebenfalls vereinfachen, da er Ihnen hilft, die für elektronische Bauteile geltenden Zölle und Abgaben zu umgehen und gleichzeitig die Einhaltung der lokalen Gesetze zu gewährleisten.
Top 2 Anlasser-Magnetventil vs. Relais Liste der Hersteller & Lieferanten
1. Ford Trucks - Anlasserrelais und Magnetspule
Domäne: ford-trucks.com
Registriert: 1997 (28 Jahre)
Einleitung: Anlasserrelais und Anlasser-Magnetspule werden im Automobilbereich oft verwechselt. Ein Anlasserrelais wird in der Regel an der Spritzwand oder am Innenkotflügel montiert und schaltet den vom Anlasser benötigten hohen Strom. Im Gegensatz dazu ist ein Solenoid ein elektrisch gesteuertes Gerät, das einen Kolben betätigt und oben auf dem Anlassermotor montiert wird, um den Anlasserantrieb zu aktivieren. Die Hauptfunktion des Relais ist...
2. Dotheton - Relais und Hubmagnete
Domäne: dotheton.com
Registriert: 2007 (18 Jahre)
Einleitung: Relais sind elektrisch gesteuerte Schalter, die in der Regel mit 10 A bis 50 A belastet werden, während Magnetspulen elektrisch gesteuerte Kolben sind, die wesentlich mehr Strom bewältigen können, in Kraftfahrzeuganwendungen oft mehr als 600 A. Ein Anlassermagnet und ein Anlasserrelais dienen demselben Zweck, können aber unterschiedlich gestaltet sein. Hubmagnete werden für Hochstromanwendungen wie Anlasser verwendet, während Relais für...
Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
Für internationale B2B-Einkäufer ist es wichtig, sich in der komplexen Landschaft der Automobilkomponenten zurechtzufinden und die Unterschiede zwischen Anlassermagneten und Relais zu verstehen. Beide Geräte spielen eine wichtige Rolle bei der Erleichterung des Zündvorgangs, doch ihre einzigartigen Eigenschaften beeinflussen die Beschaffungsentscheidungen. Eine Magnetspule, die oft eine höhere Stromstärke bewältigen kann, kann bei Anwendungen mit hohem Bedarf bevorzugt werden, während Relais ein zuverlässiges, effizientes Schalten bei geringerem Strombedarf ermöglichen.
Strategische Beschaffung bedeutet in diesem Zusammenhang nicht nur, die richtige Komponente auszuwählen, sondern auch die Dynamik der Lieferkette zu verstehen. Einkäufer müssen Faktoren wie die Zuverlässigkeit der Lieferanten, die Qualitätssicherung und die Auswirkungen regionaler Fertigungsmöglichkeiten berücksichtigen. Durch die Pflege enger Beziehungen zu Herstellern und Händlern können sich Unternehmen bessere Preise, Lieferzeiten und den Zugang zu innovativen Technologien sichern.
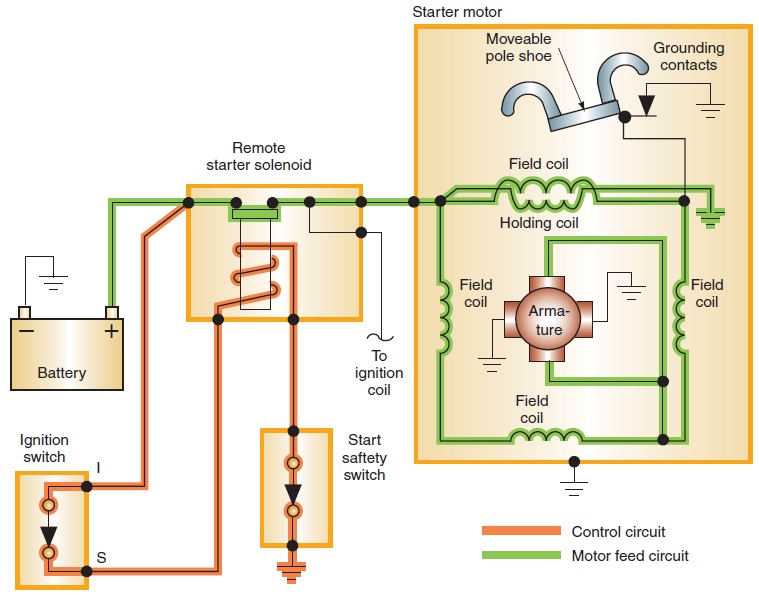
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Anlasser-Magnetspule vs. Relais
In Zukunft wird die weltweite Nachfrage nach zuverlässigen Automobilkomponenten weiter steigen, insbesondere in den Schwellenländern in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa. Durch strategische Beschaffung können sich B2B-Einkäufer so positionieren, dass sie diese Nachfrage effektiv bedienen können. Engagieren Sie sich mit Lieferanten, die die lokalen Marktbedürfnisse und -trends kennen, um sicherzustellen, dass Ihr Unternehmen in einer sich entwickelnden Landschaft wettbewerbsfähig bleibt. Nutzen Sie die Gelegenheit, Ihre Lieferkettenstrategie heute zu verbessern, um morgen widerstandsfähiger zu sein.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.