Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how does a car alternator work
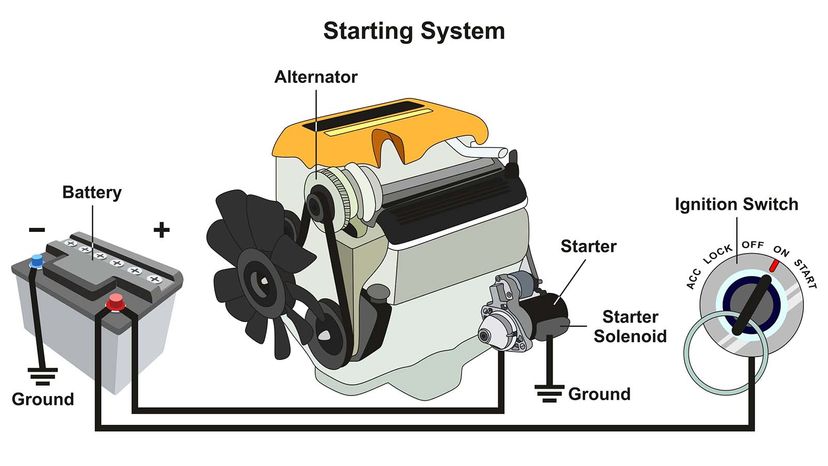
In the competitive landscape of automotive components, understanding how a car alternator works is crucial for B2B buyers looking to enhance their procurement strategies. The alternator, a key player in a vehicle’s electrical system, converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, ensuring optimal performance of batteries and electrical components. However, sourcing high-quality alternators involves navigating a complex market filled with diverse types, applications, and specifications.
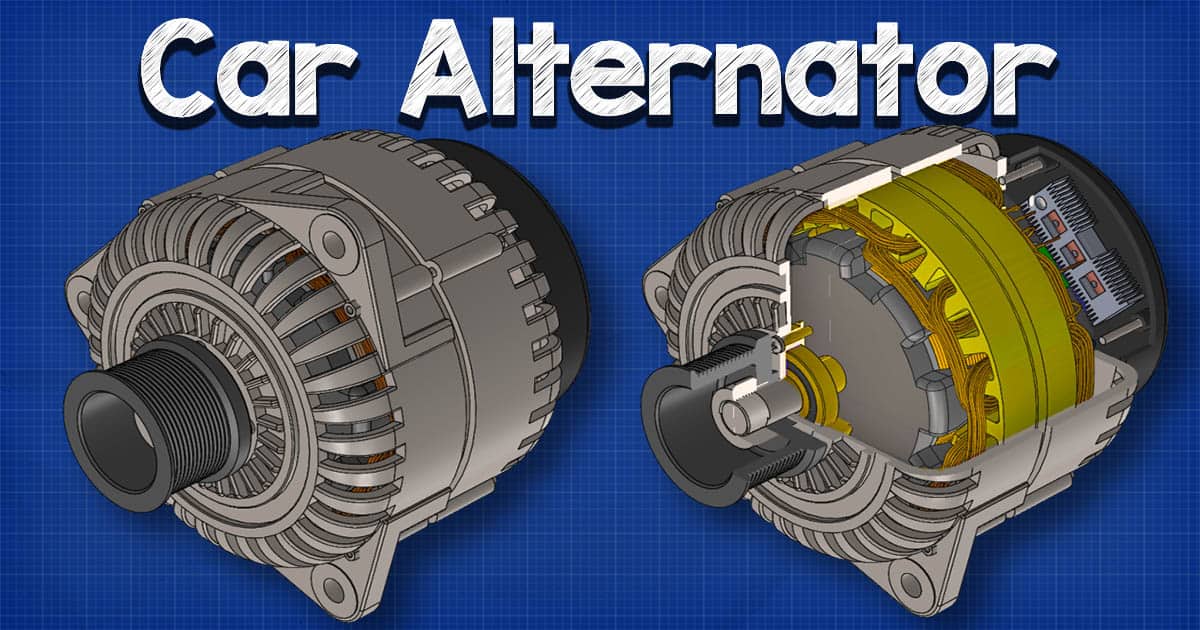
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate workings of car alternators, examining their major components such as rotors, stators, and rectifiers. It also addresses critical factors for international buyers, including supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and regional compliance standards. For stakeholders in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Brazil and Nigeria—this guide serves as an essential resource, empowering informed purchasing decisions and fostering strategic supplier partnerships.
By equipping B2B buyers with in-depth knowledge about alternators and their functionalities, this guide not only enhances your understanding but also helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing decisions. Whether you are looking to optimize your supply chain or ensure the reliability of your automotive offerings, this resource will be instrumental in navigating the global market for car alternators effectively.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 2 How Does A Car Alternator Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how does a car alternator work
- Understanding how does a car alternator work Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how does a car alternator work
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how does a car alternator work’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how does a car alternator work
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how does a car alternator work
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how does a car alternator work’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how does a car alternator work Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how does a car alternator work With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how does a car alternator work
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how does a car alternator work Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how does a car alternator work
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how does a car alternator work
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Understanding how does a car alternator work Types and Variations
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard-Lichtmaschine | Converts mechanical energy to DC; uses diodes for rectification. | Automotive manufacturing and repair shops | Pros: Reliable, widely available. Cons: Limited efficiency at low RPMs. |
| Hochleistungs-Lichtmaschine | Designed for performance; higher amperage output. | Rennsport, schwere Nutzfahrzeuge | Pros: Supports high-demand electrical systems. Cons: Higher cost, may require modifications. |
| Intelligenter Generator | Features advanced voltage regulation and diagnostics. | Fleet management, electric vehicles | Pros: Improved battery life, real-time monitoring. Cons: More complex, potentially higher repair costs. |
| Diesel Engine Alternator | Optimized for diesel applications; built for durability. | Commercial trucks, agricultural machinery | Pros: Robust design, handles higher loads. Cons: Heavier, may not fit standard vehicles. |
| Marine-Lichtmaschine | Corrosion-resistant, designed for harsh environments. | Marine vessels, offshore equipment | Pros: Durable in marine conditions. Cons: Typically more expensive due to specialized materials. |
Was sind die wichtigsten Merkmale von Standard-Generatoren?
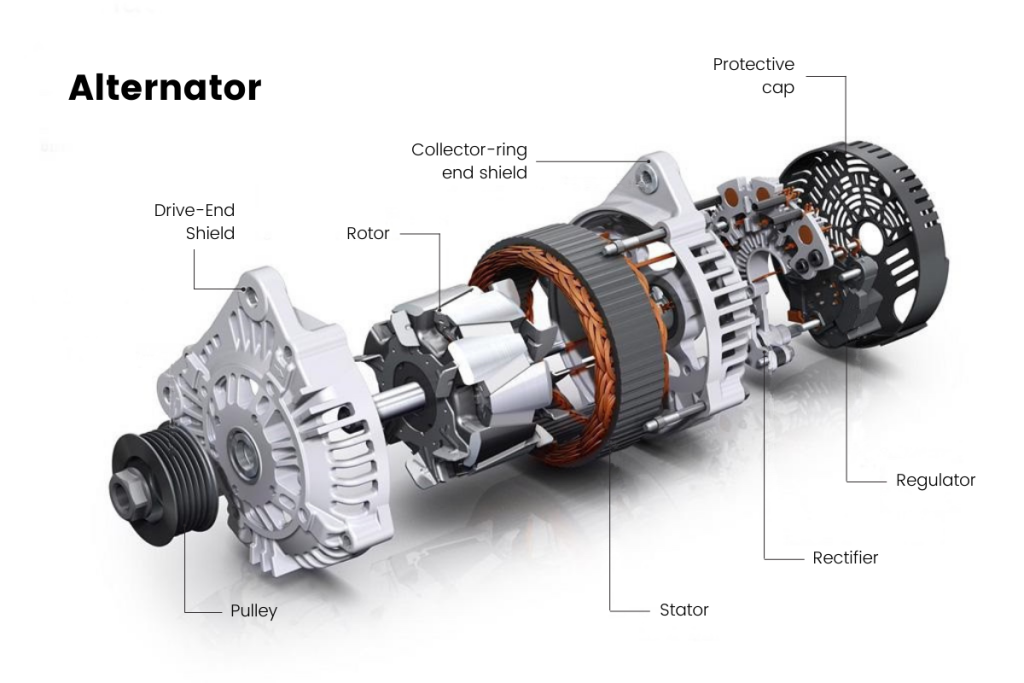
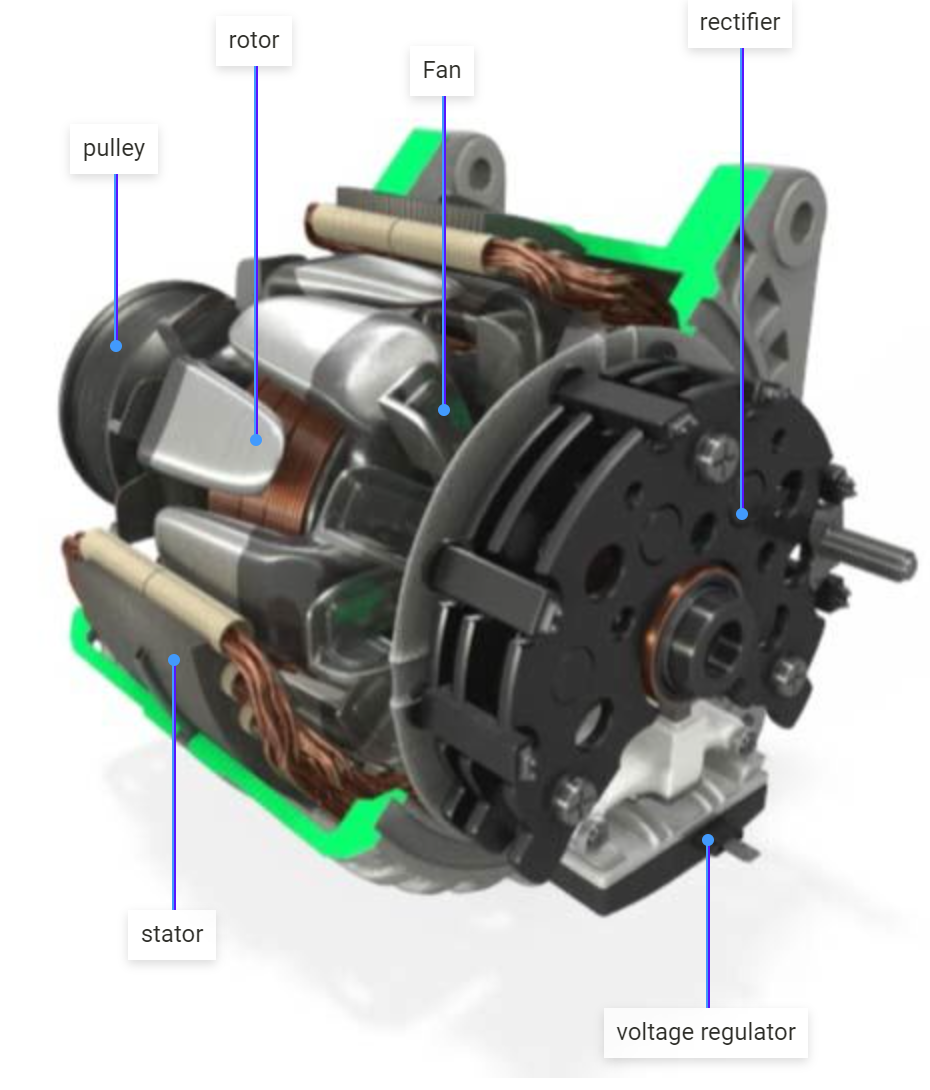
Standard alternators are the backbone of automotive electrical systems, converting mechanical energy from the engine into DC electricity. They typically feature a rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator. These components work together to ensure a steady supply of power for the vehicle’s electrical needs. B2B buyers in automotive manufacturing and repair shops will find standard alternators readily available and cost-effective, although they may not perform optimally at low RPMs, which can be a limitation in specific applications.
How Do High-Output Alternators Meet Performance Demands?
High-output alternators are tailored for performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications, providing significantly higher amperage output. They are essential for vehicles with extensive electrical systems, such as sound systems, lighting, and other accessories. B2B buyers in racing or heavy-duty vehicle sectors should consider these alternators for their enhanced capabilities, though they come at a higher price point and may require modifications to fit standard setups.
What Makes Smart Alternators Ideal for Modern Fleets?
Smart alternators incorporate advanced features such as real-time voltage regulation and diagnostic capabilities. This technology allows for better battery management and can enhance the lifespan of the vehicle’s electrical systems. Ideal for fleet management and electric vehicles, smart alternators offer B2B buyers improved efficiency and monitoring capabilities. However, their complexity may lead to higher repair costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Why Choose Diesel Engine Alternators for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Diesel engine alternators are specifically designed for the robust demands of commercial trucks and agricultural machinery. Their construction prioritizes durability and the ability to handle higher electrical loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. B2B buyers in industries reliant on diesel-powered vehicles will benefit from these alternators’ reliability. However, their heavier weight and size may limit compatibility with standard vehicles, so careful consideration is necessary.
What Are the Benefits of Marine Alternators in Harsh Conditions?
Marine alternators are constructed with materials resistant to corrosion and wear, making them ideal for use in marine environments. They are designed to withstand the harsh conditions often encountered at sea, ensuring reliable performance for marine vessels and offshore equipment. B2B buyers in the maritime industry should consider the investment in marine alternators for their durability and performance, although they typically come at a higher price due to specialized materials.
Key Industrial Applications of how does a car alternator work
| Branche/Sektor | Specific Application of how does a car alternator work | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilbau | Integration von Lichtmaschinen in Fahrzeugmontagelinien | Ensures reliable power supply for vehicle electronics | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems |
| Erneuerbare Energien | Use in hybrid and electric vehicle systems | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces reliance on fossil fuels | Durability, energy conversion efficiency, and cost-effectiveness |
| Bergbau und Schwermaschinen | Power supply for vehicles and machinery in remote locations | Maintains operational efficiency in challenging environments | Robustness, maintenance support, and availability of parts |
| Transport & Logistik | Fleet management systems that rely on vehicle electrical systems | Improves fleet reliability and reduces downtime | Scalability, supplier reliability, and warranty services |
| Landwirtschaftliche Maschinen | Alternators in tractors and farming equipment | Ensures consistent power for agricultural operations | Performance in diverse climates, serviceability, and cost |
How is a car alternator applied in automotive manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, alternators are integrated into vehicle assembly lines to ensure that all electrical systems function correctly during production. This integration is critical as it allows for the testing of electrical components before the vehicle is completed. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality alternators that meet local standards is essential. Considerations include ensuring compatibility with various vehicle models and adherence to quality certifications to avoid production delays.
What role does a car alternator play in renewable energy systems?
In the context of renewable energy, car alternators are increasingly utilized in hybrid and electric vehicle systems to enhance energy efficiency. They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, allowing for better battery management and extended vehicle range. For businesses in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing alternators that offer high energy conversion efficiency and durability is vital. International buyers should also assess the cost-effectiveness of these components to maximize return on investment.
How do alternators benefit mining and heavy equipment operations?
In the mining and heavy equipment sector, alternators provide a reliable power supply for vehicles and machinery operating in remote locations. This capability is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency, as equipment often faces harsh conditions. Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil must prioritize sourcing robust alternators that can withstand extreme environments. Additionally, maintenance support and the availability of spare parts are critical factors to consider to minimize downtime.
Why are alternators important for transportation and logistics?
For transportation and logistics companies, the reliability of fleet management systems relies heavily on the performance of vehicle electrical systems, including alternators. A dependable alternator ensures that vehicles remain operational, reducing the risk of breakdowns and improving overall fleet reliability. Key sourcing considerations for businesses in South America and Africa include scalability of supply, supplier reliability, and warranty services to protect their investment.
How do alternators enhance agricultural machinery functionality?
In agricultural machinery, alternators are essential for tractors and other equipment to ensure consistent power supply for various operations, from planting to harvesting. This reliability is crucial for farmers who depend on timely operations to maximize yield. Buyers in regions with diverse climates need to source alternators that perform well in varying conditions, with a focus on serviceability and cost. Understanding the specific power requirements of different farming equipment is also essential for optimal performance.

Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how does a car alternator work’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Alternator Components for Effective Maintenance
Das Problem:
Many B2B buyers, especially those in automotive repair and maintenance sectors, struggle with the complexities of a car alternator’s components. A lack of comprehensive knowledge about how each part, such as the rotor, stator, and rectifier, functions can lead to incorrect diagnostics and inefficient repairs. This not only prolongs downtime for vehicles but can also result in increased costs due to misdiagnoses and unnecessary part replacements. Buyers may find themselves in situations where their technicians are unsure of which component is failing, leading to frustration and potential loss of business.
Die Lösung:
To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest in robust training programs for their technicians that focus on the operational principles of alternators. Consider sourcing detailed training materials that break down the function of each component, using diagrams and interactive content. Additionally, creating a library of case studies that illustrate common alternator failures and their respective solutions can enhance understanding. Regular workshops or online webinars with experts can also keep the team updated on best practices. By fostering a culture of continuous learning, businesses can improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce repair times, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Alternators Amidst Diverse Market Options
Das Problem:
In regions like Africa and South America, B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing reliable alternators from a diverse market with varying quality standards. The proliferation of low-cost, low-quality parts can lead to rapid failure rates, causing reputational damage and financial losses. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the sheer volume of suppliers and uncertain about which products truly meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Die Lösung:
To mitigate this challenge, buyers should establish criteria for evaluating suppliers based on their reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Engaging in partnerships with reputable manufacturers or distributors known for their quality assurance processes can ensure a more reliable supply chain. Conducting thorough market research, including reading reviews and seeking testimonials from other businesses, can provide insights into supplier reliability. Additionally, consider negotiating trial orders to evaluate product performance before committing to larger purchases. By prioritizing quality over cost, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of alternator failures and enhance their service offerings.
Scenario 3: Navigating Technical Support for Alternator Issues
Das Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter difficulties when seeking technical support for alternator-related issues. Inadequate support from manufacturers or suppliers can leave buyers in a lurch when urgent assistance is needed for diagnosing or repairing alternator problems. This lack of support can lead to extended vehicle downtime, lost revenue, and frustrated customers who depend on timely service.
Die Lösung:
To overcome this pain point, buyers should actively seek suppliers that offer comprehensive technical support as part of their service package. This could include access to dedicated technical support hotlines, online troubleshooting resources, and detailed product manuals. Establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers can facilitate faster resolutions to issues. Buyers can also benefit from joining industry forums or networks where they can share experiences and solutions with peers facing similar challenges. By leveraging these resources, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce vehicle downtime, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how does a car alternator work
Was sind die wichtigsten Materialien, die in Kfz-Generatoren verwendet werden?
When considering the materials used in car alternators, it’s essential to analyze their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with the needs of international B2B buyers. This section focuses on four common materials: aluminum, copper, steel, and plastic.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Car Alternator Performance?
Aluminum is frequently used in the housing and various components of car alternators. It boasts excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and good thermal conductivity, making it ideal for automotive applications where weight and heat dissipation are critical.
Vorteile: Aluminum is durable and provides a good strength-to-weight ratio, which is advantageous for vehicle efficiency. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for cost-effective production.
Nachteile: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can be less durable under high-stress conditions compared to other metals. It may also have a lower fatigue resistance, which can be a concern in high-performance applications.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminum’s compatibility with various automotive fluids and its lightweight nature make it suitable for alternator housings. However, it is crucial to ensure that aluminum components are adequately treated to prevent galvanic corrosion when in contact with dissimilar metals.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local environmental conditions that may affect aluminum’s performance.
What Role Does Copper Play in Car Alternators?
Copper is predominantly used in the windings of the alternator due to its superior electrical conductivity. This property is vital for efficient energy transfer and overall performance.
Vorteile: Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, enhancing the alternator’s efficiency. It also has excellent thermal properties, which help in heat dissipation during operation.
Nachteile: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is higher than many other conductive materials. Additionally, copper is susceptible to corrosion if not properly coated or treated, which can lead to performance issues over time.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Copper’s compatibility with electrical systems is unmatched, making it indispensable in alternator windings. However, its weight and cost can be limiting factors for some manufacturers.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Buyers should be aware of copper’s market volatility and potential supply chain issues. Compliance with electrical standards and regulations in different regions is also crucial.
How Does Steel Enhance the Structure of Car Alternators?
Steel is often used for the rotor and stator cores in car alternators due to its strength and magnetic properties. It provides structural integrity and is essential for the electromagnetic function of the alternator.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Vorteile: Steel’s high tensile strength ensures durability and resistance to deformation under stress. It also has good magnetic properties, which enhance the alternator’s efficiency.
Nachteile: Steel is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to corrosion if not treated. The manufacturing process can also be more complex, potentially increasing production costs.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Steel’s strength is vital for the rotor and stator components, but its weight can affect the overall efficiency of the vehicle. Proper coatings or treatments are necessary to ensure longevity.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Buyers should consider local availability and treatment standards for steel. Compliance with international standards like JIS is essential for ensuring quality and performance.
What Is the Importance of Plastic in Car Alternators?
Plastic materials are often used for insulation and non-load-bearing components in alternators. They provide electrical insulation and protection against environmental factors.
Vorteile: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion. They can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility.
Nachteile: The main limitation of plastic is its lower thermal resistance compared to metals, which can lead to degradation in high-temperature environments. Additionally, not all plastics are suitable for automotive applications.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Plastic components are crucial for insulation and protection, but their performance can be compromised in extreme conditions. Selecting the right type of plastic is essential for ensuring reliability.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Buyers should evaluate the specific plastic grades used in alternators to ensure compliance with automotive standards. Understanding local climate conditions is also essential for material selection.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Car Alternators
| Material | Typical Use Case for how does a car alternator work | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium | Gehäuse und Bauteile | Leicht und korrosionsbeständig | Lower fatigue resistance | Mittel |
| Kupfer | Elektrische Wicklungen | Hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Hohe Kosten und Korrosionsanfälligkeit | Hoch |
| Stahl | Rotor- und Ständerkerne | High strength and magnetic properties | Schwerer und anfällig für Korrosion | Mittel |
| Kunststoff | Insulation and non-load-bearing parts | Leicht und kostengünstig | Geringerer Wärmewiderstand | Niedrig |
This analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in diverse markets, enabling informed decisions regarding material selection for car alternators.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how does a car alternator work
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Car Alternator?
The manufacturing process of car alternators is intricate, requiring a series of carefully controlled stages to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Car Alternator Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials. Key components such as copper wire for windings, steel for the rotor and stator, and aluminum for the housing are sourced from reputable suppliers. Rigorous material testing is conducted to verify mechanical properties, conductivity, and corrosion resistance, ensuring they meet international standards such as ISO 9001.
In preparation, materials are cut to specific dimensions, and any necessary treatments, like annealing for copper, are performed to enhance conductivity and workability. This preparation stage sets the foundation for the quality of the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Car Alternator Production?
Forming techniques play a critical role in shaping the components of an alternator. Key methods include:
-
Stanzen: This technique is commonly used to create the stator and rotor laminations. Stamping ensures precise dimensions and reduces material waste.
-
Wickeln: The stator and rotor coils are wound using specialized machines that can handle the specific gauge of wire while maintaining uniform tension. This step is crucial as it affects the electrical characteristics of the alternator.
-
Gießen: For components like the alternator housing, die-casting is often employed to achieve complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. This method not only speeds up production but also enhances the durability of the housing.
-
Bearbeitung: Final shaping of components, such as the rotor and stator, often involves CNC machining to ensure tight tolerances and surface finish quality.
These forming techniques are essential for achieving high-quality components that can withstand the operational stresses of a vehicle’s electrical system.
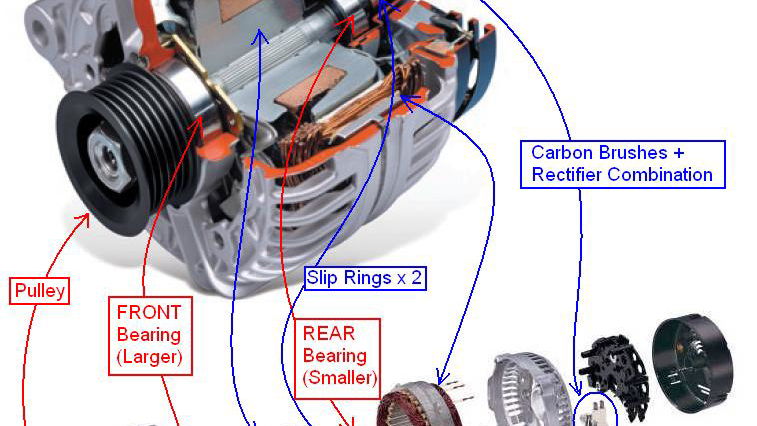
How Are Car Alternators Assembled?
The assembly stage brings together all the components into a functioning alternator. This process typically includes:
-
Inspektion von Bauteilen: Before assembly, each component undergoes an inspection to verify that it meets specified tolerances and quality standards.
-
Unterbaugruppe: Smaller groups of components, such as the rotor and stator, may be assembled separately to streamline the final assembly process.
-
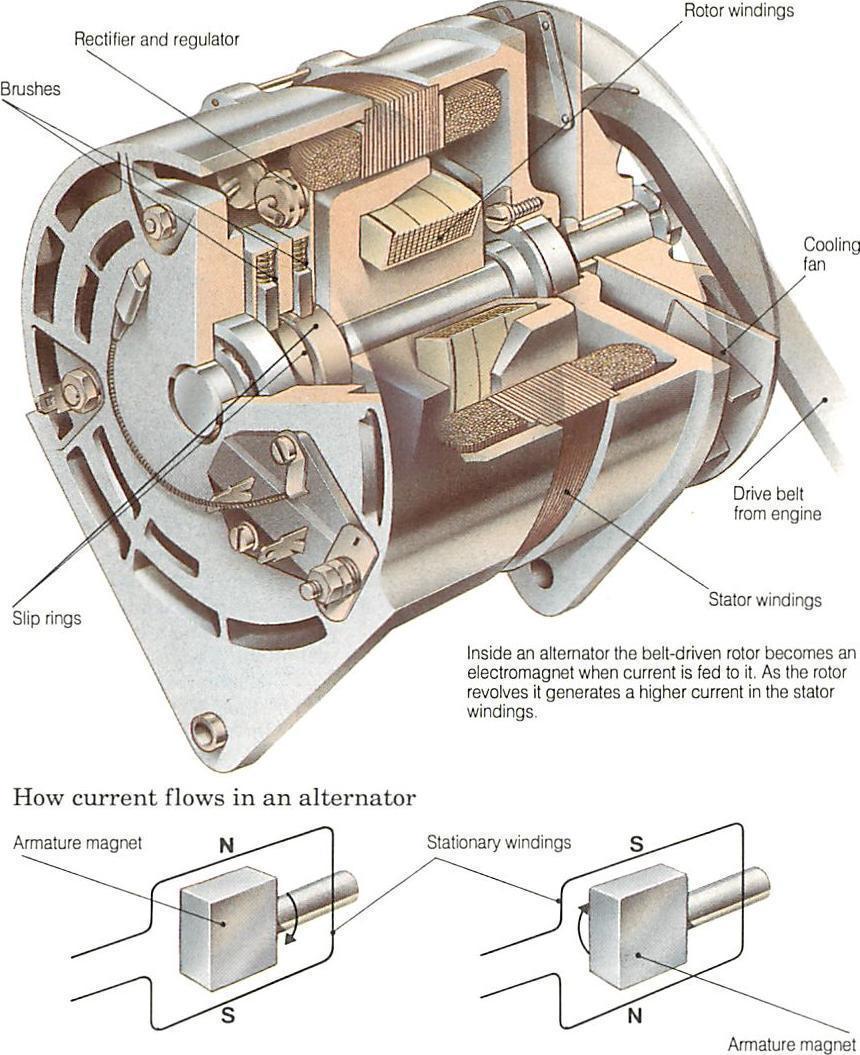
Endmontage: During this stage, the rotor is inserted into the stator, brushes and slip rings are installed, and the rectifier is connected. Proper alignment is critical to ensure efficient operation and minimize wear.
-
Elektrische Prüfung: Once assembled, the alternator undergoes electrical testing to verify that it meets output specifications. This can include testing for voltage output, current capacity, and noise levels.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Car Alternators?
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the durability and performance of car alternators. Key finishing techniques include:
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
-
Oberflächenbehandlung: Components may undergo surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
-
Ausgleichen: The rotating assembly is dynamically balanced to reduce vibrations during operation. This is vital for ensuring longevity and performance.
-
Abschließende Inspektion: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components are correctly assembled, and the alternator meets all performance specifications. This includes visual checks and functional tests.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Car Alternator Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the alternators produced are reliable and meet industry standards.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered for Car Alternators?
Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers. This standard emphasizes a quality management system that focuses on meeting customer requirements and enhancing satisfaction. Additionally, compliance with industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) can be crucial for market acceptance, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
What Are Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process ensure that any defects are identified and addressed promptly. Key checkpoints include:
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor processes and ensure components are being produced to the correct specifications.
-
Endkontrolle (FQC): After assembly, the completed alternator undergoes comprehensive testing to verify functionality and safety. This may include load testing, thermal testing, and performance evaluations.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrollpraktiken ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
B2B-Einkäufer können verschiedene Maßnahmen ergreifen, um sicherzustellen, dass ihre Lieferanten hohe Qualitätsstandards einhalten:
-
Lieferantenaudits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality control measures. This helps buyers gauge the reliability of the supplier.
-
Überprüfung von Qualitätsberichten: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand how suppliers monitor and manage quality throughout the production process.
-
Inspektionen durch Dritte: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices, ensuring that they meet international standards.
-
Certifications Verification: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications and that these are up to date. This includes checking ISO certifications and any applicable industry-specific approvals.
What Unique Quality Control Considerations Exist for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding these can help avoid delays and compliance issues.
-
Kulturelle und sprachliche Barrieren: Effective communication is critical. Buyers should ensure that there is a clear understanding of quality expectations, which may require engaging translators or local representatives.
-
Logistische Herausforderungen: Shipping delays and customs regulations can impact the timely delivery of products. Buyers should factor this into their quality assurance plans and timelines.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in car alternator production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and performance of their automotive components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how does a car alternator work’
Einführung
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in understanding the intricacies of car alternators. A well-functioning alternator is vital for vehicle performance, as it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy to power vehicle systems and charge the battery. By following this checklist, buyers can ensure they are making informed decisions when sourcing alternators or related components.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Understanding the specific requirements for your alternator is essential. Consider the vehicle types you are targeting and the power output needed. This may include factors such as voltage rating, size, and compatibility with existing electrical systems.
– Wichtige Überlegungen: Identify whether you need standard or high-performance alternators based on your application.
– Dokumentation: Collect any technical documents or specifications from the vehicle manufacturers.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Schritt 2: Marktentwicklungen und Innovationen erforschen
Stay informed about the latest advancements in alternator technology. Innovations such as smart alternators or those with advanced voltage regulation can enhance vehicle performance and efficiency.
– Sources of Information: Utilize industry reports, trade publications, and automotive technology forums.
– Competitive Analysis: Identify leading brands and emerging players in the alternator market.
Schritt 3: Potenzielle Lieferanten bewerten
Before committing to a supplier, it is crucial to vet them thoroughly. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation in the automotive sector and positive reviews from other businesses.
– Verification Methods: Request company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients in similar industries.
– Supplier Location: Consider the geographical location of suppliers, as it may affect shipping times and costs.
Schritt 4: Bewertung der Qualitätskontrollprozesse
Quality assurance is paramount in the automotive industry. Ensure that the suppliers you consider have robust quality control measures in place to prevent defects and ensure reliability.
– Zertifizierungen: Check for relevant industry certifications such as ISO 9001 or TS16949.
– Inspection Protocols: Inquire about their testing and inspection processes for alternators before they are shipped.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Schritt 5: Muster zum Testen anfordern
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the alternators to test their performance. This step allows you to evaluate the product against your specifications and ensure it meets your quality standards.
– Testing Criteria: Evaluate factors such as power output, efficiency, and durability under various conditions.
– Feedback Loop: Use the test results to provide feedback to suppliers and negotiate improvements if necessary.
Schritt 6: Verhandeln Sie die Allgemeinen Geschäftsbedingungen
Once you have identified a reliable supplier and verified their products, focus on negotiating favorable terms. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty agreements.
– Langfristige Beziehungen: Consider establishing long-term contracts for consistent supply, which can lead to better pricing and reliability.
– Contingency Plans: Discuss what measures are in place should there be a need for returns or replacements.
Schritt 7: Finalize Your Procurement Process
After completing all evaluations, finalize your procurement process. Ensure that all agreements are documented, and maintain open communication with your supplier for ongoing support and any future needs.
– Dokumentation: Keep all contracts, specifications, and communications organized for future reference.
– Monitor Performance: Once the alternators are in use, continuously monitor their performance to ensure they meet your expectations and those of your clients.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing car alternators, ensuring they select the best products for their needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how does a car alternator work Sourcing
Was sind die wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten bei der Beschaffung von Kfz-Generatoren?
When sourcing car alternators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materialien: The core materials for an alternator include metals like copper for windings, steel for the rotor, and various plastics for housing. The quality and source of these materials can significantly impact the overall cost. For instance, high-grade copper may lead to better conductivity but at a higher price.
-
Arbeit: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in manufacturing and assembly. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers may find competitive pricing.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, influencing the final pricing.
-
Werkzeuge: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider whether the tooling is a one-time investment or if it will be amortized over large production runs.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Ensuring that alternators meet safety and performance standards is essential. The costs associated with QC processes can vary based on the level of certification required (e.g., ISO, CE) and the supplier’s reputation.
-
Logistik: Transportation and shipping costs, influenced by distance and shipping methods, can add to the total expense. Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining who bears these costs during international transactions.
-
Marge: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and generate income. This margin can vary based on competition and market demand.
What Influences Pricing for Car Alternators?
Several factors can influence the pricing of car alternators, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volumen und Mindestbestellmenge (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Spezifikationen und Anpassung: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether their requirements justify the additional expenses or if off-the-shelf products can meet their needs.
-
Materialqualität und Zertifizierungen: Higher quality materials and certifications often translate to higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of premium components against budget constraints.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Supplier reliability, reputation, and historical performance can also impact pricing. A trusted supplier may offer better terms and conditions, making them a worthwhile investment.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can greatly influence the total landed cost of the alternators. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for budgeting.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Car Alternators Internationally?
B2B buyers should consider the following tips to enhance cost-efficiency and navigate pricing nuances:
-
Effektiv verhandeln: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Don’t hesitate to negotiate on bulk orders or long-term contracts.
-
Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO) bewerten: Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs associated with alternators.
-
Verstehen Sie die Preisunterschiede für verschiedene Regionen: Different regions may have distinct pricing strategies influenced by local demand, competition, and economic conditions. For instance, the pricing structure in Nigeria may differ from that in Brazil due to varying market dynamics.
-
Forschung zu Markttrends: Keeping abreast of trends in the automotive industry and material costs can help buyers anticipate price changes and make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Lokale Lieferanten in Betracht ziehen: Die Beschaffung bei lokalen Anbietern kann Logistikkosten und Vorlaufzeiten reduzieren und die Effizienz der Lieferkette insgesamt verbessern.
Haftungsausschluss für indikative Preise
Pricing for car alternators is subject to fluctuations based on market conditions, raw material costs, and geopolitical factors. B2B buyers should conduct thorough research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how does a car alternator work With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Car Alternators
In the automotive industry, the car alternator plays a critical role in converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, primarily to charge the vehicle’s battery and power its electrical systems. However, as technology advances, alternative solutions are emerging that can perform similar functions. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific operational needs.
Vergleichstabelle
| Vergleichsaspekt | How Does A Car Alternator Work | Alternative 1: Gleichstromgenerator | Alternative 2: Battery Management System (BMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Reliable DC output; supports vehicle electrical systems | Generates DC power, but typically less efficient | Manages battery discharge and charge cycles; optimizes battery life |
| Kosten | Moderate initial cost, but requires maintenance | Generally lower upfront cost, but can be less durable | Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology |
| Einfache Implementierung | Standard in most vehicles; simple installation | Requires compatibility with vehicle design | Complex integration; may require software customization |
| Wartung | Regular checks needed for wear and tear | Lower maintenance, but may require replacement sooner | Minimal maintenance; relies on software updates |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Ideal for conventional vehicles with internal combustion engines | Suitable for older vehicles or specific applications | Best for electric vehicles or hybrid systems |
Detaillierte Aufschlüsselung der Alternativen
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a DC Generator?
A DC generator is an alternative that also converts mechanical energy into direct current. While it can be less efficient than an alternator, especially at varying speeds, it tends to have a lower initial cost, making it appealing for budget-conscious buyers. However, its durability can be a concern, as DC generators may require more frequent replacements, especially in high-demand environments.
How Does a Battery Management System (BMS) Function Compared to an Alternator?
A Battery Management System (BMS) focuses on optimizing battery performance by monitoring charge and discharge cycles. It is particularly advantageous in electric and hybrid vehicles, where efficient battery use is critical. While a BMS can prolong battery life and improve overall efficiency, its complexity and higher upfront costs may deter some buyers. Additionally, integrating a BMS may require specialized expertise, adding to installation costs.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Fazit: Die richtige Wahl für Ihr Unternehmen treffen
When considering alternatives to the traditional car alternator, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs, including vehicle types, operational requirements, and budget constraints. While the alternator remains a reliable choice for conventional vehicles, options like DC generators and Battery Management Systems offer unique advantages that may better suit certain applications. Ultimately, the right solution will depend on balancing performance, cost, and ease of implementation to meet the demands of modern automotive technology.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how does a car alternator work
Was sind die wichtigsten technischen Eigenschaften eines Autogenerators?
Understanding the technical specifications of car alternators is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those involved in automotive manufacturing, repair, or parts distribution. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Werkstoffgüte
The components of an alternator are typically made from materials such as aluminum, copper, and various plastics. Aluminum is commonly used for the housing due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Copper is favored for windings because of its excellent electrical conductivity. Understanding the material grade helps in assessing durability and performance, which are critical for long-term reliability in automotive applications.
2. Ausgangsspannung
Most car alternators produce an output voltage ranging from 12V to 14.5V, essential for charging the battery and powering electrical systems. A consistent voltage output is vital to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components within the vehicle. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the alternator meets specific voltage requirements can help maintain customer satisfaction and reduce warranty claims.
3. Nennstrom (Stromstärke)
The current rating indicates the maximum electrical current the alternator can supply, typically measured in amperes (A). Common ratings range from 40A to over 200A, depending on the vehicle’s electrical demands. Understanding the current rating is crucial for buyers to ensure that the alternators they procure can handle the load of the vehicle’s electrical systems without failure.
4. Rotational Speed (RPM)
The operational efficiency of an alternator is often tied to its rotational speed, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Most automotive alternators are designed to operate effectively between 1,000 and 6,000 RPM. This specification is important for B2B buyers to match the alternator to the engine’s speed, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
5. Temperaturtoleranz
Alternators are exposed to various temperature conditions, so understanding their temperature tolerance is essential. Most automotive alternators can operate within a temperature range of -40°C to 125°C. This specification is vital for buyers in regions with extreme climates, ensuring that the alternator will function reliably under local conditions.
Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
6. Effizienzbewertung
Efficiency is a measure of how well the alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, typically expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency ratings (above 70%) indicate better performance and lower energy waste. For B2B buyers, selecting high-efficiency alternators can lead to reduced fuel consumption and lower operational costs for end-users.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Car Alternators?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
OEM refers to parts made by the manufacturer of the vehicle, ensuring a perfect fit and compatibility. B2B buyers often prefer OEM alternators due to their reliability and warranty coverage, which can reduce the risk of returns and dissatisfaction.
2. MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that can be ordered from a supplier. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to effectively manage inventory and cash flow, as lower MOQs can allow for more flexible purchasing strategies.
3. RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specified products. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare offers and negotiate better deals, making it a fundamental tool in procurement processes.
4. Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, covering aspects like shipping costs and risk transfer. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, particularly for cross-border purchases of alternators, to avoid misunderstandings and ensure compliance with trade regulations.
5. Garantiezeitraum
The warranty period is the duration for which the manufacturer guarantees the alternator against defects. Understanding warranty terms helps B2B buyers assess product reliability and reduce potential costs associated with returns and replacements.
6. Vorlaufzeit
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing the lead time is essential for B2B buyers to plan their inventory and meet customer demands efficiently, especially in industries where time is critical.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and enhance their competitiveness in the automotive sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how does a car alternator work Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends: What Are the Current Dynamics in the Car Alternator Sector?
The global car alternator market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for vehicles and advancements in automotive technology. A key factor propelling this market is the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles, which require sophisticated alternators to manage battery charging effectively. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Nigeria, are particularly influenced by these trends. The growing middle class in these regions is driving vehicle ownership, leading to an increased demand for reliable and efficient alternators.
Moreover, the integration of smart technologies in vehicles is another emerging trend. Modern alternators are being equipped with sensors and advanced electronics to optimize energy management, which appeals to tech-savvy consumers. For B2B buyers, sourcing alternators that incorporate these innovations can provide a competitive edge in their markets. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms for automotive parts is transforming sourcing strategies, allowing buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and negotiate better terms.
Another significant trend is the increasing focus on localization in supply chains. As global trade dynamics shift, many businesses are seeking local suppliers to reduce lead times and costs. This presents opportunities for local manufacturers in regions like Africa and South America to capture market share by providing competitively priced and high-quality alternators.

Illustrative image related to how does a car alternator work
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B: How Can Buyers Ensure Responsible Practices?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the automotive sector, including the production of car alternators. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly regarding resource extraction and waste generation, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing carbon footprints in their production processes.
Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) are vital indicators of a supplier’s commitment to environmental responsibility. By sourcing from manufacturers with these certifications, businesses can ensure that their products meet global sustainability standards, which is increasingly important for consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
In addition to environmental certifications, ethical sourcing also encompasses labor practices within the supply chain. Buyers should seek suppliers who guarantee fair wages and safe working conditions for their employees. By fostering partnerships with ethical manufacturers, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing base of environmentally and socially conscious consumers.
Brief Evolution/History: How Did Car Alternators Develop Over Time?
The evolution of car alternators dates back to the early 20th century when generators were the primary source of electrical power in vehicles. The introduction of the alternator in the 1960s marked a significant advancement, as it offered higher efficiency and reliability compared to traditional generators. As automotive technology progressed, alternators evolved to incorporate advanced components like rectifiers and voltage regulators, improving their performance in managing electrical systems.
Today, with the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, the design and function of alternators continue to adapt, focusing on energy efficiency and integration with complex vehicle electronic systems. Understanding this evolution helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that drive the current market and informs their sourcing decisions as they seek cutting-edge solutions for their automotive needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how does a car alternator work
-
How does a car alternator work?
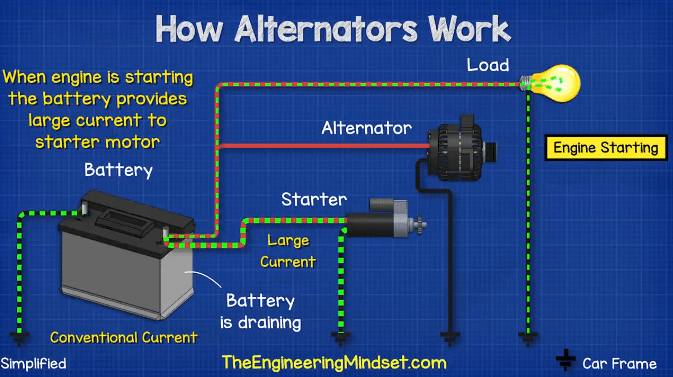
The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, primarily DC voltage, to charge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems. As the engine runs, it turns a drive belt connected to the alternator, causing its rotor to spin within the stator. This spinning induces a magnetic field that generates alternating current (AC), which is then converted to direct current (DC) through a rectifier. The voltage regulator ensures a consistent voltage output to prevent damage to the battery and electrical components. -
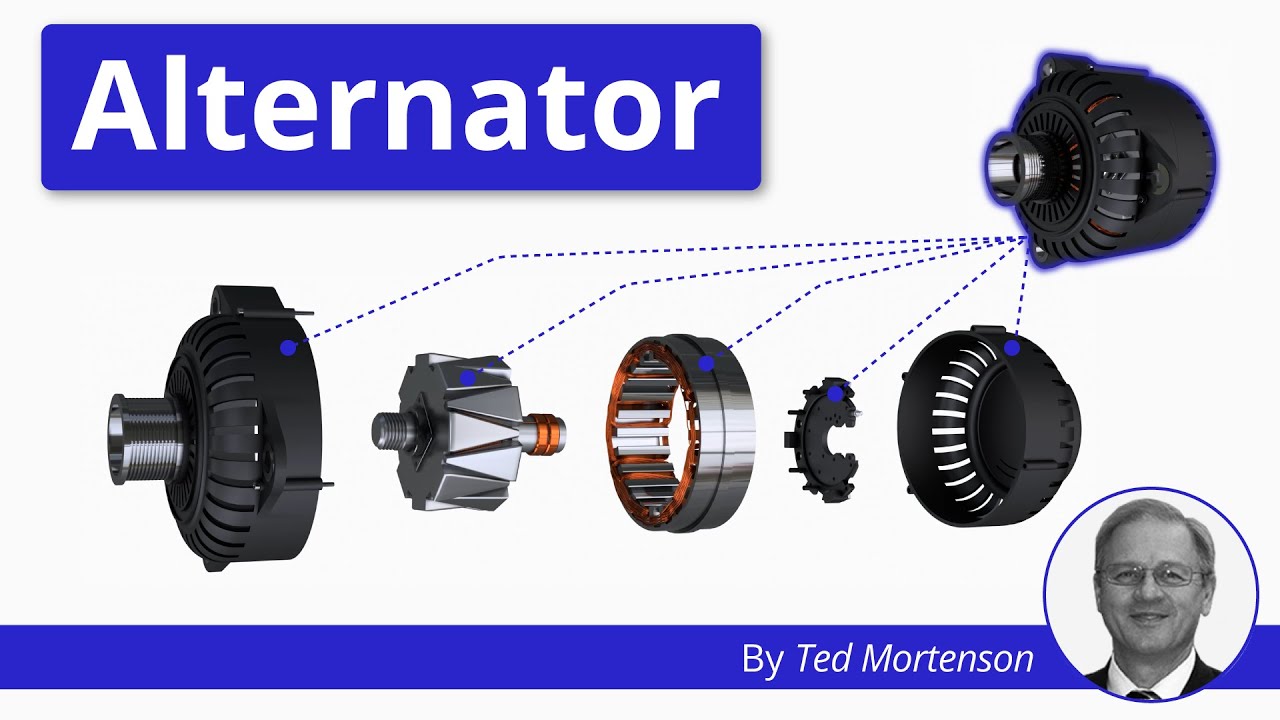
What are the main components of a car alternator?
A typical car alternator consists of several key components: the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator. The rotor, an electromagnet, spins inside the stator, which contains coil windings. This interaction generates AC voltage. The rectifier, made of diodes, converts the AC voltage to DC. The voltage regulator monitors the system and maintains the appropriate voltage level to ensure the battery is charged efficiently without risking overvoltage. -
How can I choose the right alternator supplier for my business?
When selecting an alternator supplier, consider their experience, reputation, and quality certifications. Request samples to evaluate product quality and compatibility with your requirements. Look for suppliers who offer customization options to meet specific vehicle models or regional standards. Additionally, assess their logistics capabilities and willingness to provide support for international shipping, especially if you are sourcing from regions like Africa or South America. -
Welche Anpassungsmöglichkeiten gibt es für Lichtmaschinen?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific performance or design requirements. This may include changes in voltage output, size, or connector types. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly and inquire about the supplier’s ability to accommodate these requests. Understanding the potential implications of customization on lead times and costs is also crucial, particularly for international orders. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for alternators?
The MOQ for alternators can vary significantly between suppliers, often depending on the manufacturing process and materials used. Typically, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 100 to several thousand units. When negotiating with suppliers, it’s beneficial to clarify MOQs upfront and explore options for smaller initial orders, especially if you are testing a new market or product line. -
Mit welchen Zahlungsbedingungen muss ich bei der internationalen Beschaffung von Generatoren rechnen?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation leverage. Common terms include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may also offer letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to ensure security for both parties. Always clarify payment methods accepted and any potential fees associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my alternator orders?
To maintain quality assurance, establish clear specifications and standards before placing orders. Request documentation such as quality control certificates and product testing results. It’s advisable to conduct factory audits or request third-party inspections, especially for large orders. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and any potential issues. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for shipping alternators?
When shipping alternators internationally, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling automotive components to ensure safe and timely delivery. Assess the total landed cost, including shipping, duties, and taxes, to better understand your overall expenditure. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs clearance, particularly in regions with stricter import regulations.
Top 2 How Does A Car Alternator Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Engineering Mindset – Car Alternator
Domäne: theengineeringmindset.com
Registriert: 2015 (10 Jahre)
Einleitung: The car alternator is an essential component of every combustion engine vehicle’s electrical system. It generates electricity by converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. The alternator produces alternating current (AC) electricity, which is then converted into direct current (DC) by a rectifier for use in the vehicle’s electrical components. Key parts of the alternator …
2. AutoElectro – Alternators
Domäne: autoelectro.de
Registriert: 1999 (26 Jahre)
Einleitung: Alternators generate energy to feed the electrical system and charge the battery in a vehicle. They convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) through a rectifier. Key components include: 1. Regulator – controls power distribution to the battery. 2. Rectifier – converts AC to DC. 3. Rotor – spinning mass acting as an electromagnet. 4. Slip Rings – provide direct current to the rotor. …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how does a car alternator work
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, understanding the intricacies of components like the alternator becomes essential for international B2B buyers. The alternator is a pivotal electromechanical device that not only generates DC voltage but also ensures the reliable operation of a vehicle’s electrical systems. Key components such as the rotor, stator, rectifier, and voltage regulator work in concert to maintain battery voltage, making the alternator a critical component in vehicle performance and longevity.
For businesses sourcing alternators, strategic sourcing is crucial. Partnering with reliable manufacturers can lead to enhanced product quality, reduced costs, and improved supply chain efficiency. It’s essential to evaluate suppliers based on their technological capabilities, production standards, and after-sales support to ensure a robust supply chain.
Looking ahead, as demand for electric vehicles and advanced automotive technologies rises, the role of the alternator will evolve. B2B buyers should stay informed about emerging trends and innovations in alternator technology. By doing so, they can position themselves strategically within their markets, ensuring they meet the needs of their customers while driving business growth. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure your competitive edge in this dynamic landscape.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.