Einleitung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für Generatoren und Generatoren
Da internationale B2B-Einkäufer nach zuverlässigen Energielösungen suchen, ist es wichtig, die Unterschiede zwischen Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen zu verstehen. Die Herausforderung besteht darin, die richtigen elektrischen Energieumwandlungssysteme zu beschaffen, die auf die spezifischen betrieblichen Anforderungen und regionalen Bedürfnisse abgestimmt sind. Dieser Leitfaden befasst sich mit den grundlegenden Unterschieden zwischen Generatoren und Generatoren und erläutert ihre Typen, Anwendungen und Leistungskennzahlen, um Ihnen bei Ihren komplexen Kaufentscheidungen zu helfen.
In diesem umfassenden Leitfaden werden wir die technischen Spezifikationen, die Energieeffizienz und die Wartungsanforderungen beider Systeme untersuchen. Darüber hinaus geben wir Ihnen Einblicke in die Prozesse der Lieferantenüberprüfung, um sicherzustellen, dass Sie mit seriösen Herstellern und Händlern zusammenarbeiten, insbesondere in Schwellenländern wie Nigeria, Vietnam und anderen Regionen in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa.
Dieser Leitfaden liefert Ihnen umsetzbare Informationen zu Kostenerwägungen, Anwendungsszenarien und Leistungsvergleichen und ermöglicht es Ihnen, fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen, die nicht nur die betriebliche Effizienz steigern, sondern auch Ihren strategischen Unternehmenszielen gerecht werden. Unabhängig davon, ob Sie Industriemaschinen oder Automobilanwendungen antreiben wollen, wird das Verständnis der Unterschiede zwischen Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen zu einer intelligenteren Beschaffung und optimierten Energielösungen für Ihr Unternehmen führen.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Liste der 3 größten Hersteller und Lieferanten von Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren
- Einleitung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für Generatoren und Generatoren
- Wechselstromgenerator und Generator - Typen und Variationen
- Wichtigste industrielle Anwendungen von Generatoren und Generatoren
- 3 häufige Schmerzpunkte von Nutzern bei der Frage ‘Lichtmaschine versus Generator’ und ihre Lösungen
- Leitfaden zur strategischen Materialauswahl für Generatoren und Generatoren
- Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für Generatoren und Generatoren
- Praktischer Leitfaden für die Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘Lichtmaschine versus Generator’.’
- Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Beschaffung von Generatoren und Generatoren
- Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich von Lichtmaschine und Generator mit anderen Lösungen
- Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für Generatoren und Generatoren
- Navigieren durch Marktdynamik und Beschaffungstrends im Sektor Generatoren und Generatoren
- Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer von Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren
- Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für Generatoren gegenüber Generatoren
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Wechselstromgenerator und Generator - Typen und Variationen
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC-Lichtmaschine | Wandelt mechanische Energie in Wechselstrom um; stationärer Anker, rotierendes Feld. | Automobilindustrie, Systeme für erneuerbare Energien | Vorteile: Hoher Wirkungsgrad, kompakte Größe. Nachteile: Begrenzt auf AC-Ausgang. |
| Gleichstromgenerator | Wandelt mechanische Energie in Gleichstrom um; rotierender Anker, stationäre Magnete. | Industrielle Anwendungen, Batterieladung | Vorteile: Geeignet zum Laden von Batterien. Nachteile: Geringerer Wirkungsgrad, größere Abmessungen. |
| Synchroner Generator | Erzeugt Wechselstrom; der Rotor dreht sich im Takt der Netzfrequenz. | Kraftwerke, großtechnische Energieerzeugung | Vorteile: Stabile Leistung, hohe Effizienz. Nachteile: Komplexer, erfordert Synchronisierung. |
| Asynchroner Generator | Erzeugt Wechselstrom; der Rotor stimmt nicht mit der Netzfrequenz überein. | Windkraftanlagen, kleine Energiesysteme | Vorteile: Einfaches Design, effektiv unter variablen Bedingungen. Nachteile: Weniger effizient bei konstanter Belastung. |
| Bürstenloser Generator | Elektronische Steuerung; keine Bürsten für die Wartung. | Luftfahrt, hochzuverlässige Anwendungen | Vorteile: Geringer Wartungsaufwand, hohe Zuverlässigkeit. Nachteile: Höhere Anschaffungskosten. |
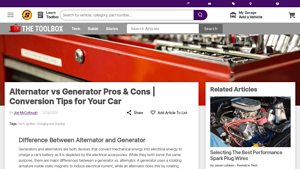
Was sind die Merkmale und die Eignung von Wechselstromgeneratoren?
Wechselstromgeneratoren werden häufig in der Automobilindustrie und im Bereich der erneuerbaren Energien eingesetzt. Sie wandeln mechanische Energie mit Hilfe eines feststehenden Ankers und eines rotierenden Magnetfelds in Wechselstrom um. Diese Konstruktion ermöglicht einen hohen Wirkungsgrad und eine kompakte Größe, wodurch sie sich ideal für Fahrzeuge und kleine Systeme für erneuerbare Energien eignen. B2B-Käufer sollten ihren Bedarf an Zuverlässigkeit und Effizienz berücksichtigen, insbesondere bei Anwendungen, die eine konstante Leistungsabgabe erfordern.
Wie unterscheiden sich DC-Generatoren in ihrer Funktionalität und Anwendung?
Gleichstromgeneratoren zeichnen sich durch ihre Fähigkeit aus, mechanische Energie in Gleichstrom umzuwandeln. Sie verfügen über einen rotierenden Anker in stationären Magneten und eignen sich daher für industrielle Anwendungen und zum Laden von Batterien. Sie können zwar effektiv Batterien aufladen, sind aber weniger effizient und größer als Lichtmaschinen. B2B-Käufer sollten bei der Auswahl von Gleichstromgeneratoren für ihren Betrieb ihre spezifischen Leistungsanforderungen und Platzbeschränkungen berücksichtigen.
Was macht Synchrongeneratoren zu einer bevorzugten Wahl für Kraftwerke?
Synchrongeneratoren sind für die Stromerzeugung unverzichtbar, da sie synchron mit der Netzfrequenz arbeiten, um stabilen Wechselstrom zu erzeugen. Ihr komplexes Design ermöglicht einen hohen Wirkungsgrad und ist ideal für die Energieerzeugung in großem Maßstab. B2B-Einkäufer im Energiesektor sollten den Bedarf an stabiler Leistung und die Fähigkeit zur Synchronisierung bewerten, die sich auf die Gesamteffizienz und -zuverlässigkeit des Betriebs auswirken können.
Warum sind Asynchrongeneratoren ideal für Windenergieanwendungen?
Asynchrongeneratoren oder Induktionsgeneratoren werden häufig in Windkraftanlagen und kleinen Energiesystemen eingesetzt. Im Gegensatz zu Synchrongeneratoren ist ihr Rotor nicht an die Netzfrequenz angepasst, was einen effektiven Betrieb unter variablen Bedingungen ermöglicht. Diese Einfachheit macht sie für B2B-Käufer im Bereich der erneuerbaren Energien interessant, insbesondere wenn Anpassungsfähigkeit und Kosteneffizienz im Vordergrund stehen.
Was sind die Vorteile von bürstenlosen Generatoren bei Anwendungen mit hoher Zuverlässigkeit?
Bürstenlose Generatoren, die elektronische Steuerungen anstelle von herkömmlichen Bürsten verwenden, sind für ihren geringen Wartungsbedarf und ihre hohe Zuverlässigkeit bekannt. Sie werden häufig in der Luftfahrt und anderen Anwendungen mit hoher Zuverlässigkeit eingesetzt, bei denen eine konstante Leistung entscheidend ist. B2B-Käufer sollten die höheren Anschaffungskosten gegen die langfristigen Vorteile eines geringeren Wartungsaufwands und einer höheren Zuverlässigkeit abwägen, wenn sie bürstenlose Generatoren für ihre Projekte in Betracht ziehen.
Wichtigste industrielle Anwendungen von Generatoren und Generatoren
| Branche/Sektor | Spezifische Anwendung von Wechselstromgenerator und Generator | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Lichtmaschinen in modernen Fahrzeugen | Hohe Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit beim Laden von Batterien | Ruf des Lieferanten, Garantiebedingungen und Wartungsunterstützung |
| Bauwesen | Generatoren für die Baustromversorgung | Sorgt für kontinuierlichen Strom für Werkzeuge und Maschinen | Kraftstoffart, Mobilität und Lärmpegel |
| Telekommunikation | Generatoren für Notstromanlagen | Unterbrechungsfreier Service bei Stromausfällen | Einhaltung lokaler Vorschriften und Kraftstoffeffizienz |
| Landwirtschaft | Wechselstromgeneratoren in Bewässerungssystemen | Optimiert den Energieeinsatz für die Wasserförderung | Energieeffizienzwerte und Haltbarkeit |
| Bergbau | Generatoren für den Einsatz an abgelegenen Standorten | Sorgt für zuverlässige Stromversorgung an netzfernen Standorten | Größe, Transportfähigkeit und Verfügbarkeit von Dienstleistungen |
Wie werden Lichtmaschinen in der Automobilindustrie eingesetzt?
Im Automobilsektor sind Lichtmaschinen aufgrund ihrer Effizienz bei der Umwandlung von mechanischer in elektrische Energie zum Standard für Ladesysteme geworden. Sie sind entscheidend für die Stromversorgung der zahlreichen elektrischen Komponenten moderner Fahrzeuge, wie Beleuchtung, Infotainmentsysteme und Servolenkung. B2B-Einkäufer sollten sich auf die Beschaffung qualitativ hochwertiger Generatoren konzentrieren, die eine lange Lebensdauer und einen minimalen Wartungsbedarf aufweisen, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika, wo die Zuverlässigkeit der Fahrzeuge von größter Bedeutung ist.
Welche Rolle spielen Generatoren im Bauwesen?
Generatoren sind in der Baubranche unverzichtbar, da sie Werkzeuge, Beleuchtung und Maschinen auf Baustellen mit begrenztem Netzzugang zuverlässig mit Strom versorgen. Sie sorgen dafür, dass der Betrieb ohne Unterbrechungen fortgesetzt werden kann, was die Produktivität steigert. Käufer in diesem Sektor sollten Faktoren wie Kraftstoffart, Mobilität (Tragbarkeit) und Geräuschpegel berücksichtigen, insbesondere in städtischen Gebieten oder in sensiblen Umgebungen im Nahen Osten und Europa.
Warum sind Generatoren für die Telekommunikation so wichtig?
Telekommunikationsunternehmen sind auf Generatoren angewiesen, um bei Stromausfällen einen unterbrechungsfreien Dienst aufrechtzuerhalten und so den Betrieb der Kommunikationsnetze zu gewährleisten. Dies ist besonders in Regionen mit unzuverlässiger Stromversorgung wichtig. Bei der Beschaffung sollten Unternehmen vor allem auf die Einhaltung lokaler Vorschriften und die Kraftstoffeffizienz des Generators achten, um die Betriebskosten und die Umweltbelastung zu minimieren.
Wie sind Wechselstromgeneratoren in der Landwirtschaft von Vorteil?
In der Landwirtschaft werden Generatoren häufig in Bewässerungssystemen eingesetzt, um die Energienutzung beim Pumpen von Wasser zu optimieren. Eine effiziente Energieumwandlung trägt zur Kostensenkung bei und unterstützt nachhaltige landwirtschaftliche Praktiken. B2B-Einkäufer sollten auf die Energieeffizienzwerte und die Langlebigkeit von Generatoren achten, insbesondere in Regionen wie Nigeria und Vietnam, wo die landwirtschaftliche Produktivität direkt mit der Verfügbarkeit von Energie verbunden ist.
Was sind die Vorteile von Generatoren im Bergbau?
Generatoren sind im Bergbau unverzichtbar, da sie an abgelegenen Orten, an denen herkömmliche Stromquellen nicht zur Verfügung stehen, eine zuverlässige Stromversorgung gewährleisten. Sie unterstützen schwere Maschinen und Verarbeitungsanlagen und gewährleisten die Betriebskontinuität. Käufer sollten die Größe und Transportfähigkeit von Generatoren sowie die Serviceverfügbarkeit berücksichtigen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie den Anforderungen anspruchsvoller Bergbauumgebungen in verschiedenen Regionen gerecht werden können.
3 häufige Schmerzpunkte von Nutzern bei der Frage ‘Lichtmaschine versus Generator’ und ihre Lösungen
Szenario 1: Herausforderungen für die Energieeffizienz im Betrieb
Das Problem: Viele B2B-Einkäufer in Branchen wie dem verarbeitenden Gewerbe und dem Baugewerbe stehen vor der Herausforderung der Energieeffizienz in ihren Betrieben. Unternehmen sind oft auf Generatoren für Hochleistungsanwendungen angewiesen, was zu hohen Betriebskosten und Energieverschwendung führen kann. Diese Ineffizienz wird in Regionen mit instabiler Stromversorgung noch verschärft, wo Unternehmen gezwungen sind, häufig Generatoren einzusetzen. Die Abhängigkeit von herkömmlichen Generatoren kann das Budget belasten, insbesondere wenn Energieeinsparungen für Nachhaltigkeitsziele entscheidend sind.
Die Lösung: Um dieses Problem zu lösen, sollten Käufer erwägen, in hocheffiziente Generatoren anstelle von herkömmlichen Generatoren zu investieren. Generatoren sind so konzipiert, dass sie mechanische Energie effizienter in elektrische Energie umwandeln, nur bei Bedarf Strom erzeugen und die Verschwendung minimieren. Bei der Beschaffung von Generatoren ist es wichtig, Modelle zu spezifizieren, die den Betriebsanforderungen Ihrer Ausrüstung entsprechen, und sicherzustellen, dass sie mit bestehenden Systemen kompatibel sind. Darüber hinaus kann ein hybrider Ansatz, bei dem sowohl Generatoren als auch Stromerzeuger eingesetzt werden, für Flexibilität sorgen: Der Generator dient als Backup bei Bedarfsspitzen, während für den regulären Betrieb auf den Generator zurückgegriffen wird. Käufer sollten auch Lieferanten auswählen, die robuste Support- und Wartungspläne anbieten können, um langfristige Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit zu gewährleisten.
Szenario 2: Überwindung von Leistungsbeschränkungen bei Anwendungen mit niedriger Geschwindigkeit
Das Problem: Unternehmen in der Automobil- und Transportbranche stoßen oft auf Schwierigkeiten, wenn sie Generatoren bei niedrigen Drehzahlen einsetzen, z. B. bei Fahrzeugen oder Maschinen im Leerlauf. Generatoren haben in der Regel Schwierigkeiten, bei niedrigeren Drehzahlen ausreichend Strom zu erzeugen, was zu einer unzureichenden Batterieladung und potenziellen Betriebsunterbrechungen führt. Dies kann besonders für Unternehmen frustrierend sein, die auf eine kontinuierliche Energieversorgung für Elektronik und Zubehör in Fahrzeugen angewiesen sind, was zu schlechter Leistung und Kundenunzufriedenheit führt.
Die Lösung: Um diese Leistungseinschränkungen abzumildern, sollten B2B-Käufer auf Generatoren umsteigen, die auch bei niedrigen Drehzahlen Strom erzeugen können. Bei der Auswahl eines Generators ist es von entscheidender Bedeutung, die spezifischen elektrischen Lastanforderungen Ihrer Fahrzeuge oder Maschinen zu ermitteln. Käufer sollten nach Generatoren mit Funktionen wie integrierter Spannungsregelung und hoher Leistung bei niedrigen Drehzahlen suchen. Partnerschaften mit Herstellern, die anpassbare Lösungen anbieten, können ebenfalls dazu beitragen, dass der Generator die speziellen Anforderungen Ihres Fuhrparks erfüllt. Regelmäßige Wartungsintervalle verlängern die Lebensdauer der Generatoren und gewährleisten eine gleichbleibende Leistung.
Szenario 3: Verwaltung der Erstinvestitionskosten für Großprojekte
Das Problem: In vielen Branchen, insbesondere in Entwicklungsregionen wie Afrika und Südamerika, stehen B2B-Einkäufer vor der Herausforderung hoher Anfangsinvestitionskosten, wenn sie elektrische Systeme für Großprojekte in Betracht ziehen. Die Entscheidung zwischen dem Kauf von Generatoren oder Lichtmaschinen kann sich erheblich auf das Budget auswirken. Generatoren scheinen zwar eine kostengünstigere Lösung zu sein, aber ihre langfristige Ineffizienz im Betrieb kann zu höheren Gesamtkosten führen, was die Investitionsentscheidung schwierig macht.
Die Lösung: Käufer sollten eine gründliche Kosten-Nutzen-Analyse durchführen, die sowohl die Anfangsinvestition als auch die langfristigen Betriebskosten berücksichtigt. Die Investition in qualitativ hochwertige Generatoren kann höhere Anfangsausgaben erfordern, aber die daraus resultierende Energieeffizienz, die geringeren Wartungskosten und die längere Lebensdauer können im Laufe der Zeit zu erheblichen Einsparungen führen. Es ist ratsam, die Generatoren von seriösen Anbietern zu beziehen, die Garantien und Kundendienst anbieten, um sicherzustellen, dass alle Probleme schnell gelöst werden können. Darüber hinaus können Finanzierungsmöglichkeiten oder Zuschüsse für energieeffiziente Technologien dazu beitragen, die Belastung durch Vorlaufkosten zu verringern, so dass Unternehmen in nachhaltigere und wirtschaftlichere Lösungen investieren können, ohne ihr Budget zu gefährden.
Leitfaden zur strategischen Materialauswahl für Generatoren und Generatoren
Was sind die wichtigsten Materialien für Generatoren und Wechselstromgeneratoren?
Bei der Auswahl von Materialien für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen beeinflussen mehrere Faktoren die Leistung, Langlebigkeit und Gesamteffizienz. Hier analysieren wir gängige Materialien, die in diesen Geräten verwendet werden, und konzentrieren uns auf ihre Eigenschaften, Vorteile, Nachteile und Auswirkungen für internationale B2B-Käufer.
Kupfer: Das Rückgrat der elektrischen Leitfähigkeit
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Kupfer ist bekannt für seine hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit, Wärmeleitfähigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit. Es arbeitet in der Regel effizient bei Temperaturen von bis zu 200 °C und kann erheblichen mechanischen Belastungen standhalten.
Vor- und Nachteile: Die hohe Leitfähigkeit von Kupfer sorgt für minimale Energieverluste und macht es ideal für Wicklungen in Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen. Allerdings ist es im Vergleich zu Alternativen wie Aluminium relativ teuer. Der Herstellungsaufwand ist mäßig, da sich Kupfer leicht formen und umformen lässt.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Bei Generatoren verbessern Kupferwicklungen die Effizienz, insbesondere bei Anwendungen mit hoher Leistung. Ihr Gewicht kann jedoch bei tragbaren Generatoren ein Problem darstellen.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Einhaltung internationaler Normen wie ASTM B170 für Kupferdraht ist unerlässlich. Länder wie Nigeria und Vietnam können unterschiedliche Präferenzen bei der Materialbeschaffung haben und bevorzugen oft lokal verfügbare Materialien, um die Kosten zu senken.
Aluminium: Eine leichte Alternative
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Aluminium bietet ein gutes Gleichgewicht zwischen Leitfähigkeit (etwa 60% der von Kupfer), geringem Gewicht und Korrosionsbeständigkeit. Es funktioniert in der Regel effizient in Umgebungen bis zu 150°C.
Vor- und Nachteile: Der Hauptvorteil von Aluminium sind die niedrigeren Kosten und das geringere Gewicht, wodurch es sich für Anwendungen eignet, bei denen das Gewicht eine Rolle spielt. Allerdings ist seine Leitfähigkeit geringer als die von Kupfer, was zu höheren Energieverlusten führen kann. Die Herstellungsprozesse können aufgrund der erforderlichen spezifischen Legierungszusammensetzungen komplexer sein.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminium wird häufig in den Stator- und Rotorkomponenten von Generatoren verwendet, wo Gewichtseinsparungen die Gesamteffizienz verbessern können. Bei Anwendungen mit hohen Anforderungen kann jedoch seine geringere Leitfähigkeit eine Einschränkung darstellen.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Käufer müssen die lokalen Vorschriften für die Beschaffung und das Recycling von Aluminium berücksichtigen. Die Einhaltung von Normen wie ASTM B221 ist entscheidend, insbesondere in Regionen mit strengen Umweltvorschriften.
Stahl: Strukturelle Integrität und Dauerhaftigkeit
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Stahl ist bekannt für seine hohe Festigkeit, Haltbarkeit und Verschleißfestigkeit. Er kann hohen Temperaturen (bis zu 300 °C) standhalten und wird häufig gegen Korrosion behandelt.
Vor- und Nachteile: Aufgrund seiner Festigkeit eignet sich Stahl für die strukturellen Komponenten von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen. Sein Gewicht kann jedoch bei tragbaren Anwendungen ein Nachteil sein. Außerdem können die Kosten je nach Art des verwendeten Stahls erheblich variieren.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Stahl wird vor allem für das Gehäuse und den Rahmen von Generatoren verwendet, um die strukturelle Integrität und den Schutz vor Umwelteinflüssen zu gewährleisten. In Wechselstromgeneratoren wird er für die Rotoreinheit verwendet.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Einkäufer sollten darauf achten, dass Normen wie die ASTM A36 für Baustahl eingehalten werden. In Regionen wie Südamerika und dem Nahen Osten kann die Beschaffung von lokalem Stahl die Kosten senken und die regionale Wirtschaft unterstützen.

Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
Dämmstoffe: Gewährleistung von Sicherheit und Effizienz
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Isoliermaterialien wie Epoxidharz und Thermoplaste bieten elektrische Isolierung und thermische Stabilität. Sie halten in der Regel Temperaturen von bis zu 180 °C stand und sind feuchtigkeits- und chemikalienbeständig.
Vor- und Nachteile: Diese Materialien sind entscheidend für die Vermeidung von Kurzschlüssen und die Langlebigkeit von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen. Sie können jedoch die Herstellungsverfahren komplizierter machen und die Gesamtkosten erhöhen.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Isoliermaterialien sind in beiden Geräten unerlässlich, um einen sicheren Betrieb zu gewährleisten und Energieverluste aufgrund von Leckströmen zu verhindern.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Einhaltung internationaler Dämmstoffnormen, wie IEC 60085, ist von entscheidender Bedeutung. Käufer in Europa und Afrika haben aufgrund der regionalen Klimabedingungen möglicherweise spezifische Präferenzen für Dämmstoffe.
Zusammenfassende Tabelle
| Material | Typischer Anwendungsfall für Wechselstromgenerator und Generator | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kupfer | Wicklungen in Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren | Hervorragende Leitfähigkeit | Höhere Kosten im Vergleich zu Alternativen | Hoch |
| Aluminium | Stator- und Rotorkomponenten in Wechselstromgeneratoren | Leicht und kostengünstig | Geringere Leitfähigkeit | Mittel |
| Stahl | Strukturelle Komponenten in Stromerzeugern | Hohe Festigkeit und Haltbarkeit | Schwerer, kann die Transportkosten erhöhen | Mittel |
| Isolierende Materialien | Elektrische Isolierung in beiden Geräten | Verhindert Kurzschlüsse und erhöht die Langlebigkeit | Erhöht die Komplexität der Herstellung | Mittel |
Diese Analyse bietet B2B-Einkäufern wichtige Einblicke in die Materialauswahl für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen und hilft ihnen, fundierte Kaufentscheidungen zu treffen, die auf ihre spezifischen regionalen Bedürfnisse und Compliance-Anforderungen zugeschnitten sind.
Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für Generatoren und Generatoren
Was sind die typischen Herstellungsverfahren für Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren?
Die Herstellungsverfahren für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen umfassen mehrere wichtige Schritte, die jeweils entscheidend dafür sind, dass das Endprodukt den Leistungs- und Qualitätsstandards entspricht. Das Verständnis dieser Prozesse ist für B2B-Einkäufer, die zuverlässige Stromerzeugungsanlagen beschaffen wollen, von entscheidender Bedeutung.
Was sind die wichtigsten Schritte bei der Herstellung von Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren?
-
Materialvorbereitung:
- Der Herstellungsprozess beginnt mit der Beschaffung hochwertiger Rohstoffe, wie Kupfer für die Wicklungen, Stahl für die Kerne und verschiedene Legierungen für das Gehäuse.
- Die Materialien werden strengen Tests unterzogen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie die vorgeschriebenen mechanischen und elektrischen Eigenschaften erfüllen, da minderwertige Materialien zu Ineffizienzen und Ausfällen führen können. -
Formung:
– Stator- und Rotorproduktion: Stator und Rotor sind das Herzstück von Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren. Der Stator, der in der Regel aus laminiertem Siliziumstahl besteht, wird durch Stanzverfahren in die gewünschte Form gebracht. Dadurch werden Wirbelstromverluste reduziert und der Wirkungsgrad erhöht.
– Wickeln: Kupferdraht wird zu Spulen für den Stator und den Rotor gewickelt. Fortschrittliche Wickeltechniken, einschließlich automatischer Wickelmaschinen, gewährleisten Präzision und Konsistenz der Spulenabmessungen, die für die elektromagnetische Effizienz entscheidend sind. -
Montage:
- Bei der Montage wird der Rotor sorgfältig in den Stator eingepasst. Hier ist Präzision gefragt, denn eine falsche Ausrichtung kann zu mechanischem Versagen oder verminderter Leistung führen.
- In dieser Phase werden Komponenten wie Lager, Gleichrichter (für Generatoren) und Spannungsregler eingebaut. Jedes Teil wird auf Kompatibilität und Funktion geprüft. -
Endbearbeitung:
- Nach der Montage werden die Geräte zur Verbesserung der Haltbarkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit nachbearbeitet, z. B. durch Lackieren oder Beschichten. Dieser Schritt ist besonders wichtig für Geräte, die in rauen Umgebungen eingesetzt werden, wie sie in Regionen wie Afrika und dem Nahen Osten üblich sind.
- Durch Endkontrollen und Tests wird sichergestellt, dass jede Einheit den elektrischen und mechanischen Spezifikationen entspricht.
Wie wird die Qualitätssicherung bei der Herstellung von Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren durchgeführt?
Die Qualitätssicherung (QS) ist ein integraler Bestandteil des Herstellungsprozesses und stellt sicher, dass sowohl Generatoren als auch Generatoren internationalen und branchenspezifischen Standards entsprechen.
Welches sind die einschlägigen internationalen Normen für die Qualitätskontrolle?
- ISO 9001: Dies ist eine weithin anerkannte internationale Norm für Qualitätsmanagementsysteme. Hersteller von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen müssen häufig die ISO 9001 erfüllen, um eine gleichbleibende Produktqualität und Kundenzufriedenheit zu gewährleisten.
- CE-Kennzeichnung: Für Produkte, die innerhalb des Europäischen Wirtschaftsraums verkauft werden, zeigt die CE-Kennzeichnung die Konformität mit den Gesundheits-, Sicherheits- und Umweltschutznormen an.
- API-Standards: Für Generatoren, die in Öl- und Gasanwendungen eingesetzt werden, ist die Einhaltung der API-Normen (American Petroleum Institute) unerlässlich, um Zuverlässigkeit und Leistung unter anspruchsvollen Bedingungen zu gewährleisten.
Was sind die QC-Kontrollpunkte im Herstellungsprozess?
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC):
- Die Materialien werden bei ihrem Eintreffen in der Produktionsstätte geprüft. Dazu gehört die Überprüfung der Einhaltung der Spezifikationen und die Durchführung von Materialtests zur Bestätigung der Qualität. -
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC):
- Während des Herstellungsprozesses werden in verschiedenen Phasen Qualitätskontrollen durchgeführt. Dazu gehören die Überwachung des Wickelprozesses, die Überprüfung der Montagetoleranzen und die Durchführung von Zwischentests der elektrischen Leistung. -
Endkontrolle (FQC):
- Sobald der Generator oder die Lichtmaschine vollständig montiert ist, findet eine umfassende Endkontrolle statt. Dabei werden unter anderem die elektrische Leistung, der Wirkungsgrad und die mechanische Integrität geprüft. Jedes Gerät, das die Normen nicht erfüllt, wird entweder nachgearbeitet oder verschrottet.
Welche gängigen Prüfverfahren werden zur Qualitätssicherung eingesetzt?
Die Prüfmethoden variieren je nach Art des Geräts und der beabsichtigten Anwendung, aber zu den üblichen Praktiken gehören:
- Elektrische Prüfung: Dazu gehört die Messung der Ausgangsspannung, des Stroms und des Wirkungsgrads unter verschiedenen Lastbedingungen.
- Thermische Prüfung: Die Bewertung des Temperaturanstiegs während des Betriebs trägt dazu bei, dass das Gerät innerhalb der vorgegebenen Grenzen sicher betrieben werden kann.
- Schwingungsprüfung: Hier wird die Haltbarkeit und Stabilität der Baugruppe geprüft, was besonders bei Anwendungen mit hoher mechanischer Belastung wichtig ist.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrollpraktiken ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
Für internationale Einkäufer, insbesondere aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika und dem Nahen Osten, ist die Überprüfung der Qualitätskontrollverfahren eines Lieferanten von entscheidender Bedeutung.
-
Lieferantenaudits: Die Durchführung von Audits vor Ort ermöglicht es den Käufern, die Herstellungsverfahren, die Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen und die allgemeinen Betriebsstandards zu bewerten. Dies ist ein wirksames Mittel, um die Einhaltung der internationalen Normen zu gewährleisten.
-
Qualitätsberichte und Zertifizierungen: Das Anfordern von Unterlagen wie ISO-Zertifizierungen oder Prüfberichten kann Aufschluss über das Engagement des Lieferanten für Qualität geben. In diesen Dokumenten sollten die Verfahren und Ergebnisse der Qualitätssicherungspraktiken detailliert beschrieben werden.
-
Inspektionen durch Dritte: Die Beauftragung von Inspektionsdiensten durch Dritte kann eine zusätzliche Sicherheit bieten. Diese unabhängigen Organisationen können die Einhaltung von Industrienormen überprüfen und unvoreingenommene Beurteilungen der Produktqualität abgeben.
Was sind die Besonderheiten der Qualitätskontrolle und Zertifizierung für internationale B2B-Einkäufer?
Bei der Beschaffung von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen sollten internationale Einkäufer bestimmte Feinheiten in Bezug auf Qualitätskontrolle und Zertifizierung beachten:
-
Regionale Normen: In verschiedenen Regionen können unterschiedliche Normen und Vorschriften gelten. Für Einkäufer ist es wichtig, die spezifischen Anforderungen in ihren Zielmärkten zu kennen, um die Einhaltung zu gewährleisten und Probleme mit dem Zoll oder den örtlichen Behörden zu vermeiden.
-
Kulturelle Erwägungen: Kommunikationsstile und Geschäftspraktiken können sich von Kultur zu Kultur erheblich unterscheiden. Die Einkäufer sollten darauf vorbereitet sein, mit diesen Unterschieden umzugehen und klare Erwartungen in Bezug auf Qualität und Lieferung zu formulieren.
-
Logistik und Lieferkette: Es ist wichtig, die logistischen Herausforderungen beim Versand und der Lieferung dieser Produkte zu verstehen. Faktoren wie Transportmethoden, Vorlaufzeiten und lokale Vorschriften können sich auf den gesamten Qualitätssicherungsprozess auswirken.
Wenn B2B-Einkäufer die Herstellungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen verstehen und wissen, wie sie die Praktiken der Lieferanten effektiv überprüfen können, können sie fundierte Entscheidungen bei der Beschaffung von Generatoren und Generatoren treffen. Dieses Wissen ist besonders wertvoll für internationale Einkäufer, die sich in einer komplexen Landschaft von Normen und Erwartungen zurechtfinden müssen.
Praktischer Leitfaden für die Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘Lichtmaschine versus Generator’.’
Einführung
Wenn es darum geht, zwischen Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen zu wählen, kann das Verstehen der wichtigsten Unterschiede und das Treffen fundierter Entscheidungen Ihren Betrieb erheblich beeinflussen. Dieser praktische Beschaffungsleitfaden soll B2B-Einkäufern eine systematische Checkliste an die Hand geben, um sicherzustellen, dass sie die richtigen Geräte für ihre Bedürfnisse beschaffen. Unabhängig davon, ob Sie im Automobil-, Industrie- oder Energiesektor tätig sind, wird die Befolgung dieser Schritte dazu beitragen, Ihren Einkaufsprozess zu rationalisieren.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Beginnen Sie damit, die technischen Anforderungen Ihrer Anwendung klar zu umreißen. Dazu gehört, dass Sie die Ausgangsleistung und die Spannungsanforderungen kennen und wissen, ob Sie Wechselstrom (AC) oder Gleichstrom (DC) benötigen.
– Leistungsabgabe: Bedenken Sie die Last, die Ihr System tragen muss.
– Spannungstyp: Entscheiden Sie, ob Sie für Ihren Betrieb Wechsel- oder Gleichstrom benötigen, da dies die Auswahl einschränken wird.
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
Schritt 2: Bewertung des Energieeffizienzbedarfs
Beurteilen Sie die Anforderungen an die Energieeffizienz Ihres Betriebs. Generatoren haben in der Regel einen höheren Wirkungsgrad als Generatoren, was sich im Laufe der Zeit in Kosteneinsparungen niederschlagen kann.
– Energieeinsparung: Schätzen Sie ab, wie viel Energie Sie mit einer Lichtmaschine einsparen können, vor allem wenn Ihre Last schwankt.
– Operative Kosten: Ein höherer Wirkungsgrad bedeutet häufig niedrigere Betriebskosten, was Generatoren zu einer langfristig rentablen Investition macht.
Schritt 3: Potenzielle Lieferanten bewerten
Bevor Sie sich zu einem Kauf verpflichten, sollten Sie die Anbieter gründlich prüfen. Fordern Sie Unternehmensprofile, Fallstudien und Referenzen von Käufern aus ähnlichen Branchen oder Regionen an, um die Zuverlässigkeit sicherzustellen.
– Geschichte des Lieferanten: Suchen Sie nach Anbietern, die sich auf Ihrem spezifischen Markt bewährt haben.
– After-Sales-Unterstützung: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Lieferant einen soliden Kundendienst anbietet, einschließlich Wartungs- und Garantieleistungen.
Schritt 4: Installations- und Wartungsanforderungen berücksichtigen
Informieren Sie sich über die Installations- und Wartungsanforderungen für jeden Gerätetyp. Wechselstromgeneratoren sind in der Regel wartungsärmer als Stromerzeuger, was ein entscheidender Faktor bei Ihrer Entscheidungsfindung sein kann.
– Komplexität der Installation: Beurteilen Sie, wie einfach die Installation ist und ob Sie Fachpersonal benötigen.
– Häufigkeit der Wartung: Bestimmen Sie die voraussichtliche Häufigkeit der Wartungsprüfungen und die mit jeder Option verbundenen Kosten.
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
Schritt 5: Überprüfung der Konformität und Zertifizierungen
Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die Produkte, die Sie in Betracht ziehen, den lokalen und internationalen Normen entsprechen. Die Einhaltung der Branchenvorschriften ist für die Sicherheit und Effizienz von entscheidender Bedeutung.
– Zertifizierungen: Achten Sie auf Zertifizierungen, die die Einhaltung von Qualitäts- und Sicherheitsstandards belegen, z. B. ISO- oder IEC-Zertifizierungen.
– Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass das Gerät den örtlichen Vorschriften in Ihrer Region entspricht, insbesondere wenn Sie in verschiedenen Märkten wie Afrika oder Südamerika tätig sind.
Schritt 6: Analysieren Sie die Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO)
Berechnen Sie die Gesamtbetriebskosten, die die Anschaffungskosten, die Betriebskosten, die Wartung und mögliche Ausfallzeiten umfassen. Diese ganzheitliche Betrachtung wird Ihnen helfen, eine fundierte Entscheidung zu treffen.
– Erstkaufpreis: Vergleichen Sie die Anschaffungskosten von Lichtmaschinen mit denen von Generatoren.
– Langfristige Einsparungen: Berücksichtigen Sie die Energieeinsparungen und die Wartungskosten, um die beste langfristige Investition zu ermitteln.
Schritt 7: Lassen Sie sich von Experten beraten
Wenn Sie sich unsicher sind, sollten Sie sich von Fachleuten in diesem Bereich beraten lassen. Die Zusammenarbeit mit Fachleuten kann Ihnen Einblicke geben, die auf Ihre spezifischen betrieblichen Anforderungen zugeschnitten sind.
– Experten aus der Industrie: Suchen Sie nach Beratern, die mit den Feinheiten Ihres Sektors vertraut sind.
– Peer-Empfehlungen: Holen Sie sich Empfehlungen von anderen Unternehmen in Ihrer Branche ein, die ähnliche Beschaffungsprozesse durchlaufen haben.
Wenn Sie diese Checkliste befolgen, können Sie bei der Beschaffung von Generatoren eine fundierte und strategische Entscheidung treffen, die letztlich Ihre betriebliche Effizienz und Effektivität steigert.
Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Beschaffung von Generatoren und Generatoren
Was sind die wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten bei der Beschaffung von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen?
Bei der Bewertung der Beschaffung von Generatoren im Vergleich zu Generatoren ist es entscheidend, die verschiedenen Kostenkomponenten zu verstehen. Zu den wichtigsten Kostenelementen gehören Material, Arbeit, Fertigungsgemeinkosten, Werkzeuge, Qualitätskontrolle, Logistik und Gewinnspannen.
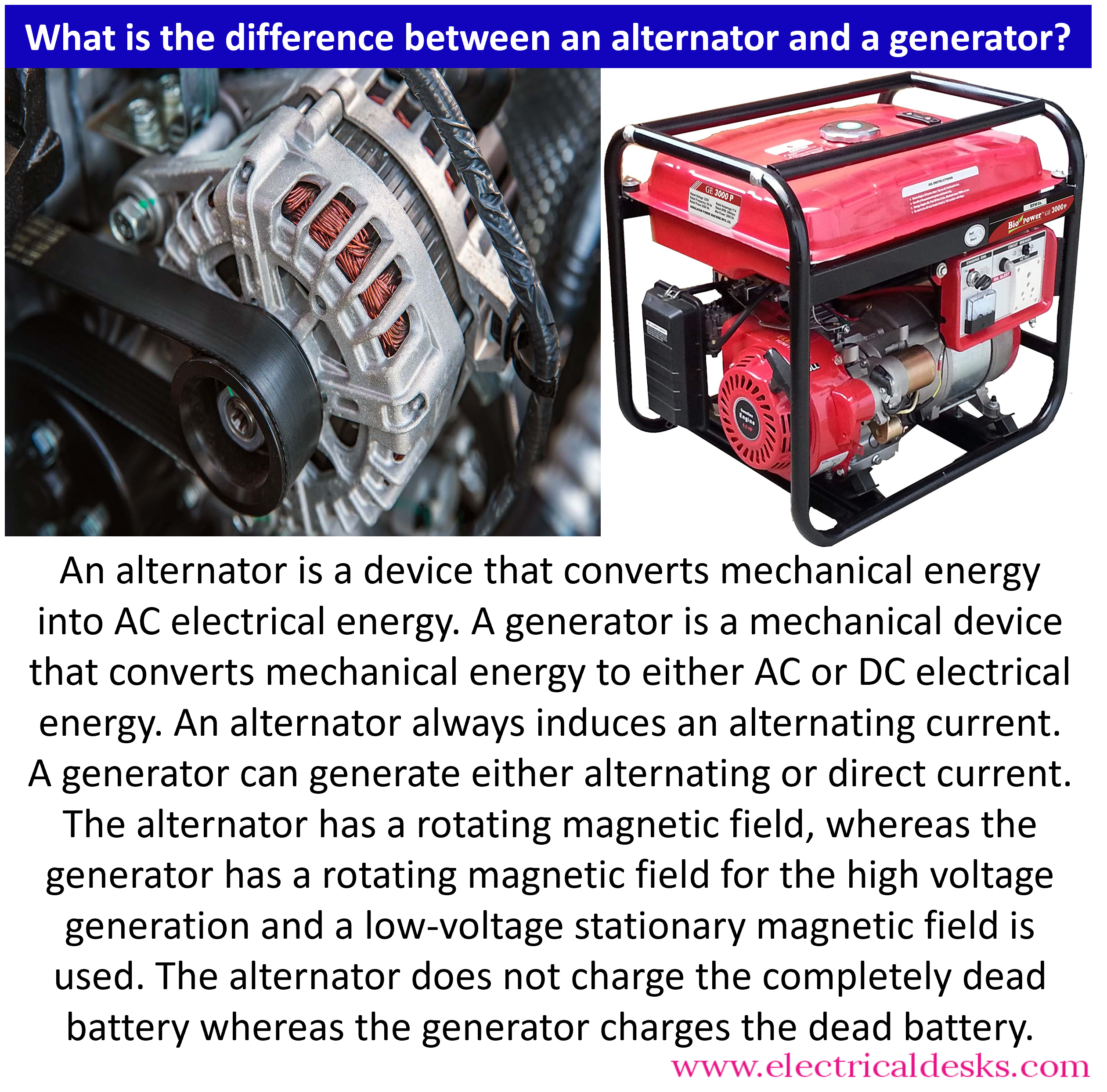
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
-
Materialien: Die Wahl der Materialien kann die Kosten erheblich beeinflussen. Wechselstromgeneratoren benötigen in der Regel leichte, hochleitfähige Materialien, um effizient zu sein, während Generatoren aus Gründen der Robustheit schwerere Materialien verwenden können. Die Preise von Rohstoffen wie Kupfer, Aluminium und Speziallegierungen schwanken je nach Marktnachfrage und Verfügbarkeit.
-
Arbeit: Die Arbeitskosten variieren je nach Region und Komplexität der Produktion. Länder mit niedrigeren Arbeitskosten können einen Wettbewerbsvorteil bieten, insbesondere bei der Massenproduktion. Allerdings sind qualifizierte Arbeitskräfte für eine qualitativ hochwertige Montage und Wartung unerlässlich, was sich auf die Gesamtkosten auswirkt.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: Hierunter fallen die indirekten Kosten im Zusammenhang mit der Produktion, einschließlich Versorgungsleistungen, Miete und Abschreibung der Anlagen. Eine wirksame Verwaltung der Gemeinkosten kann zu niedrigeren Stückkosten führen.
-
Werkzeuge: Maßgeschneiderte Werkzeuge für spezielle Designs oder Modifikationen können die Anfangskosten erhöhen, können aber notwendig sein, um einzigartige Spezifikationen zu erfüllen. Es ist wichtig, die Kosten für die Werkzeuge mit dem erwarteten Produktionsvolumen abzugleichen.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Die Gewährleistung einer hohen Qualität durch strenge Tests und Inspektionen ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere bei Komponenten, die in kritischen Anwendungen eingesetzt werden. Die mit den QC-Prozessen verbundenen Kosten sollten in der gesamten Preisstruktur berücksichtigt werden.
-
Logistik: Die Transport- und Bearbeitungskosten können erheblich sein, insbesondere bei internationalen Sendungen. Faktoren wie die Entfernung, die Transportart und die Versandbedingungen beeinflussen diese Kosten.
-
Marge: Die Lieferanten werden ihre Gewinnspannen in die Preisgestaltung einbeziehen. Die Kenntnis des Wettbewerbsumfelds kann Einkäufern helfen, bessere Bedingungen auszuhandeln.
Wie beeinflussen Preiseinflussfaktoren die Beschaffungsentscheidungen?
Mehrere Faktoren beeinflussen die Preisgestaltung von Generatoren, insbesondere für internationale Käufer.
-
Menge/Mindestbestellmenge: Höhere Bestellmengen führen in der Regel zu niedrigeren Stückkosten. Einkäufer sollten ihren Bedarf ermitteln und die Aushandlung von Mindestbestellmengen in Betracht ziehen, um von Mengenrabatten zu profitieren.
-
Spezifikationen/Anpassung: Kundenspezifische Designs oder Spezifikationen können die Kosten erhöhen. Die Käufer müssen die Vorteile der individuellen Gestaltung gegen die Budgetbeschränkungen abwägen.
-
Materialien: Die Qualität und die Art der verwendeten Materialien wirken sich direkt auf den Preis aus. Einkäufer sollten Spezifikationen bevorzugen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen übereinstimmen und gleichzeitig die Kosten im Auge behalten.
-
Qualität/Zertifizierungen: Zertifizierungen wie die ISO können die Glaubwürdigkeit von Produkten erhöhen, aber auch zu höheren Preisen führen. Die Einkäufer sollten die Bedeutung dieser Zertifizierungen in ihrer Beschaffungsstrategie berücksichtigen.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Die Zuverlässigkeit und der Ruf der Lieferanten können die Preisgestaltung beeinflussen. Langfristige Beziehungen können zu besseren Preisen und Bedingungen führen.
-
Incoterms: Das Verständnis der Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) ist entscheidend für die Bestimmung der Verantwortung für Versandkosten, Versicherung und Zölle. Dieses Wissen kann die gesamten Anlandungskosten von Produkten erheblich beeinflussen.
Welche Tipps können Einkäufer für Kosteneffizienz bei der Beschaffung nutzen?
Um die Kosteneffizienz bei der Beschaffung von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen zu maximieren, sollten Käufer die folgenden Strategien berücksichtigen:
-
Verhandlung: Eine effektive Verhandlung kann zu erheblichen Einsparungen führen. Einkäufer sollten darauf vorbereitet sein, die Bedingungen, einschließlich Preisgestaltung, Zahlungspläne und Lieferfristen, zu besprechen.
-
Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO): Bewerten Sie die TCO und nicht nur den Anschaffungspreis. Dazu gehören auch die Kosten für Wartung, Betriebseffizienz und potenzielle Ausfallzeiten, die mit der Ausrüstung verbunden sind.
-
Preisgestaltung für internationale Käufer: Käufer aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa sollten sich der regionalen Preisunterschiede, Zölle und Währungsschwankungen bewusst sein, die die Gesamtkosten beeinflussen können.
-
Bewertung der Lieferanten: Führen Sie gründliche Bewertungen potenzieller Lieferanten durch und berücksichtigen Sie dabei deren Produktionskapazitäten, Lieferzeiten und Kundenservice. Dies kann zu fundierteren Beschaffungsentscheidungen und langfristigen Partnerschaften führen.
Haftungsausschluss
Die hier genannten Preise und Kostenstrukturen sind Richtwerte und können sich aufgrund von Marktbedingungen, wirtschaftlichen Faktoren und individuellen Lieferantenvereinbarungen ändern. Käufer sollten umfassende Marktforschung und Lieferantenbewertungen durchführen, um genaue, auf ihre spezifischen Bedürfnisse zugeschnittene Preise zu ermitteln.
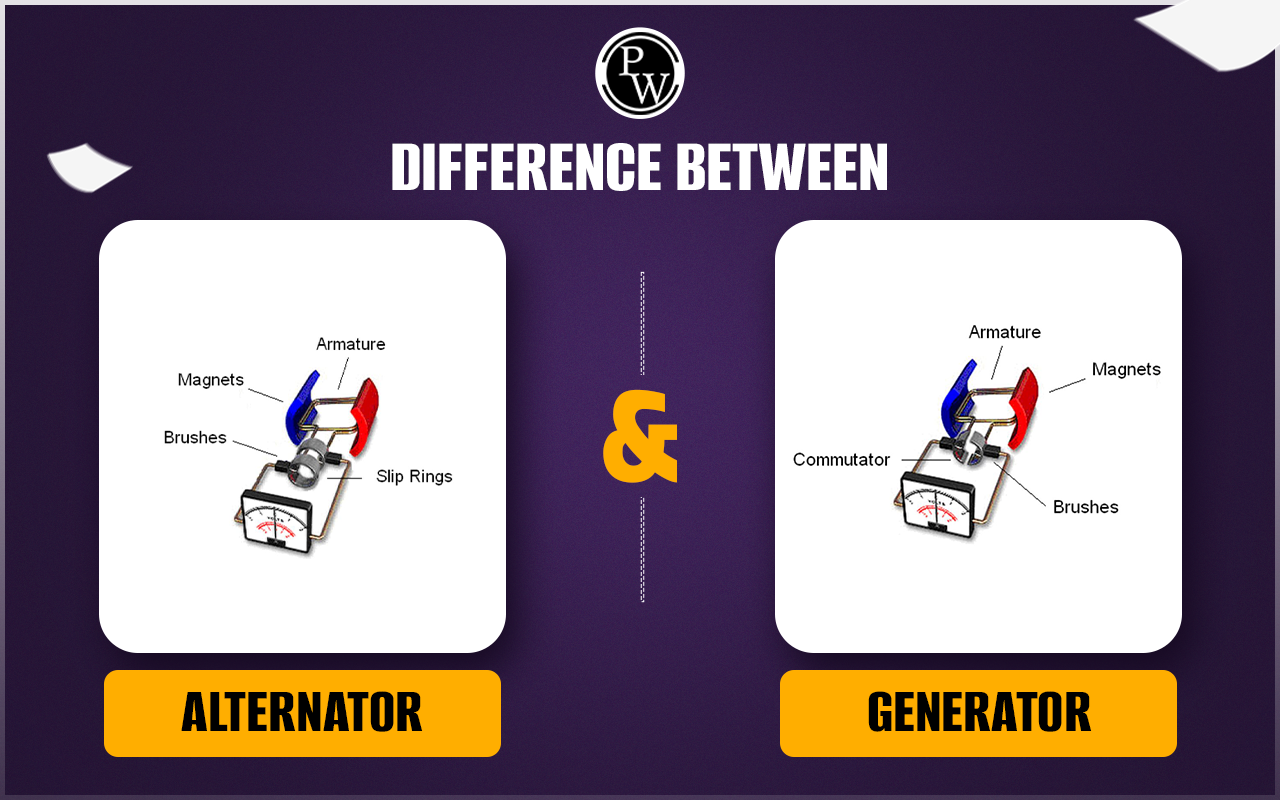
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich von Lichtmaschine und Generator mit anderen Lösungen
Alternativen zu Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren verstehen
Im Bereich der Stromerzeugung und -umwandlung sind Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen die traditionelle Wahl für viele Anwendungen, von der Automobilindustrie bis zur Industrie. Mit der Weiterentwicklung der Technologie gibt es jedoch auch Alternativen, die ähnliche oder verbesserte Funktionen bieten. In dieser Analyse werden Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren mit zwei praktikablen Alternativen verglichen: Solarstromanlagen und Batteriespeichersysteme. Jede Lösung hat einzigartige Merkmale, die sich besser für bestimmte Unternehmensanforderungen eignen.
Vergleichstabelle
| Vergleichsaspekt | Lichtmaschine vs. Generator | Solarstromanlagen | Batteriespeichersysteme |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Hoher Wirkungsgrad, AC-Ausgang | Variable Leistung, abhängig von der Sonneneinstrahlung | Stabile Leistung, skalierbare Kapazität |
| Kosten | Moderate Anfangskosten | Hohe Anfangskosten, niedrige langfristige Kosten | Mäßig bis hoch, je nach Kapazität |
| Einfache Implementierung | Relativ einfach zu installieren | Erfordert die Installation und Ausrichtung von Solarmodulen | Einfache Installation, aber richtige Dimensionierung erforderlich |
| Wartung | Geringe Wartung erforderlich | Minimale Wartung erforderlich | Mäßige Wartung für die Gesundheit der Batterie |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Automobilindustrie, kleine Stromerzeugung | Netzunabhängige Anwendungen, abgelegene Standorte | Notstromversorgung, Spitzenabschaltung, Integration erneuerbarer Energien |
Detaillierte Aufschlüsselung der Alternativen
Solarstromanlagen
Solarenergiesysteme nutzen die Energie der Sonne über Photovoltaikmodule und wandeln das Sonnenlicht in Strom um. Diese Methode ist besonders vorteilhaft für Unternehmen, die ihren ökologischen Fußabdruck verringern und Energieunabhängigkeit erreichen wollen. Während die Anfangsinvestitionen beträchtlich sein können, kann die Solarenergie im Laufe der Zeit aufgrund der geringeren Betriebskosten zu erheblichen Einsparungen führen. Allerdings kann die Leistung unbeständig sein, da die Energieerzeugung je nach Wetterbedingungen und geografischem Standort schwankt. Solarsysteme erfordern eine sorgfältige Planung und Installation, um eine optimale Energieausbeute zu gewährleisten.
Batteriespeichersysteme
Batteriespeichersysteme, wie z. B. Lithium-Ionen-Batterien, bieten eine zuverlässige Methode zur Speicherung von Energie für den späteren Gebrauch. Diese Systeme sind besonders vorteilhaft für Unternehmen, die eine unterbrechungsfreie Stromversorgung benötigen oder den Energieverbrauch in Spitzenzeiten steuern wollen. Sie lassen sich leicht mit erneuerbaren Energiequellen wie Sonnen- oder Windenergie kombinieren, um überschüssige Energie zu speichern. Die anfänglichen Kosten können je nach benötigter Kapazität moderat bis hoch sein, und die Wartung ist notwendig, um die Langlebigkeit der Batterien zu gewährleisten. Batteriesysteme sind ideal für Anwendungen, bei denen Stabilität und Zuverlässigkeit von größter Bedeutung sind.
Schlussfolgerung: Wie Sie die richtige Lösung für Ihre Bedürfnisse wählen
Wenn B2B-Einkäufer Alternativen zu Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen in Betracht ziehen, müssen sie ihren spezifischen Energiebedarf, ihre Budgeteinschränkungen und ihre betrieblichen Gegebenheiten berücksichtigen. Solarenergiesysteme eignen sich hervorragend für Unternehmen, die Nachhaltigkeit und langfristige Einsparungen anstreben, während Batteriespeichersysteme Zuverlässigkeit und Flexibilität für das Energiemanagement bieten. Im Gegensatz dazu können herkömmliche Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen immer noch die beste Wahl für Anwendungen sein, die sofortigen Strom mit hohem Durchsatz benötigen. Durch eine gründliche Analyse der Leistung, der Kosten, der einfachen Implementierung und des Wartungsbedarfs können Unternehmen fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Zielen und Nachhaltigkeitsinitiativen in Einklang stehen.
Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für Generatoren und Generatoren
Was sind die wichtigsten technischen Eigenschaften von Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren?
Das Verständnis der technischen Eigenschaften von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen ist für B2B-Einkäufer von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere wenn sie eine fundierte Kaufentscheidung treffen wollen. Hier sind einige wesentliche Spezifikationen, die Sie beachten sollten:
-
Ausgangsspannung und Stromart
– Definition: Wechselstromgeneratoren erzeugen in der Regel Wechselstrom (AC), während Generatoren sowohl Wechsel- als auch Gleichstrom (DC) erzeugen können.
– Bedeutung: Diese Unterscheidung wirkt sich auf die Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Anwendungen aus. So werden beispielsweise in Kraftfahrzeugsystemen vor allem Generatoren verwendet, da sie einen hohen Wirkungsgrad bei der Erzeugung von Wechselstrom haben, was für moderne Fahrzeuge mit zahlreichen elektrischen Anforderungen entscheidend ist. -
Effizienzbewertung
– Definition: Dieser Wert gibt an, wie effektiv ein Gerät mechanische Energie in elektrische Energie umwandelt, und wird in der Regel als Prozentsatz angegeben.
– Bedeutung: Wechselstromgeneratoren haben im Allgemeinen einen höheren Wirkungsgrad als Generatoren, der oft über 80% liegt. Ein höherer Wirkungsgrad führt zu niedrigeren Betriebskosten und Energieeinsparungen, so dass Generatoren in Branchen, in denen Energieeinsparungen von entscheidender Bedeutung sind, vorzuziehen sind. -
Größe und Gewicht
– Definition: Bezieht sich auf die physikalischen Abmessungen und die Masse der Einheiten.
– Bedeutung: Wechselstromgeneratoren sind in der Regel kleiner und leichter als Generatoren. Dies ist besonders vorteilhaft bei Anwendungen mit begrenztem Platzangebot, wie z. B. in Kraftfahrzeugen und tragbaren Stromversorgungssystemen, und ermöglicht eine einfachere Installation und geringere Transportkosten. -
RPM-Bereich (Umdrehungen pro Minute)
– Definition: Gibt die Betriebsdrehzahl an, bei der der Generator oder die Lichtmaschine effektiv Strom erzeugen kann.
– Bedeutung: Wechselstromgeneratoren können über einen breiteren Drehzahlbereich effizient arbeiten und eignen sich daher für Anwendungen mit variabler Drehzahl. Diese Flexibilität ist für Industriezweige, die eine stabile Leistungsabgabe unter wechselnden Betriebsbedingungen benötigen, unerlässlich. -
Lebensdauer der Bürste
– Definition: Bezieht sich auf die Langlebigkeit der in den elektrischen Systemen von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen verwendeten Bürsten.
– Bedeutung: Wechselstromgeneratoren haben in der Regel langlebigere Bürsten als die von Generatoren. Diese Langlebigkeit verringert die Wartungshäufigkeit und -kosten und macht Generatoren zu einer kostengünstigeren Wahl für den langfristigen Betrieb. -
Mechanismus der Kühlung
– Definition: Die Methode zur Ableitung der während des Betriebs erzeugten Wärme.
– Bedeutung: Wechselstromgeneratoren verfügen oft über fortschrittliche Kühlsysteme, die die Leistung und Langlebigkeit verbessern. Für B2B-Einkäufer ist es wichtig, die Kühlmechanismen zu verstehen, um Entscheidungen über die Zuverlässigkeit und den Wartungsbedarf in stark beanspruchten Umgebungen zu treffen.
Was sind gängige Fachausdrücke im Zusammenhang mit Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren?
Die Kenntnis des Branchenjargons ist für eine effektive Kommunikation und Verhandlung im B2B-Geschäft unerlässlich. Hier sind einige gängige Begriffe, die für Generatoren und Generatoren relevant sind:
-
OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
– Definition: Ein Unternehmen, das Teile und Geräte herstellt, die von einem anderen Hersteller vermarktet werden können.
– Bedeutung: Käufer suchen oft nach OEM-Teilen, um Zuverlässigkeit und Kompatibilität zu gewährleisten und sicherzustellen, dass die Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen die erwartete Leistung für ihre Anwendungen erbringen. -
MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
– Definition: Die kleinste Menge eines Produkts, die ein Anbieter zu verkaufen bereit ist.
– Bedeutung: Das Verständnis der MOQ ist für Einkäufer entscheidend, um den Bestand und den Cashflow effektiv zu verwalten. Sie kann auch die Verhandlungsstrategien und Kaufentscheidungen beeinflussen, insbesondere bei Großaufträgen. -
RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
– Definition: Ein Dokument, das an Lieferanten geschickt wird, um ein Preisangebot für bestimmte Produkte oder Dienstleistungen anzufordern.
– Bedeutung: Eine Anfrage ermöglicht es Einkäufern, die Preise und Bedingungen mehrerer Lieferanten zu vergleichen und so eine fundierte Kaufentscheidung zu treffen. Sie ist ein wesentlicher Schritt im Beschaffungsprozess für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen. -
Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
– Definition: Eine Reihe von Regeln, die die Verantwortlichkeiten von Käufern und Verkäufern bei internationalen Transaktionen festlegen.
– Bedeutung: Die Kenntnis der Incoterms ist für B2B-Einkäufer, die an der globalen Beschaffung beteiligt sind, unerlässlich. Die Incoterms regeln die Verantwortlichkeiten, Kosten und Risiken beim Versand und helfen, Streitigkeiten und Missverständnisse zu vermeiden. -
Vorlaufzeit
– Definition: Die Zeit von der Bestellung bis zum Erhalt der Ware.
– Bedeutung: Die Kenntnis der Vorlaufzeiten ist für das Lieferkettenmanagement von entscheidender Bedeutung. Längere Vorlaufzeiten können sich auf den Zeitplan von Projekten auswirken, weshalb es für Einkäufer wichtig ist, diesen Aspekt bei Verhandlungen mit Lieferanten zu klären. -
Garantiezeitraum
– Definition: Die Dauer, für die ein Hersteller das Produkt gegen Mängel und Leistungsprobleme garantiert.
– Bedeutung: Eine solide Garantiezeit kann den Käufern Sicherheit geben, indem sie das mit der Investition in Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen verbundene Risiko verringert und Unterstützung im Falle von Ausfällen gewährleistet.
Durch die Kenntnis dieser technischen Eigenschaften und der Fachterminologie können B2B-Einkäufer fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die auf ihre betrieblichen Anforderungen und finanziellen Ziele abgestimmt sind.
Navigieren durch Marktdynamik und Beschaffungstrends im Sektor Generatoren und Generatoren
Was sind die wichtigsten Marktdynamiken und -trends im Sektor Generatoren und Generatoren?
Der weltweite Markt für Generatoren und Generatoren erfährt aufgrund des technologischen Fortschritts und der steigenden Nachfrage nach zuverlässigen Stromquellen erhebliche Veränderungen. In Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa treibt die zunehmende Urbanisierung und Industrialisierung den Bedarf an effizienten elektrischen Systemen in die Höhe. Dieser Trend ist besonders in Entwicklungsländern zu beobachten, wo die Elektrifizierung ländlicher Gebiete und der Ausbau von Infrastrukturprojekten von entscheidender Bedeutung sind. Darüber hinaus beeinflusst der Anstieg der erneuerbaren Energiequellen den Markt, wobei Generatoren aufgrund ihrer Energieeffizienz und ihrer Fähigkeit, Wechselstrom aus erneuerbaren Energiesystemen zu erzeugen, bevorzugt werden.
Aufkommende Technologien wie intelligente Netzlösungen und IoT-fähige Geräte verändern auch die Beschaffungsstrategien. B2B-Einkäufer suchen zunehmend nach Lieferanten, die fortschrittliche Funktionen wie Fernüberwachung und vorausschauende Wartung anbieten, die die betriebliche Effizienz steigern und Ausfallzeiten reduzieren. Darüber hinaus werden durch die Integration der Automatisierung in die Fertigungsprozesse die Produktion rationalisiert und die Kosten gesenkt, so dass es für internationale Einkäufer einfacher wird, hochwertige Produkte zu wettbewerbsfähigen Preisen zu beschaffen.
Ein weiterer wichtiger Trend ist die zunehmende Konzentration auf modulare und kompakte Konstruktionen, insbesondere bei Generatoren, da die Unternehmen bestrebt sind, Platz und Gewicht in ihren Anwendungen zu optimieren. Diese Trends unterstreichen, wie wichtig es ist, über den technologischen Fortschritt und die Fähigkeiten der Lieferanten informiert zu bleiben, um fundierte Kaufentscheidungen treffen zu können.
Wie wirkt sich Nachhaltigkeit auf die B2B-Beschaffung auf dem Markt für Generatoren und Generatoren aus?
Nachhaltigkeit wird zu einer zentralen Säule in den Beschaffungsstrategien von B2B-Einkäufern im Bereich Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen. Da sich die Umweltvorschriften weltweit verschärfen, geben Unternehmen zunehmend Lieferanten den Vorzug, die sich an nachhaltige Praktiken halten. Dazu gehört die Verwendung von umweltfreundlichen Materialien und Verfahren, die den Abfall und den Energieverbrauch minimieren.
Außerdem steigt die Nachfrage nach ‘grünen’ Zertifizierungen wie ISO 14001 (Umweltmanagementsysteme) bei den Käufern, die sichergehen wollen, dass ihre Beschaffungsentscheidungen zum Umweltschutz beitragen. Auf dem Markt für Generatoren beispielsweise konzentrieren sich die Hersteller auf die Herstellung energieeffizienter Produkte, die nicht nur die gesetzlichen Anforderungen erfüllen, sondern auch langfristige Kosteneinsparungen durch geringeren Energieverbrauch ermöglichen.
Auch die ethische Beschaffung gewinnt zunehmend an Bedeutung, da die Unternehmen Transparenz in ihren Lieferketten anstreben, um sicherzustellen, dass die Materialien auf verantwortungsvolle Weise beschafft werden. Dies ist vor allem in Regionen von Bedeutung, in denen die Rohstoffgewinnung erhebliche ökologische und soziale Auswirkungen haben kann. Durch die Bevorzugung von Lieferanten, die sich zu ethischen Praktiken verpflichten, können B2B-Einkäufer ihr Markenimage verbessern und der wachsenden Vorliebe der Verbraucher für nachhaltige und sozial verantwortliche Produkte gerecht werden.
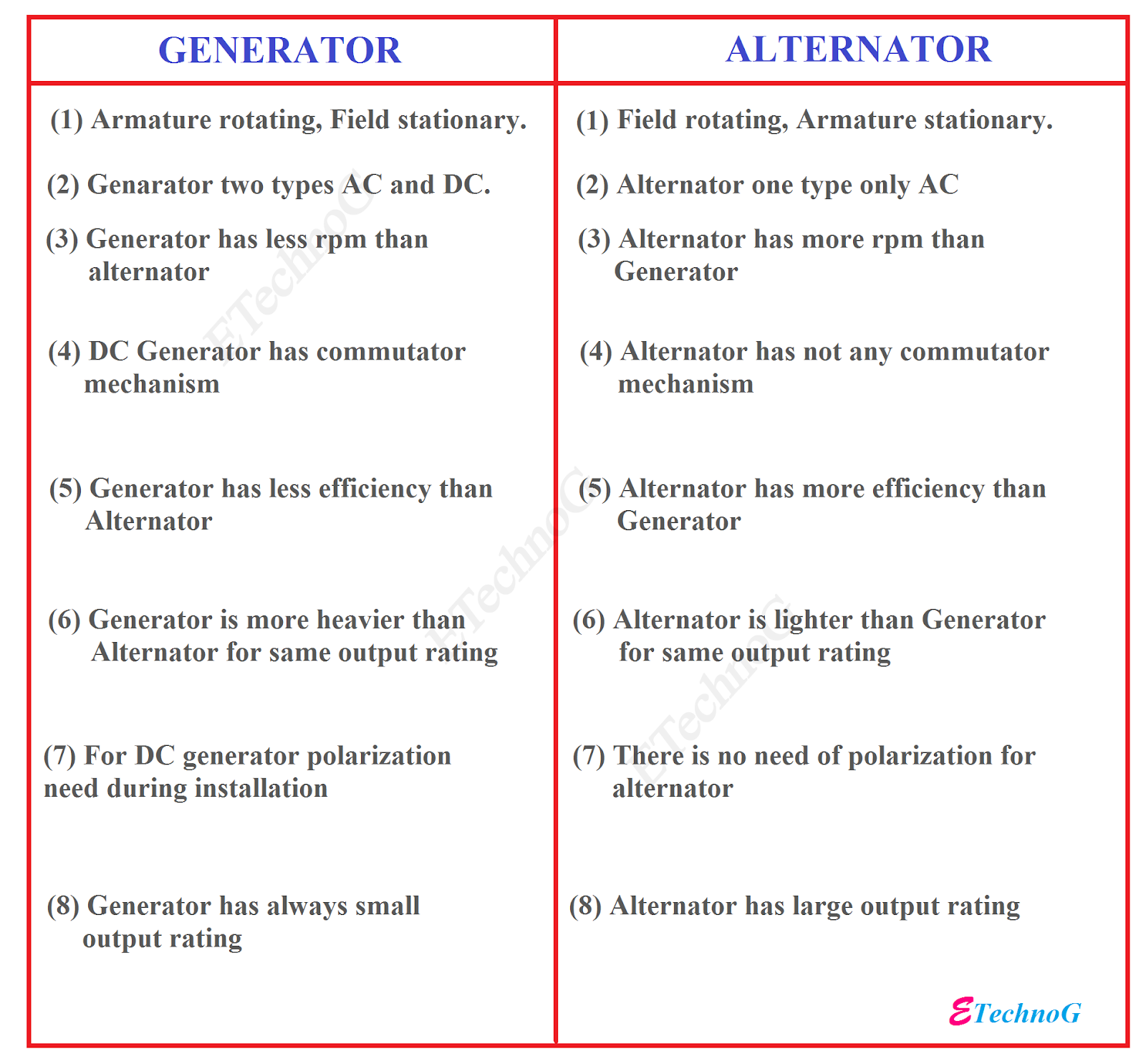
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
Welche Bedeutung hat die Entwicklung von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen für den heutigen B2B-Kontext?
Die Entwicklung von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen ist von bedeutenden technologischen Fortschritten geprägt, die ihre Rolle in elektrischen Systemen neu gestaltet haben. Ursprünglich waren Generatoren die erste Wahl für die Stromerzeugung, vor allem in frühen Automobilanwendungen. Als jedoch die elektrischen Anforderungen mit dem Aufkommen der modernen Technologie stiegen, begannen Generatoren aufgrund ihrer überlegenen Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit zu dominieren.
In den 1960er Jahren hatten Lichtmaschinen die Generatoren in Kraftfahrzeugen weitgehend abgelöst und boten eine gleichmäßigere Stromversorgung, die die wachsende Zahl elektrischer Geräte in Fahrzeugen unterstützen konnte. Diese Umstellung verbesserte nicht nur die Leistung, sondern verringerte auch den Wartungsbedarf, wodurch Generatoren für B2B-Käufer, die auf Langlebigkeit und Effizienz Wert legen, attraktiver wurden.
Heute hat sich der Schwerpunkt auf die Integration dieser Geräte in Systeme für erneuerbare Energien verlagert, bei denen Generatoren zur Umwandlung mechanischer Energie aus Windturbinen oder Wasserkraftanlagen in elektrische Energie eingesetzt werden. Diese Entwicklung macht deutlich, wie wichtig es ist, den historischen Kontext dieser Technologien zu verstehen, da er die aktuellen Beschaffungsentscheidungen und technologischen Investitionen in diesem Sektor beeinflusst.
Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer von Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren
-
Wie entscheide ich mich für einen Wechselstromgenerator oder einen Generator für meine geschäftlichen Anforderungen?
Ob Sie sich für einen Generator oder eine Lichtmaschine entscheiden, hängt von Ihrem spezifischen Strombedarf und Ihrer Anwendung ab. Wechselstromgeneratoren sind in der Regel effizienter und eignen sich für Anwendungen, die eine hohe Leistung und häufigen Gebrauch erfordern, insbesondere in Umgebungen mit variablen Lasten. Im Gegensatz dazu sind Generatoren vielseitiger und liefern sowohl Wechsel- als auch Gleichstrom, was sie ideal für industrielle Anwendungen macht, bei denen verschiedene Stromarten benötigt werden. Analysieren Sie Ihre betrieblichen Anforderungen, einschließlich Stromverbrauch, Effizienz und Wartungsaspekte, um eine fundierte Entscheidung zu treffen. -
Welches ist der beste Generatortyp für industrielle Großanwendungen?
Für groß angelegte industrielle Anwendungen sind Dieselgeneratoren aufgrund ihrer Zuverlässigkeit, ihrer Kraftstoffeffizienz und ihrer Fähigkeit, eine beträchtliche Leistung zu erzeugen, oft die beste Wahl. Sie können im Dauerbetrieb arbeiten und eignen sich für abgelegene Standorte mit begrenztem Zugang zum Stromnetz. Achten Sie bei der Beschaffung auf Faktoren wie Lastkapazität, Kraftstoffverfügbarkeit und Wartungsunterstützung. Die Zusammenarbeit mit einem seriösen Anbieter, der einen zuverlässigen Kundendienst anbietet, ist entscheidend, um die Betriebseffizienz und Langlebigkeit der Anlagen zu gewährleisten. -
Welche Faktoren sollte ich bei der Auswahl von Lieferanten für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen berücksichtigen?
Prüfen Sie bei der Auswahl der Lieferanten deren Ruf in der Branche, Erfahrung und Kundenrezensionen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass sie Zertifizierungen und Garantien anbieten, die die Produktqualität garantieren. Prüfen Sie, ob das Unternehmen in der Lage ist, Kundendienst, einschließlich Wartungs- und Reparaturdienste, anzubieten. Beurteilen Sie außerdem, wie schnell das Unternehmen auf Anfragen reagiert und ob es bereit ist, Anpassungswünsche zu erfüllen. Bei internationalen Geschäften sollten Sie sich vergewissern, dass das Unternehmen die einschlägigen Handelsbestimmungen einhält und über die notwendigen logistischen Kapazitäten für eine pünktliche Lieferung verfügt. -
Kann ich Lichtmaschinen oder Generatoren für bestimmte Anwendungen anpassen?
Ja, viele Hersteller bieten Anpassungsmöglichkeiten für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen an, um bestimmte Betriebsanforderungen zu erfüllen. Zu den Anpassungen können Anpassungen der Ausgangsspannung, der Größe und zusätzliche Funktionen wie Geräuschreduzierungstechnologie oder verbesserte Haltbarkeit für raue Umgebungen gehören. Wenn Sie mit Lieferanten über Anpassungen sprechen, sollten Sie sich über Ihre Bedürfnisse und die Betriebsbedingungen im Klaren sein. So können Sie sicherstellen, dass das Produkt den besonderen Anforderungen Ihres Unternehmens entspricht und die Gesamteffizienz erhöht. -
Wie hoch sind die Mindestbestellmengen (MOQ) für Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen?
Die Mindestbestellmengen können von Lieferant zu Lieferant sehr unterschiedlich sein und werden von Faktoren wie Produkttyp, Kundenanpassung und Produktionsmöglichkeiten beeinflusst. In der Regel haben größere Lieferanten niedrigere Mindestbestellmengen, während kleinere Hersteller möglicherweise höhere Mengen benötigen, um die Produktionskosten zu rechtfertigen. Es ist ratsam, Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen direkt mit potenziellen Lieferanten zu besprechen, um eine für beide Seiten akzeptable Mindestbestellmenge zu finden, die mit Ihrer Einkaufsstrategie und Bestandsverwaltung übereinstimmt. -
Mit welchen Zahlungsbedingungen muss ich rechnen, wenn ich Lichtmaschinen oder Generatoren international kaufe?
Die Zahlungsbedingungen für internationale Einkäufe können je nach den Richtlinien des Lieferanten und der Kreditwürdigkeit des Käufers sehr unterschiedlich sein. Üblich ist eine prozentuale Vorauszahlung, wobei der Restbetrag bei Lieferung oder nach einer bestimmten Frist fällig wird. Ziehen Sie sichere Zahlungsmethoden wie Akkreditive oder Treuhanddienste in Betracht, um die Risiken zu mindern. Es ist wichtig, Bedingungen auszuhandeln, die Ihre Interessen schützen und gleichzeitig sicherstellen, dass sich der Lieferant bei der Transaktion sicher fühlt. -
Wie gewährleiste ich die Qualitätssicherung für meine Generatoren oder Lichtmaschinen?
Um die Qualität zu gewährleisten, sollten Sie von den Lieferanten detaillierte Produktspezifikationen und Zertifizierungen verlangen. Achten Sie auf ISO-Zertifizierungen oder die Einhaltung internationaler Normen, die für elektrische Geräte relevant sind. Die Durchführung von Werksaudits oder die Forderung von Inspektionen durch Dritte vor dem Versand können ebenfalls zur Überprüfung der Produktqualität beitragen. Legen Sie in Ihrem Vertrag eindeutige Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen fest und pflegen Sie während des gesamten Produktionsprozesses eine offene Kommunikation mit dem Lieferanten, um etwaige Bedenken umgehend auszuräumen. -
Welche logistischen Überlegungen sollte ich beim Versand von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen anstellen?
Beim Versand von Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen sind Faktoren wie Versandmethoden, Kosten und Vorlaufzeiten zu berücksichtigen. Aufgrund ihrer Größe und ihres Gewichts erfordern diese Produkte unter Umständen besondere Handhabungs- und Transportvorkehrungen. Arbeiten Sie mit Logistikanbietern zusammen, die Erfahrung mit dem Versand von Schwermaschinen haben, um die Einhaltung internationaler Versandvorschriften zu gewährleisten. Berücksichtigen Sie außerdem Zölle und Steuern und stellen Sie sicher, dass alle Unterlagen korrekt sind, um Verzögerungen an den Grenzen zu vermeiden.
Liste der 3 größten Hersteller und Lieferanten von Wechselstromgeneratoren und Generatoren
1. Speedway Motors - Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren
Domäne: speedwaymotors.com
Registriert: 1996 (29 Jahre)
Einleitung: Lichtmaschinen und Generatoren sind Geräte, die mechanische Energie in elektrische Energie umwandeln, um die Autobatterie zu laden. Die wichtigsten Unterschiede sind:
- Generatoren verwenden einen rotierenden Anker in statischen Magneten, um elektrischen Strom zu induzieren, während Wechselstromgeneratoren das Magnetfeld im Leiter drehen.
- Generatoren waren effektiv für frühe Autos mit minimalem elektrischem Zubehör, haben aber mit...
2. Fragen Sie einen CFI - Hauptunterschiede zwischen Generatoren und Alternatoren
Domäne: askacfi.de
Registriert: 2001 (24 Jahre)
Einleitung: Die wichtigsten Unterschiede zwischen einem Generator und einer Lichtmaschine:
1. Stromerzeugung: Ein Generator erzeugt Strom, indem er einen Drahtanker in einem festen Magnetfeld bewegt, während ein Generator ein sich drehendes Magnetfeld in stationären Wicklungen (Stator) hat.
2. Der Wirkungsgrad: Wechselstromgeneratoren sind im Allgemeinen effizienter als Generatoren.
3. Aufbau: Wechselstromgeneratoren haben Wicklungen, die direkt mit dem Ausgangspunkt verdrahtet...
3. IH8Mud - Generatoren vs. Lichtmaschinen
Domäne: forum.ih8mud.com
Registriert: 2000 (25 Jahre)
Einleitung: Generatoren erzeugen Gleichstrom, während Wechselstromgeneratoren Wechselstrom erzeugen. Generatoren werden aufgrund von Wartungs- und Größenproblemen nicht mehr häufig verwendet. Ein Generator arbeitet, indem er eine Reihe von Wicklungen (den Anker) in einem festen Magnetfeld dreht und dabei Strom erzeugt, der proportional zur Geschwindigkeit des Ankers und der Stärke des Magnetfelds ist. Die Geschwindigkeit wird durch die Motordrehzahl gesteuert, und ...
Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für Generatoren gegenüber Generatoren
Bei der Bewertung der Unterschiede zwischen Generatoren und Lichtmaschinen müssen internationale B2B-Einkäufer mehrere entscheidende Faktoren berücksichtigen, die sich direkt auf die Betriebseffizienz und Kosteneffizienz auswirken. Wechselstromgeneratoren, die mechanische Energie in elektrische Wechselstromenergie umwandeln, bieten im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Generatoren überlegene Effizienz, Leistung und Wartungsvorteile. Sie eignen sich besonders gut für moderne Anwendungen, die eine konstante Stromversorgung erfordern, vor allem in der Automobilindustrie und im industriellen Umfeld. Umgekehrt können Generatoren zwar sowohl Wechsel- als auch Gleichstrom erzeugen, sind aber in der Regel weniger effizient und müssen häufiger gewartet werden, was sie für Unternehmen, die ihre Energielösungen optimieren wollen, weniger attraktiv macht.
Strategische Beschaffung spielt eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Beschaffung der richtigen Technologie für Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen. Wenn Käufer die einzigartigen Vorteile jeder Option kennen, können sie fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die ihre betrieblichen Möglichkeiten verbessern. Mit der Entwicklung der Märkte in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa steigt die Nachfrage nach effizienten Energielösungen weiter an.
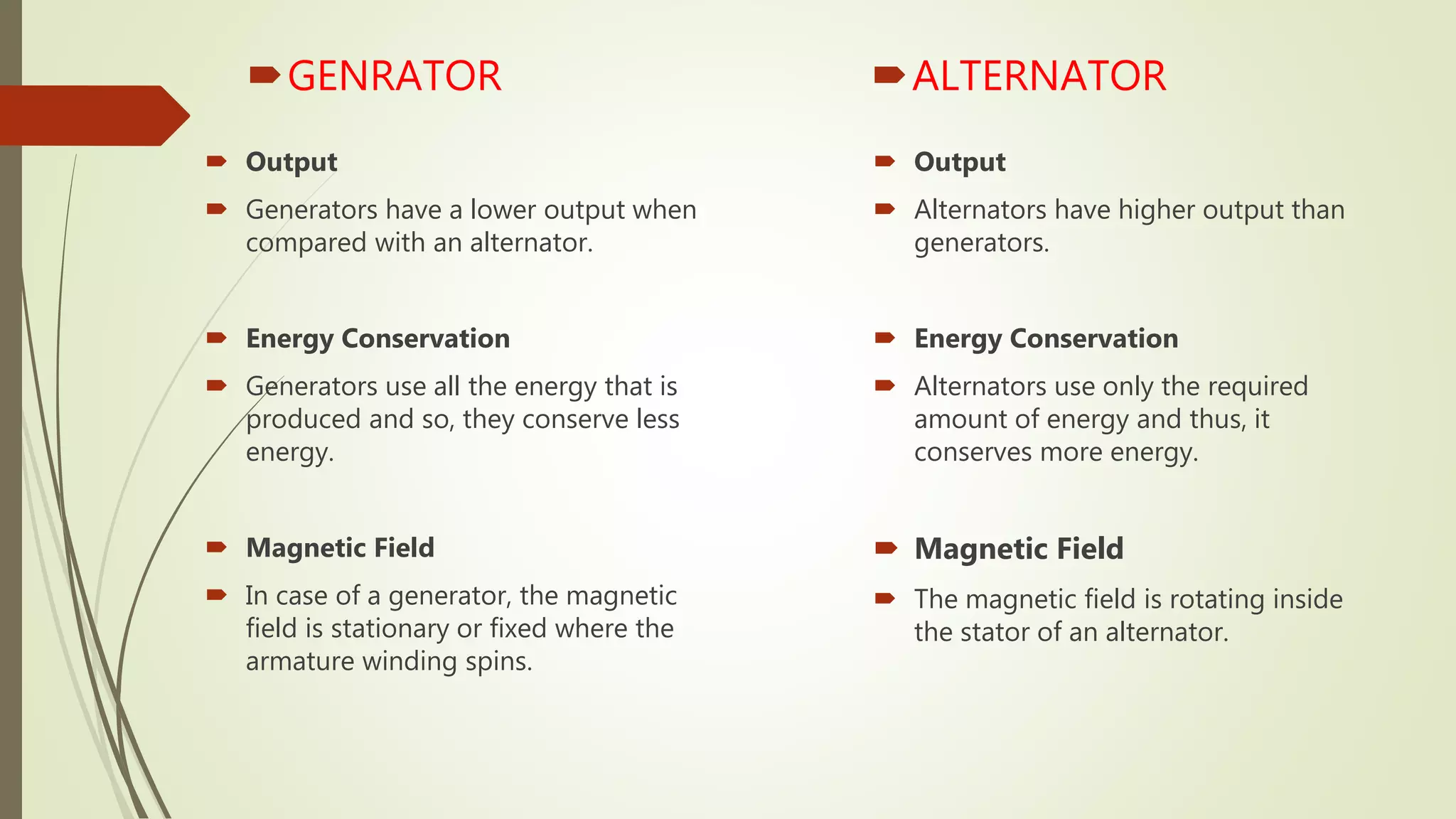
Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator
Für die Zukunft empfehlen wir B2B-Einkäufern, ihren Energiebedarf sorgfältig zu prüfen und eine strategische Beschaffung zu nutzen, um sich die effektivsten Lösungen für die Energieerzeugung zu sichern. Dieser proaktive Ansatz wird nicht nur den Betrieb rationalisieren, sondern auch zu einem nachhaltigen Wachstum in einem zunehmend wettbewerbsintensiven Umfeld beitragen.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.

Anschauliches Bild zum Thema Lichtmaschine und Generator