Einführung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Auf dem dynamischen Automobilmarkt von heute ist es für Unternehmen, die sich mit der Wartung und Reparatur von Fahrzeugen befassen, von entscheidender Bedeutung zu wissen, wie man einen Anlasser mit einem Multimeter prüft. Das Anlassermagnetventil ist ein zentrales Bauteil, das die Batterie mit dem Anlasser verbindet und dessen ordnungsgemäße Funktion für eine zuverlässige Motorleistung entscheidend ist. Die Beschaffung genauer Prüfmethoden kann jedoch eine Herausforderung sein, insbesondere für B2B-Käufer, die auf verschiedenen Märkten in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, wie Nigeria und Saudi-Arabien, tätig sind.
Dieser umfassende Leitfaden geht auf die Feinheiten der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten ein und bietet Schritt-für-Schritt-Verfahren, wichtige Werkzeuge und Tipps zur Fehlersuche. Außerdem werden verschiedene Arten von Anlassermagneten, ihre Anwendungen in verschiedenen Fahrzeugmodellen und die Bedeutung der Lieferantenprüfung zur Gewährleistung qualitativ hochwertiger Komponenten erörtert. Darüber hinaus werden Kostenüberlegungen erörtert, die fundierte Kaufentscheidungen ermöglichen, die sich an Budgetvorgaben orientieren und gleichzeitig die betriebliche Effizienz aufrechterhalten.
Dieser Leitfaden vermittelt internationalen B2B-Einkäufern praxisnahe Einblicke und praktisches Wissen, damit sie sich sicher in der komplexen Welt der Kfz-Komponententests bewegen können. Ganz gleich, ob Sie Fuhrparkleiter, Kfz-Techniker oder Teilelieferant sind - wenn Sie die Feinheiten der Anlassermagnetprüfung verstehen, können Sie Ihr Serviceangebot verbessern und die Kundenzufriedenheit in Ihren jeweiligen Märkten steigern.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 2 Wie prüfe ich ein Anlasser-Magnetventil mit Multimeter Hersteller & Lieferanten Liste
- Einführung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
- Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter Typen und Variationen
- Wichtige industrielle Anwendungen für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
- 3 häufige Benutzer Schmerzpunkte für ‘wie man Anlasser Magnetspule mit Multimeter testen’ & ihre Lösungen
- Leitfaden zur strategischen Materialauswahl für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
- Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit dem Multimeter
- Praktische Anleitung zur Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘Anlasser mit Multimeter prüfen’.’
- Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter Sourcing
- Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich der Prüfung der Anlassermagnetspule mit einem Multimeter mit anderen Lösungen
- Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
- Navigation der Marktdynamik und der Beschaffungstrends im Sektor "Prüfung der Anlasser-Magnetspule mit Multimeter
- Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
- Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter Typen und Variationen
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Widerstandsprüfung | Misst den Widerstand der Magnetspule. | Autowerkstätten, Flottenwartungsunternehmen | Vorteile: Einfach und effektiv; Nachteile: Erfordert die Kenntnis der spezifischen Widerstandswerte. |
| Kontinuitätstests | Überprüft den elektrischen Durchgang zwischen den Klemmen. | Lieferanten elektrischer Komponenten, Diagnosedienste | Vorteile: Schnelle Anzeige der Funktionalität; Nachteile: Es werden möglicherweise nicht alle Arten von Fehlern erkannt. |
| Prüfung des Spannungsabfalls | Bewertet den Spannungsabfall unter Lastbedingungen. | Wartung von Schwermaschinen, Kfz-Servicezentren | Vorteile: Zeigt Probleme unter realen Betriebsbedingungen auf; Nachteile: Komplexere Einrichtung erforderlich. |
| Direkte Aktivierungsprüfung | Manuelles Überbrücken der Magnetklemmen. | DIY-Mechaniker, Kfz-Techniker | Vorteile: Unmittelbare Rückmeldung über die Reaktion des Magneten; Nachteile: Kann riskant sein, wenn es nicht sicher gemacht wird. |
| Diagnostisches Codelesen | Verwendet OBD-II-Scanner, um Fehlercodes im Zusammenhang mit Magnetventilen zu identifizieren. | Kfz-Reparaturbetriebe, Flottenmanagement | Vorteile: Umfassende Fehleranalyse; Nachteile: Erfordert spezielle Ausrüstung und Ausbildung. |
Was sind die Merkmale der Widerstandsprüfung für Anlassermagnete?
Die Widerstandsprüfung ist eine grundlegende Methode zur Bewertung des Widerstands der Magnetspule. Durch die Messung des Widerstands kann der Techniker feststellen, ob die Magnetspule innerhalb des vom Hersteller angegebenen Bereichs funktioniert. Diese Methode eignet sich besonders für Kfz-Werkstätten und Fuhrparkwartungsunternehmen, die ein zuverlässiges und einfaches Prüfverfahren benötigen. Die Käufer müssen jedoch sicherstellen, dass sie Zugang zu spezifischen Widerstandswerten haben, da Abweichungen zu Fehldiagnosen führen können.
Wie funktioniert die Durchgangsprüfung bei Anlassermagneten?
Bei der Durchgangsprüfung wird der elektrische Fluss zwischen den Klemmen des Magneten geprüft, um sicherzustellen, dass der Stromkreis vollständig ist. Diese Methode ist schnell und liefert einen klaren Hinweis darauf, ob das Magnetventil funktionsfähig ist. Sie wird üblicherweise von Lieferanten elektrischer Komponenten und Diagnosediensten angewandt. Diese Methode ist zwar effizient, deckt aber möglicherweise nicht alle potenziellen Fehler auf, so dass weitere Tests erforderlich sind, wenn die Durchgängigkeit bestätigt wird.
Was ist eine Spannungsabfallprüfung und wie wichtig ist sie?
Bei der Spannungsabfallprüfung wird ermittelt, wie viel Spannung verloren geht, wenn der elektrische Strom unter Lastbedingungen durch den Magneten fließt. Diese Prüfung ist für die Instandhaltung von Schwermaschinen und Kfz-Servicezentren von entscheidender Bedeutung, da sie Aufschluss über die Leistung des Magneten in realen Szenarien gibt. Obwohl diese Methode effektiv ist, um Probleme zu erkennen, erfordert sie einen komplexeren Aufbau und ein besseres Verständnis elektrischer Systeme, wodurch sie für unerfahrene Techniker weniger zugänglich ist.
Warum die direkte Aktivierungsprüfung für Magnete?
Bei der direkten Aktivierungsprüfung werden die Magnetklemmen überbrückt, um den Anlasser manuell zu betätigen, was eine sofortige Rückmeldung über die Reaktion des Magneten ermöglicht. Diese Methode ist bei Heimwerkern und Kfz-Technikern wegen ihrer Einfachheit und Wirksamkeit sehr beliebt. Sie kann jedoch riskant sein, wenn keine angemessenen Sicherheitsvorkehrungen getroffen werden. Daher sollten sich Käufer der potenziellen Gefahren bewusst sein, die mit dieser Prüfmethode verbunden sind.
Wie verbessert das Lesen von Diagnosecodes die Prüfung von Magneten?
Beim Lesen von Diagnosecodes werden OBD-II-Scanner eingesetzt, um Fehlercodes im Zusammenhang mit dem Anlassermagneten abzurufen. Diese umfassende Fehleranalyse ist für Kfz-Reparaturbetriebe und das Flottenmanagement von unschätzbarem Wert, da sie eine genaue Identifizierung von Problemen ermöglicht. Diese Methode ist zwar gründlich, erfordert aber eine spezielle Ausrüstung und Schulung, was für kleinere Betriebe oder solche ohne Zugang zu modernen Diagnosewerkzeugen ein Hindernis darstellen kann.
Wichtige industrielle Anwendungen für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
| Branche/Sektor | Spezifische Anwendung für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kfz-Reparatur | Routinediagnose in Kfz-Werkstätten | Reduziert Ausfallzeiten und verbessert die Serviceeffizienz | Verfügbarkeit von Multimetern und Schulungen für Techniker |
| Schwere Maschinen | Prüfung von Magneten in Bau- und Landmaschinen | Gewährleistet die Zuverlässigkeit des Maschinenbetriebs | Langlebige Multimeter für raue Umgebungen |
| Transport & Logistik | Flottenmanagement für Nutzfahrzeuge | Verbessert die Zuverlässigkeit des Fuhrparks und reduziert die Reparaturkosten | Zugang zu Spezialausrüstung und technischer Unterstützung |
| Schiffsindustrie | Wartung von Schiffsmotoren und elektrischen Systemen | Verbessert die Sicherheit und Leistung von Schiffen | Einhaltung der Sicherheitsstandards für die Schifffahrt und der Ausrüstungszertifizierungen |
| Erneuerbare Energien | Prüfung von Startmagneten in Wind- und Solarenergieanlagen | Optimiert die Systemleistung und Energieeffizienz | Verfügbarkeit von Multimetern, die für Hochspannungssysteme geeignet sind |
Wie wird das Testen eines Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter in der Kfz-Reparaturbranche angewendet?
In der Kfz-Reparatur ist das Testen von Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter ein grundlegendes Verfahren zur Diagnose von Problemen beim Anlassen von Fahrzeugen. Werkstätten prüfen regelmäßig Magnetventile, um sicherzustellen, dass sie ordnungsgemäß funktionieren, was dazu beiträgt, Fahrzeugpannen zu vermeiden. Durch die frühzeitige Erkennung fehlerhafter Magnetspulen können die Betriebe die Reparaturzeiten minimieren und die Kundenzufriedenheit erhöhen. Für internationale Käufer, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika, ist die Beschaffung von zuverlässigen Multimetern und die Sicherstellung, dass die Techniker in ihrer Verwendung gut geschult sind, entscheidend für die Aufrechterhaltung der Servicequalität.

Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Welche Rolle spielt die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten in Schwermaschinen?
Im Schwermaschinensektor ist die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten für die Aufrechterhaltung der Zuverlässigkeit von Bau- und Landmaschinen unerlässlich. Eine Fehlfunktion der Magnetspule kann zu kostspieligen Ausfallzeiten führen, die sich auf den Zeitplan und die Produktivität von Projekten auswirken. Durch den Einsatz von Multimetern zur Bewertung der Magnetspulenfunktionalität können Unternehmen sicherstellen, dass ihre Maschinen reibungslos funktionieren. Käufer aus dem Nahen Osten und Europa sollten auf die Langlebigkeit von Multimetern achten, da die Geräte in diesen Branchen oft unter rauen Bedingungen arbeiten.
Welchen Nutzen hat diese Prüfung für Transport- und Logistikunternehmen?
Im Transport- und Logistikwesen ist die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten für das Flottenmanagement von entscheidender Bedeutung. Regelmäßige Kontrollen können unerwartete Ausfälle verhindern und so die Zuverlässigkeit von Nutzfahrzeugen erhöhen. Dieser proaktive Wartungsansatz kann zu erheblichen Kosteneinsparungen bei Reparaturen und betrieblichen Ausfallzeiten führen. Unternehmen in Regionen wie Nigeria und Saudi-Arabien sollten sich auf die Beschaffung von Multimetern konzentrieren, die robust und für die verschiedenen Fahrzeuge in ihren Flotten geeignet sind.
Warum ist die Prüfung von Magneten für die Schifffahrtsindustrie so wichtig?
Die Schifffahrtsindustrie ist in hohem Maße auf das ordnungsgemäße Funktionieren von Motoren und elektrischen Systemen angewiesen, weshalb die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten eine wichtige Aufgabe ist. Der Einsatz eines Multimeters zur Bewertung der Magnetspulenleistung gewährleistet einen sicheren und effizienten Betrieb der Schiffe. Dies ist besonders wichtig für die Einhaltung der Sicherheitsvorschriften im Seeverkehr. Einkäufer in diesem Sektor müssen bei der Beschaffung von Geräten darauf achten, dass diese den Schifffahrtsstandards entsprechen und eine genaue Diagnose ermöglichen.
Welche Bedeutung hat die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten für Anwendungen im Bereich der erneuerbaren Energien?
Bei erneuerbaren Energien, insbesondere bei Wind- und Solarenergiesystemen, ist die Prüfung von Startermagneten entscheidend für die Optimierung der Systemleistung. Ein defektes Magnetventil kann die Energieerzeugung behindern und die Gesamteffizienz des Systems beeinträchtigen. Durch den Einsatz von Multimetern zur regelmäßigen Prüfung können Unternehmen sicherstellen, dass ihre Systeme mit optimaler Leistung arbeiten. Internationale Käufer sollten nach Multimetern Ausschau halten, die für Hochspannung geeignet sind und den Vorschriften des Energiesektors entsprechen, um Zuverlässigkeit und Sicherheit zu gewährleisten.
3 häufige Benutzer Schmerzpunkte für ‘wie man Anlasser Magnetspule mit Multimeter testen’ & ihre Lösungen
Szenario 1: Schwierigkeiten bei der Identifizierung defekter Anlassermagnetkomponenten
Das Problem: Viele B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in den Bereichen Kfz-Reparatur und -Wartung, stoßen bei der Diagnose von Problemen mit Anlassermagneten auf Schwierigkeiten. In manchen Fällen scheint die Magnetspule bei einer Sichtprüfung funktionstüchtig zu sein, doch der Motor springt nicht an. Dies kann zu Frustration, Zeitverschwendung und erhöhten Arbeitskosten führen, insbesondere in Werkstätten mit hohem Werkstattaufkommen, wo Effizienz an erster Stelle steht. Ohne eine zuverlässige Methode zur effektiven Prüfung der Magnetspule können Techniker die genaue Ursache des Startproblems nur schwer feststellen, was zu unnötigem Austausch von Teilen und Unzufriedenheit beim Kunden führt.
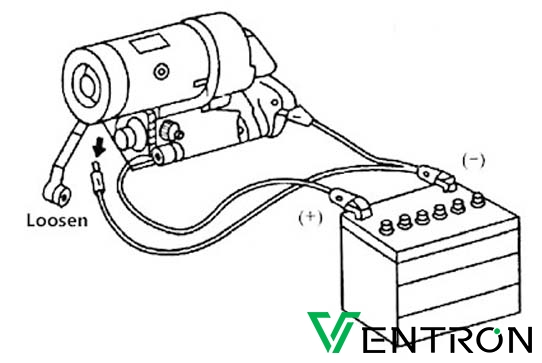
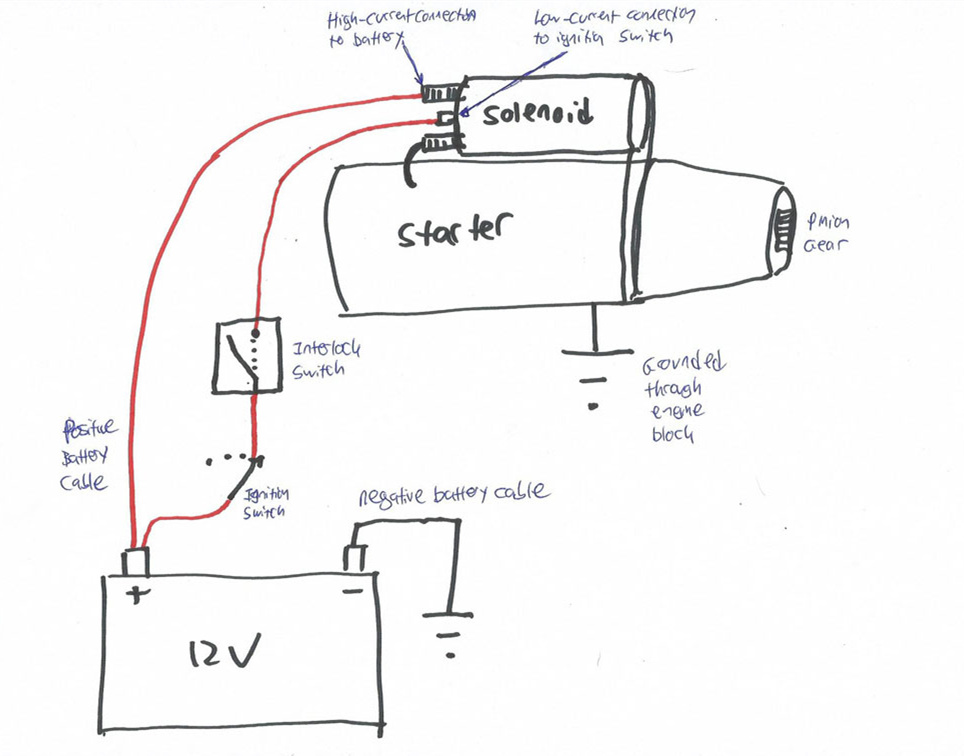
Die Lösung: Um den Zustand des Anlassermagneten genau zu beurteilen, sollten Techniker ein Multimeter verwenden, um umfassende Tests durchzuführen. Stellen Sie zunächst sicher, dass das Fahrzeug sicher ausgeschaltet und die Batterie abgeklemmt ist. Stellen Sie dann das Multimeter auf den Widerstandsmodus (Ohm) ein und messen Sie den Widerstand an den Klemmen des Magnetventils. Den angegebenen Widerstandswert finden Sie im Wartungshandbuch des Fahrzeugs. Ein deutlich höherer oder niedrigerer Wert deutet auf ein defektes Magnetventil hin. Darüber hinaus kann ein Test auf Durchgang zwischen der Batterieklemme des Elektromagneten und der Klemme des Anlassers bestätigen, ob der Elektromagnet tatsächlich Strom überträgt. Wenn Sie Ihren Technikern ein standardisiertes Prüfverfahren an die Hand geben und sie im Umgang mit Multimetern schulen, können Sie die Diagnosegenauigkeit erhöhen und die Arbeitskosten senken.
Szenario 2: Inkonsistente Multimeter-Messwerte führen zu Fehldiagnosen
Das Problem: Ein weiteres häufiges Problem für B2B-Käufer sind die uneinheitlichen Messwerte von Multimetern bei der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten. Faktoren wie schlechter Kontakt, defekte Leitungen oder sogar das Multimeter selbst können zu unzuverlässigen Messungen führen. Diese Unstimmigkeiten können zu Fehldiagnosen führen, so dass Techniker entweder ein defektes Magnetventil übersehen oder fälschlicherweise davon ausgehen, dass es defekt ist, obwohl es das nicht ist. Diese Situation verlängert nicht nur die Reparaturdauer, sondern kann auch die Kundenbeziehungen aufgrund von Verzögerungen und falscher Kommunikation über den tatsächlichen Zustand des Fahrzeugs schädigen.
Die Lösung: Um dieses Problem zu entschärfen, ist es wichtig, ein strenges Wartungs- und Kalibrierungsprotokoll für Multimeter in Ihrem Betrieb einzuführen. Überprüfen und reinigen Sie die Multimeterleitungen regelmäßig, um eine optimale Leitfähigkeit zu gewährleisten, und ersetzen Sie beschädigte oder ausgefranste Leitungen sofort. Außerdem sollten die Techniker darin geschult werden, die Kalibrierung ihres Multimeters vor dem Einsatz zu überprüfen, insbesondere bei der Diagnose kritischer Komponenten wie Anlassermagneten. Ermuntern Sie sie, die Messwerte mit einem zweiten Multimeter abzugleichen, wenn Unsicherheiten auftreten. Diese Vorgehensweise verbessert die Diagnosegenauigkeit, verringert Fehldiagnosen und stärkt das Vertrauen der Kunden in Ihre Servicequalität.
Szenario 3: Begrenzte Kenntnisse über Multimeterfunktionen und Prüfverfahren
Das Problem: Viele Techniker in der Automobilindustrie wissen nicht, wie sie die volle Funktionalität eines Multimeters bei der Prüfung von Anlasser-Magnetventilen nutzen können. Diese Unkenntnis kann zu ineffizienten Testverfahren führen, die den Zeitaufwand für die Diagnose erhöhen und möglicherweise zu verpassten Gelegenheiten für das Upselling von Reparaturdienstleistungen führen. Für B2B-Einkäufer, die in Regionen mit begrenztem Zugang zu Weiterbildungsressourcen tätig sind, kann diese Wissenslücke die Servicequalität und betriebliche Effizienz erheblich beeinträchtigen.
Die Lösung: Die Investition in umfassende Schulungsprogramme, die sich auf die praktische Anwendung von Multimetern in der Kfz-Diagnose konzentrieren, kann sich erheblich auszahlen. Entwickeln Sie Workshops oder Online-Schulungsmodule, die nicht nur die grundlegende Bedienung von Multimetern, sondern auch fortgeschrittene Testtechniken speziell für Anlassermagnete abdecken. Fügen Sie reale Szenarien und Tipps zur Fehlersuche ein, um das Verständnis zu verbessern. Erstellen Sie außerdem detaillierte Nachschlagewerke, z. B. Schnellstartanleitungen oder Spickzettel, auf die die Techniker bei ihrer Arbeit zurückgreifen können. Dieser proaktive Schulungsansatz wird Ihr Team befähigen, die Diagnosegeschwindigkeit und -genauigkeit zu verbessern und letztendlich die Kundenzufriedenheit zu erhöhen.
Leitfaden zur strategischen Materialauswahl für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Welche Materialien eignen sich am besten für die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter?
Bei der Prüfung eines Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter kann die Wahl der Materialien, die im Multimeter und seinem Zubehör verwendet werden, die Leistung und Zuverlässigkeit erheblich beeinflussen. Im Folgenden analysieren wir gängige Materialien, die in diesem Prozess eine wichtige Rolle spielen, und konzentrieren uns auf ihre Eigenschaften, Vorteile, Nachteile und Überlegungen für internationale B2B-Käufer.
Was sind die wichtigsten Eigenschaften von Kupfer in Multimetersonden?
Kupfer wird aufgrund seiner hervorragenden elektrischen Leitfähigkeit häufig für Multimetersonden verwendet. Es hat in der Regel eine Temperaturbeständigkeit von bis zu 200 °C und ist korrosionsbeständig, wenn es mit Materialien wie Nickel beschichtet ist.
Vor- und Nachteile:
Kupfersonden sind langlebig und liefern genaue Messwerte, aber sie können mit der Zeit oxidieren, was die Leistung beeinträchtigen kann. Die Kosten für Kupfer sind moderat, weshalb es eine beliebte Wahl für Hersteller ist. Allerdings steigt die Komplexität der Herstellung, wenn Beschichtungen zur Verbesserung der Korrosionsbeständigkeit aufgebracht werden.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung:
Die hohe Leitfähigkeit von Kupfer sorgt für einen minimalen Widerstand bei elektrischen Prüfungen, wodurch es sich für präzise Messungen bei der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten eignet.
Überlegungen zu internationalen Käufern:
Für Käufer in Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa ist die Einhaltung von Normen wie ASTM B170 für Kupferdraht und JIS H 3100 für Kupferlegierungen entscheidend. Käufer sollten auch die lokale Verfügbarkeit und Preisschwankungen berücksichtigen.
Wie wirkt sich das Kunststoffmaterial auf das Multimetergehäuse aus?
Kunststoff wird wegen seines geringen Gewichts und seiner isolierenden Eigenschaften häufig für das Gehäuse von Multimetern verwendet. Hochwertige Kunststoffe können Temperaturen von bis zu 85 °C standhalten und bieten eine gute Beständigkeit gegen Stöße und Chemikalien.
Vor- und Nachteile:
Kunststoffgehäuse sind kostengünstig und können in verschiedene Formen gegossen werden, was die Verwendbarkeit verbessert. Sie sind jedoch möglicherweise nicht so haltbar wie Metalle und können sich bei längerer Einwirkung von UV-Licht zersetzen.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung:
Die isolierenden Eigenschaften des Kunststoffs schützen den Benutzer während der Prüfung vor elektrischen Schlägen, was bei der Arbeit mit Hochstromkomponenten wie Anlassermagneten von entscheidender Bedeutung ist.
Überlegungen zu internationalen Käufern:
Käufer sollten sicherstellen, dass die Kunststoffe internationalen Normen wie ISO 9001 für Qualitätsmanagementsysteme entsprechen. Darüber hinaus kann es von Vorteil sein, die örtlichen Vorschriften für Kunststoffabfälle und Recycling zu kennen.

Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Welche Rolle spielt Gummi bei Multimeterzubehör?
Gummi wird häufig für die Griffe und Schutzgehäuse von Multimetern verwendet. Er hält Temperaturen von -40°C bis 70°C stand und ist von Natur aus gegen viele Chemikalien beständig.
Vor- und Nachteile:
Gummi bietet eine hervorragende Griffigkeit und verbessert die Kontrolle des Benutzers während der Prüfung. Allerdings kann er sich mit der Zeit abnutzen, insbesondere in rauen Umgebungen, was zu potenziellen Sicherheitsrisiken führen kann. Die Kosten sind in der Regel niedrig, was ihn zu einer wirtschaftlichen Wahl für Hersteller macht.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung:
Die isolierenden Eigenschaften des Kautschuks schützen vor elektrischen Schlägen und machen die Prüfung von Bauteilen wie z. B. Magneten für die Anwender sicherer.

Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Überlegungen zu internationalen Käufern:
Käufer sollten nach Gummimaterialien Ausschau halten, die die ASTM D2000-Normen für Gummiprodukte erfüllen, um Qualität und Sicherheit zu gewährleisten. Außerdem kann die Beschaffung von Kautschuk von nachhaltigen Lieferanten umweltbewusste Märkte ansprechen.
Wie trägt Stahl zur Konstruktion von Multimetern bei?
Stahl wird aufgrund seiner hohen Festigkeit und Haltbarkeit häufig für die internen Komponenten von Multimetern, wie Schrauben und Anschlüsse, verwendet. Er kann hohen Temperaturen standhalten und ist bei entsprechender Behandlung korrosionsbeständig.
Vor- und Nachteile:
Bauteile aus Stahl erhöhen die allgemeine Haltbarkeit des Multimeters und sorgen für Langlebigkeit. Sie können jedoch das Gewicht erhöhen und erfordern möglicherweise zusätzliche Beschichtungen, um Rost zu verhindern. Die Kosten sind in der Regel höher als die von Kunststoff oder Gummi.

Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung:
Die Robustheit des Stahls sorgt dafür, dass das Multimeter dem harten Einsatz in verschiedenen Umgebungen, einschließlich Kfz-Werkstätten, standhält.
Überlegungen zu internationalen Käufern:
Für internationale Einkäufer kann es entscheidend sein, die Einhaltung von Normen wie ISO 9001 für das Qualitätsmanagement und ASTM A36 für Baustahl zu gewährleisten. Außerdem ist es wichtig, die lokalen Marktpräferenzen für leichte und schwere Werkzeuge zu kennen.
Übersichtstabelle zur Materialauswahl für die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten
| Material | Typischer Anwendungsfall für die Prüfung der Anlassermagnetspule mit einem Multimeter | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kupfer | Sonden für genaue elektrische Ablesungen | Hervorragende Leitfähigkeit | Anfällig für Oxidation | Mittel |
| Kunststoff | Gehäuse für Multimeter | Leicht und isolierend | Weniger haltbar als Metalle | Niedrig |
| Gummi | Griffe und Schutzhüllen | Bietet Grip und Isolierung | Kann mit der Zeit verschleißen | Niedrig |
| Stahl | Interne Komponenten wie Schrauben | Hohe Festigkeit und Haltbarkeit | Erhöht das Gewicht und kann rosten | Hoch |
Diese Analyse bietet wertvolle Einblicke für B2B-Einkäufer, die sich über die Materialien informieren möchten, die bei der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter zum Einsatz kommen. Durch die Berücksichtigung dieser Faktoren können Käufer fundierte Entscheidungen treffen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen und Compliance-Anforderungen übereinstimmen.
Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit dem Multimeter
Was sind die wichtigsten Schritte im Herstellungsprozess von Startermagneten?
Der Herstellungsprozess für Anlassermagnete umfasst mehrere kritische Phasen, die jeweils sicherstellen sollen, dass das Endprodukt strenge Qualitäts- und Leistungsstandards erfüllt. Zu diesen Phasen gehören die Materialvorbereitung, die Formgebung, die Montage und die Endbearbeitung.
-
Materialvorbereitung: Der Prozess beginnt mit der Auswahl hochwertiger Rohmaterialien, in der Regel Kupfer für die Wicklungen, Stahl für das Gehäuse und verschiedene Isoliermaterialien. Die Lieferanten führen oft strenge Tests dieser Materialien durch, um ihre Leitfähigkeit, Haltbarkeit und Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Umwelteinflüsse zu bestätigen. Die Materialspezifikationen müssen mit internationalen Normen übereinstimmen, um Konsistenz und Zuverlässigkeit zu gewährleisten.
-
Formung: In dieser Phase werden die Rohmaterialien zu den gewünschten Komponenten geformt. Techniken wie Stanzen und Zerspanen werden eingesetzt, um das Gehäuse und die Innenteile des Magneten herzustellen. Präzision ist von größter Wichtigkeit, da selbst kleine Abweichungen die Funktion des Magneten beeinträchtigen können. Die CNC-Bearbeitung (Computer Numerical Control) wird häufig eingesetzt, um die erforderlichen Toleranzen zu erreichen und sicherzustellen, dass die Teile nahtlos zusammenpassen.
-
Montage: Sobald die einzelnen Komponenten vorbereitet sind, werden sie zusammengesetzt. Dieser Prozess kann je nach Produktionsumfang manuelle Arbeit und automatisierte Maschinen umfassen. Zu den wichtigsten Aspekten der Montage gehören das Aufwickeln der Spule, der Einbau des Stößels und die Sicherung der Anschlüsse. Während der Montage werden an verschiedenen Stellen Qualitätskontrollen durchgeführt, um eventuelle Mängel frühzeitig zu erkennen.
-
Endbearbeitung: In der letzten Phase werden Schutzbeschichtungen wie Galvanisierung oder Lackierung aufgebracht, um die Korrosionsbeständigkeit und das Aussehen zu verbessern. Dieser Schritt ist entscheidend für Produkte, die für unterschiedliche Klimazonen bestimmt sind, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika und dem Nahen Osten, wo die Umweltbedingungen sehr unterschiedlich sein können. Nach der Fertigstellung werden die Magnete weiteren Tests unterzogen, um ihre Leistung unter simulierten Betriebsbedingungen zu überprüfen.
Wie wird die Qualitätssicherung bei der Herstellung von Anlassermagneten durchgeführt?
Die Qualitätssicherung (QS) ist ein wesentlicher Bestandteil der Herstellung von Anlassermagneten und stellt sicher, dass jede Einheit bestimmte Leistungs- und Sicherheitsstandards erfüllt. Internationale Normen wie die ISO 9001 werden häufig als Rahmen für ein Qualitätsmanagementsystem verwendet.
-
Einhaltung internationaler Normen: Die Hersteller halten sich in der Regel an die Norm ISO 9001, die Kriterien für ein Qualitätsmanagementsystem festlegt. Dies gewährleistet die Konsistenz der Produktionsprozesse und fördert die kontinuierliche Verbesserung. Andere branchenspezifische Zertifizierungen, wie die CE-Kennzeichnung für europäische Märkte oder API-Normen für Komponenten, die in der Automobilindustrie verwendet werden, können ebenfalls erforderlich sein.
-
Kontrollpunkte der Qualitätskontrolle: Während des gesamten Herstellungsprozesses werden mehrere Kontrollpunkte zur Bewertung der Qualität festgelegt:
– Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): Die Rohstoffe werden bei ihrem Eintreffen geprüft, um sicherzustellen, dass sie den vorgegebenen Normen entsprechen, bevor sie in die Produktionslinie gelangen.
– In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): Während des Fertigungsprozesses führen die Bediener regelmäßige Kontrollen durch, um sicherzustellen, dass die Bauteile nach den richtigen Spezifikationen hergestellt werden.
– Endkontrolle (FQC): Nach dem Zusammenbau wird jedes Anlassermagnetventil auf seine Funktionstüchtigkeit geprüft, einschließlich Widerstands- und Durchgangsprüfungen mit Multimetern. Dieser Schritt ist entscheidend für die Identifizierung von Defekten, die die Leistung beeinträchtigen könnten. -
Gängige Prüfmethoden: Um die korrekte Funktion des Magneten zu gewährleisten, werden verschiedene Prüfverfahren eingesetzt:
– Elektrische Prüfung: Durch Widerstands- und Durchgangsprüfungen wird sichergestellt, dass die Magnetspule tatsächlich Strom leiten kann.
– Belastungstest: Dabei wird die Belastbarkeit des Magneten geprüft, um sicherzustellen, dass er den Anlasser unter realen Arbeitsbedingungen einschalten kann.
– Umweltprüfungen: Die Geräte können Tests unterzogen werden, bei denen extreme Temperaturen und Luftfeuchtigkeit simuliert werden, um die Haltbarkeit in verschiedenen Klimazonen zu gewährleisten.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrollprozesse ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
Für internationale B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, ist die Überprüfung der Qualitätskontrollverfahren eines Lieferanten von entscheidender Bedeutung, um die Zuverlässigkeit und Leistungsfähigkeit der Produkte zu gewährleisten.
-
Lieferantenaudits: Die Durchführung regelmäßiger Audits bei den Lieferanten kann Aufschluss über deren Qualitätskontrollverfahren geben. Dies kann die Überprüfung von Unterlagen, die Inspektion von Einrichtungen und die Beobachtung von Produktionsprozessen beinhalten. Audits helfen dabei, verbesserungswürdige Bereiche zu ermitteln und die Einhaltung internationaler Normen zu gewährleisten.
-
Qualitätssicherungsberichte: Das Anfordern detaillierter Qualitätssicherungsberichte von den Lieferanten kann Transparenz hinsichtlich ihrer Qualitätssicherungspraktiken schaffen. Diese Berichte sollten Daten zu Testergebnissen, Fehlerraten und Korrekturmaßnahmen enthalten, die als Reaktion auf Probleme ergriffen wurden.
-
Inspektionen durch Dritte: Die Beauftragung von externen Prüfstellen kann eine unvoreingenommene Bewertung der Qualitätskontrollverfahren eines Lieferanten liefern. Diese Agenturen können Inspektionen in verschiedenen Phasen der Produktion durchführen und eine den Industriestandards entsprechende Zertifizierung ausstellen.
Was sind die Feinheiten der Qualitätskontrolle für internationale B2B-Käufer?
Bei der globalen Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten müssen die Einkäufer bestimmte Nuancen der Qualitätskontrolle beachten, die ihre Beschaffungsentscheidungen beeinflussen können. Das Verständnis dieser Nuancen kann dazu beitragen, die mit der internationalen Fertigung verbundenen Risiken zu mindern.
-
Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften: Die verschiedenen Regionen haben unterschiedliche rechtliche Anforderungen. So ist beispielsweise die CE-Kennzeichnung für Produkte, die in Europa verkauft werden, unerlässlich, während die Einhaltung lokaler Normen auf Märkten wie Nigeria und Saudi-Arabien entscheidend ist. Die Einkäufer müssen sicherstellen, dass ihre Lieferanten alle relevanten Vorschriften einhalten, um rechtliche Probleme zu vermeiden.
-
Kulturelle und kommunikative Hürden: Effiziente Kommunikation ist im internationalen Handel von entscheidender Bedeutung. Sprachbarrieren und unterschiedliche kulturelle Normen können zu Missverständnissen hinsichtlich der Qualitätserwartungen führen. Die Einrichtung klarer Kommunikationskanäle und Erwartungen im Vorfeld kann dazu beitragen, diese Kluft zu überbrücken.
-
Logistik und Lieferkettenmanagement: Der internationale Versand kann Probleme mit sich bringen, die sich auf die Produktqualität auswirken, z. B. Schäden während des Transports oder Verzögerungen, die die Unversehrtheit empfindlicher Komponenten beeinträchtigen. Käufer sollten eng mit ihren Lieferanten zusammenarbeiten, um robuste Logistikpläne zu erstellen, die eine schützende Verpackung und pünktliche Liefertermine beinhalten.
-
Unterstützung nach dem Kauf: Die Qualitätssicherung endet nicht an der Verkaufsstelle. B2B-Einkäufer sollten Lieferanten auf der Grundlage ihrer Unterstützung nach dem Kauf bewerten, einschließlich der Garantiebedingungen, der Austauschpolitik und der Reaktionsfähigkeit des Kundendienstes. Diese fortlaufende Unterstützung ist für die Behebung von Qualitätsproblemen, die nach dem Kauf auftreten können, unerlässlich.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass es für B2B-Einkäufer, die auf der Suche nach zuverlässigen Komponenten sind, von entscheidender Bedeutung ist, die Herstellungsverfahren und Qualitätssicherungspraktiken für Startermagnete zu verstehen. Indem sie sich auf die Qualitätskontrolle der Lieferanten und die Einhaltung von Vorschriften konzentrieren, können Unternehmen sicherstellen, dass sie qualitativ hochwertige Produkte beschaffen, die ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen entsprechen.
Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Praktische Anleitung zur Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘Anlasser mit Multimeter prüfen’.’
Bei der Reparatur von Kraftfahrzeugen, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, ist das Wissen, wie man ein Anlassermagnetventil mit einem Multimeter prüft, für die Gewährleistung der Betriebseffizienz und -zuverlässigkeit unerlässlich. Dieser Leitfaden dient als umfassende Checkliste für B2B-Einkäufer, die sich die notwendigen Werkzeuge und Kenntnisse für eine effektive Prüfung von Anlassermagneten beschaffen wollen.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Vor dem Kauf eines Multimeters oder ähnlicher Werkzeuge ist es wichtig, dass Sie sich über Ihre technischen Anforderungen im Klaren sind. Berücksichtigen Sie die Fahrzeugtypen, an denen Sie arbeiten werden, und die spezifischen elektrischen Komponenten, die geprüft werden müssen.
– Spannungsbereich: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass das Multimeter die typischen Spannungspegel in Kfz-Systemen verarbeiten kann, in der Regel bis zu 12 V.
– Widerstandsmessung: Achten Sie auf ein Multimeter, das genaue Widerstandsmesswerte liefert, was für die Prüfung von Magnetspulen unerlässlich ist.
Schritt 2: Suche nach geeigneten Multimeter-Modellen
Stellen Sie gründliche Nachforschungen an, um Multimeter-Modelle zu finden, die Ihren Bedürfnissen am besten entsprechen.
– Ruf der Marke: Konzentrieren Sie sich auf Marken, die für ihre Zuverlässigkeit und Genauigkeit in der Kfz-Diagnose bekannt sind.
– Benutzerbewertungen: Prüfen Sie die Rückmeldungen und Bewertungen der Benutzer, um sich ein Bild von der Leistung und Haltbarkeit des Multimeters unter verschiedenen Bedingungen zu machen.
Schritt 3: Lieferantenzertifizierungen bewerten
Bevor Sie sich für einen Lieferanten entscheiden, sollten Sie dessen Zertifizierungen und die Einhaltung der Industrienormen überprüfen.
– Qualitätssicherung: Achten Sie auf ISO-Zertifizierungen oder ähnliche Qualitätsmanagementsysteme, die auf die Einhaltung hoher Fertigungsstandards hinweisen.
– Lokale Vorschriften: Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Lieferant die für Ihre Region geltenden gesetzlichen Anforderungen erfüllt, die sich auf die Verwendbarkeit und die Garantie der Werkzeuge auswirken können.
Schritt 4: Produktdemonstrationen anfordern
Bitten Sie die Lieferanten um Vorführungen des Multimeters und weiterer Prüfgeräte.
– Praktische Erfahrung: Eine Vorführung ermöglicht es Ihnen, die Benutzerfreundlichkeit und die Funktionen des Multimeters direkt zu beurteilen.
– Technische Unterstützung: Erkundigen Sie sich nach der Verfügbarkeit von technischem Support oder Schulungen, die für Ihr Team unerlässlich sind, um die Geräte effektiv nutzen zu können.
Schritt 5: Preise und Garantieoptionen vergleichen
Holen Sie Angebote von mehreren Anbietern ein und vergleichen Sie sie, um sicherzustellen, dass Sie das beste Angebot erhalten.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Berücksichtigen Sie nicht nur den anfänglichen Kaufpreis, sondern auch die langfristigen Kosten, z. B. für Wartung und mögliche Reparaturen.
– Garantie und Rückgabebedingungen: Überprüfen Sie die Garantiebedingungen, um zu verstehen, was abgedeckt ist und wie lange, da dies im Falle einer Störung Kosten sparen kann.
Schritt 6: Bewertung des After-Sales-Supports
Die Unterstützung nach dem Kauf ist ein entscheidender Faktor im Beschaffungsprozess.
– Verfügbarkeit von Teilen: Stellen Sie sicher, dass Ersatzteile für das Multimeter und andere Werkzeuge in Ihrer Region leicht erhältlich sind.
– Kundenservice: Bewerten Sie die Reaktionsfähigkeit des Kundendienstes des Anbieters, da dies für künftige Anfragen oder Probleme von entscheidender Bedeutung sein wird.
Schritt 7: Feedback von Branchenkollegen einholen
Wenden Sie sich schließlich an Branchenkollegen oder -foren, um sich über deren Erfahrungen mit bestimmten Multimetern und Anbietern zu informieren.
– Peer-Empfehlungen: Aus den Erfahrungen anderer zu lernen, kann wertvolle Einsichten liefern, die durch Forschung allein vielleicht nicht zu erkennen sind.
– Aufbau eines Netzwerks: Das Knüpfen von Kontakten zu anderen Fachleuten kann auch Türen zu Kooperationsmöglichkeiten und zur gemeinsamen Nutzung von Ressourcen öffnen.
Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Anhand dieser strukturierten Checkliste können B2B-Einkäufer fundierte Entscheidungen bei der Beschaffung von Werkzeugen für die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten treffen und so letztlich ihre operativen Fähigkeiten und ihr Dienstleistungsangebot verbessern.
Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter Sourcing
Bei der Beschaffung von Lösungen für die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten mit Multimetern ist es wichtig, die umfassende Kostenstruktur und Preisdynamik zu verstehen, die die Beschaffungsentscheidungen beeinflussen. Diese Analyse wird internationalen B2B-Einkäufern, insbesondere aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, helfen, fundierte Kaufentscheidungen zu treffen.
Was sind die wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten bei der Beschaffung von Multimeter-Testlösungen?
Das Verständnis der verschiedenen Kostenkomponenten ist für eine effektive Budgetierung und Finanzplanung entscheidend:

Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
-
Materialien: Die primären Materialkosten betreffen die Multimeter selbst, die sich je nach Funktionen, Genauigkeit und Haltbarkeit erheblich unterscheiden können. Zusätzliche Komponenten, wie isolierte Messfühler und Schutzgehäuse, tragen ebenfalls zu den Gesamtmaterialkosten bei.
-
Arbeit: Die Arbeitskosten umfassen nicht nur die Löhne für die in der Produktion beschäftigten Mitarbeiter, sondern auch die Kosten für Forschung und Entwicklung, insbesondere bei fortschrittlichen oder kundenspezifischen Multimetern. Qualifizierte Arbeitskräfte sind notwendig, um eine qualitativ hochwertige Produktion zu gewährleisten.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: Hierunter fallen die Ausgaben für die betrieblichen Aspekte der Produktion, z. B. für Versorgungsleistungen, die Wartung der Anlagen und die Betriebsführung. Ein effizienter Betrieb kann dazu beitragen, diese Kosten zu senken.
-
Werkzeuge: Die anfänglichen Werkzeugkosten können beträchtlich sein, insbesondere bei kundenspezifischen Geräten. Käufer sollten sich nach den Werkzeugkosten erkundigen, die mit bestimmten Anforderungen verbunden sind, da diese den Endpreis beeinflussen können.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Strenge Qualitätssicherungsmaßnahmen sind unerlässlich, um die Zuverlässigkeit und Leistungsfähigkeit der Produkte zu gewährleisten. Die mit den Prüf- und Zertifizierungsverfahren verbundenen Kosten müssen in die Gesamtpreisgestaltung einbezogen werden.
-
Logistik: Die Versand- und Bearbeitungskosten können je nach Bestimmungsort stark variieren. Internationale Käufer müssen Zollgebühren und Frachtkosten berücksichtigen, die den Gesamtkaufpreis erheblich beeinflussen können.
-
Marge: Die Lieferanten setzen oft eine Marge an, die ihr Betriebsrisiko und ihre Gewinnerwartungen widerspiegelt. Einkäufer sollten die typischen Margen in ihrer Branche kennen, um effektiv verhandeln zu können.
Welche Preiseinflussfaktoren sollten B2B-Einkäufer berücksichtigen?
Mehrere Faktoren können die Preisgestaltung von Multimetern und zugehörigen Testlösungen beeinflussen:
-
Volumen und Mindestbestellmenge (MOQ): Bei größeren Bestellungen werden in der Regel Mengenrabatte gewährt, die zu erheblichen Einsparungen führen können. Käufer sollten ihren Bedarf sorgfältig prüfen, um die Bestellmenge zu optimieren.
-
Spezifikationen und Anpassung: Sonderausstattungen können zusätzliche Kosten nach sich ziehen. Käufer sollten ihre Spezifikationen klar mitteilen, um unerwartete Kosten zu vermeiden.
-
Materialien und Qualitätszertifizierungen: Hochwertige Materialien und Zertifizierungen (z. B. ISO-Normen) führen häufig zu höheren Preisen. Käufer sollten ihr Bedürfnis nach Qualität mit dem begrenzten Budget in Einklang bringen.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Der Ruf und die Zuverlässigkeit der Lieferanten können die Preisgestaltung beeinflussen. Etablierte Lieferanten können aufgrund ihrer nachgewiesenen Erfolgsbilanz höhere Preise verlangen, bieten aber oft auch einen besseren Service und eine höhere Produktzuverlässigkeit.
-
Incoterms: Die Kenntnis der Incoterms, die bei einer Transaktion verwendet werden, ist von entscheidender Bedeutung. Sie legen die Verantwortlichkeiten von Käufern und Verkäufern in Bezug auf Versandkosten, Versicherung und Risiko fest. Dieses Wissen kann Käufern helfen, unerwartete Kosten zu vermeiden.
Was sind wirksame Einkaufstipps für Kosteneffizienz?
Internationale B2B-Einkäufer sollten mehrere Strategien in Betracht ziehen, um die Kosteneffizienz zu steigern und bessere Geschäfte auszuhandeln:
-
Bedingungen aushandeln: Offene Gespräche mit Lieferanten über Preise, Zahlungsbedingungen und Liefertermine können zu günstigeren Vereinbarungen führen.
-
Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO) bewerten: Berücksichtigen Sie neben dem Anschaffungspreis auch die langfristigen Kosten wie Wartung, Garantie und mögliche Ausfallzeiten. Etwas höhere Anschaffungskosten können auf lange Sicht zu niedrigeren TCO führen.
-
Verstehen Sie die Nuancen der Preisgestaltung für internationale Märkte: Seien Sie sich der regionalen Preisunterschiede bewusst, die durch lokale Marktbedingungen, Währungsschwankungen und wirtschaftliche Faktoren beeinflusst werden. Dieses Wissen kann den Käufern bei Verhandlungen helfen.
-
Lokale Partnerschaften anstreben: Für Einkäufer in Afrika und Südamerika kann der Aufbau von Beziehungen zu lokalen Händlern die Logistikkosten senken und die Reaktionsfähigkeit des Service verbessern.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass ein gründliches Verständnis der Kostenkomponenten, der preisbeeinflussenden Faktoren und der strategischen Verhandlungstipps internationale B2B-Einkäufer in die Lage versetzen wird, fundierte Entscheidungen bei der Beschaffung von Multimeterlösungen für die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten zu treffen. Da sich der Markt weiter entwickelt, ist es wichtig, über diese Faktoren informiert zu bleiben, um optimale Ergebnisse zu erzielen.
Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich der Prüfung der Anlassermagnetspule mit einem Multimeter mit anderen Lösungen
Bei der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten ist es wichtig, neben der Verwendung eines Multimeters auch andere Methoden zu untersuchen. Verschiedene Ansätze können in Bezug auf Effizienz, Kosten und Benutzerfreundlichkeit unterschiedliche Ergebnisse liefern. In dieser Analyse wird die Multimeter-Methode mit zwei praktikablen Alternativen verglichen: der Verwendung eines Schraubendrehers zum Überbrücken der Magnetklemmen und der Verwendung eines speziellen Anlassermagnetprüfgeräts.
| Vergleichsaspekt | Testen des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter | Alternative 1: Schraubenziehertest | Alternative 2: Dedizierter Magnetprüfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Hochgenaue Widerstands- und Durchgangsmessungen. | Schnell, aber weniger präzise; prüft hauptsächlich, ob eine Verbindung besteht. | Liefert spezifische, auf Magnetspulen zugeschnittene Diagnoseergebnisse. |
| Kosten | Mäßig; erfordert die Anschaffung eines Multimeters. | Niedrig; erfordert nur einen Schraubenzieher. | Höher; spezialisiertes Werkzeug mit unterschiedlichen Preispunkten. |
| Einfache Implementierung | Erfordert technische Kenntnisse und eine sorgfältige Einrichtung. | Sehr einfach und schnell für grundlegende Tests. | Benutzerfreundlich, oft mit klaren Anweisungen. |
| Wartung | Niedrig; Multimeter sind langlebig und wartungsarm. | Keine; Schraubenzieher ist ein Basiswerkzeug. | Mäßig; die Prüfgeräte müssen möglicherweise kalibriert oder die Batterien ausgetauscht werden. |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Ideal für eine detaillierte Diagnose und Fehlersuche. | Geeignet für schnelle Kontrollen in Notsituationen. | Am besten geeignet für Techniker, die häufig Magnetspulen testen oder eine präzise Diagnose benötigen. |
Was sind die Vor- und Nachteile der Prüfung mit einem Schraubendreher?
Bei der Prüfung eines Anlassermagneten mit einem Schraubendreher werden die Klemmen überbrückt, um zu sehen, ob der Magnet einrastet. Diese Methode ist schnell und erfordert keine Spezialwerkzeuge, so dass sie für viele Benutzer zugänglich ist. Ihre Einfachheit geht jedoch auf Kosten der Genauigkeit. Diese Methode zeigt zwar an, ob der Magnet funktioniert, gibt aber keinen detaillierten Einblick in den internen Zustand des Magneten, wie z. B. Widerstand oder Durchgang. Sie ist daher am besten als vorläufiger Test und nicht als endgültige Diagnose geeignet.
Wie effektiv ist ein spezieller Anlasser-Magnetventiltester?
Ein spezielles Prüfgerät für Anlassermagnete ist speziell für die Prüfung der Funktionsfähigkeit von Magneten ausgelegt. Diese Geräte sind oft einfach zu bedienen und verfügen über Funktionen, die klare Diagnoseergebnisse liefern. Der Hauptvorteil eines solchen Geräts besteht darin, dass es präzise Messwerte liefert, die speziell auf die Prüfung von Magnetspulen zugeschnitten sind, wodurch Techniker Probleme schnell erkennen können. Allerdings können die Kosten deutlich höher sein als die eines Multimeters oder eines Schraubendrehers, so dass es sich um eine größere Investition handelt. Außerdem ist die Lernkurve für manche Benutzer steil, wenn sie an einfachere Methoden gewöhnt sind.
Schlussfolgerung: Wie wählt man die richtige Methode zur Prüfung von Anlassermagneten?
Bei der Entscheidung über die beste Methode zur Prüfung eines Anlassermagneten sollten B2B-Käufer ihre spezifischen Bedürfnisse, ihr Budget und ihre technischen Kenntnisse berücksichtigen. Für eine detaillierte Diagnose kann die Investition in ein Multimeter die beste Option sein, da es einen umfassenden Einblick in die Leistung des Magnetventils bietet. Für schnelle Überprüfungen oder Notsituationen kann jedoch ein Schraubenzieher eine praktische Wahl sein. Für den häufigen Einsatz in professionellen Umgebungen sind spezielle Prüfgeräte ideal, die Komfort und spezielle Funktionen bieten. Die Kenntnis dieser Optionen ermöglicht es Unternehmen, fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen, die auf ihre betrieblichen Anforderungen zugeschnitten sind.
Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachterminologie für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Was sind die kritischen technischen Eigenschaften für die Prüfung eines Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter?
Bei der Prüfung eines Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter kann die Kenntnis bestimmter technischer Eigenschaften Ihre Fähigkeit verbessern, fundierte Entscheidungen über den Kauf oder die Wartung dieser Komponenten zu treffen. Hier sind einige wichtige Spezifikationen, die Sie beachten sollten:
-
Widerstandswert
Der Widerstandswert der Magnetspule ist ausschlaggebend für ihre Funktionsfähigkeit. Ein gesundes Magnetventil sollte einen Widerstandswert aufweisen, der innerhalb des vom Hersteller angegebenen Bereichs liegt und normalerweise in Ohm gemessen wird. Ein Wert, der deutlich außerhalb dieses Bereichs liegt, kann auf eine Fehlfunktion hindeuten. Für B2B-Einkäufer ist es hilfreich, diesen Wert zu kennen, um die Qualität der Magnetspule vor der Beschaffung zu beurteilen. -
Aktuelle Bewertung
Die Stromstärke gibt den maximalen elektrischen Strom an, den der Magnet ohne Ausfall verarbeiten kann. Dies ist wichtig, um sicherzustellen, dass der Magnet in der vorgesehenen Anwendung effektiv arbeiten kann, ohne zu überhitzen oder Schaden zu nehmen. Käufer sollten Magneten mit angemessenen Stromstärken den Vorzug geben, um Zuverlässigkeit und Sicherheit bei ihrem Betrieb zu gewährleisten. -
Betriebsspannung
Die Betriebsspannung gibt das elektrische Potenzial an, das für die ordnungsgemäße Funktion des Magneten erforderlich ist. Die meisten Kfz-Magnete arbeiten mit 12 V, aber es ist wichtig, diese Spezifikation mit den Anforderungen des Fahrzeugs abzugleichen. Die Kenntnis dieser Eigenschaft stellt sicher, dass sich der Magnet nahtlos in bestehende elektrische Systeme einfügt und somit Kompatibilitätsprobleme vermieden werden. -
Materialzusammensetzung
Die für die Konstruktion des Magneten verwendeten Materialien, wie Kupfer für die Verdrahtung und haltbare Kunststoffe oder Metalle für das Gehäuse, können die Leistung und Langlebigkeit beeinflussen. Hochwertige Materialien führen zu einer besseren Leitfähigkeit und Widerstandsfähigkeit gegenüber Umwelteinflüssen, was für Anwendungen in unterschiedlichen Klimazonen entscheidend ist. B2B-Einkäufer sollten die Materialspezifikationen berücksichtigen, um die Langlebigkeit in ihrer Lieferkette sicherzustellen. -
Temperaturtoleranz
Die Temperaturtoleranz gibt den Temperaturbereich an, in dem die Magnetspule effektiv arbeiten kann. Magnete, die extremen Temperaturen ausgesetzt sind, können vorzeitig ausfallen. Die Kenntnis dieser Eigenschaft hilft bei der Auswahl von Magneten, die bestimmten Umgebungsbedingungen standhalten können, insbesondere in Regionen mit extremen Wetterbedingungen.
Was sind gängige Fachbegriffe im Zusammenhang mit der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten?
Die Vertrautheit mit dem Branchenjargon ist für eine effektive Kommunikation und Entscheidungsfindung im B2B-Kontext unerlässlich. Hier sind einige gängige Begriffe im Zusammenhang mit der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten:
-
OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
OEM bezieht sich auf Teile, die vom Originalhersteller des Fahrzeugs hergestellt wurden. Der Kauf von OEM-Startermagneten gewährleistet Kompatibilität und Zuverlässigkeit, da diese Komponenten speziell für die Spezifikationen des Fahrzeugs entwickelt wurden. B2B-Käufer suchen oft nach OEM-Teilen, um die Qualitätsstandards zu wahren. -
MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
MOQ ist die kleinste Menge eines Produkts, die ein Lieferant zu verkaufen bereit ist. Die Kenntnis der Mindestbestellmenge ist für Einkäufer von entscheidender Bedeutung, um die Durchführbarkeit des Kaufs von Startermagneten zu bestimmen, insbesondere für kleinere Unternehmen oder solche mit begrenzten Budgets. Sie kann sich auf die Bestandsverwaltung und den Cashflow auswirken. -
RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
Eine Anfrage ist ein formelles Dokument, das von Einkäufern verwendet wird, um Preisangebote von Lieferanten einzuholen. Bei der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten kann das Versenden von Anfragen den Unternehmen helfen, Preise und Bedingungen zu vergleichen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie das beste Angebot für Qualitätsprodukte erhalten. Dieser Prozess ist entscheidend für die Budgetierung und Finanzplanung. -
Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
Die Incoterms legen die Verantwortlichkeiten von Käufern und Verkäufern bei internationalen Transaktionen fest, einschließlich Versand und Lieferung. Das Verständnis dieser Bedingungen ist für B2B-Einkäufer unerlässlich, um die Logistik bei der Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten von ausländischen Lieferanten effektiv zu verwalten und Klarheit über Kosten und Verantwortlichkeiten zu schaffen. -
Vorlaufzeit
Als Vorlaufzeit bezeichnet man die Zeit, die von der Bestellung bis zum Erhalt des Produkts vergeht. Für Unternehmen, die auf schnelle Reparaturen oder Ersatz angewiesen sind, ist es wichtig, die Vorlaufzeit für Anlassermagnete zu kennen. Dieses Wissen hilft bei der Bestandsplanung und reduziert Ausfallzeiten.
Durch die Kenntnis dieser technischen Eigenschaften und Handelsbedingungen können B2B-Einkäufer fundiertere Entscheidungen bezüglich der Prüfung und Beschaffung von Anlassermagneten treffen, was letztendlich zu einer verbesserten betrieblichen Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit führt.
Navigation der Marktdynamik und der Beschaffungstrends im Sektor "Prüfung der Anlasser-Magnetspule mit Multimeter
Was sind die wichtigsten Markttrends, die die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter beeinflussen?
Der Markt für Kfz-Prüfgeräte, insbesondere für Werkzeuge zur Prüfung von Anlassermagneten, erfährt ein erhebliches Wachstum, das durch mehrere globale Faktoren angetrieben wird. Der zunehmende Fahrzeugbesitz in Schwellenländern, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika, treibt die Nachfrage nach zuverlässigen Reparatur- und Wartungslösungen für Kraftfahrzeuge voran. Darüber hinaus hat die Zunahme von Elektro- und Hybridfahrzeugen zu Fortschritten in der Prüftechnik geführt, da diese Fahrzeuge oft über komplexe elektrische Systeme verfügen, die spezielle Diagnosewerkzeuge erfordern.
Ein weiterer Trend ist die zunehmende Bedeutung von Ferndiagnose und IoT-fähigen Tools. B2B-Käufer suchen zunehmend nach Geräten mit Konnektivitätsfunktionen, die eine Datenanalyse und Fehlerbehebung in Echtzeit ermöglichen und so die betriebliche Effizienz steigern. Auch die Nachfrage nach benutzerfreundlichen Geräten, die von Technikern mit unterschiedlichen Qualifikationsniveaus bedient werden können, steigt, insbesondere in Märkten mit Fachkräftemangel.
Internationale Einkäufer werden auch immer anspruchsvoller, was die Zuverlässigkeit der Lieferanten und die Produktqualität angeht. Mit der Verbreitung von Online-Marktplätzen ist die Beschaffung wettbewerbsintensiver geworden, so dass es für Unternehmen entscheidend ist, enge Beziehungen zu seriösen Herstellern und Lieferanten aufzubauen. Die Dynamik des Marktes ist daher durch eine Verlagerung hin zu Qualitätssicherung, technologischer Integration und verbesserten Dienstleistungsangeboten gekennzeichnet.
Wie können sich Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung auf B2B-Einkäufer in der Prüfgerätebranche auswirken?
Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung rücken zunehmend in den Fokus der B2B-Einkäufer im Bereich der Kfz-Prüfgeräte. Die Umweltauswirkungen von Herstellungsverfahren und der Lebenszyklus von Produkten werden immer mehr unter die Lupe genommen, und die Unternehmen werden dazu angehalten, umweltfreundlichere Praktiken anzuwenden. Für Geräte wie Multimeter, die zum Testen von Anlassermagneten verwendet werden, bedeutet dies, dass Komponenten von Herstellern bezogen werden müssen, die umweltfreundlichen Materialien und nachhaltigen Praktiken Vorrang einräumen.
Die Bedeutung von ethischen Lieferketten kann gar nicht hoch genug eingeschätzt werden. Einkäufer sind heute eher geneigt, mit Lieferanten zusammenzuarbeiten, die Transparenz in ihren Beschaffungsprozessen demonstrieren und Arbeitsstandards einhalten, die eine faire Behandlung der Arbeiter gewährleisten. Zertifizierungen wie ISO 14001 für Umweltmanagement und Fair-Trade-Zertifizierungen werden zu wichtigen Indikatoren für das Engagement eines Lieferanten für Nachhaltigkeit.

Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Da die Vorschriften für Umweltauswirkungen weltweit strenger werden, können sich Unternehmen, die in nachhaltige Praktiken investieren, besser auf dem Markt behaupten. Dieser Wandel steht nicht nur im Einklang mit den globalen Nachhaltigkeitszielen, sondern spricht auch eine wachsende Verbraucherbasis an, die die soziale Verantwortung von Unternehmen schätzt. Die Integration von Nachhaltigkeit in die Beschaffungsstrategien erfüllt also nicht nur ethische Verpflichtungen, sondern kann auch den Ruf der Marke und die Kundentreue verbessern.
Wie hat sich die Prüfung von Startermagneten im Laufe der Zeit entwickelt?
Die Entwicklung der Prüfmethoden für Anlassermagnete ist von bedeutenden technologischen Fortschritten geprägt. In der Vergangenheit war die Prüfung ein manueller Prozess, der sich stark auf visuelle Inspektionen und rudimentäre Werkzeuge stützte. Techniker verwendeten oft einfache Durchgangsprüfungen, um festzustellen, ob eine Magnetspule funktionierte. Mit dem Fortschritt der Automobiltechnik nahm jedoch die Komplexität der elektrischen Systeme in den Fahrzeugen zu, so dass anspruchsvollere Diagnosewerkzeuge erforderlich wurden.
Die Einführung von Multimetern revolutionierte das Prüfverfahren und ermöglichte präzise Messungen von Spannung, Widerstand und Durchgang. Dadurch wurde nicht nur die Genauigkeit der Diagnose verbessert, sondern auch die für die Fehlersuche benötigte Zeit verkürzt. Mit der zunehmenden Verbreitung von elektronischen Steuergeräten (ECUs) in Fahrzeugen entstand der Bedarf an fortschrittlichen Multimetern, die mit diesen Systemen verbunden werden konnten, was zur Entwicklung intelligenter Diagnosewerkzeuge führte.
Die Integration digitaler Technologien und des Internet der Dinge (IoT) in die Kfz-Diagnose stellt heute die jüngste Phase der Entwicklung dar. Moderne Multimeter, die mit Datenprotokollierungs- und Konnektivitätsfunktionen ausgestattet sind, ermöglichen es Technikern, umfassende Diagnosen und Analysen aus der Ferne durchzuführen. Diese Entwicklung unterstreicht, wie wichtig es ist, mit den technologischen Trends Schritt zu halten, da sie sich direkt auf die Effizienz und Effektivität der Prüfverfahren im Automobilsektor auswirken.
Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
-
Wie prüfe ich ein Anlasser-Magnetventil mit einem Multimeter?
Um eine Anlassermagnetspule mit einem Multimeter zu prüfen, stellen Sie zunächst die Sicherheit sicher - schalten Sie das Fahrzeug aus und klemmen Sie die Batterie ab. Suchen Sie die Magnetspule und stellen Sie Ihr Multimeter auf den Widerstandsmodus (Ohm) ein. Trennen Sie die elektrischen Anschlüsse von der Magnetspule und berühren Sie dann die kleinen Klemmen mit den Multimetersonden. Ein korrekter Messwert weist auf eine funktionierende Spule hin. Prüfen Sie als Nächstes die Magnetkontakte, indem Sie den Widerstand zwischen den Klemmen der Batterie und des Anlassers messen. Prüfen Sie abschließend den Durchgang, um sicherzustellen, dass die Magnetspule richtig funktioniert. Spezifische Widerstandswerte finden Sie immer im Wartungshandbuch des Fahrzeugs. -
Was sind die Anzeichen für ein defektes Anlasser-Magnetventil?
Häufige Anzeichen für ein defektes Anlassermagnetventil sind ein Motor, der nicht anspringt, ein langsames Anlassen des Motors oder ein klickendes Geräusch beim Versuch, das Fahrzeug zu starten. Auch eine Überhitzung der Magnetspule oder Korrosion an den Anschlüssen sind Anzeichen für einen möglichen Defekt. Wenn diese Probleme auftreten, ist es ratsam, einen gründlichen Multimetertest durchzuführen, um den Zustand der Magnetspule zu überprüfen und sicherzustellen, dass die elektrischen Anschlüsse korrekt sind. -
Woher bekomme ich hochwertige Multimeter für die Prüfung von Anlassermagneten?
Suchen Sie bei der Beschaffung von Multimetern nach Anbietern mit einem guten Ruf in der Elektronikbranche. Überprüfen Sie deren Zertifizierungen und Produktbewertungen, um die Qualität sicherzustellen. Es ist vorteilhaft, Muster zum Testen anzufordern, bevor Sie eine größere Bestellung aufgeben. Achten Sie außerdem auf Lieferanten, die Garantien oder Rückgaberegelungen anbieten, damit Sie sich auf die Zuverlässigkeit der Produkte verlassen können. -
Welche Zahlungsbedingungen sind beim Kauf von Kfz-Prüfgeräten üblich?
Die Zahlungsbedingungen können von Lieferant zu Lieferant sehr unterschiedlich sein. Zu den üblichen Bedingungen gehören Vorauszahlung, 30 oder 60 Tage netto sowie Akkreditive für größere Aufträge. Es ist wichtig, Bedingungen auszuhandeln, die mit Ihren Cashflow- und Risikomanagementstrategien übereinstimmen. Vergewissern Sie sich stets, dass die angebotenen Zahlungsmethoden sicher sind und durch Käuferschutzrichtlinien abgesichert werden. -
Gibt es Mindestbestellmengen (MOQs) für Kfz-Prüfgeräte?
Viele Lieferanten setzen MOQs durch, um die Rentabilität zu erhalten und die Produktionskosten zu kontrollieren. Die MOQs können jedoch je nach Produkt und Lieferant variieren. Für kleine Unternehmen oder Neugründungen ist es ratsam, sich nach der Flexibilität der MOQs zu erkundigen, insbesondere bei Erstbestellungen. Einige Lieferanten bieten möglicherweise niedrigere Mindestbestellmengen für bestimmte Produktlinien an oder gewähren Rabatte für Großbestellungen. -
Welche Qualitätssicherungsprozesse (QA) sollte ich bei der Beschaffung von Magneten berücksichtigen?
Erkundigen Sie sich bei der Beschaffung von Magneten nach den Qualitätssicherungsprozessen des Lieferanten, einschließlich Prüfprotokollen und Zertifizierungen. Achten Sie auf Lieferanten, die ihre Produkte strengen Prüfungen unterziehen, z. B. Prüfungen des elektrischen Widerstands und der Durchgängigkeit. Zertifizierungen wie ISO 9001 können ebenfalls auf ein Engagement für Qualität hinweisen. Fordern Sie eine Dokumentation der Qualitätssicherungsprozesse an, um sicherzustellen, dass die Produkte den Industriestandards entsprechen. -
Wie kann ich Lieferanten für Automobilkomponenten international überprüfen?
Um Lieferanten zu überprüfen, sollten Sie zunächst ihre geschäftlichen Referenzen und Zeugnisse kontrollieren. Nutzen Sie Plattformen wie Alibaba oder Global Sources, die Bewertungen und Rezensionen bereitstellen. Führen Sie Videoanrufe durch, um die Fertigungsmöglichkeiten und Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen zu besprechen. Wenn möglich, kann auch ein Besuch in den Einrichtungen des Unternehmens einen Einblick in die Arbeitsabläufe geben. Ziehen Sie außerdem in Erwägung, vor dem Versand Inspektionsdienste Dritter in Anspruch zu nehmen, um die Produktqualität zu überprüfen. -
Welche logistischen Überlegungen sollte ich bei der Einfuhr von Kfz-Teilen anstellen?
Beachten Sie beim Import von Kfz-Teilen die Zollbestimmungen, die Versandmethoden und die Lieferzeiten. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass Sie die in Ihrem Land geltenden Einfuhrzölle und Steuern kennen. Um Verzögerungen zu vermeiden, sollten Sie unbedingt mit Logistikpartnern zusammenarbeiten, die Erfahrung im Umgang mit Kfz-Teilen haben. Wählen Sie außerdem zuverlässige Versandmethoden, um sicherzustellen, dass die Produkte in gutem Zustand und pünktlich ankommen.
Top 2 Wie prüfe ich ein Anlasser-Magnetventil mit Multimeter Hersteller & Lieferanten Liste
1. Reddit - Solenoid Starthilfekabel
Domäne: reddit.com
Registriert: 2005 (20 Jahre)
Einleitung: Magnetstarterkabel, Multimeter, Batterie, Startermagnet
2. Dotheton - Anlasser-Magnetventil für 1976 CB550K
Domäne: dotheton.com
Registriert: 2007 (18 Jahre)
Einleitung: Anlassermagnet für CB550k-Motorrad von 1976, nicht original, Probleme mit der Verdrahtung und der Funktionalität, Testmethoden umfassen die Verwendung eines Ohm-Meters und das Anlegen von 12 V Gleichstrom an die Klemmen.
Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für die Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass das Wissen, wie man ein Anlassermagnetventil mit einem Multimeter testet, für die Zuverlässigkeit und Effizienz des Kfz-Betriebs unerlässlich ist. Für B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, hilft dieses Wissen nicht nur bei der Erhaltung der Fahrzeugleistung, sondern verbessert auch die Beschaffungsstrategien. Durch Investitionen in Qualitätsmultimeter und die Pflege von Partnerschaften mit zuverlässigen Lieferanten können Unternehmen ihre Wartungsprozesse optimieren und Ausfallzeiten reduzieren.
Die strategische Beschaffung spielt in diesem Zusammenhang eine zentrale Rolle, da sie es Unternehmen ermöglicht, Lieferanten zu identifizieren und mit ihnen in Kontakt zu treten, die hochwertige Komponenten und Werkzeuge anbieten. Dieser proaktive Ansatz sichert nicht nur die besten Preise, sondern auch den Zugang zu fortschrittlicher technischer Unterstützung und Ressourcen, die für die Fehlersuche und Reparaturen entscheidend sind.
Mit Blick auf die Zukunft ermutigen wir internationale Einkäufer, verschiedene Lieferantenoptionen zu erkunden und Technologien zur Verbesserung ihrer Beschaffungsstrategien zu nutzen. Auf diese Weise können Unternehmen sicherstellen, dass sie für die Herausforderungen der Automobilindustrie gut gerüstet sind, was letztlich zu einer verbesserten betrieblichen Effizienz und Kundenzufriedenheit führt. Nutzen Sie die Gelegenheit, Ihre Lieferkette zu stärken und Ihr Unternehmen mit fundierten Einkaufsentscheidungen voranzubringen.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
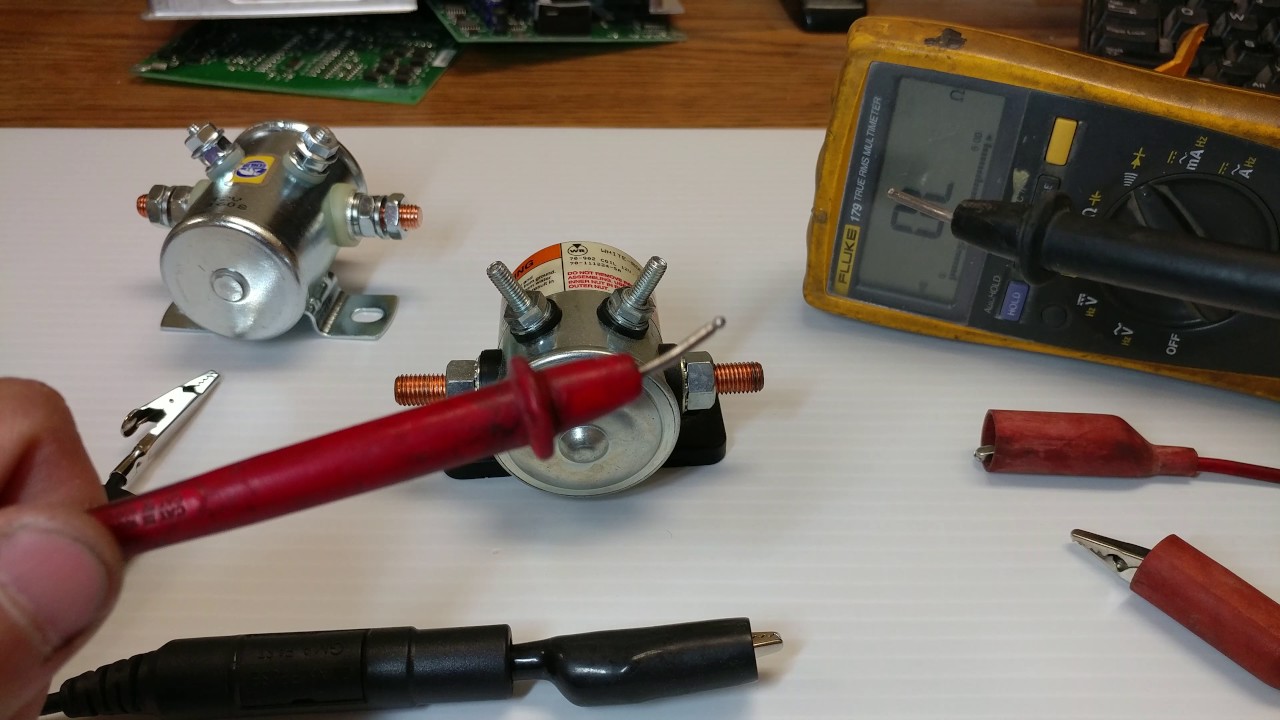
Anschauliches Bild zur Prüfung des Anlassermagneten mit einem Multimeter
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.