Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric cars vs gasoline
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, the decision between electric cars and gasoline vehicles presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of electric vehicles (EVs) versus traditional internal combustion engine cars is essential for organizations looking to optimize their fleets or invest in sustainable transportation solutions. This comprehensive guide delves into critical factors such as cost analysis, maintenance considerations, environmental impacts, and supplier vetting processes, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
As the global market shifts towards greener technologies, businesses from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia—must navigate varying regulations, infrastructure, and economic conditions. This guide equips B2B buyers with actionable insights on sourcing electric and gasoline vehicles, assessing total cost of ownership, and evaluating the long-term benefits of adopting electric mobility.
By exploring the intricacies of vehicle types and their applications, organizations can strategically align their transportation choices with sustainability goals and operational efficiencies. With a focus on empowering buyers to make informed decisions, this resource will serve as a valuable tool in the transition towards a more sustainable future in the automotive industry.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 3 Electric Cars Vs Gasoline Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric cars vs gasoline
- Understanding electric cars vs gasoline Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of electric cars vs gasoline
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric cars vs gasoline’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric cars vs gasoline
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric cars vs gasoline
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric cars vs gasoline’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric cars vs gasoline Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric cars vs gasoline With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric cars vs gasoline
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric cars vs gasoline Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric cars vs gasoline
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric cars vs gasoline
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Understanding electric cars vs gasoline Types and Variations
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batterieelektrisches Fahrzeug (BEV) | Powered solely by electric batteries; zero tailpipe emissions. | Urban delivery fleets, corporate car pools. | Vorteile: Lower fuel and maintenance costs; environmentally friendly. Nachteile: Limited range compared to gasoline cars; longer refueling times. |
| Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) | Combines electric power with a gasoline engine; can operate in electric-only mode. | Mixed-use fleets, long-distance travel. | Vorteile: Flexibility of electric and gasoline; reduced fuel costs. Nachteile: Higher initial purchase price; requires regular charging. |
| Hybrid-Elektrofahrzeug (HEV) | Uses both electric motor and gasoline engine but cannot be charged externally. | Public transport, taxi services. | Vorteile: Better fuel efficiency than traditional gas cars; lower emissions. Nachteile: Less electric-only range; more maintenance than BEVs. |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) | Uses hydrogen to produce electricity; emits only water vapor. | Heavy-duty transport, logistics companies. | Vorteile: Quick refueling; long range. Nachteile: Limited hydrogen infrastructure; higher costs. |
| Conventional Gasoline Vehicle | Powered by internal combustion engines; widely available and familiar. | Personal use, traditional logistics. | Vorteile: Established infrastructure; generally lower upfront costs. Nachteile: Higher long-term fuel costs; greater environmental impact. |
What are the Characteristics of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)?
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are fully electric cars that operate on rechargeable batteries, making them a sustainable choice for businesses focused on reducing their carbon footprint. With zero tailpipe emissions, they are ideal for urban delivery fleets and corporate car pools where short distances and frequent stops are common. When considering BEVs, B2B buyers should evaluate charging infrastructure availability and total cost of ownership, including potential government incentives for electric vehicle purchases.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
How Do Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) Function?
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) blend electric and gasoline power, allowing for electric-only operation for shorter trips and gasoline use for longer distances. This versatility makes them suitable for mixed-use fleets and businesses that require flexibility in travel. PHEVs can significantly lower fuel costs, but buyers should consider the higher initial investment and the need for regular charging to maximize efficiency.
What Makes Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) Different?
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) utilize both an electric motor and a gasoline engine, optimizing fuel efficiency without the need for external charging. They are particularly beneficial for public transport systems and taxi services, where frequent stops and starts enhance their fuel economy. B2B buyers should assess the balance between initial costs and long-term savings on fuel, as well as the maintenance needs associated with having both an electric and combustion engine.
What are the Advantages of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)?
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) convert hydrogen into electricity, offering a rapid refueling option and a long driving range, making them suitable for heavy-duty transport and logistics applications. However, the limited availability of hydrogen refueling stations presents a challenge for widespread adoption. B2B buyers should consider the infrastructure in their operational areas and the total cost of ownership when evaluating FCEVs.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
Why Choose Conventional Gasoline Vehicles?
Conventional Gasoline Vehicles are powered by internal combustion engines and remain the most familiar option for many businesses. They are often less expensive upfront and benefit from an established refueling infrastructure. However, B2B buyers must weigh the long-term fuel costs and environmental impact against the initial savings. As the market shifts towards greener alternatives, companies may also want to consider the implications of regulatory changes on gasoline vehicle usage in the future.
Key Industrial Applications of electric cars vs gasoline
| Branche/Sektor | Specific Application of electric cars vs gasoline | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery vehicles | Reduced operational costs and emissions | Availability of EV models, charging infrastructure, total cost of ownership |
| Öffentliche Verkehrsmittel | Electric buses vs. gasoline buses | Lower fuel and maintenance costs | Government incentives, fleet size, charging station access |
| Bergbau und Bauwesen | Electric utility vehicles | Enhanced safety and lower environmental impact | Battery life, ruggedness, charging solutions for remote sites |
| Landwirtschaft | Electric tractors and farm vehicles | Improved efficiency and lower fuel costs | Compatibility with existing machinery, charging options, local support services |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee transportation solutions | Reduced carbon footprint and lower costs | Incentives for EV adoption, fleet management software, vehicle availability |
How Are Electric Cars Transforming the Logistics and Delivery Industry?
In the logistics and delivery sector, electric vehicles (EVs) are increasingly used for last-mile delivery. Companies are opting for electric vans and trucks to minimize operational costs associated with fuel and maintenance. The shift to EVs also aligns with sustainability goals, reducing carbon emissions significantly. International buyers should consider local charging infrastructure and the total cost of ownership, including potential government incentives for adopting electric fleets.
What Are the Advantages of Electric Buses in Public Transportation?
Public transportation systems are embracing electric buses over traditional gasoline models to lower fuel and maintenance costs. Electric buses offer quieter operations and reduced emissions, which enhance urban air quality. For B2B buyers, key considerations include government incentives for fleet electrification, the size of the fleet, and the accessibility of charging stations to support operational efficiency.
How Do Electric Utility Vehicles Benefit Mining and Construction?
In the mining and construction industries, electric utility vehicles are becoming a preferred choice due to their lower environmental impact and enhanced safety features. These vehicles can operate in rugged terrains while producing minimal noise and emissions. Buyers in these sectors should evaluate battery life, vehicle durability, and charging solutions, especially for remote sites where traditional infrastructure may be lacking.
Why Are Electric Tractors Gaining Popularity in Agriculture?
Electric tractors and farm vehicles are revolutionizing the agriculture sector by improving operational efficiency and reducing fuel costs. These vehicles are quieter and produce fewer emissions, making them ideal for environmentally conscious farming practices. Buyers should assess compatibility with existing machinery, availability of local charging options, and support services to ensure seamless integration into their operations.
What Benefits Do Electric Vehicles Offer for Corporate Fleets?
Corporate fleets are increasingly adopting electric vehicles to enhance their sustainability efforts and reduce operational costs. EVs help companies lower their carbon footprint while also benefiting from reduced fuel expenses. When considering electric vehicles, businesses must factor in available incentives for EV adoption, fleet management software capabilities, and the overall availability of vehicles that meet their specific needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric cars vs gasoline’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Cost Management Dilemma for Fleet Operators
Das Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing fleets, face a significant challenge in assessing the long-term cost implications of switching from gasoline to electric vehicles (EVs). With fluctuating fuel prices and varying initial investment costs, decision-makers often find it difficult to predict total cost of ownership (TCO). This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in transitioning to EVs, despite their potential for lower operating costs and maintenance expenses.
Die Lösung: To effectively manage costs, fleet operators should conduct a comprehensive TCO analysis that includes purchase price, fuel costs, maintenance expenses, and potential government incentives. Start by gathering data on the average fuel economy of gasoline vehicles in your fleet and comparing it with the efficiency of the EV models under consideration. Use tools such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s EV Cost Calculator to input local electricity rates and expected mileage. Additionally, consider the availability of incentives for EV purchases or installations of charging stations, which can significantly offset upfront costs. By establishing a clear picture of both current and projected expenses, fleet operators can make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints and sustainability goals.
Scenario 2: Infrastructure and Charging Accessibility
Das Problem: One of the most pressing concerns for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and South America is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. This limitation not only affects the feasibility of EV adoption but also raises concerns about operational downtime, particularly for businesses that rely on timely deliveries and services.
Die Lösung: To address infrastructure challenges, B2B buyers should engage with local governments and utility companies to understand existing plans for charging network expansion. It is crucial to identify strategic locations for installing charging stations, especially in high-traffic areas or near operational hubs. Businesses can also explore partnerships with EV charging network providers to facilitate the installation of fast chargers at their facilities. As an interim solution, consider implementing a hybrid fleet that combines both gasoline and electric vehicles, ensuring operational continuity while gradually transitioning to a fully electric fleet as infrastructure improves. Investing in employee training on optimal charging practices can also help maximize efficiency and reduce downtime.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
Scenario 3: Environmental and Regulatory Compliance Concerns
Das Problem: B2B buyers are increasingly pressured to comply with stringent environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals. However, there can be confusion regarding the actual environmental benefits of electric vehicles compared to gasoline cars, especially in regions where the electricity grid is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
Die Lösung: To navigate this complex landscape, businesses should conduct a lifecycle assessment (LCA) of both electric and gasoline vehicles to fully understand their environmental impact. This assessment should encompass factors such as the carbon emissions from vehicle production, operation, and end-of-life disposal. Buyers should prioritize sourcing electricity from renewable sources to maximize the environmental benefits of electric vehicles. Furthermore, businesses can engage in carbon offset programs to mitigate their overall footprint while transitioning to electric vehicles. Collaborating with environmental consultants can provide tailored insights into compliance requirements and help align your fleet strategy with sustainability objectives, making the case for electric vehicles stronger in both operational and regulatory contexts.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric cars vs gasoline
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Cars vs. Gasoline Cars?
When comparing electric cars and gasoline vehicles, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials—aluminum, steel, lithium-ion batteries, and composites—focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
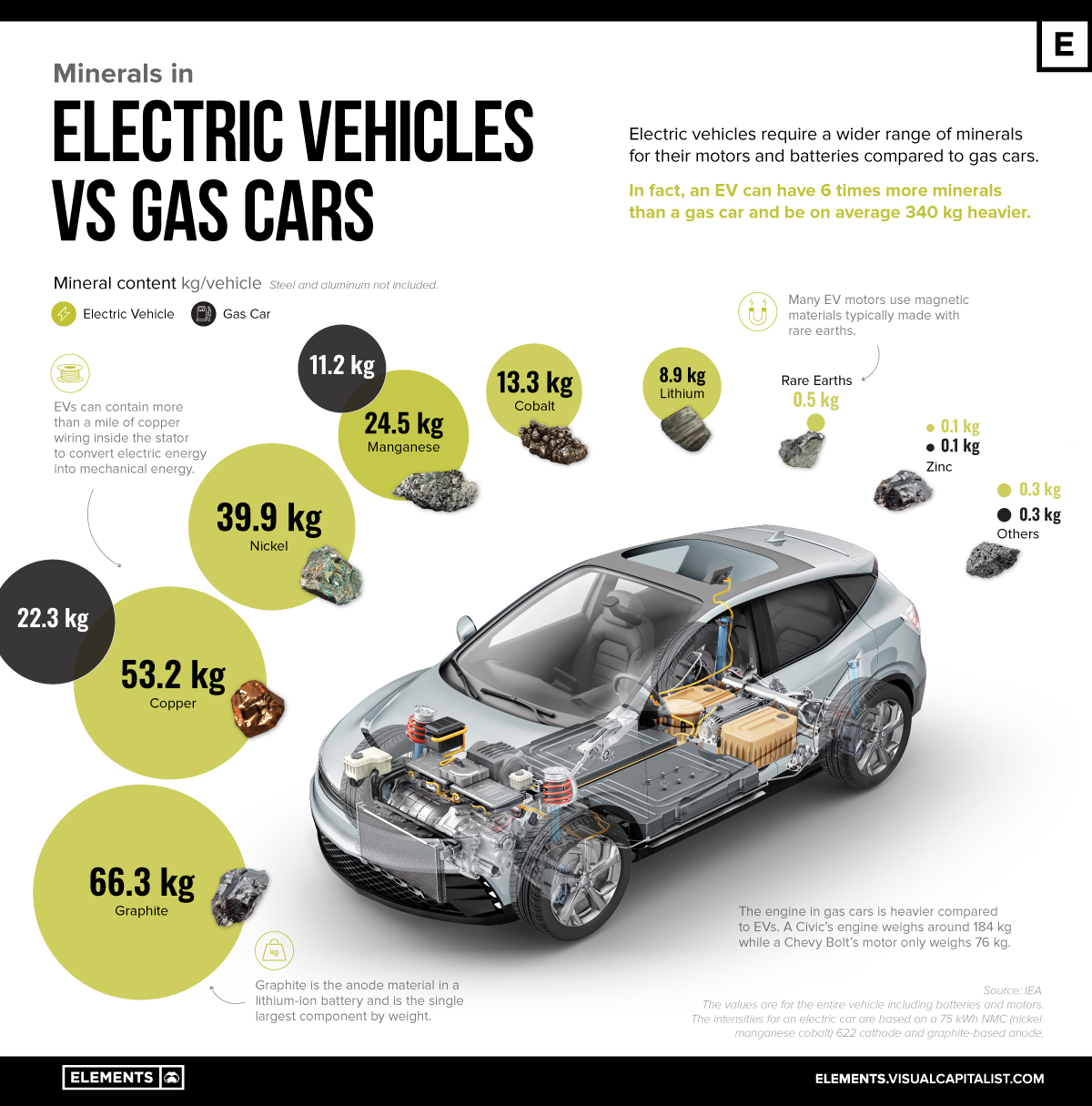
Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric and Gasoline Vehicles?
Aluminum is widely used in both electric and gasoline vehicles due to its lightweight nature, which enhances fuel efficiency and performance. Key properties include excellent corrosion resistance and a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Vorteile: Aluminum components are durable and can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for various automotive applications. The reduced weight contributes to better energy efficiency, especially in electric vehicles, leading to extended range and improved handling.
Nachteile: However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase production costs. Additionally, it has lower tensile strength compared to some steel grades, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: In electric vehicles, aluminum is often used in battery enclosures and chassis, while in gasoline vehicles, it is commonly found in engine components and body panels.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local automotive standards (e.g., DIN, ISO) when selecting aluminum components.
What Role Does Steel Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Steel remains a primary material in the automotive industry, known for its strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength and good weldability.
Vorteile: Steel is generally more affordable than aluminum, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production. Its robustness makes it suitable for structural components, enhancing the vehicle’s safety.
Nachteile: However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency, especially in electric vehicles. It is also prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Steel is widely used in the body structure and chassis of both electric and gasoline vehicles, providing essential safety features.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial for steel components, particularly for buyers in Africa and South America, where different grades may be preferred based on local conditions.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Impact Electric Vehicles?
Lithium-ion batteries are the backbone of electric vehicles, providing the energy needed for operation. Key properties include high energy density and a relatively low self-discharge rate.
Vorteile: These batteries allow for longer driving ranges and faster charging times, making them ideal for electric vehicles. Their compact size also contributes to design flexibility.
Nachteile: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, and there are environmental concerns regarding lithium extraction and battery disposal.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: In electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are essential for energy storage, directly influencing performance and range.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Buyers should be aware of the evolving regulations regarding battery recycling and disposal, particularly in Europe, where stringent environmental laws are in place.
What Advantages Do Composites Offer for Vehicle Manufacturing?
Composites, including carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly used in automotive applications due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics.
Vorteile: Composites can significantly reduce vehicle weight, improving energy efficiency and performance. They also offer excellent corrosion resistance and design flexibility.
Nachteile: The primary drawback is the high cost of materials and manufacturing processes, which can limit their widespread use in budget-friendly vehicles.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Composites are often used in high-performance electric vehicles and luxury gasoline cars, particularly in body panels and interior components.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Buyers should consider regional manufacturing capabilities and compliance with relevant standards, as composite manufacturing may require specialized facilities.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric vs. Gasoline Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric cars vs gasoline | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium | Battery enclosures, chassis | Leichtes Gewicht, korrosionsbeständig | Higher cost, lower tensile strength | Mittel |
| Stahl | Body structure, chassis | Cost-effective, robust | Schwerer, anfällig für Korrosion | Niedrig |
| Lithium-Ionen-Akku | Energy storage | High energy density, compact | Complex manufacturing, environmental concerns | Hoch |
| Verbundwerkstoffe | Body panels, interiors | Geringes Gewicht, flexible Gestaltung | High cost, specialized manufacturing | Hoch |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into material selection for electric and gasoline vehicles, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric cars vs gasoline
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Electric Cars Compared to Gasoline Vehicles?
The manufacturing processes for electric vehicles (EVs) and gasoline vehicles differ significantly due to their distinct technologies. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing components or vehicles for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Electric Vehicles?
1. Materialvorbereitung
The manufacturing of both electric and gasoline vehicles starts with material preparation. For electric vehicles, materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel are essential for battery production. These metals are often sourced from different parts of the world, making supply chain management crucial. In contrast, gasoline vehicles primarily use steel, aluminum, and plastics, which are processed into parts such as the engine and body panels.
2. Formen
In the forming stage, components are shaped into their final forms. Electric vehicles require specialized processes for battery casing and electric motor components, which often involve advanced techniques like die-casting and injection molding. Gasoline vehicles, on the other hand, utilize traditional stamping and welding processes for engine blocks and chassis.
3. Montage
The assembly phase is where the differences become more pronounced. Electric vehicles often require intricate assembly lines that integrate battery packs with the vehicle’s electrical systems. This integration is critical for performance and safety. Gasoline vehicles’ assembly processes focus on integrating mechanical systems like the internal combustion engine, fuel systems, and exhaust components.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
4. Fertigstellung
Finishing involves painting and final inspections. EVs may require additional finishing steps for their battery enclosures and electrical components to ensure waterproofing and safety. In gasoline vehicles, the finishing process often emphasizes aesthetic aspects, such as paint quality and interior trim.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Electric and Gasoline Vehicles?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in both electric and gasoline vehicle manufacturing to meet international standards and ensure consumer safety.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Control in Vehicle Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is a key standard that applies to both electric and gasoline vehicle manufacturers. It focuses on quality management systems and ensures consistent quality across all stages of production. Other industry-specific standards include:
- CE-Kennzeichnung: Required in Europe, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API-Standards: Relevant for components related to the petroleum industry, ensuring quality in fuel systems for gasoline vehicles.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Vehicle Manufacturing?
Die Qualitätskontrolle umfasst mehrere Kontrollpunkte während des gesamten Herstellungsprozesses:
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival. For EV manufacturers, battery cells are a critical focus area, requiring stringent testing for performance and safety.
-
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous checks are performed to monitor processes and ensure adherence to specifications. This includes testing electrical systems in EVs and mechanical systems in gasoline vehicles.
-
Endkontrolle (FQC): The final inspection is crucial before vehicles are released to the market. For EVs, this includes battery performance testing and safety checks, while gasoline vehicles undergo engine performance and emissions testing.
Welche gängigen Prüfverfahren werden zur Qualitätssicherung eingesetzt?
Testing methods vary based on the vehicle type but generally include:
-
Funktionelle Prüfung: Evaluates the performance of critical components, such as electric motors in EVs and engines in gasoline vehicles.
-
Haltbarkeitsprüfung: Assesses how well a vehicle can withstand stress over time, including battery lifecycle tests for EVs and engine endurance tests for gasoline vehicles.
-
Safety Testing: Essential for both types of vehicles, focusing on crash tests and electrical safety for EVs.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrollpraktiken ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
For international B2B buyers, ensuring supplier quality is paramount. Here are actionable steps:
-
Durchführung von Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with international standards and internal quality processes.
-
Request Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control measures, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
-
Beauftragung von Drittinspektoren: Hiring third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
Was sind die Feinheiten der Qualitätskontrolle und Zertifizierung für internationale B2B-Einkäufer?
Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that affect vehicle manufacturing and quality assurance:
-
Africa: Buyers should be aware of local certification requirements, which may vary significantly between countries.
-
South America: In many countries, compliance with local environmental regulations is crucial, particularly for emissions standards in gasoline vehicles.
-
Naher Osten: Buyers may need to consider the harsh environmental conditions that affect vehicle durability and performance.
-
Europa: Stringent EU regulations require compliance with both safety and environmental standards, making it essential for manufacturers to stay updated with evolving legislation.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electric and gasoline vehicles is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside rigorous quality control methods, businesses can make informed decisions when sourcing vehicles or components for their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric cars vs gasoline’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the decision-making process for procuring vehicles, particularly when comparing electric cars and gasoline cars, this guide offers a practical checklist. By following these steps, buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational needs, budget, and sustainability goals.
Schritt 1: Assess Your Organizational Needs
Begin by evaluating the specific requirements of your business. Consider factors such as vehicle usage, expected mileage, and the types of terrain your fleet will encounter. Understanding these needs will help you determine whether electric vehicles (EVs) or gasoline-powered vehicles are more suitable for your operations.
- Usage Patterns: Analyze how frequently vehicles are used and for what purposes (e.g., deliveries, employee transport).
- Range Requirements: Assess whether your routes exceed the range capabilities of available EV models.
Schritt 2: Berechnen Sie die Gesamtbetriebskosten
Understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) is essential in comparing electric and gasoline vehicles. This includes the initial purchase price, fuel costs, maintenance, and potential incentives.
- Fuel Savings: Electric vehicles generally offer lower fuel costs compared to gasoline cars. Calculate the annual fuel expenses based on your expected mileage and local electricity vs. gasoline prices.
- Maintenance Costs: Consider that EVs typically have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes.
Schritt 3: Evaluate Charging Infrastructure
For electric vehicles, the availability of charging infrastructure is a critical factor. Assess your current and future charging needs to ensure operational efficiency.
- Home vs. Public Charging: Determine if your fleet will primarily charge at a central location or require access to public charging stations.
- Installation Costs: Factor in the costs associated with installing charging stations, including any potential incentives for installation.
Schritt 4: Recherche von Lieferantenoptionen
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and service requirements. This step is vital for establishing a reliable supply chain.
- Ruf des Lieferanten: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region. Request references and case studies from other businesses with similar needs.
- Garantie und Support: Evaluate the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by suppliers, as these can significantly impact your long-term satisfaction.
Schritt 5: Understand Regulatory and Tax Incentives
Familiarize yourself with local regulations and incentives that may apply to electric vehicle purchases. These can greatly influence the financial viability of your decision.
- Government Incentives: Investigate any tax credits or rebates for electric vehicle purchases or charging infrastructure installation that may be available in your region.
- Environmental Regulations: Consider compliance with local environmental regulations, as some regions may have incentives for reducing carbon emissions.
Schritt 6: Umweltauswirkungen berücksichtigen
Reflect on the environmental implications of your vehicle choice. Electric vehicles generally produce lower emissions, especially when charged with renewable energy sources.
- Carbon Footprint Analysis: Conduct a comparison of emissions produced by electric vs. gasoline vehicles based on your expected usage.
- Sustainability Goals: Align your procurement decision with your company’s sustainability initiatives, as choosing electric vehicles can enhance your corporate social responsibility profile.
Schritt 7: Plan for Future Scalability
As your business grows, your vehicle needs may change. Ensure that your vehicle choice allows for scalability.
- Model Availability: Check the availability of various models that can accommodate future fleet expansion or diversification.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about advancements in vehicle technology and market trends, as these can affect your long-term vehicle strategy.
By systematically following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their immediate operational needs but also align with broader financial and environmental goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric cars vs gasoline Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Cars Compared to Gasoline Vehicles?
When evaluating the cost structure of electric cars versus gasoline vehicles, several key components come into play. Materialien for electric vehicles (EVs) typically include advanced battery systems, electric motors, and lightweight materials like aluminum and carbon fiber. The battery, often the most expensive part, can significantly affect the overall cost. In contrast, gasoline vehicles rely heavily on traditional components such as internal combustion engines, transmission systems, and exhaust systems, which generally have a lower material cost but higher maintenance requirements.
Arbeit costs for manufacturing EVs can be higher due to the specialized skills required to assemble battery systems and electric drivetrains. However, as automation in EV production improves, these labor costs may decrease over time. Produktionsgemeinkosten includes expenses related to the facilities and technology used in production. EV manufacturers often invest in cutting-edge technology to optimize production efficiency, which can lead to higher upfront costs but lower long-term expenses.
Werkzeuge und quality control (QC) are also critical components. The tooling required for EV production is often more complex due to the need for precise battery assembly and electrical components. QC processes must be rigorous to ensure safety and reliability, particularly as the market matures. Logistik costs can vary based on sourcing materials, especially if raw materials are sourced from different regions. For instance, lithium and cobalt are essential for batteries, and their sourcing can impact pricing significantly.
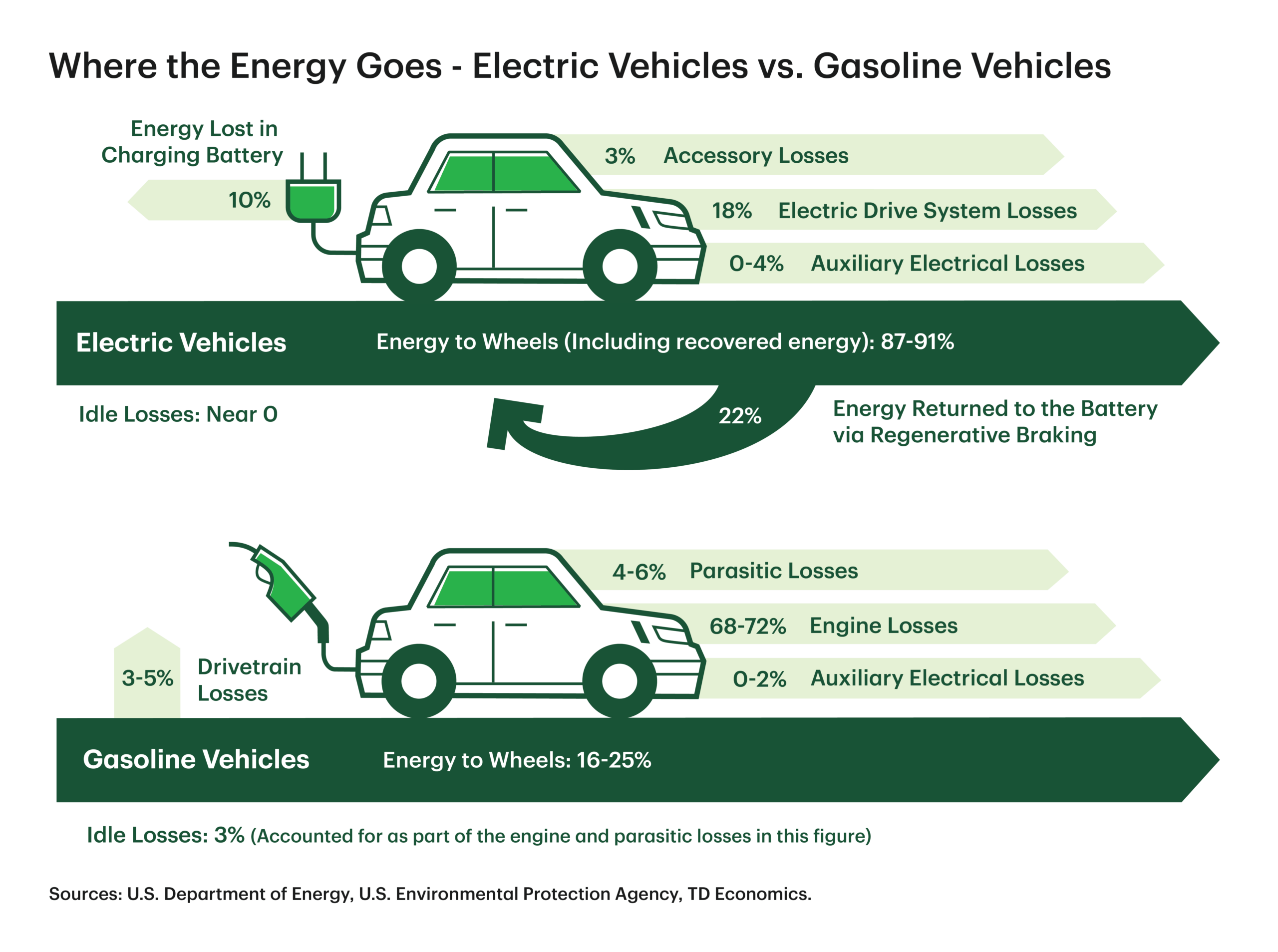
Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric and Gasoline Vehicles?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric and gasoline vehicles. Volumen und Mindestbestellmenge (MOQ) play a significant role; bulk orders generally result in lower per-unit costs. For B2B buyers, negotiating pricing based on volume can lead to substantial savings.
Spezifikationen und Anpassung also impact price. Electric vehicles often come with a range of customization options, from battery capacity to tech features, which can affect the final cost. In contrast, gasoline vehicles might offer fewer customization options, often leading to a more standardized pricing structure.
Materialqualität und Zertifizierungen are vital, particularly for international buyers. Ensuring that vehicles meet specific quality standards and certifications can add to the cost but is crucial for compliance in markets such as Europe, which has stringent regulations.
Lieferantenfaktoren, including reliability and production capacity, can also influence pricing. A supplier’s ability to deliver on time and their history of meeting quality standards can be decisive factors in negotiations.
Incoterms should be carefully considered, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage logistics costs and risks effectively.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers Looking to Optimize Costs?
B2B buyers should adopt several strategies to negotiate better pricing for electric and gasoline vehicles. First, understanding the Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO) is essential. This includes not just the purchase price, but also fuel costs, maintenance, insurance, and depreciation over time. For electric vehicles, the lower maintenance costs can lead to significant savings over the vehicle’s lifespan.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
Die Käufer sollten auch Folgendes beachten pricing nuances in international markets. For example, in regions like Africa and South America, the availability of charging infrastructure may influence the practicality of electric vehicles, thereby affecting demand and pricing. In contrast, European markets may offer more incentives for electric vehicles, impacting the cost structure favorably for buyers.
Finally, it’s critical to remain flexible during negotiations. Being open to alternative suppliers or models can provide leverage and help secure better pricing.
Haftungsausschluss für Richtpreise
Prices for electric and gasoline vehicles can vary widely based on market conditions, regional availability, and specific buyer requirements. The information provided here serves as a guideline and may not reflect real-time pricing. Always conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric cars vs gasoline With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Electric Cars and Gasoline
As global markets continue to evolve, businesses are increasingly considering various transportation solutions beyond traditional electric and gasoline vehicles. The choice between electric cars and gasoline-powered vehicles is crucial, not only for operational efficiency but also for sustainability and cost-effectiveness. This analysis explores electric cars and gasoline vehicles in comparison to two viable alternatives: hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and biofuel-powered vehicles. Understanding these alternatives will help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional contexts.

Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
Vergleichstabelle
| Vergleichsaspekt | Electric Cars Vs Gasoline | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles | Biofuel-Powered Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | High torque and acceleration; range varies by model | Comparable range to gasoline; refueling time similar to gas | Generally lower power and efficiency; varies with fuel type |
| Kosten | Higher upfront cost, lower lifetime fuel and maintenance costs | Moderate upfront cost, hydrogen infrastructure still developing | Often lower initial costs, but variable fuel prices |
| Einfache Implementierung | Charging infrastructure growing, home charging available | Limited hydrogen stations; requires investment in infrastructure | Established biofuel supply chains in some regions |
| Wartung | Lower maintenance costs; fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; similar to electric vehicles | Similar to gasoline vehicles; can require specialized knowledge |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Urban commuting, fleet operations, and long-range travel | Long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications | Agricultural transport and regions with biofuel production |
Detaillierte Aufschlüsselung der Alternativen
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) present an intriguing alternative to electric and gasoline vehicles. They operate by converting hydrogen into electricity, offering high efficiency and zero tailpipe emissions. Pros include quick refueling times comparable to gasoline vehicles and longer ranges than many battery electric vehicles. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still limited, especially in developing regions, which can pose challenges for widespread adoption. The initial investment in hydrogen technology can also be high, making it less accessible for some businesses.
Biofuel-Powered Vehicles
Biofuel-powered vehicles utilize fuels derived from renewable biological sources, such as plant materials and animal waste. This alternative can often be less expensive to implement, especially in regions where biofuels are readily available. Biofuels can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions when compared to fossil fuels. However, the performance can vary significantly based on the type of biofuel used, and these vehicles may require more frequent maintenance akin to traditional gasoline engines. Additionally, reliance on biofuels can lead to competition for land use with food production, raising ethical and sustainability concerns.
Fazit: Die richtige Lösung für Ihre Anforderungen auswählen
When selecting the most suitable transportation solution, B2B buyers must consider their operational requirements, budget constraints, and regional infrastructure. Electric cars offer a compelling balance of performance and lower long-term costs, making them ideal for urban settings and fleet operations. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles may be preferable for businesses focusing on long-distance travel or heavy-duty applications, although infrastructure remains a barrier. Meanwhile, biofuel vehicles can serve as a cost-effective option in areas with established supply chains but come with their own set of challenges. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each alternative will empower B2B buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their organizational goals and environmental commitments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric cars vs gasoline
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars vs. Gasoline Cars?
When evaluating electric vehicles (EVs) against gasoline-powered vehicles, several technical specifications are critical for B2B buyers. Understanding these properties can aid in making informed purchasing decisions, whether for fleet management or resale purposes.
Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
1. Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy the battery can store. A higher kWh rating translates to a longer range, which is crucial for businesses that require vehicles to cover extensive distances without frequent recharging. For instance, a vehicle with a 60 kWh battery may provide a range of approximately 200-300 miles, depending on driving conditions and efficiency.
2. Charging Time (hours)
Charging time refers to the duration required to fully recharge an EV’s battery. This varies depending on the charging station’s power output and the vehicle’s battery capacity. Fast chargers can reduce charging time to as little as 30 minutes for an 80% charge, which is vital for businesses operating under tight schedules. Understanding charging infrastructure and timeframes is essential for optimizing operational efficiency.
3. Torque (lb-ft)
Torque, measured in pound-feet (lb-ft), is a measure of rotational force. Electric motors typically provide higher torque at lower RPMs compared to gasoline engines, resulting in quicker acceleration. This is advantageous for businesses that require vehicles to have rapid start capabilities, such as delivery services. High torque also contributes to better performance in hilly terrains or when carrying heavy loads.
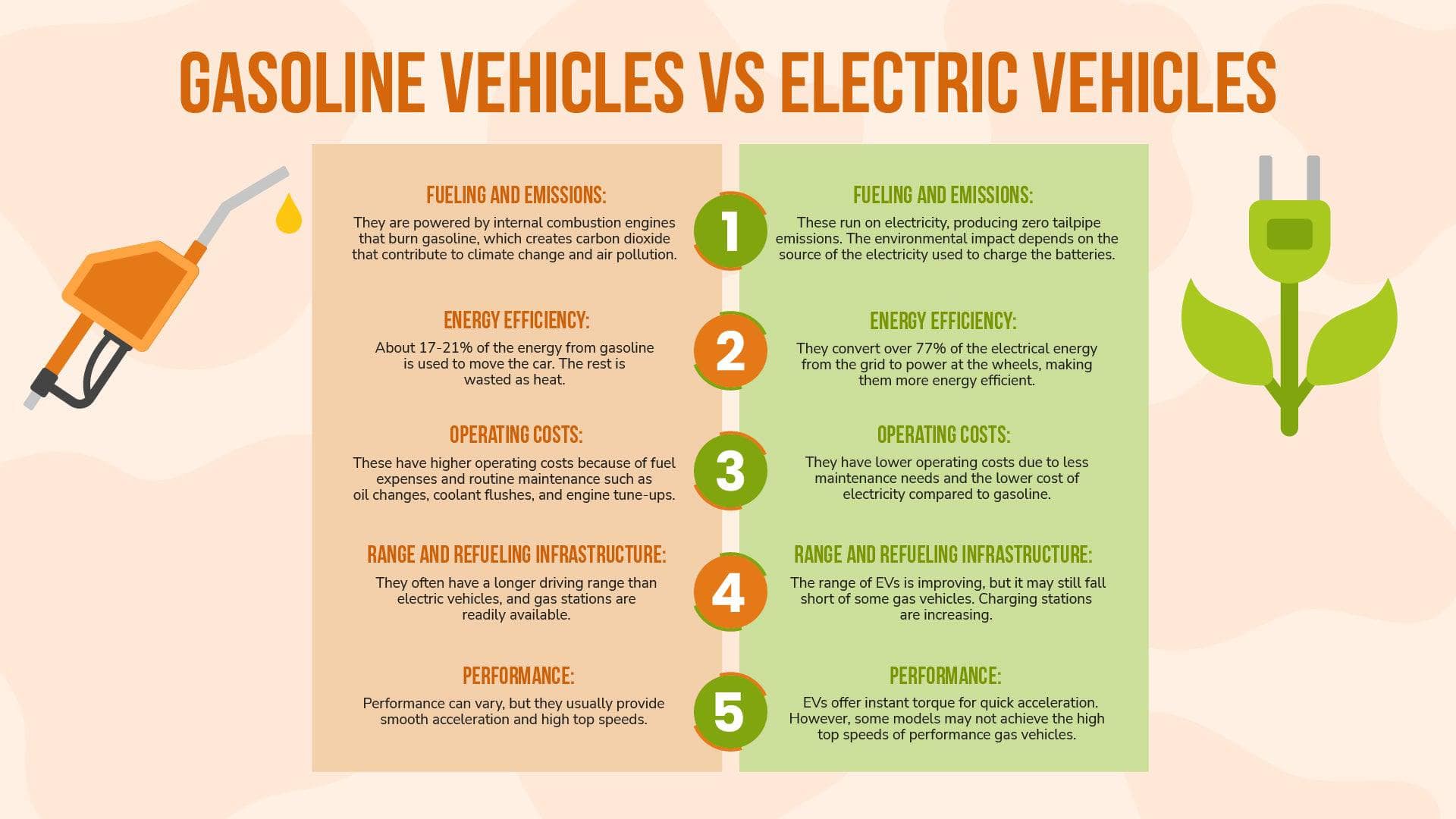
Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
4. Maintenance Costs ($)
Maintenance costs are a significant factor when assessing the total cost of ownership for both electric and gasoline vehicles. Electric vehicles generally have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and the absence of oil changes. According to industry reports, the average lifetime maintenance cost for EVs is approximately $4,600, compared to $9,200 for gasoline vehicles. This reduction can significantly impact a company’s bottom line.
5. Emissions (g CO2/mile)
Emissions, specifically measured in grams of CO2 per mile, are a crucial consideration for businesses focused on sustainability. Electric vehicles, especially when charged from renewable energy sources, emit significantly fewer greenhouse gases compared to gasoline vehicles. This can enhance a company’s corporate social responsibility profile and may provide access to incentives or tax breaks in certain regions.
Was sind gängige Fachterminologie und Jargon in der Automobilindustrie?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the automotive sector. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the automotive industry, this term often refers to parts produced by the original vehicle manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance in vehicle repairs or upgrades.
2. MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for businesses looking to purchase electric vehicles or components in bulk. Knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory planning, especially when negotiating with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the automotive industry, an RFQ can help businesses compare costs and services from multiple vendors, ensuring the best pricing and terms for vehicle procurement.
4. Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers involved in importing vehicles or components, as they clarify shipping costs, risk, and delivery responsibilities.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO refers to the comprehensive assessment of all costs associated with owning a vehicle over its entire lifecycle, including purchase price, financing, insurance, maintenance, and fuel costs. B2B buyers must evaluate TCO to understand the long-term financial implications of their vehicle choices.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the electric versus gasoline vehicle market with greater confidence, ensuring informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric cars vs gasoline Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electric vs. Gasoline Vehicle Sector?
The electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing a profound transformation driven by a confluence of factors including technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and regulatory pressures. As of 2023, the global demand for electric cars has surged, with manufacturers ramping up production to meet both consumer and governmental expectations for sustainability. In regions like Europe and North America, stringent emission regulations are encouraging businesses to transition towards EVs, while markets in Africa and South America are witnessing a gradual adoption spurred by decreasing battery costs and improved charging infrastructure.
B2B buyers should be cognizant of the emerging trends such as the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning in EV manufacturing and maintenance. Additionally, the rise of mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms is reshaping how companies approach transportation solutions, making it essential for international buyers to stay informed about innovations in fleet management and logistics.
Furthermore, as global supply chains adapt, sourcing trends indicate a shift toward local suppliers and ethical sourcing practices, particularly for critical components like batteries, which are heavily influenced by lithium and cobalt extraction. This shift not only enhances supply chain resilience but also aligns with the increasing demand for sustainability from consumers and investors alike.
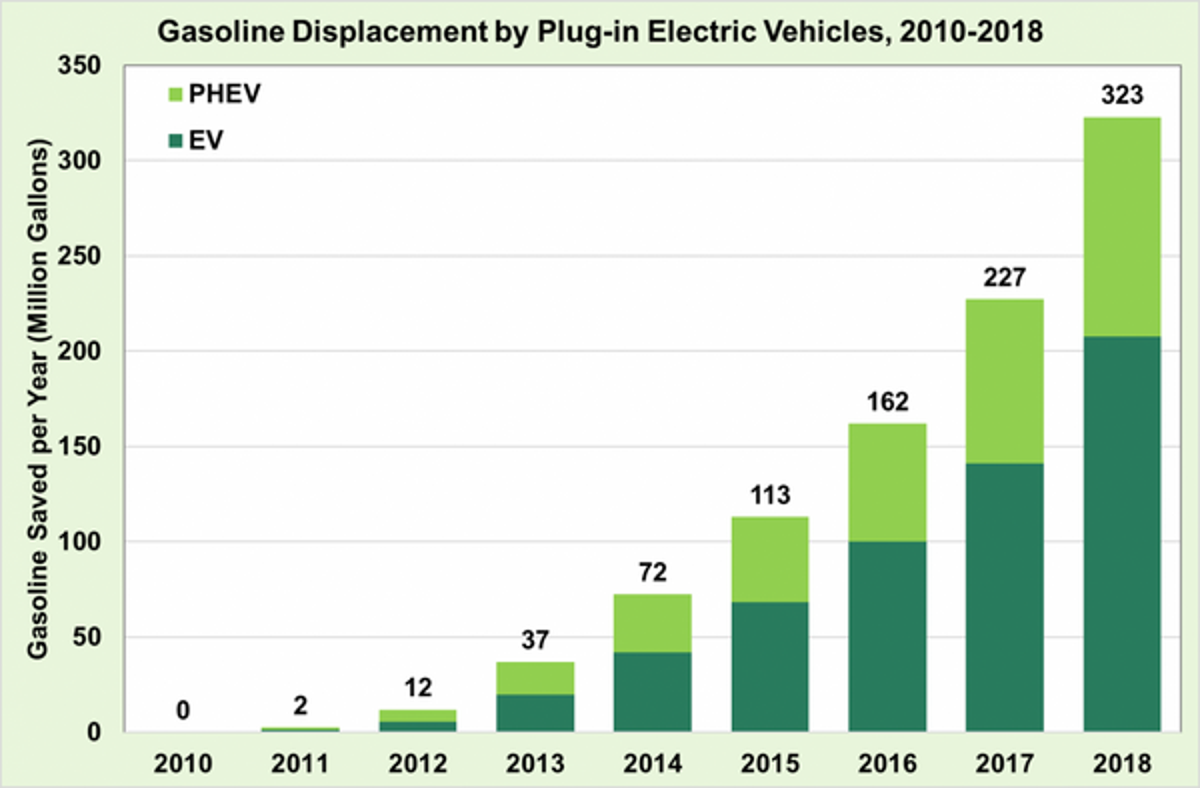
Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Electric vs. Gasoline Vehicle Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of business strategy, particularly in the automotive sector. For B2B buyers, understanding the environmental impact of both electric and gasoline vehicles is critical. Electric vehicles, while not without their own challenges, typically offer lower greenhouse gas emissions over their lifecycle compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, especially when charged with renewable energy sources.
Ethical sourcing plays an equally vital role, as the extraction of materials for EV batteries—such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel—poses significant ethical and environmental challenges. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical mining practices and who can provide transparency in their supply chains. Certifications like the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as benchmarks for evaluating suppliers.
Investing in “green” certifications not only enhances corporate responsibility but also meets growing regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for sustainability. As more businesses commit to net-zero emissions targets, the importance of ethical sourcing will only increase, shaping purchasing strategies across the sector.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Electric and Gasoline Vehicles Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of electric and gasoline vehicles dates back to the late 19th century when electric cars first emerged. However, the internal combustion engine rapidly gained dominance due to its convenience and range. The oil crises of the 1970s rekindled interest in electric vehicles, but it wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s, with the introduction of models like the Toyota Prius, that hybrid technology began to bridge the gap between gasoline and electric.
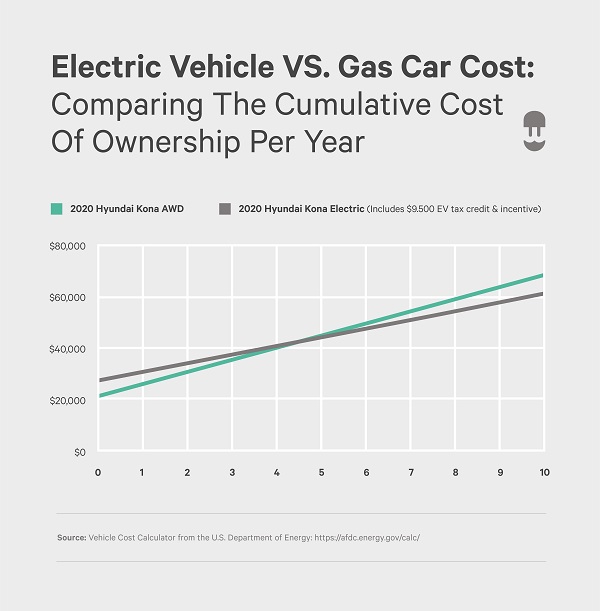
Illustrative image related to electric cars vs gasoline
The real turning point for electric vehicles came in the 2010s with advancements in battery technology, resulting in longer ranges and lower costs. As of 2023, EVs have become a viable alternative to gasoline vehicles, propelled by government incentives, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences towards sustainable transportation. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial in making informed sourcing decisions that align with both current market demands and future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric cars vs gasoline
-
How do I evaluate the total cost of ownership for electric cars vs. gasoline vehicles?
To accurately assess the total cost of ownership, consider not just the purchase price but also fuel, maintenance, insurance, and depreciation. Electric vehicles typically have lower fuel costs, as charging is generally cheaper than gasoline. Maintenance costs are also reduced due to fewer moving parts in electric vehicles. Additionally, factor in any government incentives or tax credits available for EV purchases, which can significantly influence the overall financial equation. -
What factors should I consider when choosing between electric and gasoline vehicles for my fleet?
When selecting vehicles for your fleet, evaluate the total cost of ownership, the vehicle range, charging infrastructure availability, and environmental impact. Consider your operational needs—if your routes are well within the range of electric vehicles and charging stations are accessible, EVs may be advantageous. Additionally, consider local regulations and incentives that may favor electric vehicles, as well as the long-term sustainability goals of your organization. -
What are the key environmental benefits of choosing electric cars over gasoline vehicles?
Electric vehicles (EVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing greenhouse gases and local air pollutants compared to gasoline vehicles. Additionally, if charged with renewable energy sources, the overall carbon footprint is substantially lower. As battery technologies improve, the environmental impact from manufacturing and disposal is also being addressed, making EVs a more sustainable choice in the long run. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for electric vehicles in international markets?
Begin by researching manufacturers and distributors with a proven track record in the electric vehicle sector. Check for certifications, customer testimonials, and industry affiliations. Attend trade shows and industry conferences to network with suppliers and gain insights into their capabilities. Additionally, utilize online platforms and industry reports to compare offerings and ensure that potential suppliers meet your quality and compliance standards. -
What customization options are typically available for electric vehicles?
Customization options for electric vehicles often include battery capacity, interior features, and technology integrations such as telematics systems. Some manufacturers may offer bespoke designs for fleet branding or specialized vehicle configurations to suit specific operational needs. When sourcing, inquire about the range of customization options and any additional costs or lead times associated with these modifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and manufacturer, often influenced by production capacity and demand. For large fleets, some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs, while smaller orders may necessitate negotiation. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with suppliers upfront to understand their policies and explore potential bulk purchase discounts that could optimize your procurement budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric vehicles internationally?
Payment terms for international vehicle purchases can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific agreement. Common terms include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Be sure to clarify these terms during negotiations and consider the implications of currency fluctuations and transaction fees on your overall costs. Establishing clear payment schedules can help manage cash flow effectively. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when importing electric vehicles?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a comprehensive vetting process for suppliers, including factory audits and product inspections. Request detailed documentation on compliance with international standards and certifications. Consider hiring third-party inspection services to evaluate vehicles before shipment. Additionally, set clear expectations for warranty terms and after-sales support to mitigate risks associated with quality issues post-import.
Top 3 Electric Cars Vs Gasoline Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Electric Vehicles vs. Gasoline Cars
Domäne: reddit.com
Registriert: 2005 (20 Jahre)
Einleitung: This company, Reddit – Electric Vehicles vs. Gasoline Cars, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Constellation – Electric vs. Gas Cars Comparison
Domäne: constellation.com
Registriert: 1996 (29 Jahre)
Einleitung: Electric Cars vs. Gas Cars comparison includes cost considerations beyond sticker price, such as maintenance and fuel costs. Tax credits for EV installation services and charging equipment are available, covering 30% of labor costs up to $1,000. Electric cars generally have lower maintenance costs due to fewer routine care requirements compared to gasoline engines.
3. Premium Autos – Electric vs Gas Cars Guide
Domäne: premiumautosinc.com
Registriert: 2015 (10 Jahre)
Einleitung: Electric vs Gas Cars: True Cost of Ownership Guide, 2 Locations, Contact: (951) 220-8952, Inventory includes: 2021 Jeep Wrangler Unlimited Sport 80th Anniversary (97,777 miles, $23,759), 2022 Dodge Charger SRT Hellcat Widebody (4,679 miles, $67,996), 2023 Toyota GR Corolla (23,987 miles, $32,900), 2019 Tesla Model S (34,692 miles, $25,900), 2022 Ford F-250 Super Duty 4X4 CREW CAB LARIAT (160″ WB, …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric cars vs gasoline
The transition from gasoline to electric vehicles (EVs) presents a pivotal opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways highlight that while the initial cost of EVs may still be higher, the total cost of ownership—including lower fuel and maintenance expenses—often makes them a more economically viable option in the long run. The ongoing advancements in battery technology are expected to further reduce costs and enhance vehicle performance.
Strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in navigating this complex landscape. By leveraging incentives, understanding regional energy pricing, and evaluating maintenance needs, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and operational budgets.
Looking ahead, the global shift towards electrification is not just a trend but a necessary evolution in transportation. Companies that embrace this change will position themselves competitively while contributing to environmental stewardship. We encourage international buyers to explore partnerships with EV manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers, ensuring they are at the forefront of this transformative journey.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.