Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test a starter solenoid
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive maintenance, understanding how to test a starter solenoid is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable solutions for their fleets or repair businesses. A faulty starter solenoid can lead to unexpected vehicle failures, impacting productivity and operational costs. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for international buyers, detailing various testing methods, applications across different vehicle types, and the importance of thorough supplier vetting to ensure quality components.
With a focus on regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Brazil—this resource empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. It highlights the nuances of sourcing high-quality starter solenoids, including cost considerations and the implications of regional availability. By navigating this guide, buyers will gain actionable insights into the testing process, enhancing their understanding of how to diagnose solenoid issues effectively.
Whether you’re a fleet manager, automotive parts distributor, or repair shop owner, this guide serves as a vital tool for optimizing your operations. It not only simplifies the complexities of starter solenoid testing but also ensures that you can confidently source the right parts, reducing downtime and enhancing vehicle reliability across your operations.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 2 How To Test A Starter Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to test a starter solenoid
- Understanding how to test a starter solenoid Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to test a starter solenoid
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test a starter solenoid’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test a starter solenoid
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test a starter solenoid
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test a starter solenoid’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test a starter solenoid Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test a starter solenoid With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test a starter solenoid
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test a starter solenoid Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test a starter solenoid
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test a starter solenoid
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Understanding how to test a starter solenoid Types and Variations
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sichtprüfung | Simple observation of solenoid engagement sounds | Kfz-Werkstätten, Flottenwartung | Vorteile: Schnell und einfach; Nachteile: Möglicherweise werden zugrunde liegende Probleme übersehen. |
| Elektrische Prüfung | Use of multimeter/test light to check voltage flow | Lieferanten von Autoteilen, Werkstätten | Vorteile: Accurate results; Nachteile: Requires additional tools. |
| Widerstandsmessung | Measuring resistance to identify internal faults | Vehicle diagnostics services | Vorteile: Helps pinpoint specific issues; Nachteile: More complex process. |
| Component Replacement Check | Assessing solenoid condition before replacement | Auto repair services, parts distributors | Vorteile: Saves costs on unnecessary replacements; Nachteile: Zeitaufwendig. |
| Integrated Testing Systems | Advanced diagnostic tools that test multiple components | Large automotive service centers, OEMs | Vorteile: Umfassend; Nachteile: High initial investment. |
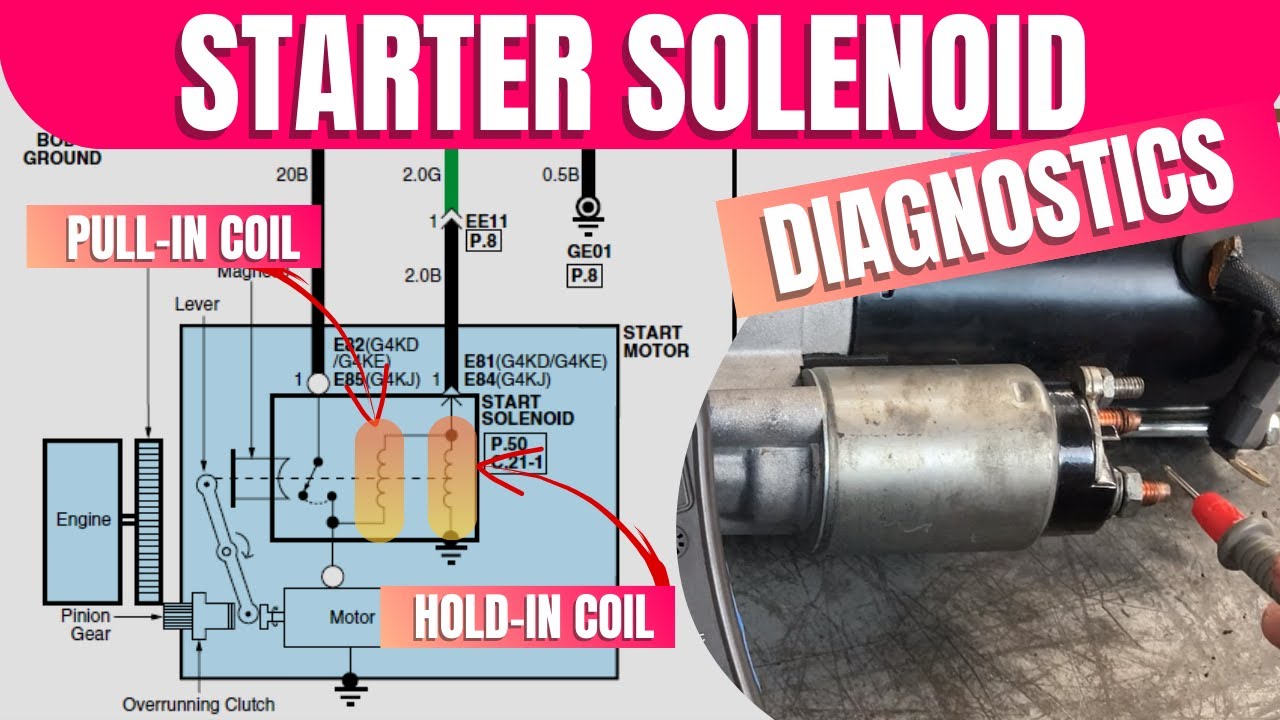
What are the Key Characteristics of Visual Inspection for Testing a Starter Solenoid?
Visual inspection is the most straightforward method, involving listening for clicking sounds when the ignition is turned. This method is particularly suitable for automotive repair shops or fleet maintenance operations that require quick assessments. However, while it is efficient, it may not reveal deeper issues, leading to potential misdiagnoses. Buyers should consider that while this approach requires no special equipment, it may not suffice for complex problems.
How Does Electrical Testing Provide Accurate Results?
Electrical testing involves using a multimeter or test light to measure voltage at the solenoid terminals. This method is beneficial for auto parts suppliers and workshops that need precise data on electrical functionality. It allows for a clear distinction between battery issues and solenoid malfunctions. However, it necessitates additional tools and expertise, which can be a barrier for smaller businesses without access to specialized equipment.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
Why is Resistance Measurement Important in Testing?
Resistance measurement is a more technical approach that assesses the internal condition of the solenoid. It is particularly useful for vehicle diagnostics services that require detailed analysis of component health. This method can identify specific internal faults that visual inspections might overlook. Nevertheless, it is more complex and requires trained personnel, which could increase labor costs for B2B buyers.
What Should Buyers Know About Component Replacement Checks?
Component replacement checks involve assessing the condition of the starter solenoid before deciding to replace it. This method is commonly used by auto repair services and parts distributors to avoid unnecessary costs. While it can save money, this approach may be time-consuming, requiring careful evaluation and testing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of saving on parts against the potential downtime incurred during thorough checks.
How Do Integrated Testing Systems Enhance Testing Capabilities?
Integrated testing systems use advanced diagnostic tools to evaluate multiple automotive components, including the starter solenoid. These systems are ideal for large automotive service centers and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) that require comprehensive diagnostics. They provide a holistic view of vehicle health but come with a higher initial investment cost. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of such systems, including improved service efficiency and accuracy in diagnostics, against the upfront financial commitment.
Key Industrial Applications of how to test a starter solenoid
| Branche/Sektor | Specific Application of how to test a starter solenoid | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kfz-Reparatur | Testing starter solenoids in vehicles for efficient diagnostics | Reduces downtime and repair costs by ensuring accurate diagnosis | Availability of specialized tools and equipment, local regulations on automotive repairs |
| Schwere Maschinen | Assessing solenoid functionality in construction and agricultural equipment | Ensures operational efficiency and minimizes equipment failure | Compatibility with various machinery models, sourcing from reliable manufacturers |
| Transportlogistik | Verifying solenoid performance in fleet vehicles | Enhances fleet reliability and reduces maintenance costs | Bulk purchasing options, warranty and support services from suppliers |
| Bergbauarbeiten | Testing starter solenoids in mining vehicles and equipment | Increases safety and operational uptime in harsh environments | Robustness of testing equipment, local service support capabilities |
| Schiffsindustrie | Evaluating solenoids in marine engines for reliable start-up | Prevents delays in operations and potential loss of revenue | Compliance with maritime safety standards, availability of marine-grade components |
How is Testing a Starter Solenoid Applied in the Automotive Repair Industry?
In the automotive repair sector, testing starter solenoids is crucial for diagnosing issues that prevent vehicles from starting. Mechanics can quickly determine whether the problem lies within the solenoid or other components such as the battery or starter motor. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces labor costs, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing specialized diagnostic tools that comply with local automotive regulations to ensure effective testing.
What Role Does Solenoid Testing Play in Heavy Machinery?
In heavy machinery, reliable operation is paramount, especially in construction and agricultural applications. Testing the starter solenoid helps prevent unexpected breakdowns that can lead to costly downtime. Businesses benefit from ensuring their equipment runs smoothly, which is essential for maintaining productivity. Buyers should focus on sourcing testing equipment that is compatible with various machinery models and can withstand harsh working conditions.
How Does Solenoid Testing Enhance Fleet Operations in Transportation Logistics?
For transportation logistics, verifying the functionality of starter solenoids in fleet vehicles is essential for operational reliability. Regular testing helps identify issues before they escalate, minimizing maintenance costs and improving vehicle uptime. This proactive approach allows logistics companies to maintain service schedules and customer commitments. When sourcing equipment, businesses should consider bulk purchasing options and ensure suppliers provide warranties and support services to mitigate risks.
Why is Starter Solenoid Testing Important in Mining Operations?
In mining operations, the reliability of vehicles and equipment is critical due to the challenging environments. Testing starter solenoids ensures that machinery starts reliably, which is vital for maintaining safety and operational efficiency. Preventing equipment failure not only protects workers but also enhances productivity. Buyers should prioritize sourcing robust testing equipment that can endure the rigors of mining conditions and ensure local service support is available.
How Does Testing Solenoids Benefit the Marine Industry?
In the marine industry, the reliability of engine start-up is crucial for operational success. Testing starter solenoids ensures that vessels can start without delay, preventing potential revenue loss from operational downtime. Regular checks can also enhance safety by reducing the risk of engine failure at sea. Buyers should ensure that any sourced components comply with maritime safety standards and are marine-grade to withstand harsh marine environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to test a starter solenoid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Identifying the Starter Solenoid Location in Various Vehicles
Das Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly those in automotive repair businesses, often face challenges in locating the starter solenoid on different vehicle makes and models. With a wide variety of engine designs and configurations, technicians may struggle to pinpoint the solenoid’s position, leading to wasted time and potentially incorrect troubleshooting. This confusion can be particularly frustrating for businesses that depend on efficiency and accuracy to maintain customer satisfaction and operational flow.
Die Lösung:
To overcome this issue, it is essential to invest in comprehensive vehicle service manuals or access online databases specific to the automotive industry. These resources provide detailed diagrams and instructions for locating the starter solenoid across various models. Additionally, utilizing diagnostic tools that interface with the vehicle’s onboard computer can help technicians gather vital information about the vehicle’s components. Training staff on common solenoid locations and variations among different brands will also enhance their ability to quickly and accurately diagnose issues. This proactive approach not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of misdiagnosis, leading to more efficient repairs.
Scenario 2: Uncertainty About Diagnosing Electrical Issues Related to the Starter Solenoid
Das Problem:
B2B buyers, especially those managing fleets or repair shops, frequently encounter electrical problems that mimic starter solenoid failures. Issues like a dead battery or faulty wiring can lead to misdiagnoses, resulting in unnecessary part replacements and additional labor costs. This uncertainty can be detrimental to businesses, affecting both the bottom line and customer trust when vehicles fail to start after service.
Die Lösung:
To effectively diagnose electrical issues, it is crucial to implement a systematic troubleshooting process that begins with a thorough inspection of the battery and wiring before testing the starter solenoid. B2B buyers should equip their teams with multimeters and test lights to check voltage and continuity in the circuit. Training on best practices for electrical testing can empower technicians to differentiate between a faulty solenoid and other electrical issues. Furthermore, establishing a standardized checklist for troubleshooting can streamline the diagnostic process, ensuring that all potential causes are systematically addressed, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnosis.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Knowledge of Testing Procedures for Starter Solenoids
Das Problem:
Many B2B buyers find that their technicians lack the necessary knowledge to properly test starter solenoids, leading to inconsistent results and unreliable repairs. Without a clear understanding of testing procedures, technicians may overlook critical steps, such as checking for current flow or resistance, which can lead to faulty repairs and increased vehicle downtime for clients. This knowledge gap can hinder operational efficiency and negatively impact customer satisfaction.
Die Lösung:
Investing in training sessions focused on electrical systems and starter solenoid testing is essential for enhancing technician skills. Workshops led by experienced professionals or online courses can provide valuable hands-on experience with testing equipment and procedures. Additionally, developing clear, step-by-step guides for testing the starter solenoid should be made readily available for technicians to reference during repairs. This structured approach ensures that all technicians have the knowledge and confidence to perform accurate tests, resulting in more reliable repairs and improved customer trust. Implementing a mentorship program where seasoned technicians guide newcomers can further solidify this knowledge within the team, promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to test a starter solenoid
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Testing a Starter Solenoid?
When testing a starter solenoid, the choice of materials used in the testing equipment can significantly impact performance and reliability. Here, we analyze four common materials utilized in the construction of tools and components for this purpose: copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic. Each material has unique properties that influence its suitability for specific applications.
How Does Copper Perform in Testing Equipment?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for wiring and connections in starter solenoid testing. Key properties include a high thermal and electrical conductivity rating, which ensures efficient energy transfer.
Vorteile: Copper’s durability and resistance to corrosion make it suitable for various environments. It is also relatively easy to manufacture into intricate shapes, allowing for versatile applications in testing equipment.
Nachteile: However, copper is heavier than other materials and can be more expensive, which may impact overall project budgets. Additionally, it may require special handling to prevent tarnishing.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Given its high conductivity, copper is ideal for applications requiring minimal resistance in electrical connections. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B187 for copper products.
Welche Rolle spielt Aluminium bei der Prüfung von Anlasser-Magnetventilen?
Aluminum is another common material used in the construction of testing tools and components. It offers a good balance of strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
Vorteile: Aluminum is lightweight, making it easy to handle and transport. Its natural resistance to corrosion enhances its longevity, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
Nachteile: While aluminum has decent electrical conductivity, it is not as effective as copper. Additionally, it may require additional coatings or treatments to improve its performance in certain applications.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminum is suitable for testing equipment that requires portability and ease of use. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that aluminum products meet local standards, such as DIN 17615.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
How Does Stainless Steel Contribute to Starter Solenoid Testing?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it a reliable choice for more rugged testing environments.
Vorteile: Its durability allows for long-term use in harsh conditions, and it can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Stainless steel components are also less likely to corrode, ensuring consistent performance.
Nachteile: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to copper and aluminum. Additionally, stainless steel is not as conductive as copper, which may limit its use in specific electrical applications.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Stainless steel is ideal for testing equipment that must endure extreme conditions. International buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel products.
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer for Testing Tools?
Plastics are increasingly being used in various testing applications due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Vorteile: Lightweight and often less expensive than metals, plastics can be molded into complex shapes, making them suitable for custom designs. They also provide good insulation properties, reducing the risk of electrical shorts.
Nachteile: However, plastics may not offer the same level of durability and resistance to extreme temperatures as metals. They can also degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Plastics are suitable for non-conductive components in testing equipment. Buyers should verify that plastic materials comply with relevant safety standards, such as ISO 9001.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
Summary Table of Material Selection for Testing a Starter Solenoid
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to test a starter solenoid | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kupfer | Wiring and connections in testing tools | Hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Schwerer und teurer | Hoch |
| Aluminium | Lightweight testing components | Leicht und korrosionsbeständig | Geringere Leitfähigkeit als Kupfer | Mittel |
| Rostfreier Stahl | Durable testing equipment for harsh environments | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and lower conductivity | Hoch |
| Kunststoff | Non-conductive components in testing tools | Kostengünstig und vielseitig | Weniger haltbar und temperaturempfindlich | Niedrig |
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of material selection for testing a starter solenoid, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to test a starter solenoid
What are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Starter Solenoids?
The manufacturing process of starter solenoids typically comprises several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial for ensuring the solenoid’s performance and longevity, which directly affects the reliability of the automotive systems they serve.
Materialvorbereitung
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, such as copper for electrical components and durable plastics or metals for housing. Suppliers should ensure that materials meet specific industry standards to guarantee performance under high temperatures and electrical loads. Advanced techniques such as chemical analysis and mechanical testing are often employed to verify material integrity before production begins.
Formung
During the forming stage, materials are shaped into the necessary components. This often includes processes like stamping, machining, and molding. For instance, copper wire is wound into coils, and metal casings are stamped from sheets. Precision in this stage is paramount, as it influences both the electrical characteristics and mechanical fit of the solenoid.
Montage
The assembly stage involves combining the formed components into a complete solenoid. This typically includes inserting the coil into the housing, attaching terminals, and ensuring that all parts fit securely. Automation plays a significant role in this stage, with robotic arms often used for precision assembly. Quality control checks, such as torque testing and visual inspections, are conducted throughout this process to ensure that all components are properly aligned and securely fastened.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
Endbearbeitung
Finally, the finishing stage includes surface treatments and coatings to enhance durability and resist corrosion. This may involve processes like anodizing or applying protective paints. It is essential for manufacturers to select finishing techniques that meet international standards, ensuring that the solenoid can withstand varying environmental conditions, particularly for buyers in regions with extreme climates.
How is Quality Control Implemented in Starter Solenoid Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of starter solenoid manufacturing, especially for B2B buyers who require reliable and durable products. The QC process typically adheres to international standards like ISO 9001, as well as industry-specific certifications such as CE and API.
What are the Key QC Checkpoints?
The QC process generally involves several key checkpoints:
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers conduct tests to verify that materials meet specified quality and safety standards. Documentation of these tests should be available for review by B2B buyers.
-
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is performed to ensure that processes are operating within defined parameters. This may include checking dimensions, electrical properties, and mechanical integrity at various stages of production.
-
Endkontrolle (FQC): Before products are packaged and shipped, a final inspection is conducted. This involves rigorous testing of completed solenoids, including electrical resistance tests, operational tests, and stress tests. Any units failing to meet quality standards are rejected and analyzed for defects.
What Testing Methods are Commonly Used?
Zu den gängigen Testmethoden gehören:
- Elektrische Prüfung: Ensuring that the solenoid activates correctly and meets specified current and resistance values.
- Mechanische Prüfung: Assessing the durability and performance under load conditions.
- Umweltprüfungen: Exposing solenoids to extreme temperatures and humidity to confirm their resilience in diverse operating conditions.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrolle ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is vital. Here are several strategies:
Durchführung von Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to QC standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports, which should detail compliance with ISO standards and any industry-specific certifications.
Anforderung von Qualitätsberichten: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These reports serve as evidence of the product’s quality and reliability.
Engaging Third-party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and the final product. This is particularly important for buyers who may not have the capability to conduct thorough inspections themselves.
Was sind die Feinheiten der Qualitätskontrolle und Zertifizierung für internationale Käufer?
International buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances that can differ by region. For instance, European buyers often prioritize CE marking to indicate compliance with EU safety standards, while buyers in the Middle East may look for API certifications for oil and gas applications.
Additionally, understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. For example, South American countries may have specific certifications for automotive parts that differ from those in Europe. Buyers should conduct thorough research or consult with experts to ensure that they are compliant with all relevant standards in their respective markets.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
Schlussfolgerung
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for starter solenoids are intricate and essential for producing reliable automotive components. By understanding these processes and implementing rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the high standards expected by international B2B buyers. Ultimately, thorough verification of supplier QC processes will empower buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring the long-term success of their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to test a starter solenoid’
Einleitung:
Testing a starter solenoid is essential for ensuring reliable vehicle operation, particularly for B2B buyers in automotive sectors. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you efficiently assess and procure the necessary components and services for testing starter solenoids. By following these steps, you can ensure you are equipped with the right tools and knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Before sourcing testing equipment or services, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider the types of vehicles you will be testing, the specific solenoid models, and the testing methods (e.g., voltage testing, resistance testing).
– Wichtige Angaben, die enthalten sein müssen:
– Vehicle makes and models you work with.
– Required testing capabilities (voltage range, resistance, etc.).
Schritt 2: Suche nach zuverlässigen Lieferanten
Identify suppliers who specialize in automotive testing equipment and components. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the market, especially those with experience in your region.
– Was Sie beachten sollten:
– Customer reviews and testimonials.
– Industry certifications and compliance with local regulations.
Schritt 3: Lieferantenzertifizierungen bewerten
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that ensure their products meet industry standards. Certifications can indicate quality and reliability, which is crucial when sourcing testing tools.
– Key Certifications to Check:
– ISO certifications.
– Any regional automotive compliance certifications.
Schritt 4: Request Product Samples or Demonstrations
Before finalizing your order, request samples or demonstrations of the testing equipment. This allows you to assess the quality and usability of the tools in real-world scenarios.
– Überlegungen:
– Ease of use and clarity of instructions.
– Compatibility with your existing equipment.
Schritt 5: Inquire About Warranty and Support Services
A robust warranty and support services are critical when investing in testing equipment. Ensure that suppliers offer comprehensive support in case of defects or operational issues.
– What to Ask:
– Length and terms of the warranty.
– Availability of technical support or training.
Schritt 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Evaluate the pricing structures of your shortlisted suppliers. Look for transparent pricing models that fit your budget while ensuring quality. Additionally, inquire about payment terms to manage cash flow effectively.
– Wichtige Überlegungen:
– Bulk purchase discounts.
– Payment plans or credit options.
Schritt 7: Eine langfristige Beziehung aufbauen
Once you have selected a supplier, consider establishing a long-term partnership. Building a relationship can lead to better pricing, priority service, and exclusive access to new products.
– Benefits of a Long-Term Relationship:
– Consistent quality in products and services.
– Enhanced communication and trust.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they are well-prepared to source the necessary equipment and services for testing starter solenoids effectively. Proper procurement not only aids in maintaining vehicle reliability but also enhances operational efficiency in your business.
Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to test a starter solenoid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Testing a Starter Solenoid?
When sourcing components and services for testing a starter solenoid, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materialien: The primary materials involved in testing a starter solenoid are electrical components such as wires, connectors, and testing equipment (e.g., voltmeters and test lights). The quality and sourcing of these materials can significantly influence costs, especially if specialized or high-quality components are required.
-
Arbeit: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled technicians performing the testing and any associated training costs. In regions with a higher cost of living, such as parts of Europe, labor can be a significant portion of the overall expenses.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with maintaining a facility. Efficient operations can help reduce overhead, impacting the overall cost of testing services.
-
Werkzeuge: The need for specialized tools for testing solenoids can also add to costs. Investing in high-quality, durable tools may incur higher upfront expenses but can lead to long-term savings through improved efficiency and reduced maintenance.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the testing of starter solenoids meets industry standards. While this can increase costs initially, it can prevent costly errors and warranty claims in the future.
-
Logistik: Shipping and handling costs are crucial for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms and logistics can help mitigate unexpected expenses related to transporting testing equipment or components.
-
Marge: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the services offered.
What Influences Pricing for Testing a Starter Solenoid?
Several factors influence the pricing of starter solenoid testing services, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volumen/MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge): Larger orders typically benefit from economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their testing needs to negotiate favorable terms based on anticipated volumes.
-
Spezifikationen und Anpassung: Custom testing solutions tailored to specific vehicle models or customer requirements can drive up costs. Clear specifications can help suppliers provide accurate quotes and minimize unexpected expenses.
-
Materialien und Qualitätszertifizierungen: The choice of materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) affects both cost and quality. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that meet relevant quality certifications to ensure reliability and compliance.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Supplier reputation, location, and capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they often provide better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. Different terms can affect shipping costs, risk allocation, and delivery timelines, all of which impact overall pricing.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Cost-Efficient Solutions?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can benefit from several strategies to optimize their procurement processes:
-
Verhandlung: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Engage in open discussions about pricing structures and be willing to explore bulk purchase agreements or long-term contracts.
-
Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO): Focus on the total cost of ownership rather than just upfront costs. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and potential downtime when evaluating suppliers and products.
-
Preisgestaltung für internationale Käufer: Be aware of fluctuations in currency exchange rates, import duties, and taxes that may affect the final cost. Having a clear understanding of these factors can help in budgeting and negotiations.
Haftungsausschluss
Prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and geographic location. Always conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing for starter solenoid testing services.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to test a starter solenoid With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Testing a Starter Solenoid
When it comes to ensuring the operational efficiency of a vehicle’s starter system, testing the starter solenoid is a crucial step. However, several alternative methods exist that can achieve similar diagnostic results. Understanding these options can help businesses make informed decisions on which solution best fits their operational needs, particularly in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
| Vergleichsaspekt | How To Test A Starter Solenoid | Multimeter-Prüfung | Professionelle Diagnosewerkzeuge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Zuverlässig für die Basisdiagnostik | Highly accurate | Comprehensive analysis |
| Kosten | Low-cost (DIY) | Moderate (tool cost) | High (service fees) |
| Einfache Implementierung | Einfach, erfordert einfache Werkzeuge | Requires knowledge of electrical systems | Requires professional training |
| Wartung | Minimal upkeep | Occasional calibration | Regular updates and maintenance |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | DIY repairs and small shops | General electrical diagnostics | Large fleets or complex systems |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Multimeter for Testing?
Using a multimeter for testing a starter solenoid offers significant accuracy in measuring voltage and current flow. This method provides more detailed insights than basic tests, allowing technicians to pinpoint issues effectively. However, it requires a certain level of expertise in electrical systems, which may pose a challenge for inexperienced users. Additionally, while the initial investment in a multimeter can be moderate, the return on investment is high for businesses dealing with multiple electrical diagnostics.
What Are the Benefits of Professional Diagnostic Tools for Testing Starter Solenoids?
Professional diagnostic tools provide a comprehensive analysis of the vehicle’s electrical system, not just the starter solenoid. These devices can identify multiple faults in one go, saving time and reducing the number of tools needed for various tests. However, the downside is the cost associated with purchasing these tools or outsourcing diagnostic services, which can be prohibitive for smaller businesses. Furthermore, the complexity of these tools often necessitates specialized training, making them less accessible for small-scale operations.
Making an Informed Decision on the Right Testing Method
When choosing the appropriate method for testing a starter solenoid, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements. For businesses with limited budgets or those that conduct infrequent repairs, the DIY method of testing may be sufficient. Conversely, companies managing larger fleets or those requiring frequent diagnostics might benefit from investing in professional diagnostic tools or multimeter testing capabilities. Ultimately, the decision should align with the business’s scale, expertise, and the complexity of the vehicles being serviced. By understanding the pros and cons of each method, buyers can select the most effective solution for their unique needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to test a starter solenoid
Was sind die wichtigsten technischen Eigenschaften für die Prüfung eines Anlassermagneten?
When evaluating a starter solenoid, several technical properties are critical to ensure efficient performance and reliability. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Werkstoffgüte
The material used in the construction of a starter solenoid typically includes high-grade metals such as copper and aluminum. Copper is favored for its excellent conductivity, while aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant. For B2B buyers, selecting a solenoid with high-quality materials can lead to enhanced durability and performance, minimizing failure rates and maintenance costs.
2. Nennstrom (Stromstärke)
The current rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current the solenoid can handle without overheating. Most automotive starter solenoids have a current rating ranging from 50 to 300 amps. Understanding the current rating is crucial for buyers to ensure compatibility with their vehicle’s electrical system and to prevent potential damage or safety hazards.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
3. Nennspannung
Starter solenoids are typically designed for a specific voltage, commonly 12V for automotive applications. It’s important for buyers to ensure that the voltage rating matches the vehicle’s electrical system to avoid malfunctions. A mismatch can lead to inadequate engagement of the starter motor or complete failure of the solenoid.
4. Resistance (Ohms)
Resistance is a critical property that affects the solenoid’s efficiency. A lower resistance value indicates better conductivity and less energy loss during operation. For B2B buyers, knowing the resistance specifications helps in assessing the solenoid’s performance under load, which is vital for ensuring reliable engine starting.
5. Betriebstemperaturbereich
This property defines the range of temperatures in which the solenoid can operate effectively. Starter solenoids typically function well between -40°C to +85°C. Understanding the operating temperature range is essential for buyers, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
6. Mechanical Tolerance
Mechanical tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the solenoid’s construction. Tighter tolerances can lead to better fit and function, reducing wear and increasing reliability. B2B buyers should consider manufacturers that adhere to stringent tolerances to ensure quality and performance consistency.
Was sind gängige Fachbegriffe im Zusammenhang mit der Prüfung von Anlassermagneten?
Navigating the procurement process for starter solenoids involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
OEM refers to parts made by the vehicle’s original manufacturer. Buyers often prefer OEM starter solenoids for their guaranteed compatibility and reliability. Understanding OEM options helps buyers make informed decisions about quality and performance.
2. MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. This term can influence purchasing strategies, especially for smaller businesses or those testing new products.
3. RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information on specific products. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare costs and terms from multiple vendors, aiding in making cost-effective purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risks, and obligations, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions.
5. Vorlaufzeit
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their inventory and production schedules effectively, minimizing disruptions in operations.
6. Garantiezeitraum
The warranty period is the time frame during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects. A clear understanding of warranty terms can protect B2B buyers from unexpected costs and provides assurance of the product’s quality.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can better navigate the procurement process for starter solenoids, ensuring they select the right products for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to test a starter solenoid Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Testing Starter Solenoids?
The global market for automotive components, particularly starter solenoids, is experiencing significant transformation driven by various factors. Key among these is the rising demand for efficient vehicle maintenance solutions, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As automotive technology evolves, so does the need for precise testing methods. With advancements in diagnostic tools and electronic systems, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking sophisticated equipment that can provide accurate readings on starter solenoid functionality.
Emerging trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies into automotive diagnostics. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to streamline operations and improve service quality. By utilizing smart diagnostic tools, businesses can enhance their troubleshooting capabilities, reduce downtime, and increase customer satisfaction. Moreover, the growing emphasis on preventive maintenance is encouraging companies to invest in reliable testing methods to avoid costly repairs.
Another critical dynamic is the shift towards online purchasing platforms. E-commerce is making it easier for B2B buyers to access a wider range of products, compare prices, and evaluate supplier credibility. This accessibility is crucial for international buyers in developing regions, as it expands their sourcing options and enables them to make informed purchasing decisions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Testing of Starter Solenoids?
As the automotive industry grapples with environmental concerns, sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount. The production and disposal of automotive components, including starter solenoids, contribute to environmental degradation, making it essential for buyers to prioritize eco-friendly practices.
B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through transparent supply chains and ethical sourcing practices. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or made from renewable resources. Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are gaining importance, as they signal a supplier’s dedication to minimizing environmental impact.

Illustrative image related to how to test a starter solenoid
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ technologies is influencing the design and manufacturing of starter solenoids. Manufacturers are exploring innovative materials and processes that reduce energy consumption and waste. For international buyers, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability not only enhances their brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Starter Solenoid Testing in the Automotive Industry?
The evolution of starter solenoid testing has been shaped by advancements in automotive technology and diagnostics. Initially, testing methods were rudimentary, relying heavily on visual inspections and basic electrical checks. However, as vehicles became more complex, the need for more sophisticated testing solutions emerged.
In the mid-20th century, the introduction of electronic ignition systems necessitated more precise testing methods for starter solenoids. With the advancement of digital multimeters and specialized diagnostic tools in the 1980s and 1990s, technicians gained the ability to perform detailed assessments of starter solenoids and their associated components. This evolution has paved the way for current practices that leverage advanced technology, allowing for quicker, more accurate diagnoses and repairs.
For B2B buyers today, understanding this historical context is crucial as it highlights the continuous need for innovation and adaptation in sourcing and testing methods. The journey from basic testing to today’s sophisticated diagnostic approaches underscores the importance of selecting reliable suppliers who can provide the latest technologies and techniques in the automotive sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to test a starter solenoid
-
How do I diagnose a faulty starter solenoid?
To diagnose a faulty starter solenoid, begin by listening for a clicking sound when attempting to start the vehicle. If you hear a click but the engine doesn’t turn over, it may indicate that the solenoid is engaging but not transferring enough power. Next, use a multimeter to check for voltage at the solenoid terminals. A lack of voltage suggests a battery or wiring issue, while voltage present without activation of the starter may indicate a defective solenoid that needs replacement. -
What tools do I need to test a starter solenoid?
Testing a starter solenoid typically requires a few essential tools: a multimeter or voltmeter to check voltage and current, a test light for visual indication of power flow, and basic hand tools to access the solenoid. Ensure you have safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, to protect yourself while working on electrical components. These tools will help you accurately diagnose and address issues with the solenoid effectively. -
What are the common signs of a bad starter solenoid?
Common signs of a failing starter solenoid include a clicking sound when the ignition is turned, a complete lack of response from the starter, or intermittent starting issues. Additionally, if the solenoid gets excessively hot or shows visible damage, it may need replacement. Addressing these symptoms early can prevent further complications with the vehicle’s starting system. -
How can I ensure the quality of starter solenoids from suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing starter solenoids, vet suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request samples to assess product quality before making bulk purchases. Additionally, inquire about quality assurance processes, warranty terms, and compliance with international standards to ensure that the components meet your operational requirements. -
Welche Anpassungsmöglichkeiten gibt es für Anlassermagnete?
Many suppliers offer customization options for starter solenoids, including variations in voltage, size, and terminal configurations to fit specific vehicle models. When contacting suppliers, provide detailed specifications of your requirements and ask about their capabilities for custom designs. This ensures that the solenoids you order will be compatible with your applications, enhancing performance and reliability. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter solenoids?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for starter solenoids can vary significantly between suppliers. Some manufacturers may require MOQs ranging from 50 to several hundred units, while others may offer flexibility for smaller orders. Always clarify MOQs during the negotiation process to ensure that your purchasing decisions align with your inventory needs and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing starter solenoids internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of starter solenoids typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Depending on your relationship with the supplier and order size, you may negotiate favorable terms. Always confirm currency exchange rates and any potential fees associated with cross-border transactions to avoid unexpected costs. -
How do I manage logistics and shipping for international orders of starter solenoids?
Managing logistics for international orders involves selecting reliable freight forwarders and understanding shipping regulations in your destination country. Discuss shipping methods, costs, and expected delivery times with your supplier. Ensure that all documentation, including customs clearance forms, is prepared to facilitate smooth delivery. Regularly communicate with your logistics provider to track shipments and address any potential delays.
Top 2 How To Test A Starter Solenoid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dotheton – Starter Solenoid for 1976 CB550k
Domäne: dotheton.com
Registriert: 2007 (18 Jahre)
Einleitung: Starter solenoid for 1976 CB550k motorcycle, non-OEM unit, requires proper wiring for functionality, tested using a multimeter for continuity and resistance (should be <2 ohms), can be tested by applying 12VDC to terminals, mechanical relay that should click when functioning.
2. Starter Solenoid – Essential Electromagnetic Switch
Domäne: linkedin.com
Registriert: 2002 (23 Jahre)
Einleitung: Starter solenoid is an electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor when the ignition key is turned to the ‘start’ position. It controls the high current needed for the starter motor, ensuring safe engagement and disengagement, reducing wear and tear. Symptoms of a bad starter solenoid include clicking noises, failure to crank, difficulty starting the engine, decreased acceleration perfor…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to test a starter solenoid
In conclusion, understanding how to effectively test a starter solenoid is essential for automotive professionals and businesses involved in vehicle maintenance and repair. Key takeaways include the importance of accurately diagnosing whether the solenoid, battery, or starter is at fault, which can prevent unnecessary costs and time delays. By employing methods such as checking for current flow and testing resistance, you can streamline your repair processes and enhance service delivery.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring access to quality components and tools necessary for effective diagnostics and repairs. International B2B buyers should prioritize establishing reliable relationships with reputable suppliers to secure high-quality starter solenoids and related parts. This not only boosts operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction through improved service reliability.
Looking ahead, as the automotive industry continues to evolve with advancements in technology, it is crucial for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to stay informed and agile. By investing in training and resources for your teams, and by leveraging strategic partnerships, you can position your business to thrive in a competitive market. Engage with your suppliers today to ensure you have the best tools and parts at your disposal for all future automotive challenges.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.

















