Einführung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
Die Komplexität der Beschaffung von Komponenten wie defekten Anlassern oder Magnetventilen kann für internationale B2B-Einkäufer entmutigend sein. Die Herausforderung besteht nicht nur darin, zuverlässige Lieferanten zu finden, sondern auch die Feinheiten dieser kritischen Kfz-Teile zu verstehen. Ein defekter Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule kann zu erheblichen Ausfallzeiten und betrieblichen Ineffizienzen führen, die die Produktivität in verschiedenen Bereichen beeinträchtigen, von der Automobilherstellung bis zum Flottenmanagement.
Dieser umfassende Leitfaden befasst sich mit den Feinheiten defekter Anlasser und Magnetventile und geht auf die verschiedenen Typen, Anwendungen und Ausfallerscheinungen ein. Er liefert auch wichtige Erkenntnisse darüber, wie Sie Lieferanten effektiv überprüfen können, um sicherzustellen, dass Sie mit Herstellern zusammenarbeiten, die strenge Qualitätsstandards erfüllen. Darüber hinaus erörtern wir Kostenaspekte und helfen Ihnen, fundierte finanzielle Entscheidungen zu treffen, die mit Ihren Unternehmenszielen übereinstimmen.
Dieser Leitfaden vermittelt internationalen Einkäufern aus Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa - insbesondere Märkten wie Deutschland und Nigeria - umsetzbare Erkenntnisse und ermöglicht es Ihnen, sich auf dem globalen Markt sicher zu bewegen. Ganz gleich, ob Sie die mit der Beschaffung verbundenen Risiken mindern oder Ihr Verständnis für die Komponenten selbst verbessern möchten, die hier vorgestellten Informationen werden Ihnen klügere Kaufentscheidungen erleichtern und letztlich Ihren Geschäftserfolg in einem wettbewerbsintensiven Umfeld fördern.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Top 3 Schlechter Anlasser oder Magnetspule Liste der Hersteller & Lieferanten
- Einführung: Navigieren auf dem globalen Markt für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
- Fehlerhafte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen - Typen und Variationen
- Wichtigste industrielle Anwendungen für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
- 3 häufige Schmerzpunkte für ‘defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen’ und ihre Lösungen
- Strategischer Leitfaden zur Materialauswahl für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
- Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung bei defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid
- Praktische Anleitung zur Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘defekter Anlasser oder Solenoid’.’
- Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für einen defekten Anlasser oder ein defektes Solenoid Beschaffung
- Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich von defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid mit anderen Lösungen
- Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachbegriffe für einen defekten Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule
- Marktdynamik und Beschaffungstrends in der Branche für defekte Anlasser und Magnetspulen
- Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer von defekten Anlassern oder Magnetspulen
- Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
- Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
Fehlerhafte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen - Typen und Variationen
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanischer Hubmagnet | Wird durch körperliche Bewegung betätigt; häufig in älteren Fahrzeugen zu finden. | Kfz-Werkstätten, Oldtimer-Restaurierung. | Vorteile: Einfaches Design, leicht zu ersetzen. Nachteile: Eingeschränkte Kompatibilität mit modernen Fahrzeugen. |
| Elektromagnetisches Relais | Nutzt elektromagnetische Felder zum Schalten von Hochleistungsstromkreisen; typischerweise in modernen Fahrzeugen zu finden. | Massenproduktion von Fahrzeugen, Zulieferer von Automobilteilen. | Vorteile: Hohe Zuverlässigkeit, vielseitig. Nachteile: Komplexer, erfordert möglicherweise besondere technische Kenntnisse. |
| Integriertes Anlasser-Magnetventil | Kombiniert Anlasser und Magnetspule in einer Einheit; häufig bei neueren Modellen. | Vertrieb von OEM-Teilen, Kfz-Servicezentren. | Vorteile: Platzsparendes Design, effizient. Nachteile: Höhere Ersatzkosten, Austausch der gesamten Einheit kann erforderlich sein. |
| Fernstart-Magnetventil | Konzipiert für Fernstartsysteme; ermöglicht das Starten ohne Schlüssel. | Anbieter von Zubehör für den Aftermarket, Automobilelektronik. | Vorteile: Bequemlichkeit, moderne Ausstattung, Attraktivität. Nachteile: Möglicherweise nicht mit allen Fahrzeugen kompatibel, potenzielle Sicherheitsrisiken. |
| Schwerlast-Magnetventil | Gebaut für Anwendungen mit hohen Drehmomenten; wird häufig in Nutzfahrzeugen verwendet. | Flottenmanagement, Reparatur schwerer Maschinen. | Vorteile: Langlebig, zuverlässig unter schweren Lasten. Nachteile: Höherer Preis, erfordert möglicherweise eine spezielle Installation. |
Was sind die Merkmale von mechanischen Magneten?
Mechanische Magnetspulen zeichnen sich durch ihren einfachen Aufbau aus, der auf einer physischen Bewegung zum Ein- und Ausschalten von Schaltkreisen beruht. Sie sind häufig in älteren Fahrzeugmodellen zu finden und lassen sich leicht austauschen, weshalb sie bei Kfz-Werkstätten und Oldtimer-Restauratoren sehr beliebt sind. Bei der Kaufentscheidung sollten Käufer auf die Kompatibilität mit bestehenden Fahrzeugsystemen und die Verfügbarkeit von Ersatzteilen achten.
Wie funktionieren elektromagnetische Relais in modernen Fahrzeugen?
Elektromagnetische Relais sind wesentliche Komponenten in modernen Fahrzeugen, die elektromagnetische Felder zum Schalten von Hochleistungsschaltkreisen nutzen. Sie zeichnen sich durch hohe Zuverlässigkeit und Vielseitigkeit aus und eignen sich daher für die Massenproduktion von Fahrzeugen und Automobilzulieferern. Käufer sollten die technischen Spezifikationen und Installationsanforderungen berücksichtigen, da diese Relais komplexer sein können als mechanische Magnetspulen, aber eine höhere Leistung bieten.
Warum sollten Sie sich bei neueren Modellen für integrierte Startermagnete entscheiden?
Integrierte Anlassermagnete vereinen Anlasser und Magnetspule in einer einzigen Einheit und stellen eine platzsparende und effiziente Lösung für moderne Fahrzeuge dar. Sie werden in der Regel von OEM-Teilehändlern und Kfz-Werkstätten angeboten. Sie sind zwar mit höheren Ersatzteilkosten verbunden, aber ihre Effizienz- und Leistungsvorteile rechtfertigen oft die Investition, insbesondere für Unternehmen, die sich auf die Wartung neuerer Fahrzeuge konzentrieren.
Was sind die Vorteile von Fernstartmagneten?
Fernstartmagnete ermöglichen das Starten von Fahrzeugen ohne Schlüssel und bieten Komfort und moderne Funktionen. Sie sind auf dem Zubehörmarkt und in der Automobilelektronik sehr beliebt. Käufer müssen jedoch sicherstellen, dass sie mit bestimmten Fahrzeugmodellen kompatibel sind, und potenzielle Sicherheitsrisiken im Zusammenhang mit Fernstartsystemen berücksichtigen.
Wann sollte man Hochleistungsmagnete für gewerbliche Anwendungen in Betracht ziehen?
Hochleistungsmagnete sind für Anwendungen mit hohen Drehmomenten ausgelegt und werden häufig in Nutzfahrzeugen und schweren Maschinen eingesetzt. Sie werden für ihre Langlebigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit bei schweren Lasten geschätzt und sind daher ideal für das Flottenmanagement und die Reparatur von schweren Maschinen. Käufer sollten den höheren Preis gegen die langfristigen Vorteile der Zuverlässigkeit und Leistung in anspruchsvollen Umgebungen abwägen.
Wichtigste industrielle Anwendungen für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
| Branche/Sektor | Spezifische Anwendung eines defekten Anlassers oder Elektromagneten | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kfz-Reparatur | Diagnose und Austausch von defekten Anlassern/Solenoids in Fahrzeugen | Gewährleistet die Zuverlässigkeit des Fahrzeugs und minimiert die Ausfallzeiten | Qualitätssicherung, Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Fahrzeugmodellen, lokale Verfügbarkeit von Teilen |
| Baumaschinen | Wartung von schweren Maschinen wie Baggern und Bulldozern | Verhindert Arbeitsunterbrechungen und steigert die betriebliche Effizienz | Langlebigkeit unter schwierigen Bedingungen, OEM- und Aftermarket-Teile, Garantie und Support |
| Landwirtschaft | Startsysteme für Traktoren und landwirtschaftliche Fahrzeuge | Maximiert die Produktivität während kritischer Anbausaisonen | Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Umwelteinflüsse, einfache Installation, Verfügbarkeit auf ländlichen Märkten |
| Transport & Logistik | Reparatur von Flottenfahrzeugen mit Startproblemen | Reduziert die Betriebskosten und verbessert die Zuverlässigkeit der Flotte | Großeinkaufsoptionen, schneller Versand für dringenden Bedarf, Kompatibilität mit mehreren Fahrzeugtypen |
| Schiffsindustrie | Funktionsweise von Anlassersystemen in Booten und Schiffen | Gewährleistet Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit im Schiffsbetrieb | Korrosionsbeständigkeit, Einhaltung der maritimen Vorschriften, lokale Beschaffungsmöglichkeiten |
Wie wirkt sich ein defekter Anlasser oder ein defektes Solenoid auf die Kfz-Reparaturbranche aus?
In der Kfz-Reparaturbranche kann ein defekter Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule zu erheblichen Problemen bei der Zuverlässigkeit des Fahrzeugs führen. Wenn Mechaniker Startprobleme diagnostizieren, stellen sie oft fest, dass ein defektes Solenoid der Übeltäter ist, was zu einem Nichtstartzustand führt. Dies kann zu längeren Ausfallzeiten des Fahrzeugs führen und sich sowohl auf die Kundenzufriedenheit als auch auf den Gewinn der Werkstatt auswirken. Für B2B-Einkäufer ist die Beschaffung qualitativ hochwertiger Anlasser und Magnetspulen, die mit einer Vielzahl von Fahrzeugmodellen kompatibel sind, von entscheidender Bedeutung. Sie sollten Lieferanten in Betracht ziehen, die robuste Garantien und Support bieten, damit sie ihren Kunden zuverlässige Lösungen anbieten können.
Welche Rolle spielt ein defekter Anlasser oder ein Magnetventil bei der Wartung von Baumaschinen?
In der Bauindustrie sind Maschinen wie Bagger und Planierraupen in hohem Maße auf effektive Anlassersysteme angewiesen. Ein defekter Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule kann den Betrieb unterbrechen und zu kostspieligen Verzögerungen führen. Wartungsteams müssen fehlerhafte Komponenten schnell diagnostizieren und ersetzen, damit die Maschinen reibungslos laufen. Einkäufer in diesem Sektor sollten sich auf die Beschaffung langlebiger Teile konzentrieren, die den rauen Arbeitsbedingungen standhalten, und sowohl OEM- als auch Aftermarket-Optionen in Betracht ziehen. Sie sollten Lieferanten auch nach ihrer Fähigkeit beurteilen, pünktlich zu liefern und Unterstützung zu leisten, insbesondere an abgelegenen Baustellen.
Wie ist der Landwirtschaftssektor von defekten Startern oder Magnetventilen betroffen?
In der Landwirtschaft sind Traktoren und andere landwirtschaftliche Fahrzeuge für eine rechtzeitige Aussaat und Ernte unerlässlich. Ein defekter Anlasser oder ein defektes Magnetventil kann zu kritischen Zeiten zu Ausfällen führen und die Produktivität beeinträchtigen. Landwirte und landwirtschaftliche Betriebe benötigen zuverlässige Komponenten, die den unterschiedlichen Witterungsbedingungen und der intensiven Nutzung standhalten können. Bei der Beschaffung dieser Teile sollten internationale Einkäufer Lieferanten bevorzugen, die mit den besonderen Herausforderungen in der Landwirtschaft vertraut sind und Lösungen anbieten können, die einfach zu installieren und zu warten sind.
Warum ist ein zuverlässiges Startsystem in Transport und Logistik so wichtig?
Für Unternehmen in den Bereichen Transport und Logistik ist ein zuverlässiger Fuhrpark unerlässlich, um das Serviceniveau aufrechtzuerhalten und die Betriebskosten zu senken. Ein defekter Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule kann zu unerwarteten Fahrzeugausfällen führen, die den Zeitplan durcheinander bringen und die Kosten erhöhen. Flottenmanager müssen sicherstellen, dass sie Zugang zu hochwertigen Ersatzteilen haben, um Ausfallzeiten zu minimieren. Zu den wichtigsten Überlegungen bei der Beschaffung gehören die Möglichkeit des Großeinkaufs, schnelle Versandoptionen und die Kompatibilität mit einer Vielzahl von Fahrzeugtypen, was die betriebliche Effizienz erheblich steigern kann.
Wie geht die Schifffahrtsindustrie mit defekten Anlassern oder Magnetspulen um?
In der Schifffahrtsindustrie ist die Funktionstüchtigkeit von Anlassersystemen entscheidend für die Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit von Booten und Schiffen. Ein defekter Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule kann zu einem Motorausfall führen, was auf See ein ernstes Risiko darstellt. Die Betreiber von Schiffen benötigen Komponenten, die korrosionsbeständig sind und den Seefahrtsvorschriften entsprechen. Internationale Einkäufer sollten sich an Lieferanten wenden, die auf Teile in Schiffsqualität spezialisiert sind und die besonderen Anforderungen der Branche kennen, damit ihre Schiffe betriebsbereit und sicher bleiben.
3 häufige Schmerzpunkte für ‘defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen’ und ihre Lösungen
Szenario 1: Intermittierende Startprobleme, die den Flottenbetrieb beeinträchtigen
Das Problem: Viele B2B-Einkäufer, die einen Fuhrpark verwalten, stehen vor großen Herausforderungen, wenn Fahrzeuge aufgrund eines defekten Anlassermagneten zeitweise nicht anspringen. Dieses Problem kann zu unerwarteten Ausfallzeiten führen, die sich auf Lieferpläne und die allgemeine betriebliche Effizienz auswirken. Die Unvorhersehbarkeit, wann ein Fahrzeug nicht anspringt, schafft logistische Alpträume, insbesondere in Branchen, in denen zeitkritische Lieferungen entscheidend sind. In Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika, wo Pannenhilfe nicht ohne weiteres verfügbar ist, können die Folgen noch gravierender sein und zu Umsatzeinbußen und Kundenunzufriedenheit führen.
Die Lösung: Um dieses Risiko zu mindern, sollten Fuhrparkmanager eine proaktive Wartungsstrategie einführen, die sich auf die frühzeitige Erkennung von Problemen mit dem Anlassermagneten konzentriert. Bei den regelmäßigen Inspektionen sollte auf gängige Symptome wie Klickgeräusche beim Versuch, das Fahrzeug zu starten, geachtet werden, da dies häufig auf ein defektes Solenoid hinweist. Darüber hinaus hilft die Investition in Diagnosewerkzeuge, die elektrische Systeme analysieren können, Probleme zu erkennen, bevor sie eskalieren. Achten Sie bei der Beschaffung von Ersatzmagneten auf qualitativ hochwertige Teile von seriösen Anbietern und berücksichtigen Sie dabei Faktoren wie die Kompatibilität mit vorhandenen Fahrzeugen und Garantiebestimmungen. Der Aufbau einer Beziehung zu einem vertrauenswürdigen Mechaniker oder Kfz-Dienstleister vor Ort kann ebenfalls eine rechtzeitige Reparatur gewährleisten und die Ausfallzeiten minimieren.
Szenario 2: Schwierigkeiten bei der Beschaffung zuverlässiger Ersatzteile
Das Problem: B2B-Einkäufer haben oft Schwierigkeiten, zuverlässige Quellen für Ersatz-Anlassermagnete zu finden, insbesondere in Regionen mit begrenztem Zugang zu Kfz-Teilen. Dies kann zu Verzögerungen bei Fahrzeugreparaturen führen, die den Geschäftsbetrieb beeinträchtigen und die Betriebskosten durch längere Ausfallzeiten erhöhen können. In Märkten wie dem Nahen Osten und Teilen Europas, wo die Fahrzeugspezifikationen stark variieren können, kann die Beschaffung des richtigen Teils zu einer komplizierten Aufgabe werden, die die Produktivität beeinträchtigt.
Die Lösung: Um diese Beschaffungsherausforderung zu meistern, sollten Einkäufer ein umfassendes Lieferantennetz aufbauen, das lokale Händler und internationale Hersteller mit einer nachgewiesenen Qualitätsbilanz umfasst. Nutzen Sie Online-Plattformen, die auf Kfz-Teile spezialisiert sind, um Preise und Verfügbarkeit zu vergleichen. Bei der Bestellung von Magneten ist darauf zu achten, dass die Teile den OEM-Spezifikationen entsprechen, um Kompatibilität und Zuverlässigkeit zu gewährleisten. Die Einrichtung eines Just-in-Time-Bestandssystems kann dazu beitragen, Verzögerungen zu vermeiden, indem sichergestellt wird, dass häufig benötigte Teile stets auf Lager sind, wodurch das Risiko längerer Ausfallzeiten verringert wird. Darüber hinaus kann der Aufbau von Beziehungen zu Lieferanten zu einer besseren Preisgestaltung und einem bevorzugten Service in kritischen Situationen führen.
Szenario 3: Erhöhte Reparaturkosten aufgrund von ignorierten Symptomen
Das Problem: Das Ignorieren der ersten Anzeichen eines defekten Anlassermagneten kann zu schwerwiegenderen Problemen führen, die für B2B-Käufer mit höheren Reparaturkosten verbunden sind. Symptome wie intermittierende Startvorgänge oder das Einschalten des Anlassers, ohne dass der Schlüssel gedreht wird, können übersehen werden, was zu einem kompletten Ausfall des Anlassers oder zu Schäden an der elektrischen Anlage führen kann. In Regionen mit rauem Klima, wie z. B. in Teilen Europas oder Afrikas, können diese Probleme den Verschleiß verschlimmern und die Wartungskosten weiter in die Höhe treiben.
Die Lösung: Um dieses Problem anzugehen, müssen B2B-Einkäufer ihre Teams vorrangig über die Symptome eines Anlasser-Magnetventils aufklären und sensibilisieren. Durch regelmäßige Schulungen des Wartungspersonals kann sichergestellt werden, dass sie die Anzeichen erkennen und eine rechtzeitige Diagnose durchführen können. Erstellen Sie einen routinemäßigen Wartungsplan, der die Überprüfung des elektrischen Systems beinhaltet, wobei der Schwerpunkt auf dem Startermagneten und seinen Anschlüssen liegt. Wenn Probleme frühzeitig erkannt werden, können sie behoben werden, bevor sie zu kostspieligen Reparaturen führen. Ziehen Sie außerdem in Erwägung, in Garantieverlängerungen oder Serviceverträge zu investieren, die elektrische Komponenten abdecken, um sich vor unerwarteten Reparaturkosten zu schützen. Dieser proaktive Ansatz spart nicht nur Geld, sondern erhöht auch die Langlebigkeit der Fahrzeugflotte.
Strategischer Leitfaden zur Materialauswahl für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
Welches sind die wichtigsten Materialien für die Herstellung von Fehlanlassern oder Magnetventilen?
Bei der Auswahl von Materialien für Fehlstarter oder Magnetspulen ist es wichtig, die Leistungsmerkmale und Umweltfaktoren zu berücksichtigen, die ihre Wirksamkeit beeinflussen. Hier analysieren wir vier gängige Materialien, die bei der Herstellung dieser Komponenten verwendet werden: Kupfer, Aluminium, Stahl und Kunststoffverbundwerkstoffe. Jedes Material hat einzigartige Eigenschaften, die sich auf die Produktleistung, die Haltbarkeit und die Eignung für bestimmte Anwendungen auswirken können.
Wie verhält sich Kupfer in Anlassern und Magnetspulen?
Kupfer ist weithin für seine hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit bekannt, was es zu einer bevorzugten Wahl für elektrische Kontakte und Leitungen in Anlassern und Magnetventilen macht. Zu den wichtigsten Eigenschaften gehören ein hoher Schmelzpunkt (ca. 1.984°F oder 1.085°C) und Korrosionsbeständigkeit, insbesondere wenn es beschichtet ist.
Vorteile: Die überragende Leitfähigkeit von Kupfer ermöglicht eine effiziente Energieübertragung, wodurch die Leistung von Anlassern und Magnetspulen verbessert wird. Außerdem ist es relativ leicht herzustellen und kann in komplizierte Formen gebracht werden.
Nachteile: Der größte Nachteil sind die Kosten, die höher sind als bei vielen Alternativen. Außerdem kann Kupfer bei unsachgemäßer Behandlung korrosionsanfällig sein, insbesondere in feuchten oder salzhaltigen Umgebungen.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Kupfer ist ideal für Hochstromanwendungen, erfordert aber unter Umständen Schutzbeschichtungen, um die Langlebigkeit unter rauen Bedingungen zu gewährleisten.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer in Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika sollten sich vergewissern, dass die lokalen elektrischen Normen eingehalten werden, und die Verfügbarkeit von Kupfer berücksichtigen, die je nach Region unterschiedlich sein kann.
Welche Vorteile bietet Aluminium für Anlasser und Magnetspulen?
Aluminium ist ein weiteres Material, das aufgrund seines geringen Gewichts und seiner guten Korrosionsbeständigkeit häufig für die Herstellung von Anlassern und Magnetventilen verwendet wird. Es hat einen Schmelzpunkt von ca. 660°C (1.221°F) und kann mäßigen Temperaturen standhalten.
Vorteile: Aluminium ist kostengünstig und bietet ein gutes Verhältnis von Festigkeit zu Gewicht, wodurch es sich für Anwendungen in der Automobilindustrie eignet, bei denen eine Gewichtsreduzierung wichtig ist. Außerdem ist es oxidationsbeständig, was in verschiedenen Umgebungen von Vorteil ist.
Nachteile: Aluminium leitet zwar Strom, ist aber nicht so effizient wie Kupfer, was die Leistung bei anspruchsvollen Anwendungen beeinträchtigen kann. Außerdem kann es im Vergleich zu Kupfer schwieriger zu schweißen und zu formen sein.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminium eignet sich für Komponenten, bei denen ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Gewicht und Leistung erforderlich ist, ist aber für Hochstromanwendungen ohne zusätzliche konstruktive Überlegungen möglicherweise nicht ideal.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer sollten sich über die spezifischen Aluminiumsorten informieren, die den lokalen Normen wie ASTM oder DIN entsprechen, und die Auswirkungen der Verwendung von Aluminium in Umgebungen mit hohen Temperaturschwankungen berücksichtigen.
Warum ist Stahl eine gängige Wahl für Anlasser und Magnetventile?
Stahl wird aufgrund seiner hohen Festigkeit und Langlebigkeit häufig für die Bauteile von Anlassern und Magnetventilen verwendet. Mit einem Schmelzpunkt von ca. 1.370°C (2.500°F) kann Stahl auch extremen Bedingungen standhalten.
Vorteile: Stahl ist sehr haltbar und kann erheblichen mechanischen Belastungen standhalten, so dass er sich für schwere Anwendungen eignet. Außerdem ist er im Vergleich zu Kupfer und Aluminium relativ preiswert.
Nachteile: Der Hauptnachteil ist sein Gewicht, was bei Automobilanwendungen, bei denen eine Gewichtsreduzierung von entscheidender Bedeutung ist, ein Nachteil sein kann. Stahl ist außerdem rostanfällig, wenn er nicht ordnungsgemäß beschichtet oder behandelt wird.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Stahl ist ideal für Gehäuse und Konstruktionsteile, kann aber zusätzliche Beschichtungen erfordern, um Korrosion zu verhindern, insbesondere in feuchtem Klima.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Die Einhaltung lokaler Normen für Stahlsorten ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, insbesondere in Regionen mit spezifischen Anforderungen für Automobilkomponenten.
Wie verbessern Kunststoff-Verbundwerkstoffe die Leistung von Anlasser und Magnetspule?
Kunststoffverbundwerkstoffe werden aufgrund ihrer Vielseitigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit zunehmend in Anlasser- und Magnetspulenanwendungen eingesetzt. Je nach Art des Verbundstoffs können sie Temperaturen von bis zu 149°C (300°F) standhalten.
Vorteile: Diese Materialien sind leicht und können in komplexe Formen gegossen werden, was innovative Designs ermöglicht. Außerdem sind sie korrosionsbeständig und nicht leitend, was sie für Isolieranwendungen geeignet macht.
Nachteile: Kunststoffverbundwerkstoffe bieten möglicherweise nicht die gleiche mechanische Festigkeit wie Metalle, was ihre Verwendung bei hochbelasteten Anwendungen einschränken kann. Außerdem können sie eine geringere thermische Stabilität aufweisen.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Verbundwerkstoffe eignen sich am besten für nicht lasttragende Bauteile und können die allgemeine Konstruktionsflexibilität von Startern und Magnetspulen verbessern.
Überlegungen für internationale Käufer: Käufer sollten sich vergewissern, dass die spezifischen Verbundwerkstoffe den lokalen Normen und Vorschriften entsprechen, insbesondere bei Anwendungen in der Automobilindustrie.
Übersichtstabelle zur Materialauswahl für Anlasser und Magnetspulen
| Material | Typischer Anwendungsfall für einen defekten Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule | Wesentlicher Vorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Einschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kupfer | Elektrische Kontakte und Verkabelung | Hervorragende elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Höhere Kosten, Korrosionsrisiko | Hoch |
| Aluminium | Strukturelle Komponenten | Leichtes Gewicht, gute Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Geringere Leitfähigkeit als Kupfer | Mittel |
| Stahl | Gehäuse und Strukturteile | Hohe Lebensdauer | Schwerer, anfällig für Rost | Niedrig |
| Kunststoffverbundwerkstoffe | Isolierende Komponenten | Leichtes Gewicht, korrosionsbeständig | Geringere mechanische Festigkeit | Mittel |
Dieser strategische Leitfaden für die Materialauswahl liefert wichtige Erkenntnisse für internationale B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere in verschiedenen Märkten wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, und hilft ihnen, fundierte Entscheidungen auf der Grundlage von Leistung, Kosten und regionalen Standards zu treffen.
Eingehender Blick: Fertigungsprozesse und Qualitätssicherung bei defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid
Was sind die wichtigsten Herstellungsverfahren für defekte Anlasser und Magnetventile?
Die Herstellung von Anlassern und Magnetventilen umfasst mehrere kritische Phasen, die jeweils eine genaue technische Planung und Qualitätskontrolle erfordern, um sicherzustellen, dass das Endprodukt sowohl den Leistungs- als auch den Sicherheitsstandards entspricht. Zu den wichtigsten Phasen des Herstellungsprozesses gehören Materialvorbereitung, Formgebung, Montage und Endbearbeitung.
Wie wird das Material für Anlasser und Magnetspulen vorbereitet?
Der erste Schritt im Herstellungsprozess ist die Materialvorbereitung. Hochwertige Materialien sind für die Langlebigkeit und Funktionalität unerlässlich. Zu den gängigen Materialien gehören Kupfer für die Verdrahtung, Stahl für das Gehäuse und verschiedene Kunststoffe für die Isolierung. Die Zulieferer unterziehen die Rohstoffe oft strengen Tests, um sicherzustellen, dass sie den Industriespezifikationen entsprechen. Dies kann Zugfestigkeitstests, Bewertungen der Korrosionsbeständigkeit und der Wärmeleitfähigkeit umfassen.
Welche Umformtechniken werden bei der Herstellung von Anlassern und Magnetspulen verwendet?
Sobald die Materialien vorbereitet sind, werden sie umgeformt. Dazu gehören in der Regel Zerspanen, Stanzen und Gießen.
-
Bearbeitung: Bauteile wie das Anlassergehäuse werden häufig aus Metallblöcken bearbeitet, um präzise Abmessungen und Oberflächengüten zu gewährleisten. Zu diesem Zweck werden in der Regel CNC-Maschinen (Computer Numerical Control) eingesetzt.
-
Stanzen: Bei Teilen wie elektrischen Kontakten wird das Stanzen eingesetzt, um einheitliche Formen in großen Mengen zu produzieren. Diese Methode ist effizient und reduziert den Materialabfall.
-
Formgebung: Kunststoffteile, wie Gehäuse oder Isolatoren, werden im Spritzgussverfahren hergestellt. Diese Technik ermöglicht komplexe Formen und ist kostengünstig für große Produktionsserien.
Wie werden Anlasser und Magnetspulen zusammengebaut?
In der Montagephase werden die einzelnen Komponenten zum Endprodukt zusammengefügt. Je nach den Möglichkeiten des Herstellers und der Komplexität der Bauteile kann dieser Prozess manuell oder an automatisierten Montagelinien erfolgen.
-
Verkabelung: Elektrische Verbindungen müssen sorgfältig hergestellt werden, um eine gute Leitfähigkeit zu gewährleisten. Löt- oder Quetschtechniken sind üblich, um Drähte an Klemmen zu befestigen.
-
Integration von Komponenten: Die Magnetspule wird normalerweise direkt auf den Anlasser montiert. Eine korrekte Ausrichtung und sichere Befestigung sind entscheidend, um Betriebsprobleme zu vermeiden.
-
Qualitätskontrollen während der Montage: Die Hersteller führen häufig Maßnahmen zur prozessbegleitenden Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC) durch, bei denen in verschiedenen Montagestufen Kontrollen stattfinden, um Fehler frühzeitig zu erkennen.
Welche Qualitätssicherungspraktiken sind für Anlasser und Magnetventile unerlässlich?
Die Qualitätssicherung (QS) ist ein Eckpfeiler des Herstellungsprozesses für Anlasser und Magnetspulen. Sie gewährleistet, dass die Produkte den internationalen Normen und den Kundenspezifikationen entsprechen.
Welche internationalen Normen gelten für die Herstellung von Anlassern und Magnetspulen?
Internationale Normen wie ISO 9001 bieten einen Rahmen für Qualitätsmanagementsysteme. Die Einhaltung dieser Normen ist für B2B-Einkäufer oft eine Voraussetzung, vor allem wenn sie in regulierten Märkten wie Europa und Nordamerika tätig sind. Darüber hinaus können branchenspezifische Zertifizierungen wie die CE-Kennzeichnung (für die Einhaltung von Gesundheits-, Sicherheits- und Umweltschutznormen) und API-Zertifizierungen (American Petroleum Institute) je nach Anwendung des Anlassers oder Magnetventils ebenfalls relevant sein.
Was sind die wichtigsten Kontrollpunkte für die Qualitätskontrolle?
Die Kontrollpunkte der Qualitätskontrolle sind von entscheidender Bedeutung für die Erkennung von Fehlern und die Gewährleistung der Produktzuverlässigkeit. Zu den wichtigsten Kontrollpunkten im Herstellungsprozess gehören:
-
Eingangsqualitätskontrolle (IQC): Bei dieser ersten Kontrolle werden die Rohstoffe und Komponenten geprüft, bevor sie in den Produktionsprozess gelangen. Sie stellt sicher, dass alle Materialien den vorgegebenen Standards entsprechen.
-
In-Process-Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): Bei der IPQC, die während des gesamten Fertigungsprozesses durchgeführt wird, werden Montage- und Produktionstechniken überwacht. Dies kann visuelle Inspektionen, Funktionstests einzelner Komponenten und die Überprüfung der Ausrichtung und Montage umfassen.
-
Endkontrolle (FQC): Nach der Montage werden die Produkte strengen Tests unterzogen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie korrekt funktionieren. Dies kann elektrische Prüfungen, Belastungstests und Leistungsbewertungen zur Simulation von Betriebsbedingungen umfassen.
Wie können B2B-Käufer die Qualitätskontrolle ihrer Lieferanten überprüfen?
Für internationale B2B-Einkäufer, insbesondere für solche aus verschiedenen Regionen wie Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa, ist die Überprüfung der Qualitätskontrolle der Lieferanten von entscheidender Bedeutung, um die Zuverlässigkeit der Produkte und die Einhaltung der lokalen Vorschriften zu gewährleisten.
Welche Methoden können Einkäufer zur Überprüfung der Qualität verwenden?
-
Lieferantenaudits: Regelmäßige Audits können helfen, die Einhaltung der Qualitätsstandards durch den Lieferanten zu beurteilen. Einkäufer sollten Einsicht in die Auditberichte verlangen, um die Qualitätsmanagementpraktiken des Lieferanten zu bewerten.
-
Anforderung von Qualitätsberichten: Die Einkäufer können detaillierte Qualitätskontrollberichte verlangen, einschließlich der Ergebnisse von IQC, IPQC und FQC. Diese Dokumente geben einen Einblick in die Qualitätsprozesse des Lieferanten und in alle während der Produktion aufgetretenen Probleme.
-
Inspektionen durch Dritte: Die Beauftragung von Inspektionsdiensten durch Dritte kann eine unvoreingenommene Bewertung der Qualitätspraktiken eines Lieferanten liefern. Diese Inspektionen können in verschiedenen Stadien des Produktionsprozesses durchgeführt werden.
-
Bescheinigungen und Konformitätsdokumente: Die Einkäufer sollten überprüfen, ob die Lieferanten über einschlägige Zertifizierungen und Konformitätsdokumente verfügen. Dazu gehört die Überprüfung auf ISO-Zertifizierungen, CE-Kennzeichnungen und branchenspezifische Normen.
Was sind die Feinheiten der Qualitätskontrolle für internationale B2B-Käufer?
Das Navigieren durch die Nuancen der Qualitätskontrolle kann für internationale Einkäufer eine Herausforderung sein. Unterschiedliche Vorschriften, Normen und Erwartungen können den Beschaffungsprozess erschweren.
Wie wirken sich regionale Normen auf die Qualitätskontrolle aus?
-
Europa: Die EU-Vorschriften verlangen oft eine strenge Einhaltung der CE-Kennzeichnung und anderer Zertifizierungen, die in anderen Regionen möglicherweise nicht so streng sind. Die Einkäufer müssen sicherstellen, dass die Lieferanten diese Standards erfüllen, um Probleme mit der Einhaltung zu vermeiden.
-
Afrika und Südamerika: Die Qualitätsstandards können sehr unterschiedlich sein. Käufer sollten sich gründlich über die örtlichen Vorschriften informieren und die Zusammenarbeit mit Lieferanten in Erwägung ziehen, die Erfahrung auf internationalen Märkten haben.
-
Naher Osten: Der Markt konzentriert sich zunehmend auf die Qualitätssicherung, und viele Käufer suchen Lieferanten mit international anerkannten Zertifizierungen. Einkäufer sollten Lieferanten bevorzugen, die ihr Engagement für Qualität unter Beweis stellen.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass es für B2B-Einkäufer von entscheidender Bedeutung ist, die Herstellungsverfahren und Qualitätssicherungspraktiken für Anlasser und Magnetspulen zu verstehen. Indem sie sich auf Materialvorbereitung, Umformtechniken, Montagemethoden und robuste Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen konzentrieren, können Käufer sicherstellen, dass sie zuverlässige Produkte beschaffen, die ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen entsprechen.
Praktische Anleitung zur Beschaffung: Eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste für ‘defekter Anlasser oder Solenoid’.’
Um B2B-Einkäufer bei der Beschaffung von zuverlässigen Anlassern oder Magnetventilen zu unterstützen, bietet dieser praktische Beschaffungsleitfaden eine Schritt-für-Schritt-Checkliste. Es ist wichtig, Qualität und Kompatibilität sicherzustellen, insbesondere bei der Beschaffung auf verschiedenen internationalen Märkten.
Schritt 1: Definieren Sie Ihre technischen Spezifikationen
Bevor Sie mit dem Beschaffungsprozess beginnen, sollten Sie die technischen Spezifikationen für den Anlasser oder die Magnetspule klar umreißen. Dazu gehören Spannungswerte, Größe und Kompatibilität mit vorhandenen Maschinen oder Fahrzeugen. Die Kenntnis dieser Spezifikationen wird Ihnen helfen, die potenziellen Lieferanten einzugrenzen, die Ihre Anforderungen erfüllen können.
Schritt 2: Recherche potenzieller Lieferanten
Führen Sie eine gründliche Recherche durch, um potenzielle Lieferanten zu finden, die auf Anlasser und Magnetventile spezialisiert sind. Suchen Sie nach Unternehmen mit einem guten Ruf in Ihrer Region, insbesondere nach solchen mit Erfahrung in der Belieferung ähnlicher Branchen wie der Ihren. Nutzen Sie Online-Plattformen, Branchenverzeichnisse und Messen, um eine Liste seriöser Lieferanten zu erstellen.
Schritt 3: Überprüfung der Lieferantenzertifizierung
Es ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, dass die von Ihnen ausgewählten Lieferanten über die erforderlichen Zertifizierungen und Qualitätsstandards verfügen. Achten Sie auf ISO-Zertifizierungen oder andere einschlägige Qualitätssicherungsnachweise, die ihr Engagement für eine hervorragende Produktion belegen. Diese Überprüfung schützt Sie vor minderwertigen Produkten und garantiert die Einhaltung internationaler Normen.
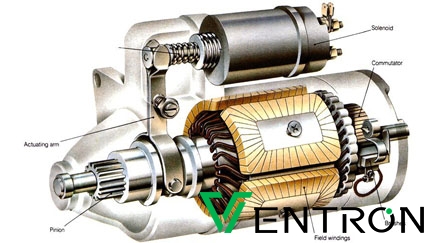
Anschauliches Bild zu defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid
Schritt 4: Anforderung von Produktmustern
Bevor Sie eine Bestellung abschließen, sollten Sie Muster der von Ihnen in Betracht gezogenen Anlasser oder Magnetspulen anfordern. Anhand von Mustern können Sie die Qualität, Leistung und Kompatibilität mit Ihren Geräten beurteilen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie diese Muster unter den tatsächlichen Einsatzbedingungen testen, um ihre Zuverlässigkeit zu bestätigen.
Schritt 5: Bewertung der Leistungshistorie des Lieferanten
Prüfen Sie die Leistungsgeschichte potenzieller Lieferanten, indem Sie sich Kundenzeugnisse und Fallstudien ansehen. Achten Sie auf Rückmeldungen zur Produktqualität, zu den Lieferzeiten und zum Kundendienst. Die Zusammenarbeit mit früheren Kunden kann Aufschluss über die Zuverlässigkeit und Reaktionsfähigkeit des Lieferanten geben.
Schritt 6: Bewertung der Garantie- und Rückgaberegelungen
Die Kenntnis der Garantie- und Rückgaberichtlinien Ihrer Lieferanten ist für die Risikominderung von entscheidender Bedeutung. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Anbieter eine angemessene Garantiezeit für seine Produkte anbietet und klare Verfahren für die Rückgabe oder den Umtausch im Falle von Mängeln vorsieht. Dies sichert Ihre Investition und gewährleistet Unterstützung bei Problemen nach dem Kauf.
Schritt 7: Bedingungen verhandeln und Verträge abschließen
Sobald Sie einen geeigneten Lieferanten gefunden haben, verhandeln Sie die Einkaufsbedingungen, einschließlich Preisgestaltung, Zahlungsbedingungen und Lieferfristen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass alle Vereinbarungen in einem formellen Vertrag festgehalten werden, um beide Parteien zu schützen. Dieser Schritt ist entscheidend, um ein klares Verständnis der Erwartungen und Verantwortlichkeiten zu schaffen.
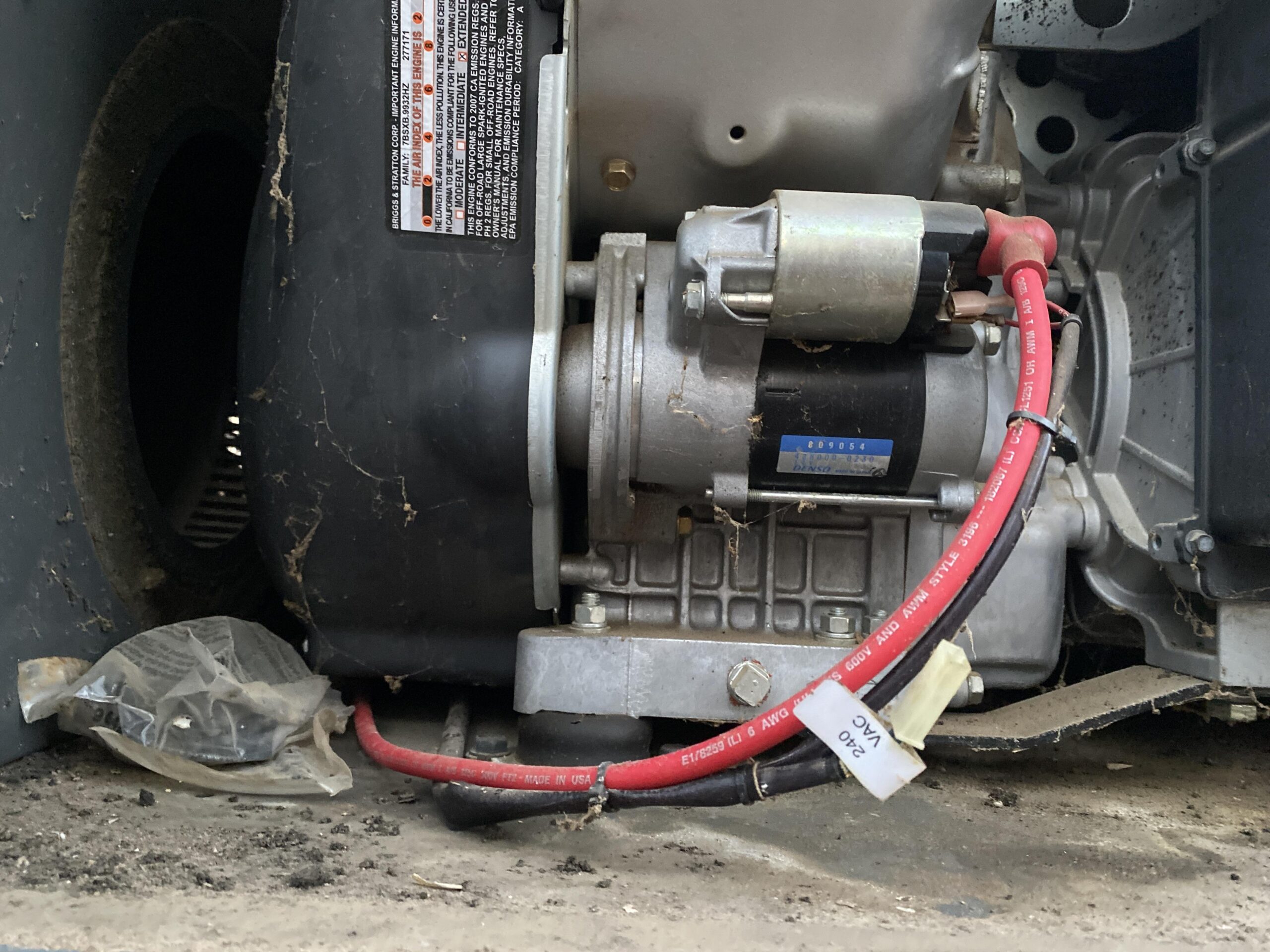

Anschauliches Bild zu defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid
Anhand dieser strukturierten Checkliste können B2B-Einkäufer effektiv hochwertige Anlasser und Magnetventile beschaffen und so sicherstellen, dass ihre betrieblichen Anforderungen erfüllt werden, während die mit der Beschaffung verbundenen Risiken minimiert werden.
Umfassende Kosten- und Preisanalyse für einen defekten Anlasser oder ein defektes Solenoid Beschaffung
Bei der Beschaffung von Fehlanlassern oder Magnetventilen ist es für internationale B2B-Einkäufer entscheidend, die umfassende Kostenstruktur und Preisdynamik zu verstehen. Dieser Abschnitt befasst sich mit den verschiedenen Kostenkomponenten, den Faktoren, die die Preise beeinflussen, sowie mit praktischen Tipps für Einkäufer, die ihre Beschaffungsstrategien optimieren wollen.
Was sind die wichtigsten Kostenkomponenten bei der Beschaffung von schlechten Startern oder Magnetventilen?
-
Materialien: Zu den Kernmaterialien für Anlasser und Magnetspulen gehören in der Regel Kupfer, Stahl und verschiedene Kunststoffe. Die Qualität dieser Materialien wirkt sich direkt auf die Leistung und Haltbarkeit der Komponenten aus. Käufer sollten die Beschaffung hochwertiger Materialien in Betracht ziehen, da diese zu geringeren Ausfallraten und einer längeren Produktlebensdauer führen können.
-
Arbeit: Die Arbeitskosten können je nach Region sehr unterschiedlich sein. In Ländern mit niedrigeren Arbeitskosten, wie z. B. in Teilen Afrikas oder Südamerikas, können die Hersteller wettbewerbsfähigere Preise anbieten. Bei der Qualität und dem Fachwissen der Arbeitskräfte sollten jedoch keine Kompromisse eingegangen werden, da qualifizierte Arbeitskräfte eine bessere Montage und Qualitätskontrolle gewährleisten.
-
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: Dazu gehören die Kosten für Versorgungsleistungen, Miete und den allgemeinen Betrieb der Fabrik. Effiziente Herstellungsverfahren können diese Gemeinkosten senken, was zu einer wettbewerbsfähigeren Preisgestaltung führt.
-
Werkzeuge: Kundenspezifische Werkzeuge für spezielle Designs oder Änderungen können eine erhebliche Vorabinvestition darstellen. Käufer sollten abwägen, ob die Werkzeugkosten über größere Produktionsläufe amortisiert werden können, damit sich die Investition lohnt.
-
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Robuste Qualitätskontrollverfahren sind für die Gewährleistung der Produktzuverlässigkeit unerlässlich. Die Einführung einer strengen Qualitätskontrolle kann zwar die Kosten erhöhen, zahlt sich aber oft durch geringere Rücksendungen und eine höhere Kundenzufriedenheit aus.
-
Logistik: Die Versand- und Bearbeitungskosten können je nach Herkunft und Bestimmungsort der Produkte stark variieren. Internationale Käufer sollten Faktoren wie Versandmethoden, Zollgebühren und lokale Steuern berücksichtigen, die die Gesamtkosten beeinflussen können.
-
Marge: Die Gewinnspannen der Lieferanten können je nach Marktnachfrage und Wettbewerb variieren. Die Kenntnis der branchenüblichen Gewinnspannen kann Einkäufern helfen, bessere Bedingungen auszuhandeln.
Was beeinflusst die Preisgestaltung von Anlassern und Magnetventilen?
-
Menge/Mindestbestellmenge: Lieferanten haben oft Mindestbestellmengen (MOQs), die sich auf die Preisgestaltung auswirken können. Größere Bestellungen führen in der Regel zu niedrigeren Stückkosten, so dass es für Einkäufer von Vorteil ist, ihre Bestellungen nach Möglichkeit zu konsolidieren.
-
Spezifikationen und Anpassung: Kundenspezifische Anlasser oder Magnetspulen, die auf bestimmte Anwendungen zugeschnitten sind, sind oft mit höheren Kosten verbunden. Käufer sollten die Vorteile der kundenspezifischen Anpassung gegen die zusätzlichen Kosten abwägen.
-
Materialien und Qualitätszertifizierungen: Bauteile aus höherwertigen Materialien oder solche, die bestimmte Branchenzertifizierungen (z. B. ISO, TS16949) erfüllen, können höhere Preise erzielen. Die Käufer sollten prüfen, ob diese Zertifizierungen für ihre Anwendungen erforderlich sind.
-
Lieferantenfaktoren: Die Zuverlässigkeit und der Ruf der Lieferanten können die Preisgestaltung beeinflussen. Etablierte Lieferanten, die sich durch Qualität auszeichnen, verlangen zwar mehr, können aber das Risiko von Fehlern und die damit verbundenen Kosten verringern.
-
Incoterms: Es ist wichtig, die im Vertrag vereinbarten Incoterms zu verstehen. Begriffe wie FOB (Free on Board) oder CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) können die Gesamtkosten erheblich beeinflussen, insbesondere bei internationalen Geschäften.
Wie können Einkäufer verhandeln und die Kosten optimieren?
-
Verhandlung: Führen Sie offene Gespräche über die Preisgestaltung, insbesondere bei Großaufträgen. Die Lieferanten sind möglicherweise bereit, bei größeren Bestellungen oder langfristigen Verträgen Rabatte zu gewähren.
-
Kosteneffizienz: Achten Sie auf die Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO) und nicht nur auf den Anschaffungspreis. Günstigere Komponenten können zu höheren Austauschraten und Gesamtkosten führen.
-
Preisgestaltung für internationale Käufer: Käufer aus Regionen wie Afrika und Südamerika sollten bei der Bewertung der Preise die Wechselkurse und die regionale Marktdynamik berücksichtigen. Außerdem kann die Berücksichtigung lokaler logistischer Herausforderungen ein klareres Bild der tatsächlichen Kosten vermitteln.
-
Haftungsausschluss für indikative Preise: Es ist wichtig zu wissen, dass die Preise je nach Marktbedingungen, Materialkosten und Verfügbarkeit der Lieferanten schwanken können. Einkäufer sollten Angebote von mehreren Lieferanten einholen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie wettbewerbsfähige Preise erhalten.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass ein gründliches Verständnis der Kostenkomponenten und der preisbeeinflussenden Faktoren bei der Beschaffung von Fehlanlassern und Magnetventilen internationale B2B-Einkäufer in die Lage versetzen kann, fundierte Kaufentscheidungen zu treffen, ihre Beschaffungsstrategien zu optimieren und letztendlich ihre betriebliche Effizienz zu steigern.
Analyse der Alternativen: Vergleich von defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid mit anderen Lösungen
Bei der Bewertung von Lösungen für Startprobleme im Automobilbereich, insbesondere im Zusammenhang mit einem defekten Anlasser oder Solenoid, ist es wichtig, praktikable Alternativen zu untersuchen, die ähnliche Funktionen erfüllen können. Diese Analyse hilft B2B-Einkäufern in Branchen wie der Kfz-Reparatur, dem Fuhrparkmanagement und dem Teilevertrieb, fundierte Entscheidungen über die besten Technologien zu treffen. Im Folgenden vergleichen wir den herkömmlichen defekten Anlasser oder die Magnetspule mit zwei alternativen Lösungen: Anlasserwechsel und intelligente Zündungssysteme.
| Vergleichsaspekt | Anlasser oder Magnetventil defekt | Austausch des Anlassers | Intelligente Zündsysteme |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Standard-Drehmoment und -Wirkungsgrad; kann bei starker Belastung versagen | Verbesserte Leistung mit neuer Technologie; oft höheres Drehmoment | Verbesserte Zuverlässigkeit und Diagnose; kann Fernstart beinhalten |
| Kosten | Im Allgemeinen geringe Kosten, aber je nach Marke/Modell unterschiedlich | Höhere Anfangsinvestitionen; die Kosten können erheblich schwanken | Höhere Anschaffungskosten aufgrund der fortschrittlichen Technologie |
| Einfache Implementierung | Mäßig; erfordert grundlegende mechanische Kenntnisse | Komplexer; erfordert möglicherweise eine professionelle Installation | Komplex; erfordert oft die Integration mit bestehenden Systemen |
| Wartung | Geringer Wartungsaufwand, muss aber bei Defekten möglicherweise ersetzt werden | Regelmäßige Wartung; die Lebensdauer variiert je nach Nutzung | Minimale Wartung; eventuell sind Software-Updates erforderlich |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Geeignet für kostenbewusste Reparaturen und Standardfahrzeuge | Ideal für ältere Fahrzeuge, die nachgerüstet werden müssen oder häufig benutzt werden | Am besten geeignet für moderne Fahrzeuge mit erweiterten Funktionen und Fernbedienungsmöglichkeiten |
Was sind die Vor- und Nachteile des Anlasserwechsels?
Der Austausch eines Anlassers ist eine gängige Alternative zur Behebung von Problemen, die durch einen defekten Anlasser oder ein defektes Solenoid verursacht werden. Diese Lösung bietet eine bessere Leistung, da neue Anlasser oft ein höheres Drehmoment und einen besseren Wirkungsgrad aufweisen. Allerdings sind die Kosten in der Regel höher als beim einfachen Austausch einer Magnetspule, und der Einbau kann, insbesondere bei komplexen Fahrzeugsystemen, professionelles Know-how erfordern. Außerdem kann ein neuer Anlasser zwar die Zuverlässigkeit deutlich erhöhen, erfordert aber unter Umständen dennoch eine regelmäßige Wartung.
Wie verbessern intelligente Zündsysteme die Fahrzeugleistung?
Intelligente Zündsysteme sind eine fortschrittlichere Alternative zu herkömmlichen Startern und Zündmagneten. In diese Systeme ist moderne Technologie integriert, die eine verbesserte Diagnose, Kraftstoffeffizienz und sogar Fernstartfunktionen ermöglicht. Ihre Leistung ist oft besser, da sie sich an verschiedene Fahrbedingungen anpassen können. Allerdings können die Komplexität der Installation und die höheren Anschaffungskosten einige Käufer abschrecken. Außerdem erfordern diese Systeme möglicherweise gelegentliche Software-Updates, was einen zusätzlichen Wartungsaufwand bedeutet.
Schlussfolgerung: Wie können B2B-Einkäufer die richtige Einstiegslösung auswählen?
Bei der Auswahl der richtigen Lösung für Kfz-Startprobleme sollten B2B-Käufer ihre spezifischen betrieblichen Anforderungen, Budgetbeschränkungen und die Komplexität der Fahrzeugsysteme, mit denen sie arbeiten, berücksichtigen. Für Unternehmen, die sich auf kostengünstige Reparaturen konzentrieren, kann der Austausch eines defekten Anlassers oder Magnetventils ausreichen. Im Gegensatz dazu können Unternehmen, die Flotten oder moderne Fahrzeuge verwalten, von Investitionen in den Austausch von Anlassern oder intelligenten Zündsystemen profitieren, um die Leistung und Zuverlässigkeit zu verbessern. Das Wissen um diese Alternativen ermöglicht es den Käufern, strategische Entscheidungen zu treffen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Zielen übereinstimmen.
Wesentliche technische Eigenschaften und Fachbegriffe für einen defekten Anlasser oder eine defekte Magnetspule
Was sind die wichtigsten technischen Eigenschaften eines defekten Anlassers oder Solenoids?
Bei der Beurteilung eines defekten Anlassers oder Elektromagneten ist die Kenntnis der kritischen technischen Eigenschaften für eine fundierte Kaufentscheidung unerlässlich. Im Folgenden sind einige wichtige Spezifikationen aufgeführt, die berücksichtigt werden sollten:
1. Werkstoffgüte
Die Materialzusammensetzung eines Anlassers oder einer Magnetspule kann seine Haltbarkeit und Leistung erheblich beeinflussen. Zu den gängigen Materialien gehören Kupfer für elektrische Komponenten und Edelstahl für das Gehäuse. Bei B2B-Geschäften wird durch die Angabe der Materialqualität sichergestellt, dass das Teil den Umgebungsbedingungen und Betriebsanforderungen standhält.
2. Nennstrom (Stromstärke)
Die Stromstärke gibt den maximalen elektrischen Strom an, den der Magnet ohne Ausfall verarbeiten kann. Diese Angabe ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, da ein unterdimensioniertes Magnetventil überhitzen und ausfallen kann, was zu kostspieligen Ausfallzeiten führt. Die Kenntnis der Nennströme hilft den Käufern bei der Auswahl von Teilen, die ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen entsprechen und gleichzeitig mit bestehenden Systemen kompatibel sind.
3. Betriebsspannung
Die Betriebsspannung, die in der Regel zwischen 12 und 24 V für Kfz-Anwendungen liegt, bestimmt, wie das Magnetventil mit dem elektrischen System des Fahrzeugs interagiert. Die Käufer müssen sicherstellen, dass die Spannungsspezifikationen den Anforderungen des Fahrzeugs entsprechen, um Leistungsprobleme zu vermeiden.
4. Drehmoment Leistung
Das abgegebene Drehmoment bezieht sich auf die Drehkraft, die der Anlasser ausüben kann, um den Motor zu starten. Dies ist wichtig, um sicherzustellen, dass der Motor unter verschiedenen Bedingungen, auch bei kaltem Wetter, anspringt. B2B-Käufer sollten die Drehmomentangaben prüfen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie Anlasser auswählen, die den spezifischen Anforderungen ihrer Motoren entsprechen.
5. Reaktionszeit
Dies ist die Zeit, die der Magnet benötigt, um nach Erhalt eines Signals vom Zündschalter einzurasten. Eine schnellere Reaktionszeit kann zu einem zuverlässigeren Startvorgang führen. Für Unternehmen ist das Verständnis der Reaktionszeit von entscheidender Bedeutung, um die Effizienz ihres Fuhrparks zu gewährleisten, insbesondere bei kommerziellen Anwendungen.
6. Abmessungen und Gewicht
Die physischen Abmessungen und das Gewicht können den Einbau und die Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Fahrzeugmodellen beeinflussen. Käufer sollten sich dieser Spezifikationen bewusst sein, um sicherzustellen, dass die Teile ohne Änderungen in die vorgesehenen Bereiche passen und somit Zeit und Kosten beim Einbau sparen.
Welche gängigen Fachausdrücke sollten Einkäufer kennen?
Die Vertrautheit mit der branchenspezifischen Terminologie kann die Kommunikation und Verhandlung bei B2B-Transaktionen erheblich verbessern. Im Folgenden finden Sie einige Schlüsselbegriffe, die für den Einkauf von Anlassern und Magnetventilen relevant sind:
1. OEM (Originalgerätehersteller)
Erstausrüsterteile sind Komponenten, die von demselben Hersteller stammen, der auch die Originalteile für das Fahrzeug produziert hat. Diese Teile werden im Allgemeinen wegen ihrer garantierten Kompatibilität und Qualität bevorzugt. Käufer sollten OEM-Teile in Betracht ziehen, um die Garantie zu erhalten und eine optimale Leistung zu gewährleisten.
2. MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
MOQ ist die kleinste Produktmenge, die ein Lieferant zu verkaufen bereit ist. Die Kenntnis der MOQ ist für Unternehmen, die ihre Lagerbestände verwalten und gleichzeitig den Produktionsanforderungen gerecht werden müssen, von entscheidender Bedeutung. Das Aushandeln von MOQs kann zu Kosteneinsparungen führen, insbesondere bei Großeinkäufen.
3. RFQ (Angebotsanfrage)
Eine Anfrage ist ein Dokument, das an Lieferanten geschickt wird, um Preise und Bedingungen für bestimmte Produkte anzufordern. Dies ist ein wichtiger Schritt im Beschaffungsprozess, der es Einkäufern ermöglicht, Angebote zu vergleichen und fundierte Kaufentscheidungen auf der Grundlage von Preis, Qualität und Lieferzeiten zu treffen.
4. Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
Incoterms sind international anerkannte Regeln, die die Verantwortlichkeiten von Käufern und Verkäufern bei der Lieferung von Waren festlegen. Die Vertrautheit mit den Incoterms hilft Unternehmen, die Versandkosten, das Risikomanagement und die Lieferfristen zu verstehen und sorgt für reibungslosere Transaktionen auf den globalen Märkten.
5. Vorlaufzeit
Als Vorlaufzeit wird die Zeit bezeichnet, die von der Bestellung bis zum Erhalt des Produkts vergeht. Die Kenntnis der Vorlaufzeiten ist entscheidend für die Planung von Lagerbeständen und Produktionsplänen. Einkäufer sollten sich nach den Vorlaufzeiten erkundigen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie ihre operativen Fristen einhalten können.
6. Garantiezeitraum
Die Garantiezeit ist der Zeitraum, in dem ein Käufer Reparaturen oder Ersatz für Mängel geltend machen kann. Die Kenntnis der Garantiebedingungen hilft den Unternehmen, das mit dem Kauf verbundene Risiko einzuschätzen, und gibt ihnen Sicherheit hinsichtlich der Langlebigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit des Produkts.
Durch das Verständnis dieser technischen Eigenschaften und Handelsbedingungen können B2B-Einkäufer die Komplexität des Einkaufs von Anlassern und Magnetventilen besser bewältigen und sicherstellen, dass sie Entscheidungen treffen, die mit ihren betrieblichen Anforderungen und Geschäftszielen übereinstimmen.
Marktdynamik und Beschaffungstrends in der Branche für defekte Anlasser und Magnetspulen
Was sind die wichtigsten Markttreiber und Trends für Fehlstarter und Magnetventile?
Der globale Markt für Fehlstarter und Magnetventile erlebt bedeutende Veränderungen, die durch technologische Fortschritte, sich verändernde Verbraucherpräferenzen und den Bedarf an verbesserter Fahrzeugzuverlässigkeit angetrieben werden. Einer der Haupttreiber ist die steigende Nachfrage nach Elektrofahrzeugen und Hybridmodellen, bei denen fortschrittliche Anlassertechnologien zum Einsatz kommen. Dieser Wandel ist besonders in Regionen wie Europa zu beobachten, wo strenge Emissionsvorschriften die Hersteller zu Innovationen veranlassen.
Zu den aufkommenden B2B-Techniktrends gehört die Integration intelligenter Technologien in Anlasser und Magnetventile, die Funktionen wie Ferndiagnose und vorausschauende Wartung ermöglichen. Diese Innovationen sind für internationale Käufer aus Afrika, Südamerika und dem Nahen Osten interessant, wo die Zuverlässigkeit von Fahrzeugen aufgrund unterschiedlicher Straßenbedingungen und infrastruktureller Herausforderungen von größter Bedeutung ist. Darüber hinaus erleichtert das Aufkommen von Online-Marktplätzen den Zugang zu Lieferanten und fördert eine wettbewerbsfähige Preisgestaltung.
Die Marktdynamik wird auch durch die Verfügbarkeit von Rohstoffen und Komponenten beeinflusst, die für die Herstellung von Anlassern und Magnetspulen erforderlich sind. Einkäufer müssen sich der geopolitischen Faktoren bewusst sein, die sich auf die Lieferketten auswirken könnten, insbesondere in Regionen, die reich an wichtigen Mineralien sind. Da sich die Hersteller zunehmend auf kosteneffiziente Beschaffungsstrategien konzentrieren, sollten internationale Einkäufer Partnerschaften mit Lieferanten bevorzugen, die sich flexibel an diese Marktschwankungen anpassen können.
Wie können sich Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Beschaffung auf B2B-Entscheidungen in der Branche für schlechte Anlasser und Magnete auswirken?
Nachhaltigkeit wird für B2B-Einkäufer im Bereich Anlasser und Magnetventile immer wichtiger, da die Auswirkungen auf die Umwelt branchenübergreifend immer mehr an Bedeutung gewinnen. Bei der Herstellung von Anlassern und Magnetspulen können Materialien und Verfahren zum Einsatz kommen, die zur Umweltzerstörung beitragen. Daher sollten Einkäufer nach Lieferanten suchen, die sich zu nachhaltigen Praktiken verpflichten, wie z. B. Abfallreduzierung, Energieeinsparung und Minimierung des CO2-Fußabdrucks.
Ethische Beschaffung spielt auch eine wichtige Rolle, wenn es darum geht, sicherzustellen, dass die in Anlassern und Magnetspulen verwendeten Materialien auf verantwortungsvolle Weise beschafft werden. Dazu gehört die Überprüfung, ob die Lieferanten faire Arbeitsbedingungen und Umweltvorschriften einhalten. Zertifizierungen wie ISO 14001 (Umweltmanagement) und ISO 45001 (Gesundheit und Sicherheit am Arbeitsplatz) können als Indikatoren für das Engagement eines Lieferanten für ethische Standards dienen.
Die Einbeziehung ‘grüner’ Zertifizierungen und Materialien in Kaufentscheidungen kann den Ruf eines Unternehmens verbessern und umweltbewusste Verbraucher ansprechen. Da die gesetzlichen Rahmenbedingungen für Nachhaltigkeit immer strenger werden, sollten B2B-Einkäufer die langfristigen Vorteile der Beschaffung bei Lieferanten berücksichtigen, die Nachhaltigkeit und ethische Praktiken in den Vordergrund stellen.
Was ist der historische Kontext von Anlassern und Magnetventilen im Automobilsektor?
Die Entwicklung von Anlassern und Magnetspulen hat die Automobilindustrie entscheidend geprägt. Ursprünglich waren die Fahrzeuge auf manuelle Anlasser angewiesen, bevor der elektrische Anlasser Anfang des 20. Diese Innovation markierte den Beginn einer neuen Ära im Automobilbau, die effizientere Motorstarts ermöglichte und die körperliche Belastung der Fahrer reduzierte.
Im Laufe der Jahrzehnte führten Fortschritte in der Elektrotechnik zur Entwicklung von Magnetspulen, die eine bessere Leistung und Zuverlässigkeit bieten. Die Integration elektronischer Steuerungen hat die Funktionalität von Anlassern und Magneten weiter verbessert, so dass sie den Anforderungen moderner Fahrzeuge gerecht werden können, einschließlich Energieeffizienz und Integration mit Bordcomputersystemen.
Da sich der Automobilsektor ständig weiterentwickelt, kann ein Verständnis des historischen Kontextes von Anlassern und Magnetventilen B2B-Einkäufern Einblicke in aktuelle Trends und künftige Innovationen geben und sie in die Lage versetzen, fundierte Beschaffungsentscheidungen zu treffen.
Häufig gestellte Fragen (FAQs) für B2B-Käufer von defekten Anlassern oder Magnetspulen
1. Wie diagnostiziere ich ein defektes Anlasser-Magnetventil?
Um ein defektes Anlassermagnetventil zu diagnostizieren, prüfen Sie zunächst, ob beim Drehen des Zündschlüssels Anzeichen eines Fehlers auftreten. Wenn keine Reaktion erfolgt, achten Sie auf ein einzelnes Klicken aus dem Motorraum, das darauf hinweist, dass die Magnetspule versucht, einzurasten, aber möglicherweise festsitzt. Wenn Sie außerdem intermittierende Startprobleme haben oder der Motor anspringt, ohne dass Sie den Schlüssel drehen, sind dies eindeutige Anzeichen für ein defektes Solenoid. Es ist ratsam, einen Techniker für eine gründliche Inspektion zu konsultieren, um zwischen Problemen mit der Magnetspule und anderen möglichen Problemen wie einer leeren Batterie oder einem defekten Anlasser unterscheiden zu können.
2. Was sind die wichtigsten Merkmale eines zuverlässigen Anbieters von Anlasser-Magneten?
Bevorzugen Sie bei der Suche nach einem Anbieter von Anlassermagneten solche mit einem guten Ruf auf dem Markt, der durch positive Bewertungen und Erfahrungsberichte untermauert wird. Suchen Sie nach Anbietern, die detaillierte Produktspezifikationen und Zertifizierungen bereitstellen, um sicherzustellen, dass ihre Magnetspulen internationalen Qualitätsstandards entsprechen. Achten Sie außerdem darauf, ob sie Anpassungsmöglichkeiten, wettbewerbsfähige Preise und günstige Zahlungsbedingungen bieten. Ein zuverlässiger Lieferant sollte auch über einen transparenten Kommunikationsprozess und effektive Logistikkapazitäten verfügen, um eine rechtzeitige Lieferung zu gewährleisten.
3. Was ist die Mindestbestellmenge (MOQ) für Anlassermagnete?
Die Mindestbestellmengen (MOQ) für Anlassermagnete können je nach Lieferant und Komplexität des Produkts erheblich variieren. In der Regel liegen die MOQs zwischen 50 und 500 Stück, je nach den Produktionskapazitäten des Herstellers und Ihren spezifischen Anforderungen. Bei Verhandlungen mit Lieferanten ist es von Vorteil, Ihre Bedürfnisse zu besprechen und zu prüfen, ob kleinere Bestellungen möglich sind, insbesondere für neue Käufer oder solche, die den Markt testen. Bestätigen Sie immer die Mindestbestellmenge, bevor Sie einen Vertrag abschließen, um unerwartete Kosten zu vermeiden.
4. Wie kann ich die Qualität von Anlassermagneten bei der Beschaffung sicherstellen?
Um die Qualität der Anlassermagnete zu gewährleisten, sollten Sie vor einer Großbestellung Muster anfordern. So können Sie die Leistung des Produkts und seine Kompatibilität mit Ihren Anwendungen beurteilen. Erkundigen Sie sich außerdem nach den Qualitätssicherungsprozessen des Lieferanten, einschließlich Prüfprotokollen und Zertifizierungen. Die Festlegung klarer Qualitätsstandards in Ihrem Kaufvertrag kann ebenfalls zur Risikominderung beitragen. Erwägen Sie, wenn möglich, die Durchführung von Werksbesichtigungen oder arbeiten Sie mit externen Prüfdiensten zusammen, um die Produktqualität vor dem Versand zu überprüfen.
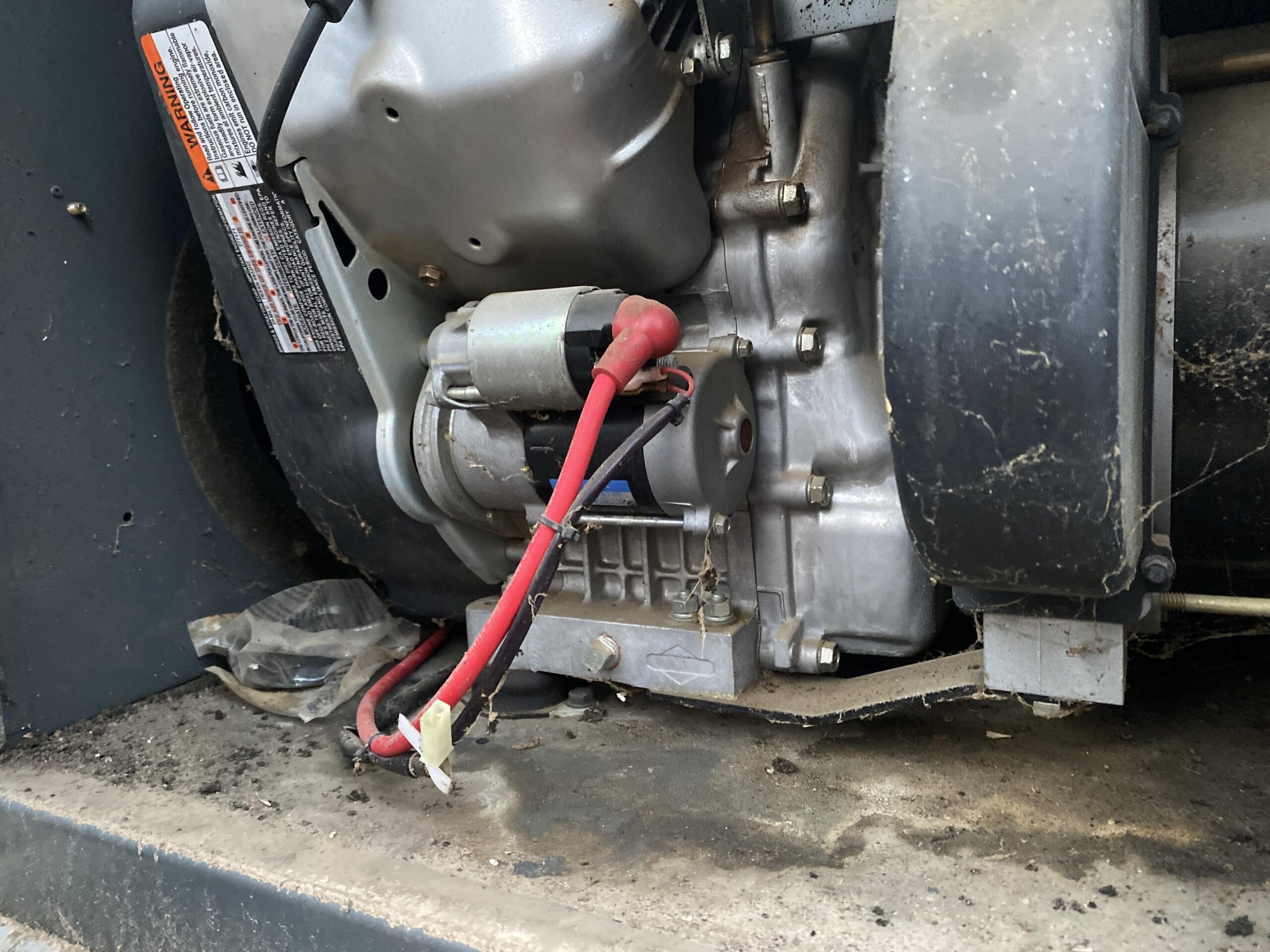

Anschauliches Bild zu defektem Anlasser oder Solenoid
5. Welche Zahlungsbedingungen sollte ich mit dem Lieferanten meines Anlassermagneten aushandeln?
Wenn Sie mit einem Lieferanten von Anlassermagneten über die Zahlungsbedingungen verhandeln, sollten Sie Optionen wie eine teilweise Vorauszahlung und die Zahlung des Restbetrags bei Lieferung oder ein Akkreditiv zur Sicherung Ihrer Transaktion in Betracht ziehen. Typische Bedingungen sind 30% im Voraus und 70% bei Lieferung, aber das kann variieren. Sprechen Sie immer über Zahlungsoptionen, die Ihren Cashflow-Anforderungen entsprechen, und stellen Sie sicher, dass diese in Ihrem Kaufvertrag festgehalten werden. Es ist auch ratsam, etwaige Vertragsstrafen für verspätete Zahlungen oder Rabatte für vorzeitige Zahlungen zu klären.
6. Welche logistischen Überlegungen sind bei der Einfuhr von Anlassermagneten wichtig?
Zu den logistischen Überlegungen für den Import von Anlassermagneten gehören die Kenntnis der Versandmethoden (Luft- oder Seefracht), der Zollbestimmungen und der möglichen Zölle in Ihrem Zielmarkt. Wählen Sie einen Logistikpartner mit Erfahrung im Umgang mit Kfz-Teilen, um die Einhaltung der Einfuhrbestimmungen zu gewährleisten. Berücksichtigen Sie außerdem die Vorlaufzeiten für Produktion und Versand, und ziehen Sie bei hoher Nachfrage Lagerlösungen in Betracht. Die Planung möglicher Verzögerungen aufgrund von Zoll- oder Transportproblemen kann ebenfalls dazu beitragen, die Lagerbestände aufrechtzuerhalten.
7. Wie kann ich Anlassermagnete für meine speziellen Bedürfnisse anpassen?
Bei der kundenspezifischen Anpassung von Anlassermagneten müssen Sie in der Regel Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen mit dem Lieferanten besprechen, z. B. Spannungswerte, Montagekonfigurationen oder Leistungsspezifikationen. Viele Hersteller bieten maßgeschneiderte Lösungen für spezielle Anwendungsanforderungen an. Legen Sie detaillierte Spezifikationen und alle relevanten technischen Zeichnungen vor, um den Anpassungsprozess zu erleichtern. Es ist wichtig, dass Sie Ihre Anforderungen klar kommunizieren und die Fähigkeiten des Lieferanten überprüfen, um sicherzustellen, dass das Endprodukt Ihren Erwartungen entspricht.
8. Was sind die häufigsten Anzeichen für einen defekten Startermagneten, auf die ich achten sollte?
Häufige Anzeichen für ein defektes Anlassermagnetventil sind ein nicht ansprechbarer Motor beim Drehen des Zündschlüssels, ein einzelnes klickendes Geräusch, das anzeigt, dass das Magnetventil versucht, einzurasten, oder intermittierende Startprobleme, bei denen das Fahrzeug manchmal, aber nicht durchgehend anspringt. Andere Symptome können darin bestehen, dass der Anlasser nach dem Loslassen des Schlüssels eingekuppelt bleibt, was zu weiteren Schäden führen kann. Wenn Sie diese Anzeichen frühzeitig erkennen, können Sie das Problem umgehend beheben und umfangreichere Reparaturen vermeiden.
Top 3 Schlechter Anlasser oder Magnetspule Liste der Hersteller & Lieferanten
1. Reddit - Anlasser-Montage
Domäne: reddit.com
Registriert: 2005 (20 Jahre)
Einleitung: Der Anlasser ist eine Baugruppe, zu der auch der Anlasser-Magnet gehört. Die Magnetspule ist ein Bauteil, das mit dem Anlasser verbunden ist und für das Einschalten des Anlassers verantwortlich ist, wenn der Zündschlüssel gedreht wird. Die meisten Menschen entscheiden sich für den Austausch der gesamten Anlasserbaugruppe und nicht nur der Magnetspule.
2. Facebook - Fehlersuche bei Problemen mit der Magnetspule
Domäne: facebook.com
Registriert: 1997 (28 Jahre)
Einleitung: Dieses Unternehmen, Facebook - Troubleshooting Solenoid Issues, ist ein namhaftes Unternehmen auf dem Markt. Für spezifische Produktdetails wird empfohlen, ihre Website direkt zu besuchen.
3. Yesterday's Tractors - Leitfaden zur Fehlersuche bei Magneten
Domäne: forums.yesterdaystractors.com
Registriert: 1997 (28 Jahre)
Einleitung: Dieses Unternehmen, Yesterday's Tractors - Solenoid Troubleshooting Guide, ist ein namhaftes Unternehmen auf dem Markt. Für spezifische Produktdetails wird empfohlen, ihre Website direkt zu besuchen.
Strategische Beschaffung Schlussfolgerung und Ausblick für defekte Anlasser oder Magnetspulen
Die strategische Beschaffung von schlechten Anlassern und Magnetspulen ist für internationale B2B-Einkäufer, die auf der Suche nach zuverlässigen und leistungsfähigen Kfz-Teilen sind, unerlässlich. Das Verständnis des Unterschieds zwischen Relais und Magnetspulen ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, da es Einkäufern ermöglicht, fundierte Kaufentscheidungen zu treffen. Das Erkennen der Anzeichen eines defekten Anlassermagneten - wie ungewöhnliche Klickgeräusche oder intermittierende Startprobleme - kann dazu beitragen, kostspielige Ausfallzeiten zu vermeiden und einen reibungslosen Betrieb zu gewährleisten.
Die Nutzung der strategischen Beschaffung verbessert nicht nur die Effizienz der Lieferkette, sondern fördert auch die Beziehungen zu Herstellern, die Wert auf Qualität und Innovation legen. Für Einkäufer aus Afrika, Südamerika, dem Nahen Osten und Europa kann die Zusammenarbeit mit Lieferanten, die strenge Qualitätsstandards einhalten, zu langfristigen Vorteilen führen, wie z. B. geringere Wartungskosten und höhere Zuverlässigkeit der Fahrzeuge.
Da sich die Automobilindustrie mit dem technologischen Fortschritt weiterentwickelt, wird die Nachfrage nach hochwertigen Komponenten weiter steigen. B2B-Einkäufer sind aufgefordert, bei der Beschaffung proaktiv zu bleiben und Lieferanten auf der Grundlage ihrer Fähigkeit zu bewerten, langlebige und effiziente Anlassersysteme zu liefern. Nutzen Sie diese Gelegenheit, um Ihre Beschaffungsstrategie zu verbessern und sicherzustellen, dass Ihr Unternehmen stabil bleibt und auf die Anforderungen des Marktes reagieren kann.
Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss und Nutzungsbedingungen
⚠️ Wichtiger Haftungsausschluss
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich zu Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Beschaffungsberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensdaten und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due Diligence durchführen. bevor Sie Kaufentscheidungen treffen. Dazu gehören die direkte Kontaktaufnahme mit Lieferanten, die Überprüfung von Zertifizierungen, die Anforderung von Mustern und die Einholung professioneller Beratung. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt ausschließlich der Leser.